Professional Documents
Culture Documents
바인더1
Uploaded by
M KCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
바인더1
Uploaded by
M KCopyright:
Available Formats
Microeconomics
Unit 2 Practice Sheet
Part 1 - Supply and Demand Practice- Use the
graph for ice cream to answer the questions below.
1. What is the equilibrium price and quantity?
2. Identify a price and quantity that could be the
result of an increase in the price of milk, a key
resource in the production of ice cream.
3. Identify a price and quantity that could be the
result of a decrease in the price of popsicles, a
substitute to ice cream.
4. Identify the area of consumer surplus at the
equilibrium price.
5. Identify the area of consumer surplus if the supply increased resulting in the equilibrium price of P3
and Q4.
6. Assume instead that the demand decreased resulting in the equilibrium price of P3 and Q2. Identify
the area of producer surplus.
7. Identify the area of consumer surplus if a price ceiling is placed at P2.
8. Identify the area of consumer surplus if a price ceiling is placed at P5.
9. Identify the area of deadweight loss if a price floor is placed at P6.
10. Assume that a per-unit tax was placed on ice cream resulting in an equilibrium price of P6 and Q1.
Identify the area of consumer surplus.
11. Assume that a per-unit tax was placed on ice cream resulting in an equilibrium price of P6 and Q1.
Identify the area of deadweight loss.
12. Assume that a per-unit tax was placed on ice cream resulting in an equilibrium price of P6 and Q1.
Identify the area of tax revenue.
13. Assume instead that consumers can get ice cream at the world price of P2. Identify the area of
consumer surplus after international trade.
14. Identify the quantity that will be imported if the world price is P2.
© Copyright Jacob Clifford 2020. Ultimate Review Packet
Teachers- Do NOT use this in your classroom. Contact me if you want to use this resource with your students
Microeconomics
Unit 2 Practice Sheet
Part 2 - Calculation Practice- Use the graph for a
competitive market to answer the questions below.
Show your work.
15. What is the quantity demanded and quantity
supplied at the price of $13?
16. Could an increase in supply result in an
equilibrium price and quantity of $12 and 30 units?
Explain.
17. Calculate the consumer surplus at the equilibrium
price.
18. Calculate the consumer surplus if a decrease in
supply results in an equilibrium price of $12.
19. Calculate the producer surplus if an increase in demand results in an equilibrium price of $12.
20. Calculate the deadweight loss if a decrease in demand results in an equilibrium price of $8.
21. Calculate the consumer surplus if a price ceiling is placed at $8.
22. What would be the equilibrium price and quantity if a $2 per-unit tax is placed on the good?
23. How much tax revenue would be generated if a $2 per-unit tax is placed on the good?
24. Would the incidence of tax from a $2 tax mostly fall on consumers or producers? Explain.
25. Calculate the consumer surplus if consumers can get this product at the world price of $7.
26. Calculate the elasticity of demand coefficient between the price of $10 and $9.
27. Calculate the elasticity of supply coefficient between the price of $10 and $12.
28. Assume the price fell from $10 to $8 causing the quantity demanded of a different product to increase
from 100 to 120 units. Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand coefficient.
29. Assume instead that the demand changes in such a way that a decrease in supply results in an
equilibrium price and quantity of $12 and 50 units. Calculate the elasticity of demand coefficient.
© Copyright Jacob Clifford 2020. Ultimate Review Packet
Teachers- Do NOT use this in your classroom. Contact me if you want to use this resource with your students
Microeconomics
Unit 2 Practice Sheet
Part 3 - FRQ Practice- Complete the following question from the 2015 AP exam (Question 3).
© Copyright Jacob Clifford 2020. Ultimate Review Packet
Teachers- Do NOT use this in your classroom. Contact me if you want to use this resource with your students
Micro Topics 2.3, 2.4 and 2.5
Elasticity Practice Sheet
Answer the questions. Be sure to explain and/or show your work.
1. The price of burgers increased from $4.00 to $4.40 and the quantity demanded decreased from 50
to 30 units per hour. Calculate the coefficient for price elasticity of demand. Show your work.
2. Given your answer to question #1, is the demand for burgers perfectly elastic, relatively elastic, unit
elastic, relatively inelastic, or perfectly inelastic? Explain how you determined your answer.
3. Assume, instead, that the quantity of burgers demanded remained at 50 (after the price change in
question #1). Would the demand for burgers be perfectly elastic, relatively elastic, unit elastic,
relatively inelastic, or perfectly inelastic? Explain how you determined your answer.
4. The price of burgers increased from $4 to $4.40 and the quantity supplied increased from 50 to 60
units. Calculate the price elasticity of the supply coefficient. Show your work.
5. Given the information in question #4, is the supply of burgers perfectly elastic, relatively elastic, unit
elastic, relatively inelastic, or perfectly inelastic? Explain how you determined your answer.
6. Suppose that the price of burgers decreased from $4.00 to $3.00 and the quantity demanded of
pizza decreased by 50%. Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand coefficient between burgers
and pizza. Show your work.
7. Given your answer to question #6, are burgers and pizza complements, substitutes, normal goods,
or inferior goods? Explain how you determined your answer.
8. If the demand for pizza is relatively inelastic, will an increase in the price of pizza cause the total
revenue for pizza restaurants to increase, decrease, or stay the same. Explain.
9. Assume that incomes increased by 40% and the quantity demanded of hot dogs decreased by 40%.
Calculate the income elasticity of hot dogs. Show your work.
10. Given your answer to question #9, are hot dogs a complement, substitute, normal good, or inferior
good? Explain how you determined your answer.
11. Given the information in question #9, is the demand for hot dogs be perfectly elastic, relatively
elastic, unit elastic, relatively inelastic, or perfectly inelastic? Explain how you determined your
answer.
© Copyright Jacob Clifford 2020
Teachers- Do NOT use this in your classroom. Contact me if you want to use this resource with your students
Microeconomics Unit 2 Study Guide
Supply and Demand
Topic 2.1- Demand Topic 2.2- Supply
1. What is the law of demand? 1. What is the law of supply?
P↑ Qd ____ P↑ Qs ____
P↓ Qd ____ P↓ Qs ____
2. Why is the market demand curve downward sloping? 2. Why is the market supply curve upward-sloping?
3. What are the five shifters of demand? 3. What are the five shifters of supply?
4. Goods A and B are substitutes. An increase in the Topic 2.4- Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
price of A will cause the demand for B to __________. 1. Identify the price elasticity of supply coefficient equation
5. Goods X and Y are complements. A decrease in the
price of X will cause the demand for Y to __________.
2. List 3 characteristics of goods with relatively inelastic
6. Good N is a normal good. A decrease in income will
supply.
cause the demand for N to __________.
7. Good R is an inferior good. A decrease in income will
cause the demand for R to __________.
Topic 2.3- Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) Topic 2.5- Other Elasticities
Inelastic Demand Elastic Demand 1. What is cross-price elasticity of demand (XED)?
2. Identify the XED equation.
3. Identify the price elasticity of demand equation.
3. What is income elasticity of demand (YED)?
4. Identify the YED equation.
Coefficient for perfectly inelastic demand =
Coefficient for inelastic demand =
Coefficient for unit elastic demand =
Coefficient for elastic demand =
Coefficient for perfectly elastic demand =
4. Use the total revenue test to fill in the blanks. 5. List 3 characteristics of goods with relatively inelastic
Inelastic Demand Elastic Demand demand.
Price ↑, TR ____ Price ↑, TR ____
Price ↓, TR ____ Price ↓, TR ____
©Copyright Jacob Clifford 2022. Ultimate Review Packet
Do not use unless you have purchased an annual license
Microeconomics Unit 2 Study Guide
Supply and Demand
Topic 2.6- Equilibrium and Consumer and Producer Surplus
1. Define consumer surplus (CS).
2. Define producer surplus (PS).
3. Define deadweight loss (DWL).
4. Calculate the CS at the equilibrium price. Show your work.
5. Calculate the CS if the price was $12. Show your work.
6. Calculate the deadweight loss if the market produced only 20 units.
Topic 2.7- Market Disequilibrium and Changes in Equilibrium
Graph #1 Graph #2 1. Draw a shortage on Graph #1. Label price
(P1), quantity supplied (Qs), and quantity
demanded (Qd). Shade in CS, PS, and DWL.
2. Draw a surplus on Graph #2. Label price
(P2), quantity supplied (Qs), and quantity
demanded (Qd). Shade in CS, PS, and DWL.
3. What is the difference between a change
in demand and a change in quantity
demanded?
4. Draw a demand decrease 5. Draw a demand increase 8. What is the double shift rule?
9. Draw an increase in demand AND an
increase in supply. What happens to the
equilibrium price and quantity?
6. Draw a supply decrease 7. Draw a supply increase
©Copyright Jacob Clifford 2022. Ultimate Review Packet
Do not use unless you have purchased an annual license
Microeconomics Unit 2 Study Guide
Supply and Demand
Topic 2.8- Government Intervention
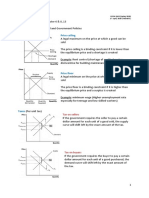
1. What is a price ceiling? 4. What is a subsidy?
2. What is a price floor?
3. A binding price ceiling must go ___________ equilibrium and results in a
____________. A binding price floor must go ___________ equilibrium.
Complete the following assuming the equilibrium price is $10
5. Identify the consumer surplus (CS)
6. Identify the producer surplus (PS)
7. Identify the CS if a price ceiling is placed at $12
8. Identify the CS if a price floor is placed at $12
Identify the following after the tax is imposed
9. The tax per unit
10. CS after tax
11. PS after tax
12. Deadweight loss
13. Total tax revenue
14. Total spending by buyers
15. Total revenue to sellers
16. Total amount of tax buyers pay
17. Total amount of tax sellers pay
Identify if buyers or sellers pay more of a tax in the
18. Is the demand curve between $12 and $10 elastic, inelastic, following situations.
or unit elastic? Explain.
20. Demand is more inelastic than supply.
19. Calculate the elasticity of supply coefficient as price 21. Demand and supply have the same elasticity.
increases from $10 to $12. Show your work.
22. Supply is more inelastic than demand.
Topics 2.9- International Trade and Public Policy
Calculate the following at the equilibrium price. The graph below shows the domestic market for rice.
1. Consumer surplus
2. Producer surplus
3. Total surplus
Calculate the following if this country buys rice from other
countries at the world price of $5. Show your work.
4. Quantity produced domestically
5. Quantity imported
6. Consumer surplus
7. Producer surplus
Identify the following if the government places a tariff of $1
on foreign rice. Show your work.
8. Consumer surplus
9. Tariff revenue
10. Deadweight loss
©Copyright Jacob Clifford 2022. Ultimate Review Packet
Do not use unless you have purchased an annual license
You might also like
- Unit 2 Practice Sheet AP MacroDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Practice Sheet AP MacroIsabella Silva GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Practice Sheet: MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Practice Sheet: MicroeconomicsEvelyn Hsu徐御庭No ratings yet
- Unit2 Study GuideDocument3 pagesUnit2 Study Guide高瑞韩No ratings yet
- 632dea5fbb6c8 Sample Question Booklet NEO 2022Document59 pages632dea5fbb6c8 Sample Question Booklet NEO 2022HariniNo ratings yet
- Abm Module 3 NewDocument21 pagesAbm Module 3 NewAiza BelandoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Supply and Demand and ElasticityDocument7 pagesBasics of Supply and Demand and ElasticityAlvin AdrianNo ratings yet
- Basics of Supply and Demand and ElasticityDocument7 pagesBasics of Supply and Demand and ElasticityJames BaratheonNo ratings yet
- Abm Applied Economics 12 - 4revised2 AbmDocument22 pagesAbm Applied Economics 12 - 4revised2 AbmJoana Sharmine ArrobangNo ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICS Key ConceptsDocument7 pagesMICROECONOMICS Key Conceptskomi kimiNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Microeconomics 5th Edition by David BesankoDocument26 pagesSolution Manual For Microeconomics 5th Edition by David BesankomohsinwazirNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: The Basic of Supply and DemandDocument9 pagesMicroeconomics: The Basic of Supply and DemandRidwan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- ABM-APPLIED ECONOMICS 12 - Q1 - W4 - Mod4.with Answer KeyDocument24 pagesABM-APPLIED ECONOMICS 12 - Q1 - W4 - Mod4.with Answer Keyely sanNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Elasticity ConceptsDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics Elasticity ConceptsCharles D. Alexander TrappNo ratings yet
- ECO20A 2023 01 Exam PaperDocument5 pagesECO20A 2023 01 Exam PapermhlabawethuprojectsNo ratings yet
- Principles 2e SSG Ch5Document14 pagesPrinciples 2e SSG Ch5VivienNo ratings yet
- Probset 1Document10 pagesProbset 1Phat Minh HuynhNo ratings yet
- Applied Eco Lesson 4Document7 pagesApplied Eco Lesson 4Raiza CabreraNo ratings yet
- MIC 3e SSG Ch4 PDFDocument14 pagesMIC 3e SSG Ch4 PDFJina NjNo ratings yet
- Individual & Market DemandDocument12 pagesIndividual & Market DemandAkshay ModakNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Set-1, All India 2016 CBSE Class 12th EconomicsDocument24 pagesQuestion Paper Set-1, All India 2016 CBSE Class 12th EconomicsAshish GangwalNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Quizzes & ActivitiesDocument10 pagesApplied Economics - Quizzes & Activitiesrowena marambaNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Week 3 With WorksheetDocument12 pagesApplied Economics Week 3 With WorksheetKate D. Paglinawan50% (2)
- CBSE Sample Paper For Class 12 Economics With SolutionsDocument11 pagesCBSE Sample Paper For Class 12 Economics With SolutionsAritroy KunduNo ratings yet
- Melc 4 Applied EconomicsDocument3 pagesMelc 4 Applied EconomicsCLARISE LAUREL100% (1)
- MARKET ANALYSISDocument8 pagesMARKET ANALYSISRuby CocalNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan An Michael BayeDocument14 pagesKumpulan An Michael BayeJermia MT ParhusipNo ratings yet
- Quiz 554Document6 pagesQuiz 554Haris NoonNo ratings yet
- Pindyck Chapter 2Document7 pagesPindyck Chapter 2Nino KazNo ratings yet
- GE Chapter 04 Solutions - FMTDocument14 pagesGE Chapter 04 Solutions - FMTAli RazaNo ratings yet
- 02Document16 pages02Paran GuptaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition by Sayre and Morris Solution ManualDocument67 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition by Sayre and Morris Solution Manualkevaxt100% (1)
- Applied Economics: Week 3: Module 3Document20 pagesApplied Economics: Week 3: Module 3Beatrice Deguzman100% (5)
- Supply and Demand Analysis: Solutions To ProblemsDocument16 pagesSupply and Demand Analysis: Solutions To ProblemssushanthvNo ratings yet
- Manila Education Center Market Pricing ModuleDocument23 pagesManila Education Center Market Pricing ModuleDalaguiado ChrisNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 8th Edition Pindyck Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesMicroeconomics 8th Edition Pindyck Solutions Manualrattingbivial7ac1gr100% (29)
- Implications of Market Pricing in Making Economic DecisionsDocument22 pagesImplications of Market Pricing in Making Economic DecisionsJessebel Dano Anthony83% (6)
- Problem Set #2 Questions and Answers on Economics ConceptsDocument2 pagesProblem Set #2 Questions and Answers on Economics Conceptskuashask2No ratings yet
- Eco 162Document17 pagesEco 162msukri_81No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Indian School of BusinessDocument3 pagesManagerial Economics Indian School of BusinessTANAY SETHNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Elasticity and Its Application QuestionDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Elasticity and Its Application QuestionMIN ENNo ratings yet
- PES Class NotesDocument7 pagesPES Class Notese33No ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Demand and Supply of Wii Console Questions and DiscussionsDocument29 pagesCase Study 1 Demand and Supply of Wii Console Questions and DiscussionsVisitacion Sunshine Baradi100% (1)
- Economic PrinciplesDocument44 pagesEconomic PrinciplesCarlos Ferreira100% (4)
- Abm Applied Economics 12 q1 w4 Mod4Document23 pagesAbm Applied Economics 12 q1 w4 Mod4edeliza avizolaNo ratings yet
- SOV E05169BCOM PBD Answer SchemeDocument7 pagesSOV E05169BCOM PBD Answer SchemeNeeraj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BE TUTORIAL 3 - STUDocument18 pagesBE TUTORIAL 3 - STUGia LinhNo ratings yet
- Econ 0-Mudule 4 (2022-2023)Document22 pagesEcon 0-Mudule 4 (2022-2023)Bai NiloNo ratings yet
- ABM-APPLIED ECONOMICS 12 - Q1 - W4 - Mod4Document23 pagesABM-APPLIED ECONOMICS 12 - Q1 - W4 - Mod4Carmilleah Freyjah100% (5)
- Solution Manual For Principles of Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Morris 1259030695 9781259030697Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Principles of Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Morris 1259030695 9781259030697aaronsmithwdkbfoiayr100% (26)
- Dynamics of Demand and SupplyDocument8 pagesDynamics of Demand and SupplyMARY MAXENE CAMELON BITARANo ratings yet
- Exercises ElasticityDocument4 pagesExercises ElasticityAA BB MMNo ratings yet
- Ch04 SolutionsDocument8 pagesCh04 SolutionsMuhammadNo ratings yet
- (Intro Micro) Bank Soal UTS - TutorkuDocument24 pages(Intro Micro) Bank Soal UTS - Tutorkuantonius.rafael10No ratings yet
- Economics Chapter QuestionsDocument36 pagesEconomics Chapter QuestionsOlaNo ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium, Supply and Demand AnalysisDocument18 pagesMarket Equilibrium, Supply and Demand AnalysisMuqadas NoorNo ratings yet
- Principles SSG Ch5Document13 pagesPrinciples SSG Ch5Tingwei HuangNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 8th Edition Pindyck Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesMicroeconomics 8th Edition Pindyck Solutions ManualBrettClinewdjc100% (60)
- Review Questions for Mid-term_Micro_to Sts (1)Document21 pagesReview Questions for Mid-term_Micro_to Sts (1)Nguyễn Thị ThờiNo ratings yet
- Copy of AP MACRO - GRAPHS GUIDEDocument2 pagesCopy of AP MACRO - GRAPHS GUIDEM KNo ratings yet
- StoryboardDocument7 pagesStoryboardM KNo ratings yet
- Words of WisdomDocument17 pagesWords of WisdomM KNo ratings yet
- ML Squibb Stage 1Document4 pagesML Squibb Stage 1M KNo ratings yet
- APS U06 6.3 Binomial and Normal Approximation Practice KEYDocument1 pageAPS U06 6.3 Binomial and Normal Approximation Practice KEYM KNo ratings yet
- APS U06 6.3 Binomial Distribution PracticeDocument2 pagesAPS U06 6.3 Binomial Distribution PracticeM KNo ratings yet
- Exploring Two-Variable Data: Unit 2 Practice SheetDocument3 pagesExploring Two-Variable Data: Unit 2 Practice SheetM KNo ratings yet
- AP Macro - 1.25.24Document97 pagesAP Macro - 1.25.24M KNo ratings yet
- APS U06 6.3 Geometric Random Variable PracticeDocument5 pagesAPS U06 6.3 Geometric Random Variable PracticeM KNo ratings yet
- FINAL - APUSH B V.B OutlineDocument10 pagesFINAL - APUSH B V.B OutlineM KNo ratings yet
- AP Lang Speech PromptDocument2 pagesAP Lang Speech PromptM KNo ratings yet
- FINAL - APUSH B V.B OutlineDocument10 pagesFINAL - APUSH B V.B OutlineM KNo ratings yet
- 3 SOAPSTone AnnotationDocument1 page3 SOAPSTone AnnotationM KNo ratings yet
- AP Stats RevDocument20 pagesAP Stats RevM KNo ratings yet
- 12.20.23 NEW R MOD FINAL Bolded AnswersDocument31 pages12.20.23 NEW R MOD FINAL Bolded AnswersM KNo ratings yet
- 1 1 04apDocument1 page1 1 04apM KNo ratings yet
- '15 FRQ 3Document1 page'15 FRQ 3M KNo ratings yet
- 12.20.23 NEW R MOD FINAL Bolded AnswersDocument31 pages12.20.23 NEW R MOD FINAL Bolded AnswersM KNo ratings yet
- MIT Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageMIT Interview QuestionsM KNo ratings yet
- Yoosin Jun - Email Letter To ProfDocument2 pagesYoosin Jun - Email Letter To ProfM KNo ratings yet
- 2.1.23 - Physics IDocument7 pages2.1.23 - Physics IM KNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Supply Demand ConsumerDocument84 pagesUnit 2 Supply Demand ConsumerJanett MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Study GuideM KNo ratings yet
- Date Name ClassDocument76 pagesDate Name ClassM KNo ratings yet
- Date Name ClassDocument76 pagesDate Name ClassM KNo ratings yet
- AP Lang Prose PassagesDocument136 pagesAP Lang Prose PassagesM KNo ratings yet
- AP Lang Prose PassagesDocument136 pagesAP Lang Prose PassagesM KNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Study GuideM KNo ratings yet
- AP Micro Unit 3 ALLDocument252 pagesAP Micro Unit 3 ALLM KNo ratings yet
- Date Name ClassDocument76 pagesDate Name ClassM KNo ratings yet
- English SolutionsDocument16 pagesEnglish Solutionsganesh pathakNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Monetary EconomicsDocument27 pagesUnit 3 - Monetary EconomicsDanielNo ratings yet
- Indirect Tax Effects on Sugary Beverages & Dr PepperDocument4 pagesIndirect Tax Effects on Sugary Beverages & Dr PepperJakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ElasticityDocument59 pagesChapter 4 - ElasticityHamdiNo ratings yet
- Applied-Economics Week1-4Document34 pagesApplied-Economics Week1-4Yuri TagalaNo ratings yet
- KrugmanDocument9 pagesKrugmanMaria100% (3)
- 04 S Elasticities (2324 S1)Document24 pages04 S Elasticities (2324 S1)rpscn4bz8wNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 11 Answers 2nd EdDocument2 pagesIGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 11 Answers 2nd EdDesreNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 EEFMDocument26 pagesUnit - 1 EEFMAppasani ManishankarNo ratings yet
- BEFA - PPT - All Units-Converted - 7 PDFDocument205 pagesBEFA - PPT - All Units-Converted - 7 PDFAravind Reddy MokireddyNo ratings yet
- Engg Eco Unit 2 D&SDocument129 pagesEngg Eco Unit 2 D&SSindhu PNo ratings yet
- ECO111 Microeconomics Class: Handed Out: Submission Due: Format: Submission Mode: Email ToDocument7 pagesECO111 Microeconomics Class: Handed Out: Submission Due: Format: Submission Mode: Email ToHoang AnhNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix and Relationship Marketing@ Bec DomsDocument11 pagesMarketing Mix and Relationship Marketing@ Bec DomsBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Econ 24 Quizzes 1 5Document54 pagesEcon 24 Quizzes 1 5Kristine LuntaoNo ratings yet
- BA 1 Microeconomics: Demand and Supply of Pandesal and TastyDocument2 pagesBA 1 Microeconomics: Demand and Supply of Pandesal and TastyAte GandaNo ratings yet
- What Is DemandDocument16 pagesWhat Is DemandUsman zafarNo ratings yet
- MBA - Business Eco - 1Document10 pagesMBA - Business Eco - 1Nikesh MunankarmiNo ratings yet
- Manual Ceteris ParibusDocument12 pagesManual Ceteris ParibusAbhitej KodaliNo ratings yet
- AC-4102 Managerial Economics SyllabusDocument15 pagesAC-4102 Managerial Economics SyllabusSharah Del Tabudlong TudeNo ratings yet
- Price Ceiling: This WeekDocument6 pagesPrice Ceiling: This WeekAdreshNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Economics of Business EnterpriseDocument31 pagesAssignment-Economics of Business EnterpriseGivaji PradeepNo ratings yet
- Retail PricingDocument27 pagesRetail PricingAbhishek Pratap Singh100% (2)
- Tariff War LashkaripourDocument64 pagesTariff War LashkaripourShourya MarwahaNo ratings yet
- BIE Hyderabad Economics SyllabusDocument7 pagesBIE Hyderabad Economics SyllabusSrikar RathoNo ratings yet
- GLS1e - Chapter2 Goolsbee Levitt EconomicsDocument74 pagesGLS1e - Chapter2 Goolsbee Levitt Economicsmrmookie100% (2)
- Question 1. Companies Often Change Colour, Package, Design, and Advertisements ForDocument6 pagesQuestion 1. Companies Often Change Colour, Package, Design, and Advertisements Forvidharshana esakkiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Land and RentDocument17 pagesChapter 11. Land and RentSantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- HUL212 MODERN MICROECONOMICS - IIT Delhi - Minor-1 - Engineering - Year-2008 - 106Document3 pagesHUL212 MODERN MICROECONOMICS - IIT Delhi - Minor-1 - Engineering - Year-2008 - 106Sachin BatwaniNo ratings yet
- FORD MOTOR COMPANY v. FUJIKURA LTD. and FUJIKURA AUTOMOTIVE AMERICA LLCDocument39 pagesFORD MOTOR COMPANY v. FUJIKURA LTD. and FUJIKURA AUTOMOTIVE AMERICA LLCsahmed_anNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Supply DemandDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Supply Demandapi-428447569No ratings yet