Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Prelim
Uploaded by
canvakepsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Prelim
Uploaded by
canvakepsCopyright:
Available Formats
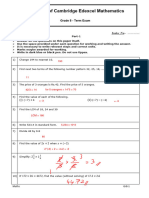
Second Preliminary Examination In Mathematics 9
Name: Date:
Grade & Section: Score:
I. Fill in the blanks to make each statement true. Choose the answers on the box.
1. Imaginary number i = and i2 = – 1 .
2. A complex number in standard form is written as , where a and b are real numbers.
3. In the complex number a + bi, a is the part of the number.
4. If x is a positive real number, then √ −x = .
5. Numbers a + bi and a – bi are of each other.
6. The product of a + bi and its conjugate is .
7. First used the term “imaginary numbers”.
8. was the first to suggest using i for term √ −1.
9. The radicand in the quadratic formula is called .
10. The quadratic equation has no real number solutions if the discriminant is .
11. The quadratic equation has two real number solutions if the discriminant is .
12. The quadratic equation has only one real number solutions if the discriminant is .
13. If a = 3, b = – 4, c = – 2, then b2 – 4ac is = .
14. The expression is the radicand in the quadratic formula.
15. A quadratic equation has no real number solution if the discriminant is .
Euclid √−1 a + bi conjugates negative
positive equal to zero real a2 – b2
Pythagoras 88 i – 56 b2 – 4ac Rene Descartes
II. Complete this chart to show the relationship between real numbers, imaginary numbers, complex
numbers, rational numbers and irrational numbers.
16. 1
17.
18.
19
20. 2 5
4 3
III. Solve the following. Express your answers in simplest form.
For numbers 1 – 5 For numbers 6 – 8
Perform the necessary operation. Use the discriminant to determine the number of roots.
1. ( 9 + 5i ) + ( 8 + 9i ) 6. 16x2 – 8x + 1 = 0
2. ( 6 + 3i ) – ( 2 + 3i ) 7. 2x2 + 2x – 13 = 0
3. ( 4 + 2i ) ( 7 – 4i ) 8. 2x2 – 3x = 4
4. ( 6 + i ) ( 2 – i )
5. ( 3 + 2i ) ( 3 – 2i )
You might also like
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- CSMQLD Spec12 ch15 (1) PDFDocument30 pagesCSMQLD Spec12 ch15 (1) PDFDNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Class 8 - NodrmDocument327 pagesMathematics For Class 8 - NodrmNEET/AAIMS COMPLETE PREPARATIONNo ratings yet
- 311 Maths Eng Lesson8Document28 pages311 Maths Eng Lesson8Adnan NajemNo ratings yet
- 98Document96 pages98Silviu100% (4)
- Class Ix Subject: Mathematics: Gists of The LessonsDocument8 pagesClass Ix Subject: Mathematics: Gists of The LessonsMadhusudan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Alg2 03 02Document8 pagesAlg2 03 02vinctor songNo ratings yet
- F17 XBnotes 2Document25 pagesF17 XBnotes 2Anonymous Sp94mhNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Number System WorksheetsDocument12 pagesClass 9 Maths Number System Worksheetskarthikag656No ratings yet
- Half Yearly Grade 8Document3 pagesHalf Yearly Grade 8Pm EkycNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RealnumberDocument21 pagesChapter 1 RealnumberjamaludinizzadNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Mathematics IDocument60 pagesFundamental of Mathematics INIKHIL MITTAL100% (1)
- Study Material Class - Vii, Term - II (Mathematics)Document102 pagesStudy Material Class - Vii, Term - II (Mathematics)YASHVI MODI0% (1)
- Complex Number PDFDocument5 pagesComplex Number PDFBEED 02 CTENo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Grade 9Document4 pages1st Summative Test Grade 9Orlyn Tubo AninoNo ratings yet
- TIMO 2018 卷S1fDocument5 pagesTIMO 2018 卷S1fsingarumah09No ratings yet
- Algebra Handout #8: 1 ProblemsDocument3 pagesAlgebra Handout #8: 1 ProblemsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- MM115 Complex Numbers FOR STUDENTS MatejaDocument22 pagesMM115 Complex Numbers FOR STUDENTS MatejaDavid ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesLecture NotesmonicalingkeNo ratings yet
- Concise Selina Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Rational and Irrational Numbers PDFDocument46 pagesConcise Selina Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Rational and Irrational Numbers PDFAakash BhojaneNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers: Vicky Neale Michaelmas Term 2019Document19 pagesComplex Numbers: Vicky Neale Michaelmas Term 2019Peter PNo ratings yet
- Math II Unit 1 Acq Lesson 2 Complex NumbersDocument15 pagesMath II Unit 1 Acq Lesson 2 Complex Numbersdpool2002No ratings yet
- Class IX Maths IITFoundation & Olympiad Study Package (PDFDrive)Document216 pagesClass IX Maths IITFoundation & Olympiad Study Package (PDFDrive)Vinayak GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Theory - English Fundamental of Mathematics - 01Document18 pages1 - Theory - English Fundamental of Mathematics - 01Shubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Secondary Mathematics 7.Document67 pagesSecondary Mathematics 7.Vikrant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Algebra Chapter 1 PDFDocument23 pagesAlgebra Chapter 1 PDFanon_94727000No ratings yet
- Module 1-ECE 1Document11 pagesModule 1-ECE 1Santy Enril Belardo Jr.No ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Grade 9Document4 pages1st Summative Test Grade 9MalouNo ratings yet
- Precalculus NotesDocument5 pagesPrecalculus NotesMuneebKhanNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers: 8.1.1 The BackgroundDocument34 pagesComplex Numbers: 8.1.1 The BackgroundjayNo ratings yet
- Department of Education - Western Province First Term Evaluation Grade 8 Mathematics Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Index No: .Document5 pagesDepartment of Education - Western Province First Term Evaluation Grade 8 Mathematics Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Index No: .SharanyaaNo ratings yet
- No - System Class 9Document3 pagesNo - System Class 9sdcom93No ratings yet
- 3.1: Complex Numbers: Skills To DevelopDocument12 pages3.1: Complex Numbers: Skills To DevelopJea Mae G. BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Complex Numbers: Math 170: Ideas in Mathematics (Section 002)Document5 pagesNotes On Complex Numbers: Math 170: Ideas in Mathematics (Section 002)Ardit ZotajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01: Basic Mathematics and Logarithm - ModuleDocument24 pagesChapter 01: Basic Mathematics and Logarithm - ModuleSuraj100% (1)
- Subsets of Real Numbers PDFDocument5 pagesSubsets of Real Numbers PDFSyaoran LiNo ratings yet
- 1 Math-AlgebraDocument4 pages1 Math-AlgebraJeric Gader BriosoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 12 Understanding The Principles of MathematicsDocument129 pagesGrade 10 12 Understanding The Principles of MathematicsChristabel C kangoNo ratings yet
- TIMO 2018 卷S2fDocument7 pagesTIMO 2018 卷S2fjp100% (1)
- Funda Mental S of M Athem Atics: JEE-MathematicsDocument5 pagesFunda Mental S of M Athem Atics: JEE-Mathematicsc kumarNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Complex Numbers (S)Document24 pages1.2 - Complex Numbers (S)sureintharaanNo ratings yet
- Documents - null-XI - Maths - Module-1 - Basic Maths (Theory)Document23 pagesDocuments - null-XI - Maths - Module-1 - Basic Maths (Theory)pushpendradiwaker7No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part: Paper 1 Question-Answer BookDocument11 pagesMATHEMATICS Compulsory Part: Paper 1 Question-Answer BookTommy IpNo ratings yet
- Dream World School, Ballari, KarnatakaDocument61 pagesDream World School, Ballari, Karnatakassewbay bayNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Complex Numbers: StructureDocument22 pagesUnit 2 Complex Numbers: StructureMitanshu ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics, Paper - Iia: Part - IIIDocument4 pagesMathematics, Paper - Iia: Part - IIISumanth YadavallyNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument4 pagesTerm PaperpasanNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers Ext 2 Yr 12Document55 pagesComplex Numbers Ext 2 Yr 12Natalie ChenNo ratings yet
- LTS2Document96 pagesLTS2Phuoc My LuuNo ratings yet
- Unit Overview: Complex NumbersDocument13 pagesUnit Overview: Complex NumbersI Made AstawanNo ratings yet
- FHMM 1114 General Mathematics I: Lecture Chapter 1Document35 pagesFHMM 1114 General Mathematics I: Lecture Chapter 1LimShuLingNo ratings yet
- Geometry II: Richard Earl Trinity Term 2007Document12 pagesGeometry II: Richard Earl Trinity Term 2007lmaraujo67No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document73 pagesChapter 2Abdi MosisaNo ratings yet
- Complex Vector Spaces PDFDocument42 pagesComplex Vector Spaces PDFmechmaster4uNo ratings yet
- Mathematics by ChandaDocument129 pagesMathematics by ChandaSelisho100% (1)
- Fort Street 2023 Extension 2 SolutionsDocument46 pagesFort Street 2023 Extension 2 Solutionsmujtabaibrahim39No ratings yet
- Quarter 1-Module 2: MathematicsDocument14 pagesQuarter 1-Module 2: MathematicsRobert Cruz88% (25)
- ch4 PDFDocument44 pagesch4 PDFAndrew Borg100% (1)
- Multinomial Coe Cients and More Counting Problems: Scott She EldDocument17 pagesMultinomial Coe Cients and More Counting Problems: Scott She EldzahiruddinNo ratings yet
- All Star Quiz 2017 Algebra and Number Theory Time Alotted: 3 DaysDocument3 pagesAll Star Quiz 2017 Algebra and Number Theory Time Alotted: 3 DaysHarris LeeNo ratings yet