Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Naveen Kumar - LASERs Application in Welding
Uploaded by
naveen.kumar.cd.met200 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views7 pagesLaser functioning in welding operations
Original Title
20145097_Naveen Kumar_LASERs Application in Welding
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLaser functioning in welding operations
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views7 pagesNaveen Kumar - LASERs Application in Welding
Uploaded by
naveen.kumar.cd.met20Laser functioning in welding operations
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
CY517
LASERs: Application in Welding
Image Credits: Weldologic
Submitted To: Presented By:
V Ramanathan, IIT (BHU) Varanasi Naveen Kumar 20145097
Introduction
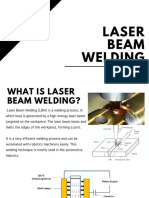
Laser Welding uses a highly concentrated beam
of light on a very tiny spot so that the area under
the laser beam absorbs the light and becomes
highly energetic. As powerful laser beams are
used, the electrons in the area get excited to a
point where the material melts as the result of
the atoms breaking the bonds with each other.
Laser welding can also be used to join plastics.
Two most common lasers used in a laser welding
machine are:
Gas lasers
Solid-state lasers
Examples of these lasers can be CO2 laser and
one of the most common used solid state laser
i.e. Nd-YAG.
Image Credits: Weldologic
Working Principle of Laser
Generation of Laser Beam Amplification Focusing Delivery to the welding zone
Interaction with Metals Molten Pool Formation Solidification Weld Formation
Image Credits: Weldologic, CanadianMetalWorking, WesterMans, Clean-Air, lasergods, servorobot, weldingproductivity
Advantages
Precision: Laser welding allows for precise control of the heat-affected zone
and weld geometry, making it suitable for intricate and small-scale welding
applications.
Speed: Laser welding is a high-speed process, and it can be significantly
faster than traditional welding methods.
Minimal Distortion: The concentrated heat source minimizes distortion in
the welded components.
Minimal Heat-Affected Zone: Laser welding produces a small heat-affected
zone, reducing the risk of metallurgical changes in the base metal.
Versatility: Laser welding can be used for a wide range of metals and alloys,
including steel, aluminum, and titanium.
High Quality: Laser-welded joints often exhibit high quality, with good
mechanical properties and low porosity.
Non-Contact: Laser welding is a non-contact process, which means that
there is no physical contact between the welding equipment and the
workpiece
Technology involved in Laser Welding
Laser Source
Beam Delivery System
Focusing Optics
Motion Control System
Gas Delivery System
Real Time Monitoring and Feedback
Specialized Techniques like Hybrid-Laser Welding
Image Credits: theFabricator, spilasers, amadaweldtech.eu, IPG Photonics
Areas of Improvement
Power and Speed, increasing the power output of lasers and the welding
speed can lead to faster and more efficient welding processes. High-power
lasers can handle thicker materials and improve production rates
Fiber Lasers have become increasingly popular due to their high beam
quality, reliability, and energy efficiency. Ongoing developments in fiber
laser technology may lead to even more energy-efficient and cost-effective
systems
Welding of Dissimilar Materials, welding of dissimilar materials, such as
metals and plastics.
Miniaturization for smaller manufacturers and field applications
Welding in Challenging Environments such as underwater welding for
marine applications or in space for aerospace projects
Easily Operatable
Cost Reduction
Environmental Consideration
Thank You
Image Credits: Weldologic
You might also like
- Pioneer XV HTD 1Document12 pagesPioneer XV HTD 1naupas007No ratings yet
- LASER WEAPONS TECHNOLOGYDocument29 pagesLASER WEAPONS TECHNOLOGYSai Shubhankar100% (3)
- Laser Beam Welding PDFDocument27 pagesLaser Beam Welding PDFFayaz latheef100% (5)
- Laser WeldingDocument17 pagesLaser WeldingSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument17 pagesLaser Beam WeldingSwati AgarwalNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument285 pagesOpticsqwerty100% (3)
- Laser Beam Welding GuideDocument7 pagesLaser Beam Welding GuideBhargav Srinivas KolliNo ratings yet
- 2030 Student GuideDocument326 pages2030 Student GuideZach Brownfield100% (1)
- Mathematical Analysis of Quasi-Simultaneous Laser Welding on PolymersFrom EverandMathematical Analysis of Quasi-Simultaneous Laser Welding on PolymersNo ratings yet
- Laser Physics and Applications PDFDocument263 pagesLaser Physics and Applications PDFHamza QayyumNo ratings yet
- Quotation For Fiber Laser Cutting Machines 4 KW: NF - PRO 315 VentoDocument25 pagesQuotation For Fiber Laser Cutting Machines 4 KW: NF - PRO 315 VentobeemasundarNo ratings yet
- Laser Welding UtkarshDocument24 pagesLaser Welding Utkarshpankaj kumar0% (1)
- Laser Beam Welding Explained in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesLaser Beam Welding Explained in 40 CharactersRamu AmaraNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument14 pagesLaser Beam Weldingpatel mihirNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument7 pagesLaser Beam WeldingVysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument13 pagesLaser Beam WeldingAadip KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Laser WeldingDocument7 pages1 - Introduction To Laser WeldingmarcosilleraNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument23 pagesWeldingMathan EverNo ratings yet
- Laser Walsh ReviewDocument21 pagesLaser Walsh ReviewZahoor KhaniNo ratings yet
- Laser Welding MaterialDocument15 pagesLaser Welding MaterialRajanikantJadhavNo ratings yet
- A Review On Hybrid Laser Arc WeldingDocument22 pagesA Review On Hybrid Laser Arc WeldingAkshay AcchuNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Welding GuideDocument14 pagesLaser Beam Welding GuideAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Share 'NIKHIL LBW Seminar - Docx'Document37 pagesShare 'NIKHIL LBW Seminar - Docx'NIKHIL SHARMANo ratings yet
- tmp9930 TMPDocument16 pagestmp9930 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument7 pagesLaser Beam WeldingCarlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Laser PPT 2Document15 pagesLaser PPT 2Dhiraj KolheNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology: Unit - IDocument18 pagesManufacturing Technology: Unit - Iapi-271354682100% (1)
- LBM 123Document7 pagesLBM 123Akash KumarNo ratings yet
- A Literature Review On CO Laser WeldingDocument7 pagesA Literature Review On CO Laser Weldingkamal touilebNo ratings yet
- Maintenance LaserDocument7 pagesMaintenance LaserRaghunandanNo ratings yet
- Space Welding TermpaperDocument11 pagesSpace Welding Termpapersai vamsiNo ratings yet
- Eng 013Document3 pagesEng 013balamuruganNo ratings yet
- A Study on Behavior of Materials UnderDocument17 pagesA Study on Behavior of Materials UnderIlker CetinNo ratings yet
- Standardizare Și Terminologie În Ingineria Sudării-Limba EnglezăDocument7 pagesStandardizare Și Terminologie În Ingineria Sudării-Limba EnglezăAlexandraIoanaProdanNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument2 pagesLaser Beam WeldingmonokoeNo ratings yet
- LBW Laser Beam WeldingDocument9 pagesLBW Laser Beam WeldingISHITA TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Effect of Laser Welding Process Parameters On Mechanical P Roperties of Stainless Steel-316Document11 pagesEffect of Laser Welding Process Parameters On Mechanical P Roperties of Stainless Steel-316kamal touilebNo ratings yet
- Dhiraj Kolhe LaserDocument15 pagesDhiraj Kolhe LaserDhiraj KolheNo ratings yet
- Differences of CO2 and Solid-State Laser Welding in Industrial Flat Steel ProductionDocument8 pagesDifferences of CO2 and Solid-State Laser Welding in Industrial Flat Steel ProductionJJNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining: SAHIL DEV (10406EN016) Mech Idd Part VDocument22 pagesLaser Beam Machining: SAHIL DEV (10406EN016) Mech Idd Part VGowthamNo ratings yet
- On Laser Applicayion in IndustaryDocument15 pagesOn Laser Applicayion in IndustaryDhiraj KolheNo ratings yet
- 32 Applsci 13 12352Document12 pages32 Applsci 13 12352sylwka.inoNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam MachiningDocument3 pagesLaser Beam MachiningpankajNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument6 pagesLaser Beam WeldingJackson Silalahi SidabaribaNo ratings yet
- Laser-Hybrid WeldingDocument2 pagesLaser-Hybrid WeldingVysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Welding: Prepared by Rutik Patel PRN: 8021072651 ME-PART2 (Production Engineering)Document16 pagesLaser Beam Welding: Prepared by Rutik Patel PRN: 8021072651 ME-PART2 (Production Engineering)Rik PtlNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Laser Beam MachiningDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Laser Beam Machininggw131ads100% (1)
- 18 Applications in Material ProcessingDocument38 pages18 Applications in Material Processingkaushik4208No ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining Research PaperDocument5 pagesLaser Beam Machining Research Paperfv55wmg4100% (1)
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFPablo ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Am DG Laser WeldingDocument8 pagesAm DG Laser WeldingAJI RAJNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On: Laser IgnitionDocument25 pagesSeminar Report On: Laser Ignitionmahammad kamaluddeenNo ratings yet
- Technical TR Laser WeldingDocument1 pageTechnical TR Laser WeldingFaurica GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Technical TR Laser WeldingDocument1 pageTechnical TR Laser WeldingFaurica GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument13 pagesLaser Beam WeldingRohan ViswanathNo ratings yet
- Group Discussion, Interview Skills, Presentations, and More Covered in Learning Objectives DocumentDocument80 pagesGroup Discussion, Interview Skills, Presentations, and More Covered in Learning Objectives DocumentShashwarya ShashuNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam WeldingDocument16 pagesLaser Beam WeldingAdarsh GondNo ratings yet
- LBMDocument22 pagesLBMrkhurana00727No ratings yet
- Rakesh Seminar Report2Document18 pagesRakesh Seminar Report2Siriganti RakeshNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument6 pagesLaserhmoa2050No ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: SJB Institute of TechnologyDocument41 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: SJB Institute of TechnologyChidu KNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Welding Research PaperDocument4 pagesLaser Beam Welding Research Paperfvfee39d100% (1)
- A Review On Critical Aspects of 316ln Austenitic Stainless Steel WeldabilityDocument7 pagesA Review On Critical Aspects of 316ln Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldabilitykamal touilebNo ratings yet
- Lasers-Based Manufacturing Applications: Laser Welding (Revisited)Document36 pagesLasers-Based Manufacturing Applications: Laser Welding (Revisited)Eleftherios VourkosNo ratings yet
- Compact Laser System for Sensitive Surface CleaningDocument2 pagesCompact Laser System for Sensitive Surface CleaningIncriptat OnEarthNo ratings yet
- Third Year 5 Semester Syllabus: (Applicable From The Academic Session 2018-2019)Document23 pagesThird Year 5 Semester Syllabus: (Applicable From The Academic Session 2018-2019)Tignangshu ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Epson AcuLaser C8500 SMDocument570 pagesEpson AcuLaser C8500 SMmorrison1981No ratings yet
- Micro Epslon PDFDocument76 pagesMicro Epslon PDFAlan VisintinNo ratings yet
- Audio Laser Communication PDFDocument21 pagesAudio Laser Communication PDFHesham Sadat100% (3)
- Experimental Study of Diode-pumped Nd:YAG Laser ComponentsDocument3 pagesExperimental Study of Diode-pumped Nd:YAG Laser ComponentsbluegenesterNo ratings yet
- D1492 Re OPMAN, EXCEL HR, ENGLISHDocument84 pagesD1492 Re OPMAN, EXCEL HR, ENGLISHkhawar mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Keyence Hybrid Laser 3-Axis MD-X2020A - SpecsheetDocument9 pagesKeyence Hybrid Laser 3-Axis MD-X2020A - SpecsheetTatiana PerezNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: 906-0014-00 Rev 8 EN 2002 Rofin-Sinar UK Ltd. Rofin SC X30Document62 pagesOperating Manual: 906-0014-00 Rev 8 EN 2002 Rofin-Sinar UK Ltd. Rofin SC X30Maria Tzagaraki100% (2)
- Sony MDS-JE640 Service ManualDocument66 pagesSony MDS-JE640 Service ManualDavid MackenzieNo ratings yet
- RD 17699Document1,007 pagesRD 17699vladimiripkNo ratings yet
- 500WLaser Mold Welding Machine ManualDocument19 pages500WLaser Mold Welding Machine ManualphukaifrNo ratings yet
- UNIT I and II - ESSAY AND SHORT QUESTIONS PDFDocument8 pagesUNIT I and II - ESSAY AND SHORT QUESTIONS PDFSãkëth RèddièNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Agri R2021 (1&2)Document26 pagesB.Tech. Agri R2021 (1&2)krishnansriNo ratings yet
- Photons - FactRecallDocument3 pagesPhotons - FactRecallKatsuki BakugoNo ratings yet
- 650nm5mw Laser Diode FU-650LD-5Q-70Document7 pages650nm5mw Laser Diode FU-650LD-5Q-70allNo ratings yet
- Multipulse Laser Damage in Potassium Titanyl Phosphate: Statistical Interpretation of Measurements and The Damage Initiation MechanismDocument7 pagesMultipulse Laser Damage in Potassium Titanyl Phosphate: Statistical Interpretation of Measurements and The Damage Initiation MechanismsankhaNo ratings yet
- Pioneer FH p800btDocument100 pagesPioneer FH p800btzmlopezNo ratings yet
- 6 LaserDocument117 pages6 Laserzohaib khalidNo ratings yet
- Learning About FA Sensors and Displacement Sensors: Beginner's GuideDocument12 pagesLearning About FA Sensors and Displacement Sensors: Beginner's GuideLarry HareNo ratings yet
- Opto-Electronics Solution - LabDocument3 pagesOpto-Electronics Solution - LabgrmalikjeeNo ratings yet
- Laser Cooling and Trapping of Neutral AtomsDocument79 pagesLaser Cooling and Trapping of Neutral AtomsNacer ItourarNo ratings yet
- MIRA900Document2 pagesMIRA900Z Zijian WangNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD Rv222 Ver 1.1Document86 pagesSony HCD Rv222 Ver 1.1Carlos Raul100% (2)