Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Sciences p1 QP Gr11 Nov 2018 - English
Uploaded by
zintlemagudu12Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life Sciences p1 QP Gr11 Nov 2018 - English
Uploaded by
zintlemagudu12Copyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL
SENIOR CERTIFICATE
GRADE 11
NOVEMBER 2018
LIFE SCIENCES P1
MARKS: 150
TIME: 2½ hours
This question paper consists of 18 pages.
2 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write ALL the answers in your ANSWER BOOK.
3. Start the answers to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
4. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in
this question paper.
5. Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
6. ALL drawings must be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
7. Draw diagrams, flow charts or tables only when asked to do so.
8. The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
9. Do NOT use graph paper.
10. You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass
where necessary.
11. Round off all calculations to two decimals after the comma.
12. Write neatly and legibly.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 3
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions.
Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question
number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 Carbon dioxide is carried in the blood mainly as …
A carb amino haemoglobin.
B carbonic acid in the erythrocytes.
C bicarbonate ions in the red blood cells.
D gas bubbles in the blood plasma.
1.1.2 The blood that exits the liver contains … compared to the blood that
enters the liver.
A less glucose
B more oxygen
C more glucose
D less urea
1.1.3 The graphs below (A, B, C and D) represent the relationship between
the rate of photosynthesis and temperature.
A B C D
Rate of photosynthesis
Rate of photosynthesis
Rate of photosynthesis
Rate of photosynthesis
20 40 60 20 40 60 20 40 60 20 40 60
Temperature(°C) Temperature(°C) Temperature(°C) Temperature(°C)
Which ONE of the graphs (A, B, C or D) represent the correct
relationship between the temperature and the rate of photosynthesis?
A D
B A
C B
D C
Copyright reserved Please turn over
4 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
1.1.4 The following components are involved in cellular respiration:
(i) Energy
(ii) Carbohydrates
(iii) Carbon dioxide
(iv) Water
(v) Oxygen
Which ONE of the following combinations show the correct way in which
the components are involved?
A (ii) + (iii) (i) + (iv) + (v)
B (ii) + (iv) (i) + (iii) + (v)
C (i) + (ii) (iii) + (iv) + (v)
D (ii) + (v) (i) + (iii) + (iv)
1.1.5 E.coli bacteria living in the colon of the human digestive system is an
example of …
A parasitism.
B mutualism.
C competition.
D commensalism.
1.1.6 Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a medical term to describe a disease of
the digestive system. Symptoms usually occur after certain foods or
drinks were consumed. It can cause sudden and severe diarrhoea.
What consequence can this have for a person?
A Too much water and nutrients will be absorbed in the digestive tract
B Too little water will be absorbed, but the nutrients will be absorbed
C Too little nutrients will be absorbed, but water will be absorbed
D Too little water and nutrients will be absorbed
1.1.7 The sequence of plant succession on a bare piece of land is described
below:
(i) Trees start to grow
(ii) Mosses and lichens grow and form soil when they die
(iii) Soil thickens and small shrubs grow
(iv) Soil develops and then grasses and small plants grow
Which of the following sequences leads to the emergence of stable
climax community?
A (i)(ii) (iv)(iii)
B (ii) (i) (iv)(i)
C (ii)(iv)(iii)(i)
D (ii)(iii)(iv)(i)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 5
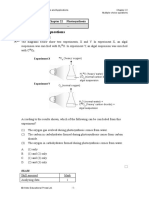
1.1.8 An experiment was set up to investigate whether oxygen is released
during photosynthesis. The result of the experiment is represented in the
following diagram.
Bell jar A Bell jar B
After a short time, the The candle continues to
candle went out burn for a longer period
The following deductions were made before arriving at the final
conclusion.
(i) Photosynthesis reduces the amount of CO2 inside bell jar B
(ii) The oxygen in bell jar A was completely used up and the burning
is not supported
(iii) The photosynthesis increases the amount of oxygen inside
bell jar B
(iv) The vapour produced inside bell jar A due to combustion
extinguished the burning candle
Which ONE of the following set of deductions is correct?
A (i) and (iv) only
B (i), (ii) and (iii) only
C (i), (iii) and (iv) only
D (iii) and (iv) only
1.1.9 Which ONE of the following represents an example of where there is no
social organisation and the chances of survival are reduced?
A Division of labour in a bee hive
B A school of fish moving in various formations
C A predator hunting alone
D An alpha male in a lion pack is the only one to reproduce with the
females
Copyright reserved Please turn over
6 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
1.1.10 A child is taken to the hospital and diagnosed with a form of
malnutrition. Upon further investigation, doctors learnt that the child
used only maize meal as food. From what type of malnutrition is this
child most likely to suffer?
A Anorexia
B Kwashiorkor
C Marasmus
D Bulimia (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write
only the term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.9) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 A type of malnutrition in which the person consumes large quantities
of high-energy food
1.2.2 The form in which excess glucose is stored in a plant
1.2.3 Different populations occurring in a particular area
1.2.4 The one-way movement of organisms out of a population to a new
area
1.2.5 The anaerobic respiration that occurs in yeast cells
1.2.6 The type of energy absorbed by chlorophyll
1.2.7 The type of relationship between two organisms where one
completely outcompetes the other
1.2.8 The type of competition between members of different species
1.2.9 The position an organism occupies in an ecosystem (9 x 1) (9)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN І applies to A ONLY, B
ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN ІІ. Write A only, B
only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the
ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN І COLUMN ІІ
1.3.1 Substances that need to be A: Amino acids
digested before absorption B: Glucose
1.3.2 Raw material(s) essential for A: Oxygen
photosynthesis B: Carbon dioxide
1.3.3 Examples of mutualism A: Nitrogen fixing bacteria on the
roots of legumes
B: Barnacles on whales
(3 x 2) (6)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 7
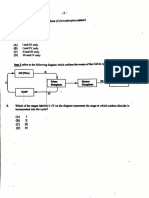
1.4 The following diagrams represent investigations involved in a process which
takes place in green plants. The plant/leaves represented as A and C were
exposed to sunlight for 4–5 hours.
white area
B
green area
Aluminium
foil paper
A
C
1.4.1 Which investigation (A, B or C) is designed to test for the following?
(a) Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis (1)
(b) Light is required for photosynthesis (1)
(c) Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis (1)
1.4.2 Give the LETTER of the investigation that does not show a control. (1)
1.4.3 Which investigation(s) need(s) a chemical to test for whether
photosynthesis took place? (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
8 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
1.5 The diagram below shows a diagrammatic representation of the digestive
system.
Mouth
Stomach
Small
P Q
intestine
Large
intestine
1.5.1 Name the part of the alimentary canal represented by X. (1)
1.5.2 By which process is food moved through structure X? (1)
1.5.3 Name the glands P and Q that release their secretions into the small
intestine. (2)
1.5.4 Name the part of the alimentary canal where the digestion of proteins
begins. (1)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 9
1.6 The diagram below represents the structure of a chloroplast.
1.6.1 Identify:
(a) Part C (1)
(b) Structure D (1)
1.6.2 Give the function of the part labelled A. (1)
1.6.3 Name the part that will be active in light only. (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
Copyright reserved Please turn over
10 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The table below shows a comparison between the fertility rates of people in
developed and developing countries from 1950 to 2010.
Year Developed countries Developing countries
1950 2,8 6,1
1960 2,7 6,1
1970 2,2 5,4
1980 2,0 4,1
1990 2,0 3,4
2000 2,0 3,0
2010 2,1 2,7
2.1.1 Define the term fertility rate. (2)
2.1.2 Describe the trend in the fertility rates of both developed and
developing countries. (3)
2.1.3 Give any TWO possible reasons for the trend in the fertility rates
mentioned in QUESTION 2.1.2. (2)
2.1.4 If the trend shown in developed countries continues, explain the likely
effects on their economies over the next 60 years. (3)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 11
2.2 The diagram below shows the structure of the human urinary system.
C
D
2.2.1 Give labels for the following parts:
(a) A (1)
(b) B (1)
(c) E (1)
2.2.2 Give ONE difference between the composition of blood in C and D. (2)
2.2.3 The part labelled B consists of millions of micro-tubules called
nephrons where blood is being filtered and purified. A part of the
nephron is the Malpighian corpuscle/body.
Draw a labelled diagram of a Malpighian corpuscle/body. (4)
2.2.4 The flow of urine into the urinary bladder can be blocked at the part
labelled A. The blockage causes severe pain and possible infection.
(a) What is the possible cause of blockage of urine in the part
labelled A? (1)
(b) Give a possible preventative measure to avoid such blockages
in the urinary system. (1)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
12 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
2.3 An investigation was performed to calculate the number of locusts in a maize
field. Fifty locusts were caught in little cages, marked with little dots and then
released again. Two weeks later 96 locusts were caught and 8 of them had
dots on them.
2.3.1 Which method was used to determine the population size? (1)
2.3.2 By using the formula below, calculate the estimated number of locusts
in the maize field. Show all calculations.
MxC
P= (3)
R
2.3.3 Mention TWO ways in which the accuracy of this investigation could
be improved. (2)
2.4 The diagram below shows a structure associated with the digestive system.
A
B
2.4.1 Identify the structure shown in the diagram. (1)
2.4.2 Name the following parts:
(a) A (1)
(b) B (1)
2.4.3 In which part of the digestive tract would this structure be found? (1)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 13
2.4.4 Explain TWO structural adaptations of the part mentioned in
QUESTION 2.4.3 that enables it to perform its functions. (4)
2.4.5 In which part (C or D) would you expect to find more nutrients? (1)
2.4.6 Explain your answer in QUESTION 2.4.5. (2)
2.4.7 Celiac disease is a disorder that makes human bodies react to gluten
(a protein found in wheat, rye, barley and grains). The response by the
immune system eventually damages the structures illustrated in the
diagram above.
Explain the effects of this disease in the human body. (2)
[40]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
14 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
QUESTION 3
3.1 The graph below represents an interaction between two organisms in an
ecosystem.
Carrying capacity
120
Population size(number of organisms)
Number of lady
100 birds
Number of green
flies
A
80
60
40
20
0
Mar-98
Apr-98
May-98
Jul-98
Mar-99
Apr-99
May-99
Jul-99
Feb-98
Oct-98
Feb-99
Oct-99
Aug-98
Sep-98
Nov-98
Dec-98
Aug-99
Sep-99
Jan-98
Jun-98
Jan-99
Jun-99
Time (months)
3.1.1 Give a suitable heading for the graph. (2)
3.1.2 What phase of growth is represented by A? (1)
3.1.3 Identify the prey population in the above graph. (1)
3.1.4 Explain why the chances of lady birds and green flies reaching the
carrying capacity is limited. (3)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 15
3.2 An extract on renal failure and its treatment is given below. (The diagram
below represents a dialysis machine, used to treat patients with renal failure.)
dialysis fluid dialysis fluid
to patient’s A
blood
vessels
from B
patient’s Pump
blood
vessels
Dialysis membrane
(Dialysis tubing)
Kidneys can become so damaged that they no longer function properly, and
we say that the person has renal failure. People with severe renal failure can
be treated by dialysis, using a dialysis machine, to purify the blood. Dialysis
is the separation of molecules by size, the smaller molecules diffusing through
a dialysis tubing (selectively permeable membrane). The process takes
between three and six hours and needs to be done two or three times a week.
3.2.1 Describe what renal failure is. (2)
3.2.2 Which process is illustrated in the diagram above? (1)
3.2.3 At what point in the diagram (A or B) would you expect the highest
concentration of urea? (1)
3.2.4 Describe how the purification of blood takes place in the dialysis
machine. (3)
3.2.5 Explain why dialysis tubing needs to be selectively-permeable. (2)
3.2.6 Renal failure affects the osmoregulatory function of the kidney, so that
it no longer excretes water efficiently. Explain the effect of renal failure
on the patient’s blood pressure. (3)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
16 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
3.3 The apparatus below was used to carry out an investigation on aerobic
respiration.
The experiment was set up as follows:
17 seeds of the same kind were used.
The seeds and the apparatus were sterilised before the investigation.
Once set up, the apparatus was placed in a dark cupboard at 35 °C
A control was also set up.
cotton wool plug
germinating
seeds
cotton wool plug
clear lime water
3.3.1 Formulate a hypothesis for this investigation. (2)
3.3.2 What is the significance of sterilising the seeds before they are
used? (1)
3.3.3 Give TWO controlled variables in this investigation. (2)
3.3.4 Explain how you would set up a control for this investigation. (3)
3.3.5 Explain why germinating seeds were used in this investigation. (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2018) LIFE SCIENCES P1 17
3.4 An experiment was carried out to calculate the rate of photosynthesis in a
group of plants at different concentrations of carbon dioxide. This was
repeated at two different light intensities. The results are given below.
Rate of photosynthesis (Arbitrary units)
CO2 concentration (%) Low light intensity High light intensity
0,00 0 0
0,02 20 20
0,04 29 35
0,06 35 47
0,08 39 68
0,10 42 84
0,12 45 89
0,14 46 90
0,16 46 90
0,18 46 90
3.4.1 Identify the dependent factor in the above graph. (1)
3.4.2 Up to what values does CO2 concentration act as a limiting factor at
high light intensities? (1)
3.4.3 Name TWO limiting factors of photosynthesis other than the ones
mentioned in QUESTION 3.4.2. (2)
3.4.4 Draw a line graph to represent the rate of photosynthesis under
various concentrations of CO2 at low light intensity. (7)
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
Copyright reserved Please turn over
18 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/NOVEMBER 2018)
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
James is training for a race by running 20 km every day. Describe how oxygen is
taken into his body and how it moves into his blood stream. Also describe how the
carbon dioxide produced in his body during training is controlled to maintain normal
levels.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
NOTE: No marks will be awarded for answers in the form of a chart or diagram.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Copyright reserved Please turn over
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2022 Gr11 Eastern CapeDocument16 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2022 Gr11 Eastern CapeKgomotsoNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2020Document14 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2020Sanza Anathiey Certified JrNo ratings yet
- Grade 10: National Senior CertificateDocument13 pagesGrade 10: National Senior CertificateMalerh VVE Marlon 223100% (1)
- Life Sciences p2 QP Gr10 Nov2017 - English - EcDocument16 pagesLife Sciences p2 QP Gr10 Nov2017 - English - EcMarian Mackenzie-RossNo ratings yet
- Life Science Paper 1 GR11 Question Paper NOV 2015 1Document14 pagesLife Science Paper 1 GR11 Question Paper NOV 2015 1wwowo2606No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 18, 2021Document10 pagesAdobe Scan Oct 18, 2021Vidushi KochharNo ratings yet
- TOTAL: 150 Time: 2 Hours Instructions and Information: Grade 11 Life Sciences November ExaminationDocument16 pagesTOTAL: 150 Time: 2 Hours Instructions and Information: Grade 11 Life Sciences November ExaminationJustinCase1991No ratings yet
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Biology - 4Document3 pagesBiology - 4Nassrah JumaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2019 EngDocument18 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2019 EngZiyanda SingasheNo ratings yet
- Envi 2010 U1 P1Document11 pagesEnvi 2010 U1 P1Chanell M.100% (1)
- Ucd 2020 Bio f5Document13 pagesUcd 2020 Bio f5NOOR HAFEZAH BT MOHD MOKHTIAR MoeNo ratings yet
- J2E Science MidTermExam2022 P1 QDocument9 pagesJ2E Science MidTermExam2022 P1 Qm-10391646No ratings yet
- Code No. 86 Pre-Board Examination-2 (January - 2020) : General Instructions: (I) (Ii) (Iii) (Iv) (V) (Vi) (Vii)Document6 pagesCode No. 86 Pre-Board Examination-2 (January - 2020) : General Instructions: (I) (Ii) (Iii) (Iv) (V) (Vi) (Vii)Sara 15No ratings yet
- STPM Trial Exam 2010 Biology Paper 1Document21 pagesSTPM Trial Exam 2010 Biology Paper 1Diong JayhueyNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-04 at 4.31.07 PMDocument22 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-04 at 4.31.07 PMronghui009No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES P2 QP GR10 NOV2018 - EnglishDocument16 pagesLIFE SCIENCES P2 QP GR10 NOV2018 - Englishonthabiseng mathNo ratings yet
- Bio - SSC - 2 - Model - Paper 20-9Document9 pagesBio - SSC - 2 - Model - Paper 20-9mughishassan0No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES P2 QP GR10 NOV2020 - EnglishDocument16 pagesLIFE SCIENCES P2 QP GR10 NOV2020 - EnglishSkyla GallantNo ratings yet
- s.4 Bio Progressive Test Term 11 2011Document6 pagess.4 Bio Progressive Test Term 11 2011Arafat TamaleNo ratings yet
- X SciencepracticepaperDocument7 pagesX Sciencepracticepaper6A 29 Ruchit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- SCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020Document11 pagesSCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020JoanNo ratings yet
- Set 1 QnaDocument13 pagesSet 1 QnaJolene ChiaNo ratings yet
- The Core of Chemistry Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesThe Core of Chemistry Practice QuestionsBerton LiuNo ratings yet
- FORM TP 2012176: Caribbean Examinations Council Advanced Proficiency Examination Environmental Science UNIT 1 - Paper 01Document12 pagesFORM TP 2012176: Caribbean Examinations Council Advanced Proficiency Examination Environmental Science UNIT 1 - Paper 01saraNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2Document8 pages10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- 2011 HSC Exam BiologyDocument36 pages2011 HSC Exam BiologyWayiz AliNo ratings yet
- SP Dse Bio 1 1Document31 pagesSP Dse Bio 1 1ddd dddNo ratings yet
- HHW Biology X PDFDocument9 pagesHHW Biology X PDFNikhil bhatiNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Biology: Photosynthesis Combined ScienceDocument33 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Biology: Photosynthesis Combined Scienceart arlxNo ratings yet
- NSO Science Sample Paper 1 For Class 4Document19 pagesNSO Science Sample Paper 1 For Class 4Chhaya BoroleNo ratings yet
- Biology June 2014 PDFDocument11 pagesBiology June 2014 PDFDenise ParkinsonNo ratings yet
- Biology Ssc-Ii: Version No. Roll NumberDocument8 pagesBiology Ssc-Ii: Version No. Roll NumberMahwishbukhariNo ratings yet
- Science 2 Level: Class - 7Document5 pagesScience 2 Level: Class - 7s67206095saurabhNo ratings yet
- Chem 10 AnsDocument7 pagesChem 10 AnsMudassir HussainNo ratings yet
- Science Exclusive Sample PaperDocument12 pagesScience Exclusive Sample PaperbadasserytechNo ratings yet
- O-Levels Combined Science 2018-3Document83 pagesO-Levels Combined Science 2018-3AsherNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Previous Year Question Paper 2020Document174 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Previous Year Question Paper 2020RITESH RajNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/22Sarah KKC0% (1)
- Nseb 2010Document13 pagesNseb 2010spsarathyNo ratings yet
- Science Sample Paper 6Document8 pagesScience Sample Paper 6LVAM GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - STD XDocument28 pagesQuestion Bank - STD XParth DevNo ratings yet
- Respiration (Multiple Choice) QP SolvedDocument9 pagesRespiration (Multiple Choice) QP SolvedRiddhima ShahNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 2 2017 p1Document13 pagesCape Biology Unit 2 2017 p1Amarah MohammedNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE TEST - tYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONSDocument1 pageSUMMATIVE TEST - tYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONSJeng JengNo ratings yet
- Biology Year 11 2019 Exam ChoiceDocument26 pagesBiology Year 11 2019 Exam ChoiceannaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Applied Approach 4th Edition Thompson Manore Test BankDocument18 pagesNutrition Applied Approach 4th Edition Thompson Manore Test Bankpatriciadonaldsonsbmfyoqwnp100% (23)
- SC 2024 SP-9Document16 pagesSC 2024 SP-9Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Respiration (Multiple Choice)Document27 pagesRespiration (Multiple Choice)mohamed Aita100% (1)
- Ii Mid Term Test-2018 Marks:35 Time: 1h 15m I. Answer All The Questions 8 X 1 8 Part - ADocument2 pagesIi Mid Term Test-2018 Marks:35 Time: 1h 15m I. Answer All The Questions 8 X 1 8 Part - ASamuelNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p2 Gr11 QP Nov 2019 - Eng DDocument24 pagesLife Sciences p2 Gr11 QP Nov 2019 - Eng DaaliyamosavelNo ratings yet
- ch22 Test 1Document6 pagesch22 Test 1Cloris WongNo ratings yet
- GjngjrenjgnfjngngnjfgDocument12 pagesGjngjrenjgnfjngngnjfgm.athallahramadhanalfisyahrinNo ratings yet
- Bio 1999 PaperDocument17 pagesBio 1999 PaperMatteo FortuNo ratings yet
- Prelims 2 - Science - Grade 10 - 20-21 - FinalDocument11 pagesPrelims 2 - Science - Grade 10 - 20-21 - FinalGaurav ZalaNo ratings yet
- Gayaza High School: Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education Biology (Theory) Paper 1 2 Hours 30 MinutesDocument14 pagesGayaza High School: Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education Biology (Theory) Paper 1 2 Hours 30 MinutesSsendagala Joseph CollineNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Jesus Chavez AffidavitDocument21 pagesJesus Chavez AffidavitThe Dallas Morning NewsNo ratings yet
- Filehost - CIA - Mind Control Techniques - (Ebook 197602 .TXT) (TEC@NZ)Document52 pagesFilehost - CIA - Mind Control Techniques - (Ebook 197602 .TXT) (TEC@NZ)razvan_9100% (1)
- Delegated Legislation in India: Submitted ToDocument15 pagesDelegated Legislation in India: Submitted ToRuqaiyaNo ratings yet
- OPSS 415 Feb90Document7 pagesOPSS 415 Feb90Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Foucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)Document11 pagesFoucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)YashinNo ratings yet
- 30rap 8pd PDFDocument76 pages30rap 8pd PDFmaquinagmcNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Lesson 2 DramaDocument38 pagesGroup 2 Lesson 2 DramaMar ClarkNo ratings yet
- Name: Nur Hashikin Binti Ramly (2019170773) Course Code: Udm713 - Decision Making Methods and Analysis Assignment Title: Need Gap AnalysisDocument2 pagesName: Nur Hashikin Binti Ramly (2019170773) Course Code: Udm713 - Decision Making Methods and Analysis Assignment Title: Need Gap AnalysisAhmad HafizNo ratings yet
- Food Combining PDFDocument16 pagesFood Combining PDFJudas FK TadeoNo ratings yet
- Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of X80 PipelineDocument13 pagesStress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of X80 Pipelineaashima sharmaNo ratings yet
- SHS StatProb Q4 W1-8 68pgsDocument68 pagesSHS StatProb Q4 W1-8 68pgsKimberly LoterteNo ratings yet
- UXBenchmarking 101Document42 pagesUXBenchmarking 101Rodrigo BucketbranchNo ratings yet
- NI 43-101 Technical Report - Lithium Mineral Resource Estimate Zeus Project, Clayton Valley, USADocument71 pagesNI 43-101 Technical Report - Lithium Mineral Resource Estimate Zeus Project, Clayton Valley, USAGuillaume De SouzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 4 PDFVarun SinghalNo ratings yet
- Img - Oriental Magic by Idries Shah ImageDocument119 pagesImg - Oriental Magic by Idries Shah ImageCarolos Strangeness Eaves100% (2)
- Https Emedicine - Medscape.com Article 1831191-PrintDocument59 pagesHttps Emedicine - Medscape.com Article 1831191-PrintNoviatiPrayangsariNo ratings yet
- ENTRAPRENEURSHIPDocument29 pagesENTRAPRENEURSHIPTanmay Mukherjee100% (1)
- Book Review On PandeymoniumDocument2 pagesBook Review On PandeymoniumJanhavi ThakkerNo ratings yet
- Aqualab ClinicDocument12 pagesAqualab ClinichonyarnamiqNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease (711) - AguilarDocument7 pagesContract of Lease (711) - AguilarCoy Resurreccion Camarse100% (2)
- Peter Honigh Indian Wine BookDocument14 pagesPeter Honigh Indian Wine BookVinay JohnNo ratings yet
- ANNAPURNA Sanitary Work 3 FinalDocument34 pagesANNAPURNA Sanitary Work 3 FinalLaxu KhanalNo ratings yet
- Photo Essay (Lyka)Document2 pagesPhoto Essay (Lyka)Lyka LadonNo ratings yet
- Pharmaniaga Paracetamol Tablet: What Is in This LeafletDocument2 pagesPharmaniaga Paracetamol Tablet: What Is in This LeafletWei HangNo ratings yet
- Human Development IndexDocument17 pagesHuman Development IndexriyaNo ratings yet
- The Skylane Pilot's CompanionDocument221 pagesThe Skylane Pilot's CompanionItayefrat100% (6)
- Repair and Field Service BrochureDocument4 pagesRepair and Field Service Brochurecorsini999No ratings yet
- 4-Page 7 Ways TM 20Document4 pages4-Page 7 Ways TM 20Jose EstradaNo ratings yet
- Concordia: The Lutheran Confessions - ExcerptsDocument39 pagesConcordia: The Lutheran Confessions - ExcerptsConcordia Publishing House28% (25)
- Approach To A Case of ScoliosisDocument54 pagesApproach To A Case of ScoliosisJocuri KosoNo ratings yet