Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.2.3 Units
Uploaded by
d3van070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page1.2.3 Units
Uploaded by
d3van07Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
1.2.
3 Units
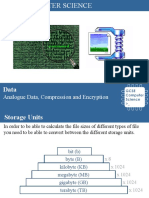
Units of data storage
⮚ Bit (b)
Capital ‘B’ is bytes; lower case ‘b’ is bits
⮚ Nibble (4 bits)
1B is 8 times 1b
⮚ Byte (8 bits)
⮚ Kilobyte (1,000 bytes)
⮚ Megabyte (1,000 KB)
⮚ Gigabyte (1,000 MB)
⮚ Terabyte (1,000 GB)
⮚ Petabyte (1,000 TB)
Conversion into binary to be processed
⮚ Binary – only 2 states
- On (1) or off (0)
⮚ Advantages of having only 2 states
1. Easier to manufacture
2. Therefore cheaper
3. More reliable
⮚ Examples
1. RAM
2. Hard disk
3. Optical disk
4. Flash memory
Data capacity + calculations
⮚ Number of files that can be stored = size of storage ÷ size of file(s)
⮚ Text file size = bits per character × number of characters
⮚ Image file size = colour depth × image height (px) × image width (px)
⮚ Sound file size = sample rate × duration (s) × bit depth
You might also like
- The Absolute Beginner's Guide to Binary, Hex, Bits, and Bytes! How to Master Your Computer's Love LanguageFrom EverandThe Absolute Beginner's Guide to Binary, Hex, Bits, and Bytes! How to Master Your Computer's Love LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Task 1 Bytes and File SizesDocument2 pagesTask 1 Bytes and File Sizesapi-377315743No ratings yet
- 1.3 Data Storage and File CompressionDocument6 pages1.3 Data Storage and File CompressionCiara HuteauNo ratings yet
- Objective 1.3 - Hardware ComponentsDocument3 pagesObjective 1.3 - Hardware ComponentsAmp CrewNo ratings yet
- 08 - 29-Data Storage CapacityDocument11 pages08 - 29-Data Storage CapacityWena Prado - AbuelNo ratings yet
- File Formats - RevisionDocument15 pagesFile Formats - RevisionJasonNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Data Storage and CompressionDocument21 pagesCh1 Data Storage and CompressionKhin Kyawt Zue Han Zue ZueNo ratings yet
- Convertion and CalculationsDocument2 pagesConvertion and CalculationsFue NoirNo ratings yet
- Activity Guide - Bytes and File Sizes: Stanford University - CS 101 - Kilobytes Megabytes GigabytesDocument2 pagesActivity Guide - Bytes and File Sizes: Stanford University - CS 101 - Kilobytes Megabytes GigabytesGeoMatrixNo ratings yet
- Analogue Data, Compression and EncryptionDocument30 pagesAnalogue Data, Compression and EncryptionRahul KNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument9 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingNiñabeth DavidNo ratings yet
- CSS 11 Q3 W3 Data RepresentationDocument100 pagesCSS 11 Q3 W3 Data RepresentationGEL SyNo ratings yet
- Mahmud RAHMAN - 1.2 Workbook (Part 2)Document30 pagesMahmud RAHMAN - 1.2 Workbook (Part 2)Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- BYTESDocument3 pagesBYTESAndrés AyalaNo ratings yet
- Data Representation & Architecture-1Document10 pagesData Representation & Architecture-1mohamoud BileNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 17 & 18Document31 pagesLecture - 17 & 18YOUR FATHERNo ratings yet
- Multimedia DataDocument1 pageMultimedia Datadump mailNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document7 pagesLecture 8adeel khanNo ratings yet
- U2l1 Activity Guide - Bytes and File SizesDocument1 pageU2l1 Activity Guide - Bytes and File Sizesapi-358253386No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Data RepresentationDocument1 pageChapter 1 Data RepresentationSamira YasserNo ratings yet
- Mensuration of Computer MemoryDocument2 pagesMensuration of Computer MemoryMithz SuneNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Workbook - Part 2Document30 pages1.2 Workbook - Part 219subedarzNo ratings yet
- Carry Out Mensuration and CalculationDocument16 pagesCarry Out Mensuration and CalculationRomulo BajNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document9 pagesWeek 2usmanaslam17621No ratings yet
- Computer - Memory UnitsDocument2 pagesComputer - Memory UnitsジョージNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.01: Plagiarism Will Be Graded ZeroDocument2 pagesAssignment No.01: Plagiarism Will Be Graded ZeroRizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Calculating Data StorageDocument8 pagesCalculating Data StorageRichard Sugbo50% (2)
- 2 LabDocument4 pages2 Labsir lazybonesNo ratings yet
- File Management Sytem and Data StorageDocument22 pagesFile Management Sytem and Data StorageNathan NathanNo ratings yet
- 1 3+Data+Storage+and+CompressionDocument69 pages1 3+Data+Storage+and+Compressionhaotongxu14No ratings yet
- Digital RepresentationDocument2 pagesDigital RepresentationRose GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Memory Measurement: Unit Abbreviation StorageDocument1 pageMemory Measurement: Unit Abbreviation Storagenorbert78_2015No ratings yet
- How Big Is My File? KB, MB, GB: Unit Abb. EquivalentDocument1 pageHow Big Is My File? KB, MB, GB: Unit Abb. EquivalentGabbar DaNo ratings yet
- Perform Mensuration and Calculation 2Document14 pagesPerform Mensuration and Calculation 2Jose BundalianNo ratings yet
- Memory Units Conversion GR 9Document5 pagesMemory Units Conversion GR 9Chris DegraciaNo ratings yet
- Manipulate Units of StorageDocument2 pagesManipulate Units of StorageNickyStephensNo ratings yet
- Sadaf CompDocument10 pagesSadaf CompSadaf ButtNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Assessment GuideDocument13 pagesComputer Science Assessment GuidefrayashtiaNo ratings yet
- An Understandable Guide To Everything From Bytes To YottabytesDocument13 pagesAn Understandable Guide To Everything From Bytes To YottabytesVim SamNo ratings yet
- Binary ConversionDocument18 pagesBinary ConversionSherlyn Flores VillarNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3-UNDERSTAding-computer-storage 20240304 201634 0000.pdf 20240304 204120 0000Document10 pagesLesson-3-UNDERSTAding-computer-storage 20240304 201634 0000.pdf 20240304 204120 0000colbyschein05No ratings yet
- 04a Memory Units and TableDocument2 pages04a Memory Units and TableInomusa MhlopeNo ratings yet
- Data StorageDocument7 pagesData StorageMaserati. MTNo ratings yet
- Compiled NotesDocument81 pagesCompiled Notescalmmedown66No ratings yet
- Computer Memory Units PDFDocument2 pagesComputer Memory Units PDFsadam solangiNo ratings yet
- What Are BitsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Bitsmarry mineNo ratings yet
- Bits and BytesDocument2 pagesBits and BytesLariemeevaNo ratings yet
- Bits and BytesDocument1 pageBits and Byteslsimm2020No ratings yet
- Number RepresentDocument35 pagesNumber RepresentAtreyee HaldarNo ratings yet
- A4 Solutions - Compare and ConvertDocument3 pagesA4 Solutions - Compare and ConvertSage PaclibarNo ratings yet
- Byte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, GigabyteDocument3 pagesByte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabytesan nicolasNo ratings yet
- Data RepresentationDocument21 pagesData RepresentationVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Bits BytesDocument6 pagesBits BytesjudaswashereNo ratings yet
- Data Representation - AQA Computer Science Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesData Representation - AQA Computer Science Cheat Sheet: by ViaindiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Basic Compression ConceptsDocument20 pagesLecture 1 Chapter 1 Basic Compression ConceptsMido AlaaNo ratings yet
- Computer SainsDocument32 pagesComputer SainsMohd HafizsalehuddinNo ratings yet
- Computer Science PDFDocument129 pagesComputer Science PDFDarenNo ratings yet
- Storage CapacityDocument2 pagesStorage Capacityapi-270667413No ratings yet
- Sempersol Nullcon Reena Prince Presentation On SteganographyDocument120 pagesSempersol Nullcon Reena Prince Presentation On SteganographyPrince BoonliaNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Hide 1definitions 2examples of Use 3see Also 4references 5external LinksDocument3 pagesDefinitions: Hide 1definitions 2examples of Use 3see Also 4references 5external LinksLakshanmayaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3 Embedded SystemsDocument1 page1.1.3 Embedded Systemsd3van07No ratings yet
- 1.2.4 Data StorageDocument1 page1.2.4 Data Storaged3van07No ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell StructureDocument3 pages1.1 Cell Structured3van07No ratings yet
- 1.2 DivisionDocument2 pages1.2 Divisiond3van07No ratings yet