Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy 4
Uploaded by
ysabelle roco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document discusses the electromagnetic spectrum, which is the full range of electromagnetic radiation organized by frequency or wavelength. It is divided into separate bands including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each band has different characteristics such as how waves are produced, how they interact with matter, and their applications. Radio waves have the lowest photon energy and longest wavelengths, while gamma rays have the highest photon energy and interact strongly with matter.
Original Description:
Original Title
anatomy 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the electromagnetic spectrum, which is the full range of electromagnetic radiation organized by frequency or wavelength. It is divided into separate bands including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each band has different characteristics such as how waves are produced, how they interact with matter, and their applications. Radio waves have the lowest photon energy and longest wavelengths, while gamma rays have the highest photon energy and interact strongly with matter.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesAnatomy 4
Uploaded by
ysabelle rocoThe document discusses the electromagnetic spectrum, which is the full range of electromagnetic radiation organized by frequency or wavelength. It is divided into separate bands including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each band has different characteristics such as how waves are produced, how they interact with matter, and their applications. Radio waves have the lowest photon energy and longest wavelengths, while gamma rays have the highest photon energy and interact strongly with matter.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Electromagnetic spectrum
76 languages
Article
Talk
Read
Edit
View history
Tools
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
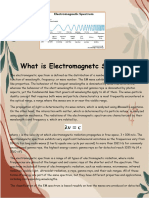
A diagram of the electromagnetic
spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths,
as well as the equivalent blackbody temperature
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation,
organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands,
with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high
frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays,
and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different
characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their
practical applications.
Radio waves, at the low-frequency end of the spectrum, have the lowest photon
energy and the longest wavelengths—thousands of kilometers, or more. They can be
emitted and received by antennas, and pass through the atmosphere, foliage, and most
building materials.
Gamma rays, at the high-frequency end of the spectrum, have the highest photon e
You might also like
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum of RadiationDocument4 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum of RadiationGanaka KodithuwakkuNo ratings yet
- Electromagentic SpectrumDocument24 pagesElectromagentic SpectrumJanelyn Garin100% (1)
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument26 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumArjune PantallanoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument31 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMNo ratings yet
- EM Waves and Spextrum PDFDocument45 pagesEM Waves and Spextrum PDFJoanna SeproNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Learning OutcomesDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Learning OutcomesAbhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticDocument4 pagesElectromagneticDini Sukaseal100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesputri_latifah100% (3)
- Energy in The Earth System: How Do Radiation and Convection Currents Affect Phenomena On Earth?Document51 pagesEnergy in The Earth System: How Do Radiation and Convection Currents Affect Phenomena On Earth?Noroña S.R.No ratings yet
- Science & Technology 10: Week 3 & 4 Second QuarterDocument55 pagesScience & Technology 10: Week 3 & 4 Second QuarterAthena MayNo ratings yet
- Fme10 q2 w1 Em-WavesDocument6 pagesFme10 q2 w1 Em-WavesLouis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumhamidkatebiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMr. Borges50% (2)
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaNo ratings yet
- Karen May P. UrlandaDocument47 pagesKaren May P. UrlandaKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument25 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumshasagailNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument25 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumMark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- What Is The EM SpectrumDocument13 pagesWhat Is The EM SpectrumJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Gepend Bahan AjarDocument25 pagesGepend Bahan AjareuritmikNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q2-Week 3 - 4 Application of Electromagnetic WavesDocument26 pagesG10 Science Q2-Week 3 - 4 Application of Electromagnetic WavesKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument65 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumCLester MadShadowNo ratings yet
- EMnotes 2Document25 pagesEMnotes 2tripathiansh447No ratings yet
- Uv VisablespectroscopyatheerDocument18 pagesUv Visablespectroscopyatheerareej juttNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics (Gamma Ray Definition, Uses, Wavelengths)Document1 pageIgcse Physics (Gamma Ray Definition, Uses, Wavelengths)Riya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Regions: The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesRegions: The Electromagnetic SpectrumIrene PontillasNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves and MicrowavesDocument10 pagesRadio Waves and MicrowavesShelly Ryn SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum, The Entire Distribution ofDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum, The Entire Distribution ofHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- 1-Transmission Line TypesDocument20 pages1-Transmission Line TypesManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Ec Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesEc Seminar ReportDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic SpectrumAsim ZargarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Introduction To EMFTDocument19 pagesIntroduction To EMFTVikas KaushikNo ratings yet
- G1o U2l1 - Electromagnetic Wave 10 - 1819 - 22Document73 pagesG1o U2l1 - Electromagnetic Wave 10 - 1819 - 22Erika Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Their Applications: (Part 1)Document23 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Their Applications: (Part 1)Ej AlfuenteNo ratings yet
- S10 - Q2 - Week 2Document7 pagesS10 - Q2 - Week 2Evefel Ruth SanchezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpectrosDocument64 pagesIntroduction To SpectrosMOHAMMED ABDUL HAINo ratings yet
- Applied Physics IiDocument5 pagesApplied Physics IiParas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document6 pagesUntitled 2Faizal DinjoeNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - UPHDocument20 pagesEM Waves - UPHSHIVA THAVANI100% (1)
- Obt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 1Document30 pagesObt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 1Jayashree Sathiyanarayanan100% (2)
- Em Spectrum 2Document20 pagesEm Spectrum 2Karan YadavNo ratings yet
- EM Notes 2Document23 pagesEM Notes 2Jared PataniNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 Q2-Module-2 RemovedDocument17 pagesGenPhysics2 Q2-Module-2 RemovedJasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Waves Packet KEYDocument44 pagesWaves Packet KEYlauraNo ratings yet
- History: Spectrum IsDocument23 pagesHistory: Spectrum IsMuhamad NurhudayahNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer QuizDocument4 pagesScience Reviewer Quiz28. Pinera, Yna Angela S.No ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry - Unit-4Document28 pagesApplied Chemistry - Unit-4indigalakishoreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 - EM WavesDocument8 pagesLecture 2.1 - EM WavesAPPLE CAGUNGUN-BELGICANo ratings yet
- Physics 20 - The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument45 pagesPhysics 20 - The Electromagnetic SpectrumHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ami Question BankDocument23 pagesAmi Question BankjaisathiNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 2Document19 pagesGenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 2Jasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Electro Magentism Itnereferation in The Metropolita AreaDocument8 pagesElectro Magentism Itnereferation in The Metropolita AreaAndreescu CristianNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumRuperto Alarilla Palomaria Jr.No ratings yet
- G10 Science Q2 W1 Electromagnetic WavesDocument47 pagesG10 Science Q2 W1 Electromagnetic WavesnickanormacaraegNo ratings yet
- Em SpectrumDocument42 pagesEm Spectrumshei市No ratings yet
- Cy Complete PDFDocument225 pagesCy Complete PDFAakarshNo ratings yet
- Common Properties of Light Renzej - 20240309 - 201256 - 0000Document52 pagesCommon Properties of Light Renzej - 20240309 - 201256 - 0000Lidelyn Jane CañalitaNo ratings yet
- AyesaDocument2 pagesAyesaysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- JudyDocument1 pageJudyysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- JorishDocument1 pageJorishysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- Types of Motion: Physics PortalDocument2 pagesTypes of Motion: Physics Portalysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- SeasonnnnDocument3 pagesSeasonnnnysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Electromagnetic WaveDocument2 pagesAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Waveysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- No Homework PolicyDocument6 pagesNo Homework Policyysabelle rocoNo ratings yet