Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geocentric and Helio Centric
Uploaded by
Kyawmoe LwinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geocentric and Helio Centric
Uploaded by
Kyawmoe LwinCopyright:
Available Formats
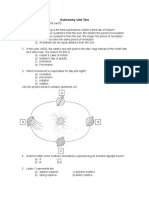
1. Who proposed the geocentric model?
a) Copernicus
b) Ptolemy
c) Galileo
d) Newton
2. What is the main idea behind the geocentric model?
a) The Earth is at the center of the universe
b) The Sun is at the center of the universe
c) The Moon is at the center of the universe
d) The universe has no center
3. What were the main components of the geocentric model?
a) Earth, Sun, and Moon
b) Earth, Sun, Moon, and stars
c) Earth, Sun, planets, and stars
d) Earth, Moon, and planets
4. How did the geocentric model explain the motion of celestial bodies?
a) By their orbit around the Earth
b) By their orbit around the Sun
c) By their irregular movements
d) By their fixed position in the sky
5. What were some limitations of the geocentric model?
a) It couldn't explain retrograde motion
b) It couldn't predict eclipses accurately
c) It couldn't account for the varying brightness of planets
d) All of the above
6. What were some alternative models proposed to replace the geocentric model?
a) Heliocentric model
b) Tychonic model
c) Both a and b
d) None of the above
7. How did the geocentric model eventually give way to the heliocentric model?
a) Through the observations and calculations of Tycho Brahe
b) Through the work of Johannes Kepler
c) Through the publication of Copernicus' "De Revolutionibus"
d) All of the above
8. What was the major contribution of the geocentric model to the development of astronomy?
a) It accurately explained the motion of celestial bodies
b) It provided a foundation for further observations and discoveries
c) It accurately predicted the positions of stars and planets
d) It revolutionized our understanding of the universe.
Certainly! The heliocentric model is a significant concept in the history of astronomy. Here are some key
points about the heliocentric model:
1. Who proposed the heliocentric model?
a) Copernicus
b) Ptolemy
c) Galileo
d) Newton
2. What is the main idea behind the heliocentric model?
a) The Earth is at the center of the universe
b) The Sun is at the center of the universe
c) The Moon is at the center of the universe
d) The universe has no center
3. What were the main components of the heliocentric model?
a) Earth, Sun, and Moon
b) Earth, Sun, Moon, and stars
c) Earth, Sun, planets, and stars
d) Earth, Moon, and planets
4. How did the heliocentric model explain the motion of celestial bodies?
a) By their orbit around the Earth
b) By their orbit around the Sun
c) By their irregular movements
d) By their fixed position in the sky
5. What were some limitations of the geocentric model that the heliocentric model addressed?
a) It couldn't explain retrograde motion
b) It couldn't predict eclipses accurately
c) It couldn't account for the varying brightness of planets
d) All of the above
6. What were some key contributions of the heliocentric model to the development of astronomy?
a) It provided a simpler explanation for the motion of celestial bodies
b) It paved the way for a more accurate understanding of the solar system
c) It helped in predicting planetary positions more accurately
d) All of the above
7. How did the heliocentric model revolutionize our understanding of the universe?
a) By establishing the Sun as the central body in the solar system
b) By challenging the Earth-centric view of the cosmos
c) By leading to new discoveries about the nature of planetary motion
d) All of the above
You might also like
- Summative Test 1Document3 pagesSummative Test 1Pangangan NHS100% (2)
- Cosmic PerspectiveDocument5 pagesCosmic PerspectiveChuah Chong YangNo ratings yet
- Life in The Universe 3rd Edition Bennett Test BankDocument14 pagesLife in The Universe 3rd Edition Bennett Test Bankpaulnunezencsakobtq100% (11)
- The 88 Official Constellations Cover The Celestial SphereDocument29 pagesThe 88 Official Constellations Cover The Celestial SphereJeus Bencio100% (1)
- Sci 11 Physical Science 4th Quarter Div2 PDFDocument7 pagesSci 11 Physical Science 4th Quarter Div2 PDFLANIFER Songahid100% (1)
- Astronomy TestDocument6 pagesAstronomy TestRoldan OrmillaNo ratings yet
- Moons MotionDocument338 pagesMoons MotionmktshaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 4: Week 1-7Document34 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 4: Week 1-7Mica MandocdocNo ratings yet
- Dark MatterDocument25 pagesDark Mattergaming so MatejNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 4: Week 1-8Document37 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 4: Week 1-8Aleia Nicole Ocampo100% (2)
- Bill Nye Earths SeasonsDocument1 pageBill Nye Earths Seasonsapi-4358323770% (1)
- Physci Worksheet 1-2Document2 pagesPhysci Worksheet 1-2Candy PadizNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE 9 Physical ScienceDocument15 pagesQ2 MODULE 9 Physical ScienceG Boy100% (2)
- Solar System KEY PDFDocument32 pagesSolar System KEY PDFAchmad FahrizaNo ratings yet
- 4th Q Physical Science M1 and M2 ASTRONOMYDocument24 pages4th Q Physical Science M1 and M2 ASTRONOMYEvangeline AgtarapNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module 1 Physical ScienceDocument10 pagesQ4 Module 1 Physical ScienceMelancholy0% (1)
- Summative Test #1 2nd Q PsDocument4 pagesSummative Test #1 2nd Q PsKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (1)
- 2nd SUMMATIVE TEST Physical Science 12Document4 pages2nd SUMMATIVE TEST Physical Science 12Marina AbanNo ratings yet
- 2nd QUARTERLY EXAMINATION Physical Science 12Document5 pages2nd QUARTERLY EXAMINATION Physical Science 12Marina Aban100% (2)
- Essential Cosmic Perspective 8th Edition Bennett Test BankDocument17 pagesEssential Cosmic Perspective 8th Edition Bennett Test Bankrubyhien46tas100% (25)
- Test Bank For Astronomy Today 8 e 8th Edition Eric Chaisson Steve McmillanDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Astronomy Today 8 e 8th Edition Eric Chaisson Steve McmillanPaul Fuselier100% (34)
- Test Bank For Life in The Universe 4Th Edition Bennett Shostak 0134089081 9780134089089 Full Chapter PDFDocument34 pagesTest Bank For Life in The Universe 4Th Edition Bennett Shostak 0134089081 9780134089089 Full Chapter PDFodessa.metzler642100% (13)
- Life in The Universe 4th Edition Bennett Shostak Test BankDocument13 pagesLife in The Universe 4th Edition Bennett Shostak Test Bankbeulah100% (22)
- 4th Quarter Test PHYSICS 12Document4 pages4th Quarter Test PHYSICS 12Cris ElcarteNo ratings yet
- Physical Science PetaDocument6 pagesPhysical Science PetaRyan CortezNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Astronomy IDocument6 pagesPractice Questions For Astronomy ItabilinNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesFinal Examination Physical ScienceKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Trinary1 Question BankDocument30 pagesTrinary1 Question BankDrake Emerson RuppelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant WorldsDocument17 pagesChapter 13 Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant WorldsEdwin ChuenNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Astronomy I - EXAM 1Document8 pagesPractice Questions For Astronomy I - EXAM 1John Paul Sarmiento LatojaNo ratings yet
- Astro 100 Mini-Practice Exam (Midterm #1)Document7 pagesAstro 100 Mini-Practice Exam (Midterm #1)samia aliNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 in Physci. q2Document4 pagesSummative Test 1 in Physci. q2Ryan CortezNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 in Physci. q2Document4 pagesSummative Test 1 in Physci. q2Ryan CortezNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument7 pagesAnswersmy nNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - CosmologyDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 - CosmologyJanath De SilvaNo ratings yet
- EXAM in PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument8 pagesEXAM in PHYSICAL SCIENCEjennilyn bulaonNo ratings yet
- Direction: Read The Following Statement Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument8 pagesDirection: Read The Following Statement Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerPaul Senen DiduloNo ratings yet
- Thursday, October 24th 2019 in ClassDocument2 pagesThursday, October 24th 2019 in ClassSaadNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Study Guide ACTIVITYDocument4 pagesAstronomy Study Guide ACTIVITYtabilinNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Questions OnlyDocument42 pagesPart 2 Questions Onlyarmando licanda BSE Math 2ANo ratings yet
- Physical Science Make-Up ActivityDocument18 pagesPhysical Science Make-Up ActivityRyan CortezNo ratings yet
- 1st Lesson Test BiologyDocument2 pages1st Lesson Test BiologySergio Mora OrtizNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Perspective The Solar System 8th Edition Bennett Test BankDocument17 pagesCosmic Perspective The Solar System 8th Edition Bennett Test Bankantiloquyillesivepch100% (27)
- Cosmic Perspective 7th Edition Bennett Test BankDocument16 pagesCosmic Perspective 7th Edition Bennett Test Bankthuyhai3a656100% (32)
- Ebook Cosmic Perspective 7Th Edition Bennett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesEbook Cosmic Perspective 7Th Edition Bennett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFselenatanloj0xa100% (11)
- How Many Planets Are There in Our Solar System?Document20 pagesHow Many Planets Are There in Our Solar System?Griel GenNo ratings yet
- Copernican, Ptolemaic, TychonicDocument5 pagesCopernican, Ptolemaic, TychonicEsther Macugay100% (1)
- Cte Astron Midterm-DraftDocument8 pagesCte Astron Midterm-DraftWill Militar Jr.No ratings yet
- Midterm SolutionsDocument12 pagesMidterm Solutionsozworld3100% (1)
- Mars, Jupiter, & Saturn Show Because: Retrograde MotionDocument28 pagesMars, Jupiter, & Saturn Show Because: Retrograde MotionKarenNo ratings yet
- 4TH QRTR ExamDocument2 pages4TH QRTR ExamAlexander AlcazarinNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Galaxies, Big BangDocument17 pagesPractice Questions - Galaxies, Big BangMeow MooMooNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesEarth Science Diagnostic TestBaisalam MandingNo ratings yet
- Geocentrism vs. HeliocentrismDocument17 pagesGeocentrism vs. HeliocentrismJohn FrancisNo ratings yet
- CollegeDocument7 pagesCollegeangelicavalenzona7No ratings yet
- Life in The Universe 3rd Edition Bennett Test BankDocument35 pagesLife in The Universe 3rd Edition Bennett Test Bankjaundicecrincum05ba2100% (23)
- Essential Cosmic Perspective 8th Edition Bennett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesEssential Cosmic Perspective 8th Edition Bennett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFoglepogy5kobgk100% (12)
- Earth and Life Science Midterm Exam2019-2020Document3 pagesEarth and Life Science Midterm Exam2019-2020Wenralf NagangdangNo ratings yet
- 1 Eso GeographyDocument3 pages1 Eso GeographyEva Barreiro RománNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 1 LAS DUE On APRIL 12 2024Document3 pagesPhysical Science Week 1 LAS DUE On APRIL 12 2024Ya NaNo ratings yet
- DLP 3Document3 pagesDLP 3Nica Angela Anzures HUMSS 10BNo ratings yet
- Astronomy TestDocument6 pagesAstronomy TestSaida Mtz GNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice (2 Points Each) : Astronomy Unit TestDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice (2 Points Each) : Astronomy Unit TestSaida Mtz GNo ratings yet
- We Live in the Helical Solar System: Our Home in a Helical UniverseFrom EverandWe Live in the Helical Solar System: Our Home in a Helical UniverseNo ratings yet
- Interplanetary Mission Design JPL 1990Document41 pagesInterplanetary Mission Design JPL 1990pap1723No ratings yet
- b03 Ia15 T en BDocument1 pageb03 Ia15 T en BSyaroNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 Q2 Module-2 Gravity v5Document25 pagesGeneralPhysics1 Q2 Module-2 Gravity v5rexilldatorNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 (Topic: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation)Document1 pageActivity 1 (Topic: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation)John JohnnyNo ratings yet
- The Earth As A PlanetDocument7 pagesThe Earth As A Planetjohanna imreNo ratings yet
- Astro 100 Mini-Practice Exam (Midterm #1)Document7 pagesAstro 100 Mini-Practice Exam (Midterm #1)samia aliNo ratings yet
- 4 All The Questions in The Spaces Provided. 1 (A) Define Gravitational Potential at A PointDocument2 pages4 All The Questions in The Spaces Provided. 1 (A) Define Gravitational Potential at A PointTanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Grav PhetDocument3 pagesGrav PhetpiaNo ratings yet
- Math-Assignment-Part-3 - 1 - (7585779 - 1 - 1942-1-1634011863s00287752)Document2 pagesMath-Assignment-Part-3 - 1 - (7585779 - 1 - 1942-1-1634011863s00287752)Yann FeutseuNo ratings yet
- Cambridge School, Greater Noida Class 8 Ch-Stars and The Solar System AssignmentDocument2 pagesCambridge School, Greater Noida Class 8 Ch-Stars and The Solar System Assignmentrithvik evokeNo ratings yet
- G11 Quiz #6 SLDocument6 pagesG11 Quiz #6 SLJana AljurfNo ratings yet
- Optional Challenge 1Document2 pagesOptional Challenge 1eminadz33% (3)
- Sci-5 - q4 - Phases of The MoonDocument26 pagesSci-5 - q4 - Phases of The MoonBUENA ROSARIONo ratings yet
- Celestial Navigation: NAV 4 233L3Document47 pagesCelestial Navigation: NAV 4 233L3Tony1412No ratings yet
- 1.3 Mass and WeightDocument25 pages1.3 Mass and WeightLaw PeterNo ratings yet
- Solar and Lunar EclipsesDocument5 pagesSolar and Lunar EclipsesPrincess Ika AritonangNo ratings yet
- 8 Phases of The MoonDocument4 pages8 Phases of The MoonBhel D. GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Mass, Weight and Gravitational Field - NotesDocument2 pagesMass, Weight and Gravitational Field - NotesaasrajNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Sumana Ahmed Dawani - GravitationalForceSEDocument5 pagesKami Export - Sumana Ahmed Dawani - GravitationalForceSEsumanaNo ratings yet
- 6 Freefall 161127184900Document13 pages6 Freefall 161127184900CHELCEE C. ENARIONo ratings yet
- Bansalclasses: PhysicsDocument16 pagesBansalclasses: Physicsmayank singhNo ratings yet
- Casuyon Kim-ACTIVITY 1 Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument2 pagesCasuyon Kim-ACTIVITY 1 Origin and Structure of The EarthakyNo ratings yet
- Astronomical Event Astronomical Object Syzygy Occultation Transit Solar Eclipse Lunar EclipseDocument3 pagesAstronomical Event Astronomical Object Syzygy Occultation Transit Solar Eclipse Lunar EclipseFrelen LequinanNo ratings yet
- Planetary Orbits Worksheet: NameDocument6 pagesPlanetary Orbits Worksheet: NametabilinNo ratings yet
- The Phases of The Moon Worksheet CompleteDocument3 pagesThe Phases of The Moon Worksheet CompleteBrandonNo ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanics - Gen - SolutionsDocument18 pagesOrbital Mechanics - Gen - SolutionsNouman1203No ratings yet