Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 2
Uploaded by
usmanaslam176210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesWeek 2
Uploaded by
usmanaslam17621Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
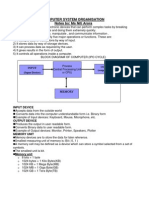
Computing Fundamentals
Data encoding & storage
Week 2 Instructor: Shehzad Aslam
Data Storage
Computers are Binary
How files are stored?
How images?
What about video & audio?
How PDF?
Data Encoding deals with format of data
What’s inside files?
Demo about RTF
Gates & Flip flops
Bit (binary digit) 0 or 1
Boolean operations by George Boole
AND, OR, XOR
Gates produces the Boolean operation result i.e True or False
Collection of gate circuit use to build flip flops
Maintain output unless a pulse is provided
Many flip flops can be used to hold data
Very large scale integration (VLSI)
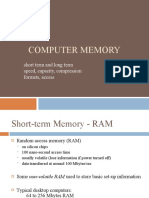
Memory Organization - RAM
Manageable units termed as cells, typically 8 bits
Has unique name called address
Data in the cell can be accessed randomly
Design technology
DRAM (dynamic RAM)
SDRAM (synchronous RAM)
Memory Units
Bit
Byte
Kilobyte (KB)
Megabyte (MB)
Gigabyte (GB)
Terabyte (TB)
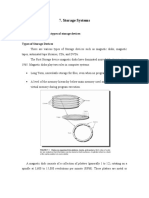
Mass Storage – Hard disk
Magnetic plates mounted on spindle having read / write head
Plate is divided into tracks & sectors
Logical division of tracks & sectors can be re-adjusted during formatting
Mechanical disk has few delays
Seek time: time to move head from one track to other
Rotation delay: half time to fully rotate disk; also called latency
Access time is: Seek time + rotation delay
Transfer speed is usually in MB/sec
Disk is sealed in casing to protect from dust
Representing Strings
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) table
Each letter, number, symbols are assigned a number
That number is saved in memory
ASCII table is used to show letter / number / symbol shape
Each letter is represented in 7bits resulting in 128 characters
Extended ASCII is 8bits resulting in 256 characters
Unicode is 16bits having 65,536 characters
Representing Audio
Measured amplitude of wave and sampled at constant rate
Telephonic communication
8000 samples per second
Music Recording
44,100 samples per second
Each sample in 16 bits
Stereo in 32 bits
Representing Image
Pixel (picture element) value is store in bit map
Red, green, blue component stored separately each in 8 bits
Or gray intensity is saved
Bitmap has rescaling problem i.e. more zoom is more grainy look
So image can be as geometric structure
Can be saved as bitmap or geometric values
Reading
Chapter 1 from Computer Science an Overview
You might also like
- Nintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8From EverandNintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8No ratings yet
- Storage Devices and Multimedia DevicesDocument25 pagesStorage Devices and Multimedia DevicesJoevertVillartaBentulanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Computer Studies Notes On Data Storage (Zafar Ali Khan)Document14 pagesIGCSE Computer Studies Notes On Data Storage (Zafar Ali Khan)EthanielNo ratings yet
- Perform Mensuration and Calculation & Prepare and Interpret Technical DrawingDocument6 pagesPerform Mensuration and Calculation & Prepare and Interpret Technical DrawingPaul Sotto NgujoNo ratings yet
- Bits and Bytes: Weesan LeeDocument19 pagesBits and Bytes: Weesan LeeasdasdasdjdsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1.1 Data Representation: Computer Science 2210 (Notes)Document12 pagesChapter: 1.1 Data Representation: Computer Science 2210 (Notes)Athuai DoorNo ratings yet
- Computer System Organisation - NotesDocument9 pagesComputer System Organisation - NotesNiti Arora0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - 2Document5 pagesChapter 2 - 2randyNo ratings yet
- Secondary Storage and MediaDocument33 pagesSecondary Storage and MediaBharti PahujaNo ratings yet
- Uma-L10 (The Computer Memory)Document13 pagesUma-L10 (The Computer Memory)Anirban Datta Roy.No ratings yet
- SS2 (1ST) PT1Document6 pagesSS2 (1ST) PT1Kimmy AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Memory, Storage (RAM, Cache, HDD, ODD, SSD, Flashdrives)Document57 pagesMemory, Storage (RAM, Cache, HDD, ODD, SSD, Flashdrives)Akhila DakshinaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Tapes Cd-Rom: Adil Yousif, PHDDocument31 pagesMagnetic Tapes Cd-Rom: Adil Yousif, PHDSamahir AlkleefaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3 Data StorageDocument12 pages1.1.3 Data StorageTrynosNo ratings yet
- Memory and Storage and A Little BitDocument32 pagesMemory and Storage and A Little BitWalid_Sassi_TunNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Data Storage and File CompressionDocument6 pages1.3 Data Storage and File CompressionCiara HuteauNo ratings yet
- GCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.5 Memory, Storage and MediaDocument6 pagesGCSE CS (2210) / IGCSE CS (0478) P1 NOTES Chapter 1.3: Hardware and Software 1.3.5 Memory, Storage and MediacollenNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Hardware & SoftwareDocument30 pagesSection 1: Hardware & SoftwareNorth Ruimveldt Secondary SchoolNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of computer hardware and softwareDocument30 pagesFundamentals of computer hardware and softwareJoshua BrownNo ratings yet
- Lecture Class03 1Document41 pagesLecture Class03 1TanafeNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationsDocument21 pagesComputer ApplicationsdudungNo ratings yet
- Difference Between RAM and ROMDocument7 pagesDifference Between RAM and ROMJan Carlo Balatan Pablo100% (2)
- Computer Science an overview chapter 1 pdf notesDocument82 pagesComputer Science an overview chapter 1 pdf notesK DHSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Hardware BasicsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Hardware BasicsJohn FrandoligNo ratings yet
- Indore School Computer OrganizationDocument48 pagesIndore School Computer OrganizationMarieFernandesNo ratings yet
- Data Representation FundamentalsDocument33 pagesData Representation FundamentalsMayor ParasharNo ratings yet
- CGMB 234: Multimedia Systems DesignDocument33 pagesCGMB 234: Multimedia Systems DesignAbirami KannanNo ratings yet
- Memory HierarchyDocument6 pagesMemory Hierarchymuhammadaflah23524No ratings yet
- CPE 101-Chapter3_updated2022Document25 pagesCPE 101-Chapter3_updated2022akilroberto17No ratings yet
- CPE 101-Chapter3 Updated2022Document25 pagesCPE 101-Chapter3 Updated2022The boy thats lost in the woodsNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICESDocument25 pagesChapter3 SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICESPrince kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CoDocument53 pagesUnit 4 CoKarthikNo ratings yet
- CSS9-Q2-LESSON-5 IIDocument5 pagesCSS9-Q2-LESSON-5 IILe Bryll T. SinceroNo ratings yet
- DBMS File Organization, Indexes: Platters Read/write Head ArmDocument16 pagesDBMS File Organization, Indexes: Platters Read/write Head ArmMohit VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Module VI - Secondary StorageDocument24 pagesModule VI - Secondary StorageMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Stallings Chapter 5 External Memory TypesDocument37 pagesStallings Chapter 5 External Memory TypesAriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document42 pagesChapter 2-1Snehesh Bhoir100% (1)
- Storage Systems: 1. Explain Various Types of Storage DevicesDocument24 pagesStorage Systems: 1. Explain Various Types of Storage DevicesVijiya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- GCSE (J277) Keywords For GcseDocument16 pagesGCSE (J277) Keywords For GcseEmma StevensNo ratings yet
- CD RomDocument2 pagesCD Romnadeembhai887No ratings yet
- Hard Disk PPT Tamil.1Document19 pagesHard Disk PPT Tamil.1amuljune0% (3)
- Basic Computer Hardware Maintenance GuideDocument36 pagesBasic Computer Hardware Maintenance GuideKumera Dinkisa ToleraNo ratings yet
- Memory, Storage Devices & MediaDocument8 pagesMemory, Storage Devices & MediaZubayar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Representing Text and Images in BinaryDocument5 pagesRepresenting Text and Images in BinaryfhafanaNo ratings yet
- Data RepresentationDocument21 pagesData RepresentationVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Hardware MaintenanceDocument35 pagesBasic Computer Hardware Maintenanceflash driveNo ratings yet
- Types of EcommerceDocument23 pagesTypes of EcommercebankapriyankaNo ratings yet
- Unit-III: Memory: TopicsDocument54 pagesUnit-III: Memory: TopicsZain Shoaib MohammadNo ratings yet
- Computer SpecificationsDocument35 pagesComputer SpecificationsArturo Tejero100% (2)
- Computers: Hardware and Software: ComputerDocument27 pagesComputers: Hardware and Software: ComputerDaniya AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Types of Hardware DevicesDocument13 pagesTypes of Hardware Devicesanon_678973145No ratings yet
- Memory Basics: Emt 235 Digital Electronic Principles 2Document58 pagesMemory Basics: Emt 235 Digital Electronic Principles 2gurdianskyNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument35 pagesUnit IIjayNo ratings yet
- Tee Course Grade 10: Module 7 - PC Hardware Memory and Storage DevicesDocument30 pagesTee Course Grade 10: Module 7 - PC Hardware Memory and Storage DevicesLokendra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument2 pagesMemoryMaintenance CircleNo ratings yet
- Data Storage and Access Methods: Min Song IS698Document50 pagesData Storage and Access Methods: Min Song IS698Mohammad Hamayun ShamsNo ratings yet
- K B M B G B T B P B 1024 Bytes 1024 KB 1024 MB 1024 GB 1024 TBDocument9 pagesK B M B G B T B P B 1024 Bytes 1024 KB 1024 MB 1024 GB 1024 TBJensen Ryan LimNo ratings yet
- CompressionDocument71 pagesCompressionChirag GalaNo ratings yet
- Midterm PracticeDocument7 pagesMidterm PracticeZhang YoudanNo ratings yet
- Digital Video Part 2Document8 pagesDigital Video Part 2aleksandar.haNo ratings yet
- 4.1. MOS Capacitor Deep Trench Isolation For CMOS Image SensorsDocument4 pages4.1. MOS Capacitor Deep Trench Isolation For CMOS Image SensorsLuật TrầnNo ratings yet
- Biostar G41D3 (Ver 7.0) PDFDocument32 pagesBiostar G41D3 (Ver 7.0) PDFEl TécnicoNo ratings yet
- 2n5087 CDIL Datasheet - RetroamplisDocument5 pages2n5087 CDIL Datasheet - Retroamplisnanodocl50990% (1)
- EMDK For .NET Version 2.9 Release NotesDocument5 pagesEMDK For .NET Version 2.9 Release NotesCleijonatas S SilvaNo ratings yet
- Dell-1708fp User's Guide En-UsDocument55 pagesDell-1708fp User's Guide En-UsFareez TaherNo ratings yet
- Users Manual Vip 3430 B g2 Vip 3430 D g2 enDocument63 pagesUsers Manual Vip 3430 B g2 Vip 3430 D g2 enJose CeceñaNo ratings yet
- CM As-I Master ST Et200sp Manual 2013-04 En-UsDocument150 pagesCM As-I Master ST Et200sp Manual 2013-04 En-UsAbez FiveNo ratings yet
- SAP and IoTDocument37 pagesSAP and IoTwthiendia100% (1)
- 1RE PDS Bentley Instrumentation Wiring LTR en LR 0116Document2 pages1RE PDS Bentley Instrumentation Wiring LTR en LR 0116luciaNo ratings yet
- Ups InverterDocument32 pagesUps InverterSuheil AjeebNo ratings yet
- 1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan BhagatDocument32 pages1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan Bhagatabhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- PersonDB - SQLite Example Using Entity Framework 5Document26 pagesPersonDB - SQLite Example Using Entity Framework 5Jales JaqueNo ratings yet
- GOT2000 - UserManual Monitor - SH 081196 I PDFDocument614 pagesGOT2000 - UserManual Monitor - SH 081196 I PDFFanny Achmad Hindrarta KusumaNo ratings yet
- ERP-Technology Background and ReviewDocument20 pagesERP-Technology Background and ReviewHaris RazaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Syllabus Plus Other InformationDocument10 pagesElectronics Syllabus Plus Other InformationCutry CarryNo ratings yet
- Operating System (B.tech) (Unit 5 Notes)Document25 pagesOperating System (B.tech) (Unit 5 Notes)janani100% (1)
- OI Server Manager User GuideDocument58 pagesOI Server Manager User GuideEduardo Andres Ramos RojasNo ratings yet
- Dual Channel Hall Effect Direction Detection Sensor IC: Description Features and BenefitsDocument12 pagesDual Channel Hall Effect Direction Detection Sensor IC: Description Features and BenefitsPankaj D PatelNo ratings yet
- Egg Dropping Puzzle Solved Using Dynamic ProgrammingDocument5 pagesEgg Dropping Puzzle Solved Using Dynamic ProgrammingTanisha JindalNo ratings yet
- UNIT II r20 (Iot)Document43 pagesUNIT II r20 (Iot)Yadavilli Vinay100% (1)
- Start-Up & Upgrade Guide: Applies To SINUMERIK 810/840D Software Version 06.04.15.00Document17 pagesStart-Up & Upgrade Guide: Applies To SINUMERIK 810/840D Software Version 06.04.15.00craftiNo ratings yet
- Configuring DNP 3.0 On The Ge D2X Platform in Configpro 4.XxDocument23 pagesConfiguring DNP 3.0 On The Ge D2X Platform in Configpro 4.XxSalvador FayssalNo ratings yet
- Standard CellDocument53 pagesStandard CellShwethNo ratings yet
- 20 01 2022 21 58 38Document42 pages20 01 2022 21 58 38Alarcón Cruz Miguel ÁngelNo ratings yet
- 40Gb/s TIA AGCDocument14 pages40Gb/s TIA AGCAsif JahangirNo ratings yet
- IPM Savina 300Document230 pagesIPM Savina 300DenisNo ratings yet
- Glpi Network Asset Management OverviewDocument41 pagesGlpi Network Asset Management OverviewKailash ChouguleNo ratings yet
- 74HC HCT299Document24 pages74HC HCT299rajivsharma1610No ratings yet
- Pt855tadm b112016Document406 pagesPt855tadm b112016viktorNo ratings yet
- PV2HVMDocument1 pagePV2HVMfaabbasNo ratings yet