Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bab 10 Pembiayaan Jangka Pendek MK 1.id - en
Uploaded by
putraparso960 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views25 pagesOriginal Title
bab_10_pembiayaan_jangka_pendek_mk_1.id.en
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views25 pagesBab 10 Pembiayaan Jangka Pendek MK 1.id - en
Uploaded by
putraparso96Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Translated from Indonesian to English - www.onlinedoctranslator.
com
CHAPTER 10
TERM FINANCING/FUNDING
SHORT
1. Short Term Funding Type
There are two types of short-term funding based on
the category of spontaneity towards the level of
company activity, namely:
1. Spontaneous financing: a type of funding that
changes automatically with changes in the level
of company activity (for example, seen from
company sales).
2. Non-spontaneous financing: a type of funding
that does not change automatically with
changes in the company's level of activity.
2. Spontaneous financing
2.1.1. Types of Spontaneous Funding
This type of funding follows the company's activities. There is
some examples of spontaneous types of funding: accounts
payable and accrual accounts. Accounts payable arises
because the company purchases supplies from suppliers
on credit.
2.2. Evaluate Cash Discount Offers
Cash deductions can be made by companies that
providing credit sales (creditors). The purpose of this
deduction is for debtors to pay off their debts more
quickly. Costs are borne by creditors. But if there is a
cash discount offer and the company (debtor) does
not take advantage of it, then there is a lost
opportunity cost.
The effective interest cost of the offer can be calculated
as follows (one year is assumed to be 360 days).
2 360
kd = - - - - - × ------ = 36.7% 98
20
The above calculation uses a simple interest rate
(does not include multiplication effects). If we want
to include the doubling effect, we can calculate it
as follows.
2
kd = ( 1 + ----- )360 / (30-10)– 1 = 43.86%
98
If the company doesn't take advantage of cash discounts, it can
reduce the cost of lost opportunities by extending
the payment period (stretching), by paying after
the maturity date. In some situations, such
stretching efforts may be possible. Suppliers will
allow such practices. But in other situations, such
stretching efforts will of course make suppliers
unhappy. Thus companies must pay attention to
the negative effects of such stretching.
3. Funding is not spontaneous
If sales increase, and the company wants to add
funds from the bank, the company will submit a
request for additional funds to the bank. Then the bank
will evaluate the application and determine whether
the application is accepted or not. Another alternative,
if the company wishes
issue securities, then the company must process
the issuance of these securities. This process
cannot be done automatically.
3.1. Commercial Paper (CP)
Large companies can issue CP instruments for
meet their financial needs. CP is a short-term debt
security (with a term of 30-90 days), without
collateral, issued by large companies and sold
directly to investors. Usually only large companies
can issue CP. These sales can be through financial
exchanges or directly to potential buyers
(investors). CP is an alternative to short-term debt
obtained through banks. CP instruments are sold
directly to investors, so the instruments do not
pass through financial intermediaries, for
example banks.
33.2. Credit Loans
3.2.1. Loan Type
Credit loans can come from banking institutions and
non-bank financial institutions.
There are two types of loans from banks:
1. Transaction credit, namely credit intended for
certain specific purposes.
2. Line of Credit. With this loan, the borrower can
borrow up to a certain maximum amount,
which is the ceiling (upper limit) of the loan.
3.2.2. Calculating the Effective Interest Rate on Credit
Loans
Interest or effective costs earned by the company will be
depending on several factors such as the loan interest
rate, minimum cash balance, and other fees. Suppose a
company takes a loan of IDR 10 million. The loan interest
rate is 20% per year. The company borrows for 3
months. One year is assumed to have 360 days. Interest
is calculated before tax. What is the effective interest
rate (TBE) that the company is paying?
Interest = IDR 10 million × (0.2 / 360) × 90 = Rp. 500,000
TBE = (1 + (500,000 / 10,000,000))360 / 90– 1 = 0.2155
or 21.55%
The effective interest rate paid is 21.55%, which is modest
higher than the nominal interest rate.
3.3. Factoring
3.3.1. Understanding Factoring
Factoring or factoring means selling receivables
From the perspective of companies that have
receivables, factoring has benefits because
companies do not need to wait until receivables are
due to obtain cash. The receivables side also benefits
because factoring is an investment alternative.
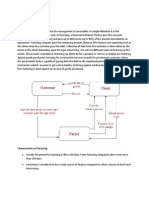
In factoring, there are three parties involved, namely:
1. The party who sells the receivables and needs cash,
this party is referred to as party 1
2. The party who owes the debt to party (1), namely party 2
3. The party who buys the receivables and gives cash
to party (1), namely party 3. This party is also called a
factor.
Factoring started from sale credit Which
resulting in accounts receivable. Companies that
have receivables (Party 1) need funds quickly to
fund operational activities. Party 1 can sell trade
receivables to a factor or factoring company (party
2). Party 2 gives cash to party 1. Now the
receivables belong to party 2. Party 3 collects the
receivables from party 2 and party 2 pays the
receivables to party 3.
Factoring eligibility is largely determined by reputation
the company in debt (party 3). Party 1's reputation
is relatively unimportant in this transaction. The
factor thus must evaluate party 3, whether party 3
has the ability to pay receivables or not. If not,
then the receivables are high risk receivables and
therefore not worth buying.
Specifically, factoring has benefits in terms of
party 1 as follows,
1. The company is free from managing receivables
administration problems. With factoring, the accounts
receivable ledger is usually held by the factor.
2. The company is free from the risk of bad debts. If the
sale of receivables is carried out without recourse,
then the risk that the receivables will be collected is
completely borne by the factor. The company will be
free from uncollected receivables.
3. Companies can obtain funds by guaranteeing receivables.
There is practically no real collateral (real goods) in this
receivable transaction.
4. The procedure is relatively simple and fast.
Simply by showing a sales invoice, the company
can get the funds it wants.
5. By offering trade debt to buyers/customers,
the company can offer competitive
alternatives in line with the buyer's domestic
competition.
6. If the company and factor have been in contact for a long time, sales
of receivables can be carried out continuously. The decision process
will be faster because it is only determined by the buyer's
reputation.
3.3.2. Who Needs Factoring?
Situations where factoring is used:
1. Companies can use factoring services to obtain
funds and strengthen their cash flow.
2. Sometimes business conditions worsen so that financial
ratios are not good.
3. Sometimes there are companies that are growing rapidly but
do not have a credit division.
4. The company is growing rapidly as in point (3) above, the need
for funds exceeds the existing funds. The company can sell its
receivables.
5. The loan process with factoring can take place
relatively quickly. This advantage is increasingly felt if
the company grows rapidly and the need for funds is
felt to be urgent.
In short, companies that need funding
Factoring is a company that is not served by a bank, either
because the company is not bankable (not worthy in the eyes of
the bank) or because it does not want to go to the bank.
3.3.3. Factoring Financing
Factoring costs usually consist of two types: costs
sales commission (factoring commission) and interest costs.
Commission fees are charged because the receivables
monitoring function is transferred to the factor. Factor maintains
the ledger of receivables sold, assumes the risk of receivables,
and also collects receivables.
Interest costs are calculated starting from the time the funds are given to
the company arrives at the time of payment of
receivables to the factor. In general, factoring
interest costs are usually higher than bank interest
costs (can be around 2% above the general interest
rate). This happens because factoring risk is higher
than bank credit risk.
In terms of factors, although the risk of factoring is quite high,
But factors have advantages that ordinary
companies don't have. First, the factor is usually a
financial institution (can be a banking or non-bank
financial institution). Such institutions usually have
better information about credit risks than ordinary
companies. Second, by holding a diversified
portfolio of accounts receivable, factors can reduce
unsystematic risk, namely risk associated with a
specific company.
3.4. Guaranteeing Receivables
With this alternative, ownership of the receivables is still in place
company hand. If the loan is not paid, the
receivables used as collateral can be used to pay off
the loan. Guarantee can be provided for all
receivables.
There are two costs associated with guaranteeing receivables:
(1) processing fees, and (2) interest fees.
3.5. Guaranteeing Merchandise (Inventory)
The procedures used will be the same as underwriting
receivables. The lender will evaluate the value of the
inventory, then will provide a loan at a certain
percentage of the inventory value
guaranteed. The company can guarantee all its
merchandise. Companies can also guarantee
certain supplies (merchandise). Lenders can invite
independent third parties, to ensure that
merchandise sales will be used to pay off the loan.
Total costs include two things: fees
processing/administration and interest fees.
3.6. Bank Acceptance
3.6.1. Bank Acceptance Creation Process
Acceptance is a statement of the accepting bank's ability to
make payment on a term note issued by the exporter, at the
maturity date of the note in question
Bank acceptance begins with a payment order to a bank
for a certain amount of money in some future period. Then, instead
of waiting for some future period, the company that has the warrant
can sell to another party at a discount. Companies can have money
faster. Meanwhile, the party who buys obtains interest income (the
difference between the nominal value and the selling price) from the
acceptance. Bank acceptance is a fairly popular way to fund export-
import transactions. Acceptance instruments usually have maturities
between 30 and 270 days with most being 90 days. The time period
can be negotiated to suit the time period for the goods to arrive.
3.6.2. Selling or Withholding Acceptance
For example, the draft asks for payment of IDR 1 million to the bank
The importer charges a commission fee of 1.5%,
the draft period is 60 days. If the exporter decides
to hold the acceptance until maturity, the exporter
will receive a discount of:
Face value IDR 1,000,000
Commission IDR 1 million - (0.015 x 60 / 360 x IDR 1 million) - IDR 2,500
---------------
Commission net value - - IDR 997,500
One year is assumed to be 360 days. Commission will
received by the bank is IDR 2,500. For example, the
interest for bank acceptance is 6%. If the exporter
decides to sell the acceptance, he will receive:
Commission net value Rp. 997,500
Interest (Rp. 1 million x (0.06 x 60/360)) - IDR 10,000
--------------
Net acceptance value - Rp. 987,500
At maturity, the importing bank will receive IDR 1 million
from the importer. Commission fees will be paid by the
exporter. Whether he will sell or retain the acceptance, the
exporter will compare the interest rate on the acceptance with
the interest rate in the financial market.
3.7. Repos
Repo or abbreviated as Rp, is an abbreviation of
repurchase agreement. For example, if a
securities dealer (seller) needs funds, he can sell
securities to investors accompanied by an
agreement that he will buy back the securities at
a certain time at a higher value than the purchase
value. This high value reflects the principal value
accompanied by loan interest. Securities that are
often used as collateral are SBI (in Indonesia) or
'T-Bills (in the United States).
Repo terms (repo terms) are the same as regular repo, only
the period is longer, namely more than 30 days.
Repo loans are seen as low-risk loans, because the
loans are guaranteed by securities issued by the
government.
Reverse repo is the opposite of repo. This is the dealer
looking for parties who have securities, then
buying the securities accompanied by a promise to
sell the securities in some future period at a higher
price. The higher price reflects the loan principal
plus loan interest.
If the term of the repo is short enough, letter
The value that is used as collateral may not need to
change hands physically (to the investor), because this
method is not practical.
4. Evaluate Short Term Funding Sources
Financial managers can evaluate with
using the framework: overall funding
strategy, costs, availability, and flexibility.
Funding Strategy. The financial manager can choose
aggressive, moderate, or conservative funding
strategies. Each will have different
consequences. With an active strategy, the
financial manager will use greater short-term
funding compared to long-term funding
(because the interest rate on short-term loans is
smaller than the interest rate on long-term
loans).
Cost. As explained in the previous section, managers
Finance needs to calculate funding costs which include
interest costs and other costs. The cost effective
(actually paid) cost that it should be
noticed by the financial manager. Besides explicit costs,
financial managers must also look at implicit costs, which
are difficult to quantify.
Availability. An alternative may provide
cheap and worth choosing. But if the company
cannot access these alternatives, then the
company cannot use them. For example, CP is
usually issued by large companies that already
have a name. Small companies thus cannot use
CP. Banker's Acceptance which is usually used for
export/import trade.
Flexibility. Manager finance in a way general
want flexibility, although do
loan. Spontaneous funding (accounts payable,
salaries payable) provides a spontaneous source of
funds, thus tends to increase flexibility. Bank debt
alternatives may reduce flexibility if banks impose
many conditions. Line of credit loans can provide
increased flexibility compared to transaction loans.
You might also like
- Leveraged Buyouts: A Practical Introductory Guide to LBOsFrom EverandLeveraged Buyouts: A Practical Introductory Guide to LBOsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Factoring Is A: Invoice DiscountingDocument5 pagesFactoring Is A: Invoice DiscountingnoushinesabaNo ratings yet
- Sources of Short and Secured FinancingDocument4 pagesSources of Short and Secured FinancingIsaiah CruzNo ratings yet
- IInd Unit - Factoring and Venture CapitalDocument28 pagesIInd Unit - Factoring and Venture Capitalguna57617No ratings yet
- Factoring in IndiaDocument3 pagesFactoring in IndiachikuraniNo ratings yet
- FINANCE MANAGEMENT FIN420 CHP 7Document28 pagesFINANCE MANAGEMENT FIN420 CHP 7Yanty Ibrahim100% (3)
- 07 BSIS 2 Financial Management Week 14 15Document5 pages07 BSIS 2 Financial Management Week 14 15Ace San GabrielNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS FINANCE Week 11Document6 pagesBUSINESS FINANCE Week 11Ace San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Working Capital FinancingDocument11 pagesWorking Capital FinancingShaRiq KhAnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Short Term FinancingDocument45 pagesChapter 8 - Short Term FinancingCindy Jane Omillio100% (1)
- LM05 Working Capital & LiquidityDocument16 pagesLM05 Working Capital & LiquiditySYED HAIDER ABBAS KAZMINo ratings yet
- fINAL PPT REPORTING-SPECIAL TOPICSDocument26 pagesfINAL PPT REPORTING-SPECIAL TOPICSFelicity Joy CruelNo ratings yet
- What Is FactoringDocument22 pagesWhat Is Factoringshah faisal100% (1)
- Spontaneous FinancingDocument3 pagesSpontaneous Financingmohi80% (1)
- Finance ExamDocument9 pagesFinance ExamTEOH WEN QINo ratings yet
- Alternate Source of Finance, Private and Social Cost-Benefit, Public Private PartnershipDocument20 pagesAlternate Source of Finance, Private and Social Cost-Benefit, Public Private PartnershipRewant MehraNo ratings yet
- Managing Financial Resources and DecisionsDocument18 pagesManaging Financial Resources and DecisionsAbdullahAlNomunNo ratings yet
- Sources of Business FinanceDocument4 pagesSources of Business FinancedrywitNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance - CreditDocument12 pagesSources of Finance - CreditSanta PinkaNo ratings yet
- Short Term Sources of FinanceDocument3 pagesShort Term Sources of FinanceRachit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Sources and Uses of FundsDocument46 pagesModule 8 - Sources and Uses of FundsKrista SuyatNo ratings yet
- 2 Assignment: Department of Business AdministrationDocument14 pages2 Assignment: Department of Business AdministrationFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Financing: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDocument13 pagesShort-Term Financing: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToMohammad Salim HossainNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Business Financing Case Study On: Great Service Cleaning and Maintenance CompanyDocument9 pagesDifferent Types of Business Financing Case Study On: Great Service Cleaning and Maintenance CompanyElias ChembeNo ratings yet
- AC 313 Sources of Finance - Margaret Aeka ID 22700021Document10 pagesAC 313 Sources of Finance - Margaret Aeka ID 2270002122700021maaeNo ratings yet
- FM Chapter 14Document6 pagesFM Chapter 14Ma. Christina ErminoNo ratings yet
- Subject Code-B-103 Section A: Part One:: A. Ignored Non-Corporate EnterpriseDocument8 pagesSubject Code-B-103 Section A: Part One:: A. Ignored Non-Corporate EnterpriseRamusubu PsrkNo ratings yet
- Short Term FinanceDocument11 pagesShort Term Financethisispurva100% (1)
- Capter 4 FM IIDocument7 pagesCapter 4 FM IIbmulat87No ratings yet
- Business vs Consumer LoansDocument10 pagesBusiness vs Consumer LoansDandreb SardanNo ratings yet
- FINMNN1 Chapter 4 Short Term Financial PlanningDocument16 pagesFINMNN1 Chapter 4 Short Term Financial Planningkissmoon732No ratings yet
- Bill DiscountingDocument17 pagesBill Discountingjohar_priyanka3723100% (1)
- Factoring and Forfaiting Services ExplainedDocument11 pagesFactoring and Forfaiting Services ExplainedPriyanka MahawarNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance: Long Term Finance - Its Meaning and PurposeDocument4 pagesSources of Finance: Long Term Finance - Its Meaning and PurposeClinton GonsalvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Senior SecurityDocument23 pagesChapter 12 Senior SecuritySumonNo ratings yet
- Business Finance PPT - 12 Short Term Sources of FinancingDocument25 pagesBusiness Finance PPT - 12 Short Term Sources of FinancingELMSS100% (1)
- Working Capital Loan: LoansDocument5 pagesWorking Capital Loan: LoansNiharika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Sources and Uses of FundsDocument17 pagesChapter 4 - Sources and Uses of Fundsmarissa casareno almueteNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit VIDocument21 pagesAssignment Unit VIHạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Business Finance TADocument9 pagesBusiness Finance TAOlivier MNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Q1) 1) Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument9 pagesFinancial Management: Q1) 1) Analysis of Financial StatementsKrishnanand AnvekarNo ratings yet
- Small Scale EnterprisesDocument2 pagesSmall Scale EnterprisesHilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Factoring, Forfeiting and DiscountingDocument2 pagesFactoring, Forfeiting and DiscountingConfie03 HazardNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities Management: Prepared by Keldon BauerDocument35 pagesCurrent Liabilities Management: Prepared by Keldon BauerMónica GarzaNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating:: Working Capital LoansDocument7 pagesCredit Rating:: Working Capital Loansdon faperNo ratings yet
- Forfaiting:: Trade Finance FactoringDocument9 pagesForfaiting:: Trade Finance FactoringR.v. NaveenanNo ratings yet
- Summary Corporate Finance (David Hillier, Lain Clacher, Stephen Ross, Randolph Westerfield, Bradford Jordan)Document44 pagesSummary Corporate Finance (David Hillier, Lain Clacher, Stephen Ross, Randolph Westerfield, Bradford Jordan)Akash JhaNo ratings yet
- WCM Unit 5 Second TopicDocument6 pagesWCM Unit 5 Second TopicParul varshneyNo ratings yet
- 5 Consumer Financ-2Document13 pages5 Consumer Financ-2thullimilli leelaprasadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-8 - Sources of Finance & Short Term FinanceDocument8 pagesChapter 6-8 - Sources of Finance & Short Term FinanceTAN YUN YUNNo ratings yet
- Raising DebtDocument4 pagesRaising DebtvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Acct 504 Exam Question GuideDocument15 pagesAcct 504 Exam Question Guideawallflower1100% (1)
- Banking Chapter FiveDocument44 pagesBanking Chapter FivefikremariamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3arina7No ratings yet
- Famd Assingnment: The Sources of FinanceDocument11 pagesFamd Assingnment: The Sources of FinanceCoulibaly YounoussouNo ratings yet
- Sources of Short-Term Funds: Construction GroupDocument54 pagesSources of Short-Term Funds: Construction GroupRia MendezNo ratings yet
- Factoring and ForfaitingDocument7 pagesFactoring and ForfaitingemildaraisonNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance and Decision MakingDocument34 pagesSources of Finance and Decision MakingWaleed Ahmad100% (1)
- Assignment 2 Fin536Document6 pagesAssignment 2 Fin536mypinkladyNo ratings yet
- Menangani Differential Atau Perbedaan Atau SelisihDocument5 pagesMenangani Differential Atau Perbedaan Atau SelisihNadilla VidyaNo ratings yet
- Assgnt Acfn 3202 2020extDocument2 pagesAssgnt Acfn 3202 2020extbethelhemNo ratings yet
- Cap Budegt ProbsDocument4 pagesCap Budegt ProbsAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Assessing ROA and ROE metrics for NBFC scorecardDocument5 pagesAssessing ROA and ROE metrics for NBFC scorecardShaurya SinghNo ratings yet
- Dividend - UPDATEDDocument83 pagesDividend - UPDATEDAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Artist Management ManualDocument315 pagesArtist Management ManualGina92% (13)
- Chapter 26 MCQs On International TaxationDocument26 pagesChapter 26 MCQs On International TaxationSuranjali Tiwari100% (1)
- 24.2 Exam Taking Skills Sample Questions Week 1 An Introduction To Cost Accounting March 28 2Document46 pages24.2 Exam Taking Skills Sample Questions Week 1 An Introduction To Cost Accounting March 28 2Jamaica DavidNo ratings yet
- Management ProjectDocument20 pagesManagement ProjectPrasad BhumkarNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting - QUIZ 7Document4 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting - QUIZ 7JINGLE FULGENCIONo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument3 pagesBalance SheetSimha SimhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Notes To Financial Statements (Part 2)Document6 pagesChapter 7 - Notes To Financial Statements (Part 2)ShekNo ratings yet
- SMBR LK Konsolidasian Audit 2021 CompressedDocument129 pagesSMBR LK Konsolidasian Audit 2021 CompressedAhdan SNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Answers To End of Module QuestionsDocument40 pagesModule 3 Answers To End of Module QuestionsYanLi100% (3)
- Assignment Chapter 12Document17 pagesAssignment Chapter 12Nicolas ErnestoNo ratings yet
- CAMEL ModelDocument31 pagesCAMEL ModelVengatesh SlNo ratings yet
- PAS 16 PPE framework & standardsDocument23 pagesPAS 16 PPE framework & standardsAnneNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Expansion Project Cash FlowsDocument368 pagesAnalysis of Expansion Project Cash FlowsRoy HemenwayNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial ManagementDocument17 pagesIntroduction to Financial ManagementJOSCEL SYJONGTIANNo ratings yet
- Ceres Gardening Company Submission PDFDocument7 pagesCeres Gardening Company Submission PDFnikki tamboli81% (16)
- LavBay Capital Total Return Fund overviewDocument4 pagesLavBay Capital Total Return Fund overviewSangeetSindanNo ratings yet
- FM II Chapter 1Document23 pagesFM II Chapter 1Amanuel AbebawNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedDocument27 pagesCash Flow Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2004 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reservedmabkhan_25No ratings yet
- ACG 4803 Exam 3 Study GuideDocument11 pagesACG 4803 Exam 3 Study GuideMinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Walmart Vs TargetDocument6 pagesWalmart Vs TargetNoble S WolfeNo ratings yet
- CapBud Problem Quiz 1Document4 pagesCapBud Problem Quiz 1Sittie Ayeenah Yusoph ArindigNo ratings yet
- Chapter c3Document47 pagesChapter c3bobNo ratings yet
- Format Lembar Kerja AkuntansiDocument29 pagesFormat Lembar Kerja AkuntansiBudi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Cashflow Practice Solution-AdditionalDocument5 pagesCashflow Practice Solution-AdditionalNadjah JNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Venture Capital Private Equity and The Financing of Entrepreneurship 1st Edition Lerner Solutions Manual PDFDocument13 pagesDwnload Full Venture Capital Private Equity and The Financing of Entrepreneurship 1st Edition Lerner Solutions Manual PDFdemivoltnotpatedf6u2ra100% (9)