Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Text 2dididid
Uploaded by
hussainshakeel.mzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Text 2dididid
Uploaded by
hussainshakeel.mzCopyright:
Available Formats
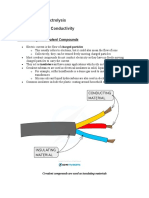
Chemistry
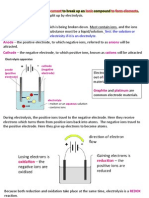
electrolysis below produces gases A and B.
solution of
socium chionide
CarDon
cathode
power supply
" Why does the solution conduct electricity?
, Identify each gas, and describe a test you could carry out to confirm its
identity.
e Name one product manufactured from: i gas A
gas B
di Write half-equations to show how the two
gases are produced.
it The overall reaction is a redox reaction.
Explain why.
e The solution remaining after the electrolysis will turn litmus paper blue.
i What is the name of this solution? it State one chemical property for it.
" List the ions that are present in concentrated solutions of:
i sodium chloride
ii
copper(II) chloride
, Explain why and how the ions move, when each solution is electrolysed using
platinum electrodes.
c Write the half-equation for the reaction at: i the anode
ii
the cathode
during the electrolysis of each solution. d Explain why the anode reactions for
both solutions are the same.
e i The anode reactions will be different if the solutions are made very dilute.
Explain why. ii Write the half-equations for the new anode
reactions.
/ Explain why copper is obtained at the cathode, but sodium is not.
° Name another solution that will give the same products as the concentrated
solution of sodium chloride does, on electrolysis.
h Which solution in a could be the electrolyte in an electroplating experiment?
'rode
'ode ed, or
いしいし
inode
Core syllabus content
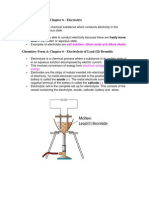
1 Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is carried out
molten lead
oromiue
a The bulb will not light until the lead bromide
has melted. Why not?
b What will be seen at the anode? c Name the substance in b.
d What will be formed at the cathode?
2
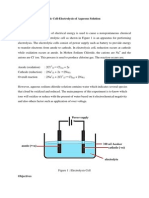
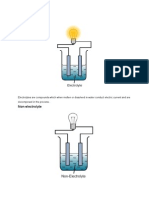
Six substances A to F were dissolved in water, and connected in turn into the
circuit below.
A represents an ammeter, which is used to measure current. The table shows the
results.
sed
alides
he lalf-
he
is of
1)
ipure
solution
Substance Current (amperes) At cathode
(-) At anode
(+)
0.8 copper chlorine
1.0 hydrogen chlorine
0.0
0.8 hydrogen chlorine
E 1.2 hydrogen oxygen
F 0.7 silver oxygen
a Which solution conducts best? b Which solution is a non-electrolyte? c Which
solution could be:
i silver nitrate? ii copper (II) chloride? iii sugar?
iv dilute sulfuric acid?
d i Two of the solutions give the same products at the electrodes. Which two?
ii Name two chemicals which would give those products, when connected into the
circuit as concentrated solutions.
1. **Why does the solution conduct electricity?**
- The solution conducts electricity due to the presence of ions formed from the
dissociation of sodium chloride in water.
2. **Identify each gas, and describe a test you could carry out to confirm its
identity.**
- Gas A: Hydrogen. Test: Collect the gas in a tube and ignite it; it should
produce a pop sound.
- Gas B: Chlorine. Test: Introduce damp blue litmus paper; it should turn red
and then bleach it.
3. **Name one product manufactured from:**
- Gas A: Hydrogen - Used in the production of ammonia.
- Gas B: Chlorine - Used in the manufacture of PVC.
4. **Write half-equations to show how the two gases are produced.**
- Hydrogen: 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻
- Chlorine: 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
5. **Explain why the overall reaction is a redox reaction.**
- Redox involves both reduction and oxidation. In this case, hydrogen is reduced
(gains electrons), and chlorine is oxidized (loses electrons).
6. **The solution remaining after electrolysis turns litmus paper blue.**
- The solution is sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Chemical property: It is caustic and
alkaline.
7. **List ions present in concentrated solutions of:**
- i) Sodium chloride: Na⁺, Cl⁻
- ii) Copper(II) chloride: Cu²⁺, Cl⁻
8. **Explain why and how ions move during electrolysis using platinum electrodes.**
- Ions move to conduct electricity. At the anode, Cl⁻ ions lose electrons
(oxidation), move towards the anode. At the cathode, Na⁺ ions gain electrons
(reduction), move towards the cathode.
9. **Write half-equations for the reaction at:**
- i) Anode: 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
- ii) Cathode: 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻
10. **Explain why anode reactions for both solutions are the same.**
- Both solutions involve chloride ions, leading to similar oxidation reactions
at the anode.
11. **Anode reactions differ if solutions are very dilute.**
- Explanation: In dilute solutions, water is preferentially oxidized at the
anode, forming oxygen gas.
- Half-equations: 2H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
12. **Why copper is obtained at the cathode, but sodium is not.**
- Sodium is more reactive and stays in solution as ions, while less reactive
copper is reduced and deposited at the cathode.
13. **Name another solution giving the same products as concentrated sodium
chloride does on electrolysis.**
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) will yield the same products.
14. **Which solution in a could be the electrolyte in an electroplating experiment?
**
- Copper(II) chloride solution.
**Electrolysis of Molten Lead Bromide:**
1. **Bulb won't light until lead bromide has melted. Why not?**
- Bulb requires a complete circuit. Solid lead bromide does not conduct, so the
bulb remains unlit.
2. **What will be seen at the anode?**
- Bromine gas will be seen at the anode.
3. **Name the substance in b.**
- Bromine gas.
4. **What will be formed at the cathode?**
- Lead metal will be formed at the cathode.
**Six Substances A to F in Water:**
a. **Which solution conducts best?**
- Copper chloride solution (1.0 amperes).
b. **Which solution is a non-electrolyte?**
- Substance E (0.0 amperes).
c. **Identify solutions for i-iv.**
- i) A: silver nitrate
- ii) B: copper (II) chloride
- iii) C: sugar
- iv) D: dilute sulfuric acid
d. **Two solutions with the same products:**
- i) Copper chloride (A) and silver nitrate (F).
- ii) Chemicals: CuCl₂ and AgNO₃.
You might also like
- Melting Point of MetalsDocument3 pagesMelting Point of MetalsrhapknexxNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsDocument11 pagesElectrolysis: Electrolysis Electric Current Ionic To Form ElementsLana Arsyad100% (2)
- Electrolysis QuestionsDocument53 pagesElectrolysis QuestionsAahaan ShethNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisChemistryKlipz97% (34)
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- Revision Test Electrolysis OlevelsDocument5 pagesRevision Test Electrolysis OlevelsMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Important Questions SolvedDocument4 pagesICSE Class 10 Chemistry Important Questions Solvedvij200950% (2)
- Summative Test For Science 7Document2 pagesSummative Test For Science 7Claudene Gella100% (4)
- ElectrochemistryDocument43 pagesElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument83 pagesElectrolysismoizbadri100% (3)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Experiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument8 pagesExperiment 2: Electrolytic Cell-Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionNad Sng90% (21)
- Bgcse Double Award Paper 3 2016 - SolutionsDocument15 pagesBgcse Double Award Paper 3 2016 - Solutionsrose tebogo100% (2)
- Science Folio: Importance of Maintaining Cleanliness of The Air - Form 1Document11 pagesScience Folio: Importance of Maintaining Cleanliness of The Air - Form 1Amirul Ariff Ghazali67% (6)
- Experiment 2: Electrolytic Cell - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument10 pagesExperiment 2: Electrolytic Cell - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionimizzNo ratings yet
- Presentation KPTDocument79 pagesPresentation KPTNor Fatihah Ab Malek100% (1)
- Checkup On Chapter 8: Questions Revision ChecklistDocument2 pagesCheckup On Chapter 8: Questions Revision ChecklistShahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Class X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyDocument4 pagesClass X Test Electrolysis and MetullargyToshiGMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis and Electroplating QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectrolysis and Electroplating QuestionsManash SinghaNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Electrolysisspurohit1991No ratings yet
- Electrolysis reactions and observationsDocument35 pagesElectrolysis reactions and observationsBOOKwormNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis key-H.w(4)-Ionic compoundsDocument4 pagesElectrolysis key-H.w(4)-Ionic compoundsbedo lucyNo ratings yet
- H.W (4) - Electrolysis of Aqueous Solution of Ionic Compounds-G9 PDFDocument4 pagesH.W (4) - Electrolysis of Aqueous Solution of Ionic Compounds-G9 PDFbedo lucyNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3Document6 pagesMarking Scheme Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 3aikubing100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6Elynn TanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Lab Results SummaryDocument4 pagesElectrolysis Lab Results SummaryCornelius PaunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document30 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- Xii Chem Prep. Paper 2023Document3 pagesXii Chem Prep. Paper 2023HiraNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Sample Experiment - Sample 1 - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument3 pagesAssessment of Sample Experiment - Sample 1 - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionORONGSANTINo ratings yet
- Form 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsDocument9 pagesForm 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsGono TakaduuNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument33 pagesElectrolysisborglingchompersNo ratings yet
- C12 Electrochemistry IgcseDocument33 pagesC12 Electrochemistry IgcseAnna DixonNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of molten lead bromideDocument38 pagesElectrolysis of molten lead bromidehemanth PNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 ElectrolysisJayadevi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 - ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 - ElectrolysisMysterious SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- LXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014Document5 pagesLXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014HNo ratings yet
- 09 ElectrolysisDocument2 pages09 ElectrolysisSean R GrantNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesKey Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisKim KatNo ratings yet
- Studies of Heavy Metals: Unit - 7Document3 pagesStudies of Heavy Metals: Unit - 7Rabin KCNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- Electrolysis Chemistry (Quick Check Que)Document3 pagesElectrolysis Chemistry (Quick Check Que)Lei YinNo ratings yet
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 6Document11 pagesRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 6Vincent Vetter100% (1)
- Electrolysis WorksheetDocument1 pageElectrolysis WorksheetzainulabideenmuhammadnaqviNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMPavithiranNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateDocument16 pagesChemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateVinayNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetDocument83 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY WorksheetbhargavintnaiduNo ratings yet
- 25 E28093 Eletroquimica IDocument22 pages25 E28093 Eletroquimica INatinha32No ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMDocument47 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-19 at 3.39.23 PMWalaa AdelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ElectrochemistryAshraf Shaharudin100% (1)
- Answer H W - 8: When A Dilute Salt Water Is Electrolyzed, A Colorless Gas Is Given Off at The Anode. The Gas IsDocument5 pagesAnswer H W - 8: When A Dilute Salt Water Is Electrolyzed, A Colorless Gas Is Given Off at The Anode. The Gas IsMoustafa NassarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Redox Reactions, Cells, Batteries and ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry: Redox Reactions, Cells, Batteries and ElectrolysisfelixNo ratings yet
- FORM 4 Chemistry Lesson 23 ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesFORM 4 Chemistry Lesson 23 ElectrochemistrySiang DanielNo ratings yet
- Notes On ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesNotes On Electrolysisapi-3819012No ratings yet
- ElectroDocument48 pagesElectroMang friesNo ratings yet
- Peka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesPeka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryWong Wai Lun75% (8)
- UC Davis Chemistry Lab ManualDocument105 pagesUC Davis Chemistry Lab ManualpathisharmaNo ratings yet
- 5070 w03 QP 3Document8 pages5070 w03 QP 3mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationKiTTyNo ratings yet
- Instant Freezing Water Trick: CH CO Na Na CLDocument1 pageInstant Freezing Water Trick: CH CO Na Na CLViraj GhodkiNo ratings yet
- HCL MSDS PDFDocument6 pagesHCL MSDS PDFcryovikas1975No ratings yet
- STPM 2019 Sem 2uDocument7 pagesSTPM 2019 Sem 2uAprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- Physical Prop DataDocument392 pagesPhysical Prop Dataapi-3750488100% (1)
- BAI 4 ĐỒNG VÀ HỢP CHẤTDocument41 pagesBAI 4 ĐỒNG VÀ HỢP CHẤTLinhh ChiiNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds PDFDocument18 pagesNaming Compounds PDFJohn Jade BasuelNo ratings yet
- Cleaning in The LabDocument8 pagesCleaning in The LabHon Kirimi Mwobobia IINo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class XII Experiment Project-Sterilization of Water Using Bleaching PowderDocument17 pagesChemistry Class XII Experiment Project-Sterilization of Water Using Bleaching PowderKamaljoshi4100% (1)
- 08RedoxNotes 221010 132804Document24 pages08RedoxNotes 221010 132804Abdullah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document16 pagesGroup 1Abdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- N Series Cartridge For Gases/vapors Protection (NIOSH Standard)Document2 pagesN Series Cartridge For Gases/vapors Protection (NIOSH Standard)Diego MartinezNo ratings yet
- Halo DerivativesDocument5 pagesHalo DerivativesBHASWATI MANDALNo ratings yet
- What Are AlkanesDocument9 pagesWhat Are AlkanesShayne MawondeNo ratings yet
- Practice tests for restatements, negatives, who/whereDocument8 pagesPractice tests for restatements, negatives, who/wherelatif nazamudinNo ratings yet
- Chlorine in AirDocument5 pagesChlorine in AirZahra Debrian PutriNo ratings yet
- Intro to Solid-State Chem PS 1Document10 pagesIntro to Solid-State Chem PS 1JayNo ratings yet
- Ozone Layer Protection by UV-Absorbing Stratospheric OzoneDocument21 pagesOzone Layer Protection by UV-Absorbing Stratospheric OzoneAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medi-Gas Check Full Range CatalogueDocument20 pagesMedi-Gas Check Full Range CatalogueShamshad HussainNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical For Halide IonsDocument3 pagesChemistry Practical For Halide IonsasdfghiNo ratings yet
- Total Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument1 pageTotal Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsAmol AdsulNo ratings yet
- Msds Al2o3 PDFDocument6 pagesMsds Al2o3 PDFNazuah Ushwatun HassanahNo ratings yet
- MSDS For MercuryDocument9 pagesMSDS For Mercurycelia pasiguanNo ratings yet
- Ent Alphy Bond EnergyDocument2 pagesEnt Alphy Bond EnergyAlejandro GuerreroNo ratings yet