Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NOTES
Uploaded by
Carel Mae Geollegue Teatro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesNOTES FOR STUDENTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNOTES FOR STUDENTS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views10 pagesNOTES
Uploaded by
Carel Mae Geollegue TeatroNOTES FOR STUDENTS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Lesson Objectives:
1. Explain internal control affecting Liabilities and Equity
and potential misstatements on assets and how
weakness in internal control increase risk of
misstatement.
2. Explain the relationship between governance, business
ethics, risk management and internal control and how the
various principles, frameworks and processes interact and
enable professional accountants to contribute positively
to their organizations, profession and society.
Internal Control for Liabilities & Equity
A. Liabilities
What are potential misstatements on accounts payable
and how weakness in internal control increase these
risks?
Description of Examples Internal Control
Misstatement Weakness
Inaccurate recording Fraud
of a purchase or
● A bookkeeper ● Inadequate
disbursement
prepares a check segregation of
for himself and duties between
records it as having record keeping and
been issued to check preparation.
major supplier.
● Failure to review
and cancel
supporting
Error
documents by
● A disbursement is check signer.
made to pay an
invoice for goods
that have not been ● Ineffective control
received. for matching
invoices with RR
before
disbursement are
authorized.
Fraud
● Goods are ordered ● Ineffective control
but delivered to an for matching
Misappropriation of
inappropriate invoices with RR
purchases
address and stolen before
disbursement are
authorized.
Duplicate recording of Error
purchases
● A purchase is ● Ineffective control
recorded when an for review and
invoice is received cancellation of
from a vendor and supporting
recorded again documents by the
when a duplicate check signer.
invoice is sent by
the vendor.
Fraud
● Purchase journal ● Ineffective board of
“closely early” with director’s audit
Late(early) recording this period’s committee.
of purchase purchases as
● Undue pressure to
having occurred in
the subsequent meet earnings
period. target.
What internal controls are applicable over Debt?
1. Authorization by the Board of Directors.
a. By-laws should clearly state that board of directors
are required to approved borrowings.
b. Treasurer prepares report on any proposed
financing, explaining the need for funds, effect of
borrowing upon future earnings and the estimated
financial position of the company in comparison with
others in the industry both before and after
borrowing and alternative methods of raising funds.
c. Authorization shall include matters such as choice of
bank or trustee, type of security, registration with
SEC, agreements with investment banker, listing of
bonds on security exchange and compliance with
requirements of state of incorporation.
d. Board of directors shall be furnished copy of report
stating net amount of received and its disposition.
2. Use of Independent Trustee
Trustee does not have access to the issuance of
company assets or accounting records but are paid
by the company as independent part who is charged
with the protection of creditor’s interest and with
monitoring the company’s compliance with the
provision of indenture.
3. Assigned Trustee to Pay Interest on Bonds and Notes
Payable.
B. Equity
Three (3) principal elements of strong internal control
over equity
1. proper authorization of transaction by the board of
directors and corporate office.
2. segregation of duties in handling these transactions
3. maintenance of adequate records.
What internal controls are applicable on Equity?
1. Control of Share Capital Transactions by the Board of
Directors
2. Independent Registrar and Stock Transfer Agent
3. Internal Control over Dividend
Relationship between Corporate Governance, Business
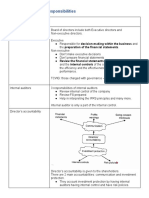
Ethics, Risk Management and Internal Control
CORPORATE
INTERNAL
Figure 24.1
A. Corporate Governance relationship to Business Ethics
A well defined and enforced corporate governance provides a
Structure that, at least in theory, works for the benefit of
everyone concerned by ensuring that the enterprises adheres
to accepted ethical standards and best practices as well as to
formal law.
Figure 24.2
An effective ethics programme requires continual
reinforcement of strong values. Organizations are challenged
with how to make its employees live and imbibe the
organization codes and values. To ensure the right ethical
climate a right combination of spirit and structure is required.
B. Corporate Governance relationship to Risk
Management
So, risk as defined by ISO as the effect of uncertainty on the
entity’s objectives. When there are no objectives, there are no
risks. But that’s not company were made for, therefore should
always be assessed in light of the entity’s objectives. Under
the principle 12 of Code of Corporate Governance, “To ensure
the integrity and proper governance in the conduct of its
affairs, the company should have…enterprise risk
management framework.” Below is the summary review of
OECD for the need of risk management.
● Perhaps one of the greatest shocks from the financial crisis
has been the widespread failure of risk management. In many
cases risk was not managed on an enterprise basis and not
adjusted to corporate strategy. Risk managers were often
separated from management and not regarded as an
essential part of implementing the company’s strategy. Most
important of all, boards were in a number of cases ignorant of
the risk facing the company.
● It should be fully understood by regulators and other
standard setters that effective risk management is not about
eliminating risk taking, which is a fundamental driving force in
business and entrepreneurship. The aim is to ensure that
risks are understood, managed and, when appropriate,
communicated.
● Effective implementation of risk management requires an
enterprise-wide approach rather than treating each business
unit individually. It should be considered good practice to
involve the board in both establishing and overseeing the risk
management structure.
● The board should also review and provide guidance about
the alignment of corporate strategy with risk-appetite and the
internal risk management structure.
● To assist the board in its work, it should also be considered
good practice that risk management and control functions be
independent of profit centres and the “chief risk officer” or
equivalent should report directly to the board of directors
along the lines already advocated in the OECD Principles for
internal control functions reporting to the audit committee or
equivalent.
● The process of risk management and the results of risk
assessments should be appropriately disclosed. Without
revealing any trade secrets, the board should make sure that
the firm communicates to the market material risk factors in a
transparent and understandable fashion. Disclosure of risk
factors should be focused on those identified as more relevant
and/or should rank material risk factors in order of importance
on the basis of a qualitative selection whose criteria should
also be disclosed.
● With few exceptions, risk management is typically not
covered, or is insufficiently covered, by existing corporate
governance standards or codes. Corporate governance
standard setters should be encouraged to include or improve
references to risk management in order to raise awareness
and improve implementation.
C. Corporate Governance relationship to Internal Control
Internal control activities ensure that companies adhere to
corporate governance guidelines. As shown in figure 24.3,
internal control is important element of COSO ERM
Framework. Corporate governance sets the standards and
recommends procedures; internal controls ensure those
procedures are being followed. Internal controls also ensure
there is an audit trail that can be retraced during internal and
external audits.
Figure 24.3
Following objectives of Internal Control supports the
objectives of good corporate governance which are
summarized as follows:
● Ensure achievement of the organization objectives,
including its stated goals and business targets in an
effective and efficient manner.
● Ensure economical and effective use of resources and
adequately safeguard the organization’s assets against
unauthorized use or disposition.
● Ensure compliance with applicable legislation and
regulations.
● Ensure maintenance of proper records for providing
reliable financial, managerial and operating information
for decision-making, evaluation of activities or
publication.
● Ensure adequate control for the risks inherent in
operations.
To conclude, a good corporate governance can be achieved
when it applies high ethical standards, have established risk
management process and implement internal controls.
You might also like
- Chapter 17 ReportingDocument6 pagesChapter 17 ReportingAngel Jasmin TupazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Internal Control Affecting Liabilities and Owner's EquityDocument16 pagesChapter 17 - Internal Control Affecting Liabilities and Owner's Equityshaiyni qyNo ratings yet
- Module 16Document3 pagesModule 16AstxilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 12 - Internal Control (Week 13) : Required: (A)Document12 pagesTutorial 12 - Internal Control (Week 13) : Required: (A)嘉慧100% (1)
- 2RAC - Revision 2019 Lecture 11Document7 pages2RAC - Revision 2019 Lecture 11Jia YinNo ratings yet
- Governance, Business Ethics, Risk Management and Internal Control ReportingDocument5 pagesGovernance, Business Ethics, Risk Management and Internal Control ReportingApril Joy ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Affecting Liabilities and EquityDocument8 pagesInternal Control Affecting Liabilities and EquityPrincess Carol HolandaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Aol Case 1Document6 pagesAssessment Aol Case 1Gusti PanduNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 - Similar QuestionsDocument10 pagesAssign 2 - Similar Questionscyics TabNo ratings yet
- Audit of LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesAudit of LiabilitiesGille Rosa Abajar100% (1)
- Principles of AuditingDocument48 pagesPrinciples of Auditingthangarajbala123No ratings yet
- Expert Q&A SolutionsDocument3 pagesExpert Q&A SolutionsSitiNadyaSefrilyNo ratings yet
- INTERNAL CONTROLS Mekong Capital's Guide to Best PracticesDocument11 pagesINTERNAL CONTROLS Mekong Capital's Guide to Best PracticesYang Ying Chan100% (1)
- Auditing owners' equity accounts and verifying opening balancesDocument5 pagesAuditing owners' equity accounts and verifying opening balancesKinas AnugrahaningNo ratings yet
- Auditing Liabilities AssertionsDocument7 pagesAuditing Liabilities AssertionsSanjeevParajuliNo ratings yet
- Ensuring The Integrity of Financial InformationDocument24 pagesEnsuring The Integrity of Financial InformationGaluh Boga KuswaraNo ratings yet
- Aud689 Feb2022 SsDocument6 pagesAud689 Feb2022 SsAlexNo ratings yet
- Audit Of Liabilities Substantive ProceduresDocument28 pagesAudit Of Liabilities Substantive ProceduresHello Kitty100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Revenue CycleDocument12 pagesChapter 4: Revenue CycleCyrene CruzNo ratings yet
- Audit CH 1Document5 pagesAudit CH 1Amit harchandNo ratings yet
- FAU Review Note - Chapter 2 Auditor's ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesFAU Review Note - Chapter 2 Auditor's ResponsibilitiesMonikachhna HuotNo ratings yet
- Ais Fraud-Case StudyDocument3 pagesAis Fraud-Case StudyErica AlimpolosNo ratings yet
- S.no Company Name Auditor's Name Type Topic Particulars Principle Auditor's ResponseDocument56 pagesS.no Company Name Auditor's Name Type Topic Particulars Principle Auditor's ResponsealokjaseNo ratings yet
- Audit and AssuranceDocument11 pagesAudit and AssurancequratulainNo ratings yet
- Internal Controls-Sales and Collection CycleDocument4 pagesInternal Controls-Sales and Collection CyclebabyNo ratings yet
- Auditing Part 3Document10 pagesAuditing Part 3Trisha BanzonNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Weaknesses in Purchase SystemDocument6 pagesInternal Control Weaknesses in Purchase SystemNatala WillzNo ratings yet
- Audit & Assurance 2012Document13 pagesAudit & Assurance 2012S M Wadud TuhinNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance 100 Important Suggested Answers 1642753035Document114 pagesAudit and Assurance 100 Important Suggested Answers 1642753035Alaka BelkudeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Solution cs302Document9 pagesMidterm Solution cs302Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Financial AuditDocument3 pagesFinancial AuditHenny FaustaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction To AuditingDocument14 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To AuditingHitesh VNo ratings yet
- Test 5Document12 pagesTest 5Maithili KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 General Types of Audit - PPT 123915218Document32 pagesChapter 3 General Types of Audit - PPT 123915218Clar Aaron Bautista100% (2)
- STANDARD OF AUDITING SUMMARY REVISION WITH CASE STUDIES UPLOADED ON 11th MAY 2017 636302080328521091 PDFDocument48 pagesSTANDARD OF AUDITING SUMMARY REVISION WITH CASE STUDIES UPLOADED ON 11th MAY 2017 636302080328521091 PDFVinoth AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document9 pagesChapter 15Dhey LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Complete Auditing Notes Better VersionDocument61 pagesComplete Auditing Notes Better Versionbrilliant FrancisNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Controls For Life Insurance Company ReservesDocument14 pagesFinancial Accounting Controls For Life Insurance Company ReservesDany AryantoNo ratings yet
- 004 - Red Flags-Bank AudtsDocument41 pages004 - Red Flags-Bank Audtschandra sekharNo ratings yet
- F8 (AA) Kit - Que 82 - Blackberry CoDocument3 pagesF8 (AA) Kit - Que 82 - Blackberry CoChrisNo ratings yet
- Audit of Liabilities ProceduresDocument9 pagesAudit of Liabilities Procedureskara albueraNo ratings yet
- Study and Evaluation of Internal ControlDocument3 pagesStudy and Evaluation of Internal ControlRose Medina BarondaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 AnsDocument10 pagesChapter 15 AnsDave ManaloNo ratings yet
- Arens Auditing16e SM 22Document20 pagesArens Auditing16e SM 22김현중No ratings yet
- BT kiem toanDocument5 pagesBT kiem toantrangnguyen.31221021691No ratings yet
- At 07 Internal Control ConsiderationDocument11 pagesAt 07 Internal Control ConsiderationJobby JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter+11 Transactional+CycleDocument35 pagesChapter+11 Transactional+Cyclemohazka hassan100% (1)
- Jawaban Chapter 18Document34 pagesJawaban Chapter 18Heltiana Nufriyanti75% (4)
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Bangladesh Professional Stage: Knowledge Level Additional Sheet - Internal ControlDocument4 pagesThe Institute of Chartered Accountants of Bangladesh Professional Stage: Knowledge Level Additional Sheet - Internal ControlShahid MahmudNo ratings yet
- Auditing Assignment-2 Submitted To Keerti Mam Submitted by Bhavna PathakDocument9 pagesAuditing Assignment-2 Submitted To Keerti Mam Submitted by Bhavna PathakBhavnaNo ratings yet
- Cfo Advisory CmaasDocument27 pagesCfo Advisory Cmaasanjali aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Aap - 12 & 13Document3 pagesAap - 12 & 13escarnelaaNo ratings yet
- Interloop Financials 2023Document31 pagesInterloop Financials 2023Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- CFAP-6-Winter-2021Document10 pagesCFAP-6-Winter-2021os96529No ratings yet
- Chap015 FinancingInvesting ProcessDocument16 pagesChap015 FinancingInvesting ProcessSiti dea rahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 AuditingDocument9 pagesChapter 14 Auditingmeiwin manihing100% (1)
- AuditingDocument40 pagesAuditingIrina IordacheNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument7 pagesInternal ControlSaharAnsarayNo ratings yet
- Auditing and EthicsDocument97 pagesAuditing and EthicsdeterminemsNo ratings yet
- International Aerospace Olympiad 2020: Group C Study MaterialDocument13 pagesInternational Aerospace Olympiad 2020: Group C Study Material8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Misconceptions About The Catholic Church - Listverse PDFDocument15 pagesTop 10 Misconceptions About The Catholic Church - Listverse PDFMaryvincoNo ratings yet
- Tendernotice 2Document133 pagesTendernotice 2Pratik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Japanese Occupation Court Ruling ValidityDocument2 pagesJapanese Occupation Court Ruling ValidityGlen VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Defamation of Public Officials Under American Rule of LawDocument9 pagesDefamation of Public Officials Under American Rule of LawSugar Fructose GalactoseNo ratings yet
- Well Construction Journal - May/June 2014Document28 pagesWell Construction Journal - May/June 2014Venture PublishingNo ratings yet
- Nature The Gentlest MotherDocument4 pagesNature The Gentlest MotherMeeta Sharma100% (2)
- List of Students with Registration DetailsDocument69 pagesList of Students with Registration Detailsharshasg92No ratings yet
- How Children Learn LanguageDocument8 pagesHow Children Learn LanguageFakhruRozyNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Question Bank Class 8Document9 pagesSCIENCE Question Bank Class 8anupNo ratings yet
- Shades of White: Rendering in WatercolorDocument4 pagesShades of White: Rendering in WatercolorMichael Reardon100% (4)
- Ticket 3586662689Document2 pagesTicket 3586662689dev dNo ratings yet
- PE Week QuizDocument2 pagesPE Week QuizMarvin RetutalNo ratings yet
- Monitor Pressao Arterial ProCheck - IB-WW1YB-3Document58 pagesMonitor Pressao Arterial ProCheck - IB-WW1YB-3jpmarques19660% (1)
- Computerized Scholarship Monitoring SystemDocument11 pagesComputerized Scholarship Monitoring SystemCharles VegasNo ratings yet
- AP10 - Q2 - Mod3 - Mga Dahilan at Epekto NG Migrasyon PDFDocument1 pageAP10 - Q2 - Mod3 - Mga Dahilan at Epekto NG Migrasyon PDFZyral Alliyah SantiagoNo ratings yet
- About The Rosary of Our LadyDocument2 pagesAbout The Rosary of Our LadyINONG235No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris ASPD Dikpora Feb 2022Document15 pagesBahasa Inggris ASPD Dikpora Feb 2022WIBI CAM100% (1)
- Certificates Search For King and Queen 2019Document13 pagesCertificates Search For King and Queen 2019Kebu YenNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Training: String Manipulation and Simple Classical ReportDocument33 pagesSAP ABAP Training: String Manipulation and Simple Classical ReportpraveengkumarerNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument14 pagesTurbineArjit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- English For Business: Level 1Document24 pagesEnglish For Business: Level 1anonymous9196806No ratings yet
- MITSUMI M49SP-2K stepping motor datasheetDocument2 pagesMITSUMI M49SP-2K stepping motor datasheetMarcos George0% (1)
- SSG Accomplishment ReportDocument7 pagesSSG Accomplishment ReportTeacheer Dan91% (22)
- Humor, Humility and National Identity in Pride and PrejudiceDocument13 pagesHumor, Humility and National Identity in Pride and PrejudiceLuz SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Four Modes of DeliveryDocument21 pagesFour Modes of DeliveryRyan AbellaNo ratings yet
- Bulletin 10/19/2014Document8 pagesBulletin 10/19/2014smchicagoNo ratings yet
- Black Magic v03n04 1967-01.american Art AgencyDocument82 pagesBlack Magic v03n04 1967-01.american Art AgencyJulieta de la HuertaNo ratings yet
- Level 1 Writing Supplementary MaterialsDocument132 pagesLevel 1 Writing Supplementary MaterialsDiễm Quỳnh TrầnNo ratings yet