Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave
Uploaded by
ysabelle roco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesElectromagnetic waves transport energy through electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other as the wave travels. Charged particles like electrons and protons create these electromagnetic fields when they move, and this electromagnetic radiation includes light. Mechanical waves require a medium like water, air, or other matter to travel through and are caused by vibrations or disturbances in that medium, transmitting energy by causing consecutive collisions between molecules. Examples are water waves and sound waves, which cannot travel through a vacuum without a medium.
Original Description:
Original Title
Anatomy of an Electromagnetic Wave
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectromagnetic waves transport energy through electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other as the wave travels. Charged particles like electrons and protons create these electromagnetic fields when they move, and this electromagnetic radiation includes light. Mechanical waves require a medium like water, air, or other matter to travel through and are caused by vibrations or disturbances in that medium, transmitting energy by causing consecutive collisions between molecules. Examples are water waves and sound waves, which cannot travel through a vacuum without a medium.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave
Uploaded by
ysabelle rocoElectromagnetic waves transport energy through electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other as the wave travels. Charged particles like electrons and protons create these electromagnetic fields when they move, and this electromagnetic radiation includes light. Mechanical waves require a medium like water, air, or other matter to travel through and are caused by vibrations or disturbances in that medium, transmitting energy by causing consecutive collisions between molecules. Examples are water waves and sound waves, which cannot travel through a vacuum without a medium.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Anatomy of an Electromagnetic Wave
Energy, a measure of the ability to do work, comes in many forms and can transform
from one type to another. Examples of stored or potential energy include batteries and
water behind a dam. Objects in motion are examples of kinetic energy. Charged
particles—such as electrons and protons—create electromagnetic fields when they
move, and these fields transport the type of energy we call electromagnetic radiation, or
light.
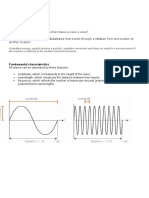
What are Electromagnetic and Mechanical waves?
Mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves are two important ways that energy is
transported in the world around us. Waves in water and sound waves in air are two
examples of mechanical waves. Mechanical waves are caused by a disturbance or
vibration in matter, whether solid, gas, liquid, or plasma. Matter that waves are traveling
through is called a medium. Water waves are formed by vibrations in a liquid and sound
waves are formed by vibrations in a gas (air). These mechanical waves travel through a
medium by causing the molecules to bump into each other, like falling dominoes
transferring energy from one to the next. Sound waves cannot travel in the vacuum of
space because there is no medium to transmit these mechanical waves.
You might also like
- What Is Kinetic EnergyDocument2 pagesWhat Is Kinetic Energyapi-218158367100% (4)
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismDocument23 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismUma Venkata SumanthNo ratings yet
- PEMF ClinicalStudies 1Document38 pagesPEMF ClinicalStudies 1OaNa Miron100% (3)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- C12 Electromagnetic WavesDocument80 pagesC12 Electromagnetic WavesmarianrosecardanioNo ratings yet
- Waves Week 3Document16 pagesWaves Week 3Georgette MatinNo ratings yet
- Types of Waves EnergyDocument4 pagesTypes of Waves Energyjayson pintorNo ratings yet
- EM WaveDocument15 pagesEM WaveAlvin GultiaNo ratings yet
- All About WavesDocument2 pagesAll About WavesAlexs VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Unidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)Document32 pagesUnidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Factsheet No WaveDocument6 pagesFactsheet No WaveJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument1 pageThis Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeANMOLNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument23 pagesWave Motionanubh50No ratings yet
- Propagation of WaveDocument18 pagesPropagation of WaveVipul KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Significant Contribution/s in The Development of Electromagnetic Wave TheoryDocument3 pagesActivity 1: Significant Contribution/s in The Development of Electromagnetic Wave TheorySanny SuanNo ratings yet
- Waves: General ViewDocument3 pagesWaves: General ViewAdri PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Force. A Fundamental Force in Nature, The Electromagnetic Force ActsDocument1 pageElectromagnetic Force. A Fundamental Force in Nature, The Electromagnetic Force ActsKyle Haven DelcastilloNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pages5.2 Electromagnetic WavesYuvaraniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Electromagnetic Theor1Document10 pagesWhat Is The Electromagnetic Theor1gabezneNo ratings yet
- Phys101 - Finals Quiz 1Document2 pagesPhys101 - Finals Quiz 1Natasha AcaoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism EssayDocument2 pagesElectromagnetism EssayelectromagnetNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveAngelo John R. JavinezNo ratings yet
- Waves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyDocument4 pagesWaves:: Wave Disturbance Medium or Space Accompanied by A Transfer of EnergyAriyan Abrar SaifNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Microwave Energy: Chapter TwoDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of Microwave Energy: Chapter TwoSoma GhoshNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Magnetic FieldsDocument3 pagesElectric Fields and Magnetic FieldsPuneeth SiddappaNo ratings yet
- Science Q3Document7 pagesScience Q3Jaycel StudiesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting SystemDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Part 1illumination and General Lighting Systemmahato4120No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: WavesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: WavesKyera LovesNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Complete The FollowingDocument2 pagesElectricity: Complete The FollowingDanissaNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields On Human's HealthDocument18 pagesBiological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields On Human's HealthMarina ZaraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Observations: Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Radiation or EMR) Refers To The Waves (OrDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Observations: Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Radiation or EMR) Refers To The Waves (OrYancy MiclatNo ratings yet
- Student Guide: Exploring Wind EnergyDocument40 pagesStudent Guide: Exploring Wind EnergyskilmagNo ratings yet
- 4.2 DraftDocument5 pages4.2 DraftCarlos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Competency 6 Ay 2023 2024 2Document14 pagesCompetency 6 Ay 2023 2024 2chaibalinNo ratings yet
- Rina B. InggrisDocument9 pagesRina B. InggrisRidwan Alfian NoorNo ratings yet
- Guia 1 Ingles AngeloDocument13 pagesGuia 1 Ingles AngeloAlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- Different Types of WavesDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Waveselladionisio01No ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETICDocument8 pagesELECTROMAGNETICagustinjucylynNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Radiationpeacekalman63No ratings yet
- Waves: Done By: Sama Majed Grade: 8DDocument7 pagesWaves: Done By: Sama Majed Grade: 8DSama Al HayekNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Wave1Document5 pagesDifferent Types of Wave1Patrick Joshua ZacariasNo ratings yet
- IM Production, Propagation and Detection of EM WavesDocument2 pagesIM Production, Propagation and Detection of EM WavesNur ShaNo ratings yet
- The Comparison of Transverse Waves and Longitudinal WaveDocument1 pageThe Comparison of Transverse Waves and Longitudinal WaveAMID InstituteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateDocument8 pagesAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateBhaskarKhersaNo ratings yet
- Wave Particle DualityDocument7 pagesWave Particle DualityMNo ratings yet
- Waves ItroductionDocument2 pagesWaves ItroductionQuinone QuentinNo ratings yet
- Oscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumDocument2 pagesOscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumApril Joy Gelilang PulgaNo ratings yet
- EM WAVE PPT OriginalDocument39 pagesEM WAVE PPT Originalsujithrasuji773No ratings yet
- Q2 Lesson 1 Theories and Propagation of EM WavesDocument29 pagesQ2 Lesson 1 Theories and Propagation of EM Wavesluna IINo ratings yet
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveTrideep BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETISMDocument16 pagesELECTROMAGNETISMFelyzia NiamhNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Wavekanishksajankar735No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Q2Document33 pagesLesson 1 Q2odnimernNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 10Document6 pagesElectromagnetism 10Felyzia NiamhNo ratings yet
- Physics: TheoryDocument5 pagesPhysics: TheoryIrshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Stage 7 Physics Strand NotesDocument8 pagesStage 7 Physics Strand NotesMazuba ChibbelaNo ratings yet
- Group Activity 2 EM Wave Propagation and TransmissionDocument3 pagesGroup Activity 2 EM Wave Propagation and Transmissionjessonpena2No ratings yet
- Mini Project DocumentationDocument51 pagesMini Project DocumentationSravanthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- AyesaDocument2 pagesAyesaysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- JudyDocument1 pageJudyysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- JorishDocument1 pageJorishysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- Types of Motion: Physics PortalDocument2 pagesTypes of Motion: Physics Portalysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- SeasonnnnDocument3 pagesSeasonnnnysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 4Document2 pagesAnatomy 4ysabelle rocoNo ratings yet
- No Homework PolicyDocument6 pagesNo Homework Policyysabelle rocoNo ratings yet