Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Creative Writing Assessment Rubric - Guide To Making Judgement
Uploaded by
Sonia KamalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Creative Writing Assessment Rubric - Guide To Making Judgement
Uploaded by
Sonia KamalCopyright:
Available Formats
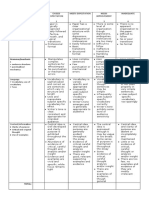
Student Name: Date:
Year 1 Very High High Sound Developing Emerging
Rubric/Guide to
Has a thorough understanding and uses Has a clear understanding and uses a
Making Judgement a high level of skill in both familiar and high level of skill in familiar situations. Is
Has an understanding and uses skills in Understands aspects of and uses varying A basic understanding and is beginning to
familiar situations. levels of skill in familiar situations. use skills in familiar situations.
Creative Writing new situations. beginning to use skills in new situations.
Text Structure • Includes the following when writing: • Includes most of the following, in a • Recognises and predominately follows • Requires some support to recognise • Requires significant support to
The organisation of the ‣ title logical order when writing: the structure: the appropriate structure of a creative produce a written text.
structural components of ‣ orientation (who, what, when and ‣ title ‣ title story. • Has difficulty recognising the
a text. where) ‣ orientation (who, what, when and ‣ orientation (who, what, when and • May use a modelled text for structural elements.
‣ series of events (including a where) where) assistance/prompts. • Text may have some structural
complication) ‣ series of events (including a ‣ series of events (including a • Some of the structural elements elements but may not be relevant or
‣ ending (including a resolution) complication) complication) may have been included without it is difficult to recognise the structure.
• Has included important relevant ‣ ending (including a resolution) ‣ ending (including a resolution) assistance. • Writer relies on drawings to
details. • Has included details, although some • Attempts to put this into a logical • Has included and illustration with communicate text using labels.
• Text is organised and logical by are not necessary. order when writing. labels.
referring to learned knowledge. • Beginning to use visual components • Some elements may be lacking in
• Uses appropriate paragraphs. and selecting images for maximum detail.
impact. • Has included an illustration with some
relevance to the story.
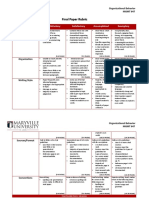
Sentence Structure and • Consistent in sentence structure when • Applies their knowledge into their • Identifies the parts of a simple • Requires some support to identify the • Requires significant support to identify
Vocabulary writing. Goes beyond what is expected writing. sentence that represent: parts of a simple sentence. the parts of a simple sentence.
The production of for Year 1, for example: • Effectively uses adjectives, adverbs ‣ what’s happening? (verb) • Uses limited vocabulary and may be • Often omits correct spacing between
grammatically correct, ‣ simple connections are made and unusual verbs to make a sentence ‣ what state is being described? (verb) repetitive. words.
structurally sound and between ideas by using compound more vivid. ‣ who or what is involved? (noun • Needs reminding to use correct • Struggles to read own writing back and
meaningful sentences. sentences with two or more clauses. • Beginning to use a limited bank of group/phrase) spacing between words. relies on memory for an oral retell.
Use of appropriate ‣ sometimes expands noun groups/ conjunctions. ‣ the surrounding circumstances
language choices. phrases using articles (the, a and an) • Learning to plan written (adverb group/phrase)
and adjectives. communication so that readers follow • Understands a simple sentence
‣ understands there are three types the sequence of the ideas or events. expresses a single idea.
of nouns. • New vocabulary is used in parts. • Experiments using different words
‣ applies new vocabulary that represent nouns, verbs, adjectives
appropriately. and adverbs.
Punctuation • Consistently uses punctuation • Uses full stops correctly. • Recognises that full stops, question • Understands the use of full stops. • Does not recognise the difference
The use of correct and correctly. • Predominately uses question marks marks and exclamation marks, signal • Requires some support to: between the various sentence types.
appropriate punctuation • The punctuation usage goes beyond and exclamation marks correctly. sentences that make statements, ask ‣ recognise the difference between • Uses punctuation randomly in their
that aids reading of a that expected for Year 1, for example: questions, express emotion or give the various sentence types writing.
piece of text. ‣ recognises that capital letters signal commands. ‣ apply this in their writing
proper nouns • Attempts to apply this knowledge in
‣ commas are used to separate items their writing.
in lists • Punctuation may have been overused.
Page 1 of 2 visit twinkl.com.au
Year 1 Rubric/Guide to Making Judgement Creative Writing
Spelling • Consistently uses a range of spelling • Correctly spells one and two syllable • Correctly spells some one and two • Requires some support to: • Has difficulty recognising one and two
The accuracy of spelling strategies accurately. words with common letter patterns syllable words with common letter ‣ Recognise one and two syllable syllable words.
and the difficulty of • Goes beyond what is expected for e.g. known blends ‘bl’, ‘st’. patterns e.g. known blends ‘bl’, ‘st’. words • Unable to build word families from
words used. Year 1, for example: • Understands that a letter can • Builds word families from common ‣ Build word families from common common morphemes.
‣ shows a knowledge of morphemic represent more than one sound and morphemes e.g. play, plays, playing. morphemes • Applies basic knowledge of letters and
word families by attempting to use applies this correctly when spelling • Uses visual memory to write high- ‣ Recognise the letters that represent sounds to spell words.
prefixes and suffixes words. frequency words. more than one sound • Relies heavily on environmental print.
‣ uses knowledge of letter patterns • Correctly spells an increasing number • Understands that a letter can • Relies on environmental print for some
and morphemes to attempt spelling of high-frequency words. represent more than one sound. high frequency words (limited visual
not predictable from their sounds memory).
‣ uses most letter-sound matches
when writing words of one or more
syllables
Editing • Consistently re-reads and edits own • Actively re-reads own work. • When prompted: • Requires support to read own work. • Minimal or no evidence of appropriate
Ability to re-read and work. • Attempts to edit own work to improve ‣ re-reads own work • Requires encouragement to discuss editing skills.
edit own work to check • Goes beyond what is expected for meaning, spelling and punctuation. ‣ discusses possible changes to changes to improve own work.
for meaning, spelling, Year 1, for example: improve meaning, spelling and
punctuation and ‣ edits text for spelling, sentence- punctuation
grammar. boundary, punctuation and text
structure
Teacher Name:
Page 2 of 2 visit twinkl.com.au
You might also like
- au-l-1682144967-year-3-semester-1-writing-assessment_ver_1Document9 pagesau-l-1682144967-year-3-semester-1-writing-assessment_ver_1khadijahesham00No ratings yet
- English SLO G VDocument27 pagesEnglish SLO G VRehanKakarNo ratings yet
- Au L 1682253346 Year 5 Semester 1 Writing Assessment Ver 1Document10 pagesAu L 1682253346 Year 5 Semester 1 Writing Assessment Ver 1Alaa IsmailNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem 1st Quarter ENGLAPP ReviewerDocument4 pages2nd Sem 1st Quarter ENGLAPP ReviewerGummy Min0903No ratings yet
- Grade 6 English HL Term 1-4 Atp 2021Document19 pagesGrade 6 English HL Term 1-4 Atp 2021Amichand MarajNo ratings yet
- English Subject Plan 3 2018-2019Document6 pagesEnglish Subject Plan 3 2018-2019Diana Natalia Navarrete CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Collaborative EssayDocument4 pagesModule 2 Collaborative EssayDinu ElenaNo ratings yet
- Writing Workshop 7 Scoring RubricDocument1 pageWriting Workshop 7 Scoring RubricJorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ELL Assessments and Language Skill Packs Writing Scoring Rubrics Grades 1-2Document4 pagesELL Assessments and Language Skill Packs Writing Scoring Rubrics Grades 1-2api-372488634No ratings yet
- Persuasive Descriptors and Teaching Points Prim and Sec Feb 2020Document9 pagesPersuasive Descriptors and Teaching Points Prim and Sec Feb 2020api-699698539No ratings yet
- UNIT 8 Individual Activity 1Document2 pagesUNIT 8 Individual Activity 1babyboyNo ratings yet
- Circular - Project & VivaDocument5 pagesCircular - Project & VivaellipticaldonutNo ratings yet
- Section B: Ashton Park School English Paper Two Exam Section BDocument21 pagesSection B: Ashton Park School English Paper Two Exam Section BNeil BradfordNo ratings yet
- Writing Skills and StrategiesDocument30 pagesWriting Skills and StrategiesTeachThought89% (9)
- TOEFL Perf Feedback PDFDocument9 pagesTOEFL Perf Feedback PDFwleaNo ratings yet
- Readingachievementstandard Grade1Document2 pagesReadingachievementstandard Grade1api-224946979No ratings yet
- W1 PowerPointDocument18 pagesW1 PowerPointLaura Cabello HiguerasNo ratings yet
- Written Assessment RUBRICDocument2 pagesWritten Assessment RUBRICJoaquín MorenoNo ratings yet
- HMPE3 Module1 Lagaya, Jairo D. 2HM4Document6 pagesHMPE3 Module1 Lagaya, Jairo D. 2HM4LAGAYA, JAIRO D.No ratings yet
- F Lit 6 La Week 17-18Document3 pagesF Lit 6 La Week 17-18RoanneNo ratings yet
- Journal Marking SchemeDocument1 pageJournal Marking SchemeAna Paula BalgacNo ratings yet
- Essay Topics and Rubric Dec7Document3 pagesEssay Topics and Rubric Dec7api-444224161No ratings yet
- Grasps 3Document13 pagesGrasps 3ÄllypÖt DiÖnisioNo ratings yet
- 9 ENG Short Story R&J Unit Assignment 2024Document3 pages9 ENG Short Story R&J Unit Assignment 2024mahi4740.patelNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Writing Rubric: 5 (Exceptional Pass) 4 (High Pass) 3 (Low Pass) 2 (High Fail) 1 - 0.5 (Low Fail)Document2 pagesLevel 3 Writing Rubric: 5 (Exceptional Pass) 4 (High Pass) 3 (Low Pass) 2 (High Fail) 1 - 0.5 (Low Fail)Justin BasicNo ratings yet
- ATP 2023-24 Gr 6 English HL FinalDocument23 pagesATP 2023-24 Gr 6 English HL Finalpaseka1124No ratings yet
- Speaking and Listening Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesSpeaking and Listening Assessment RubricSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- FIRST_GRADE 11_PETA 01 GUIDELINESDocument1 pageFIRST_GRADE 11_PETA 01 GUIDELINESJeanNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument9 pagesReading and WritingEmziey ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Final SCOPE AND SEQUENCE OF COMPOSINGDocument2 pagesFinal SCOPE AND SEQUENCE OF COMPOSINGZiyad AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Writing One Point RubricDocument2 pagesArgumentative Writing One Point Rubricapi-614253116No ratings yet
- Type of TextsDocument1 pageType of TextsVirgilio HernandezNo ratings yet
- Annual teaching plans for English FAL Grade 5Document22 pagesAnnual teaching plans for English FAL Grade 5Hangwy MtikaneNo ratings yet
- 9 Issues Challenges in Emerging LiteratuDocument5 pages9 Issues Challenges in Emerging LiteratuJo Ann TupasNo ratings yet
- Evaluating A College Essay Rubric For ExamDocument2 pagesEvaluating A College Essay Rubric For ExamNinfa LansangNo ratings yet
- Speaking and Listening Scheme of WorkDocument2 pagesSpeaking and Listening Scheme of WorkSheyma.M.No ratings yet
- Narrative RubricDocument2 pagesNarrative Rubricapi-312022809No ratings yet
- Problem-Solution Essay RubricDocument2 pagesProblem-Solution Essay Rubric白卡持有人No ratings yet
- Final Paper - RubricDocument1 pageFinal Paper - RubricYear Yveneil Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Literary Analysis Literary Theory Presentation RubricDocument2 pagesLiterary Analysis Literary Theory Presentation Rubricapi-403618226No ratings yet
- Speaking and Listening Group DiscussionDocument2 pagesSpeaking and Listening Group Discussionapi-25916272No ratings yet
- Washington State University Sample Lesson Plan TemplateDocument6 pagesWashington State University Sample Lesson Plan Templateapi-575450234No ratings yet
- Writer's Workshop General Writing Rubric Part 1Document1 pageWriter's Workshop General Writing Rubric Part 1eva.bensonNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Vocabulary 1Document12 pagesGrammar and Vocabulary 1Angelica MonterosoNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay Drafting AssignmentDocument7 pagesArgumentative Essay Drafting Assignmentalysanajla04No ratings yet
- General Essay RubricDocument2 pagesGeneral Essay RubricCorina ManninenNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentapi-393180311No ratings yet
- Hamoy UNIT 6 Individual ActivityDocument3 pagesHamoy UNIT 6 Individual ActivitybabyboyNo ratings yet
- The Teaching of WritingDocument30 pagesThe Teaching of WritingAsykabirru Hadziq HanifNo ratings yet
- English RubricsDocument2 pagesEnglish Rubricsapi-662977389No ratings yet
- Final Paper Rubric: Criteria Unsatisfactory Satisfactory Accomplished ExemplaryDocument2 pagesFinal Paper Rubric: Criteria Unsatisfactory Satisfactory Accomplished ExemplaryJoshua FoxNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 English FAL teaching plan 2021-2023Document25 pagesGrade 6 English FAL teaching plan 2021-2023Ayanda Siphesihle Ndlovu100% (3)
- The Rubrics - Report WritingDocument1 pageThe Rubrics - Report WritingJaya Surya GudivadaNo ratings yet
- Indonesian A LAL Workshop Cat.2 Workbook (Dragged)Document1 pageIndonesian A LAL Workshop Cat.2 Workbook (Dragged)Babtista EzraNo ratings yet
- RW Reviewer BAWAL ISHAREDocument5 pagesRW Reviewer BAWAL ISHAREIvan TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Romeo and JulietDocument10 pagesRomeo and JulietElynna TanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan X Dean - ReadingDocument8 pagesLesson Plan X Dean - ReadingEko BudiNo ratings yet
- Rubric for Evaluating Narrative WritingDocument2 pagesRubric for Evaluating Narrative Writingjef_xavier1938No ratings yet
- Updated 3rd Grade WritingDocument9 pagesUpdated 3rd Grade Writingapi-482274317No ratings yet
- Ar Ise 1643761454 Stories of The Prophets in Islam Display Poster - Ver - 1Document1 pageAr Ise 1643761454 Stories of The Prophets in Islam Display Poster - Ver - 1Sonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Dolch Primer Sight WordsDocument7 pagesDolch Primer Sight WordsSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Animal GrowthDocument16 pagesAnimal GrowthSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Dolch Primer Sight WordsDocument7 pagesDolch Primer Sight WordsSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Money Grade 1Document18 pagesMoney Grade 1Sonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Repeating Letter SoundsDocument11 pagesRepeating Letter SoundsSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- MoneyDocument16 pagesMoneySonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Interactive English 101 Prelim TestDocument5 pagesInteractive English 101 Prelim TestJim Roger Malabo LorenzoNo ratings yet
- SOW ENGLISH YEAR 2 Penjajaran (2021)Document12 pagesSOW ENGLISH YEAR 2 Penjajaran (2021)ruganhaurNo ratings yet
- B1 UNIT 9 Flipped Classroom Video WorksheetDocument1 pageB1 UNIT 9 Flipped Classroom Video WorksheetivanNo ratings yet
- Types of Sentences ExplainedDocument7 pagesTypes of Sentences ExplainedOklan Livia PinontoanNo ratings yet
- Budgeted Lesson Plan in English - 7Document10 pagesBudgeted Lesson Plan in English - 7LannaGamboaCarinoNo ratings yet
- OxfordFirstSPaG PunctuationDocument2 pagesOxfordFirstSPaG PunctuationCarolyne AchiengNo ratings yet
- Sentence ExpansionDocument3 pagesSentence ExpansionTahir PutragaNo ratings yet
- Categorical and Hypothetical Propositions - Self-Educated AmericanDocument8 pagesCategorical and Hypothetical Propositions - Self-Educated AmericanRain Tolentino100% (1)
- 7 Meeting (PREPOSITION)Document13 pages7 Meeting (PREPOSITION)mnhi010217No ratings yet
- Clauses: Cluases of PurposeDocument4 pagesClauses: Cluases of PurposeQuiet SoundsNo ratings yet
- What is ComplementationDocument46 pagesWhat is ComplementationMarjorie MagcantaNo ratings yet
- Figures of Transposition Types and ExamplesDocument51 pagesFigures of Transposition Types and ExamplesG12 Karelle Louise MarananNo ratings yet
- Predicate - What Is A PredicateDocument4 pagesPredicate - What Is A PredicateSahirSk100% (1)
- Exercises On Noun ClausesDocument2 pagesExercises On Noun ClausesJennifer Garcia Erese100% (1)
- Translation TechniquesDocument3 pagesTranslation TechniquesMade Depresi JiwaNo ratings yet
- Definition ParagraphDocument20 pagesDefinition ParagraphDung NgọcNo ratings yet
- Adding Emphasis in EnglishDocument2 pagesAdding Emphasis in EnglishtoptenacademyNo ratings yet
- Internal Semantics TheoriesDocument97 pagesInternal Semantics TheoriesPhan Thi Mai AnhNo ratings yet
- English Tutor1Document182 pagesEnglish Tutor1hamisuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Study GuideDocument20 pagesUnit 2 - Study GuideAbigail RijoNo ratings yet
- 2 ChapterDocument16 pages2 ChapterAjoy SharmaNo ratings yet
- PHK 1 - 9E - 31 (4 Agustus 2020)Document5 pagesPHK 1 - 9E - 31 (4 Agustus 2020)RedMinecraft 2270No ratings yet
- EPC3403 E Portfolio Updated VersionDocument9 pagesEPC3403 E Portfolio Updated VersionshamsaNo ratings yet
- Materi MKU B.inggris 3 Sks LockedDocument41 pagesMateri MKU B.inggris 3 Sks Lockedbalapindonesia 201MNo ratings yet
- Writing Rubric for Secondary Grades 6-8Document1 pageWriting Rubric for Secondary Grades 6-8Huong NguyenNo ratings yet
- SCORE: 2/5: There Are Many Who Pretend To Despise and Belittle That Which Is Beyond Their ReachDocument2 pagesSCORE: 2/5: There Are Many Who Pretend To Despise and Belittle That Which Is Beyond Their ReachLeizl May TortogoNo ratings yet
- The Oral Approach and Situational Language TeachingDocument51 pagesThe Oral Approach and Situational Language TeachingBeck Cky67% (3)
- Housekeeping Room Attendant Level 1 CVQDocument127 pagesHousekeeping Room Attendant Level 1 CVQMALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- Learning Tagalog Course Book 1 B&W Sample PDFDocument34 pagesLearning Tagalog Course Book 1 B&W Sample PDFrachel fellerNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument9 pagesAssignmentsunknownNo ratings yet