Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Null 1
Null 1
Uploaded by
enginerrmohamedsalah1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
null-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageNull 1
Null 1
Uploaded by
enginerrmohamedsalah123Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Ans Sec2
1. Doping is the process of adding impurity atoms to a
semiconductor in order to modify its conductive properties.
2. A pentavalent atom (donor) has five valence electrons and a
trivalent atom (acceptor) has three valence electrons.
3. An n-type material is formed by the addition of pentavalent
impurity atoms to the intrinsic semiconductive material.
4. A p-type material is formed by the addition of trivalent
impurity atoms to the intrinsic semiconductive material.
5. The majority carrier in an n-type semiconductor is the free
electron.
6. The majority carrier in a p-type semiconductor is the hole.
7. Majority carriers are produced by doping.
8. Minority carriers are thermally produced when electron-hole
pairs are generated.
9. A pure semiconductor is intrinsic. A doped (impure)
semiconductor is extrinsic.
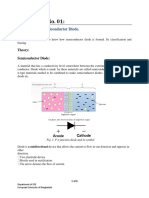
10. A pn junction is the boundary between p-type and n-type
semiconductors in a diode.
11. Diffusion is the movement of the free electrons (majority
carriers) in the n-region across the pn junction and into the p
region.
12. The depletion region is the thin layers of positive and
negative ions that exist on both sides of the pn junction.
13. The barrier potential is the potential difference of the
electric field in the depletion region and is the amount of
energy required to move electrons through the depletion
region.
14. The barrier potential for a silicon diode is approximately
0.7 V.
15. The barrier potential for a germanium diode is
approximately 0.3 V.
You might also like
- Project On SemiconductorsDocument10 pagesProject On SemiconductorsDharma Teja79% (127)
- Unit IvDocument10 pagesUnit Ivmesfin snowNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors CH14 Part 2Document17 pagesSemiconductors CH14 Part 2Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor NotesDocument8 pagesSemiconductor NotesAaryaNo ratings yet
- Iare - Ece - Edc - PPT - 0Document197 pagesIare - Ece - Edc - PPT - 0KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document15 pagesLecture Note 1nehal hasnain refathNo ratings yet
- Material Science AssignmentsDocument5 pagesMaterial Science AssignmentspaeinjamaludinNo ratings yet
- ED Unit 1Document38 pagesED Unit 1Gowrishankark EEE-Associate ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Semiconductor DevicesDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Semiconductor DevicesMuhammad Sufyan100% (2)
- ' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument8 pages' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices: SemiconductorsDocument27 pagesSemiconductor Devices: SemiconductorsHassan Badiru AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Appl Phy Chap# 1Document55 pagesAppl Phy Chap# 1Jameel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1abram samNo ratings yet
- 2 Fundamental Solid-State PrinciplesDocument32 pages2 Fundamental Solid-State Principlesannemarie1979No ratings yet
- Lecture-2 SlidesDocument67 pagesLecture-2 Slidestanisha guptaNo ratings yet
- 13semiconductor Device 275-292Document14 pages13semiconductor Device 275-292kushwah_770145566No ratings yet
- AjphysicsDocument17 pagesAjphysicsAadi JainNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesPN Junction Lecture Notessuperbangadak100% (1)
- Lecture-1 EeeDocument5 pagesLecture-1 EeehossennullNo ratings yet
- Electrons in The Outer Shell Than The Semiconductor. Each Atom of DopantDocument38 pagesElectrons in The Outer Shell Than The Semiconductor. Each Atom of Dopantfisho abukeNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument28 pagesSemiconductorsYashika MittalNo ratings yet
- Ec8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NotesDocument96 pagesEc8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NoteschandanpgowdachandanpNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Semiconductor DiodesDocument10 pagesChapter - 2 Semiconductor DiodesShashi Bhushan KotwalNo ratings yet
- (L2) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 24th DecDocument66 pages(L2) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 24th DecAshfaq khanNo ratings yet
- ECE220a - Topic 2Document9 pagesECE220a - Topic 2John RivasNo ratings yet
- 14.semiconductor NotesDocument20 pages14.semiconductor NotesMohitha Reddy CNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument19 pagesPhy ProjectVatsal BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Physics VivaDocument17 pagesPhysics VivaANIRUDDHA PAUL70% (10)
- ADC Unit 1 LM PN JunctionDocument37 pagesADC Unit 1 LM PN JunctionKeerthi SadhanaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 SemiconductorDocument10 pages2.4 SemiconductorDevdas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor PhysicsDocument18 pagesSemiconductor PhysicsMahmud HasanNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument27 pagesElectronicsHuraira AbidNo ratings yet
- 2 Intrinsic Semiconductor and Extrinsic SemiconductorDocument9 pages2 Intrinsic Semiconductor and Extrinsic SemiconductorAayushmanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics - NNDocument6 pagesSemiconductor Electronics - NNBalaji Class-10thNo ratings yet
- EC 104 Unit 1 Part-1Document64 pagesEC 104 Unit 1 Part-1Harsh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Atomic Structure 2. The Elements, The Periodic Table: FundamentalsDocument5 pagesThe Atomic Structure 2. The Elements, The Periodic Table: FundamentalsTomNo ratings yet
- EC 104 Unit-1 1st JuneDocument189 pagesEC 104 Unit-1 1st JuneHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument12 pagesSemiconductorsROHANNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics (PDF - Io)Document10 pagesSemiconductor Electronics (PDF - Io)kingbossff16No ratings yet
- Course: Basic Electronics Course Code: PHY-421 Class: BS 1 Topic: P-Type and N-Type Semiconductor MaterialsDocument29 pagesCourse: Basic Electronics Course Code: PHY-421 Class: BS 1 Topic: P-Type and N-Type Semiconductor MaterialsSOFIA BS Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory 2 PDF FreeDocument24 pagesPhysics Investigatory 2 PDF Freethevloger007No ratings yet
- Solids MSDocument18 pagesSolids MSBikky BirajiNo ratings yet
- PN Junction and DiodeDocument68 pagesPN Junction and DiodeDan MwirigiNo ratings yet
- Project Semi ConductorDocument20 pagesProject Semi ConductorSahil SinghNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic SemiconductorDocument3 pagesExtrinsic SemiconductorGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic SemiconductorsDocument22 pagesIntrinsic SemiconductorsGilbertNo ratings yet
- Extrinsic Semiconductor: An Extrinsic Semiconductor Can Be Further Classified IntoDocument2 pagesExtrinsic Semiconductor: An Extrinsic Semiconductor Can Be Further Classified IntoRitvik ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors: Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument25 pagesSemiconductors: Physics Investigatory ProjectSjssjsjsjjs100% (4)
- Applied Electronics I Exit Exam NotesDocument242 pagesApplied Electronics I Exit Exam Notesassefa295No ratings yet
- EEM33 Analog Electronics PDFDocument109 pagesEEM33 Analog Electronics PDF126 N.EZHILARASAN EEERNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions PDFDocument4 pagesViva Questions PDFRiya SalujaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument23 pagesPhysics ProjectGNag R'Varma100% (1)
- Semiconductor Theory Theory SupportDocument17 pagesSemiconductor Theory Theory SupportathomeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Principles of SemiconductorsDocument6 pagesUnit 4. Principles of SemiconductorsGunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Theory of PN Junction-ModifiedDocument20 pages3.2 Theory of PN Junction-Modifiedraunak guptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 01Document6 pagesExperiment 01AhmodNo ratings yet
- Ch1 EECE169 CSE16 Semiconductor DiodesDocument45 pagesCh1 EECE169 CSE16 Semiconductor Diodessabbir hossainNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Null 2Document1 pageNull 2enginerrmohamedsalah123No ratings yet
- Section 3 in ElectronicsDocument1 pageSection 3 in Electronicsenginerrmohamedsalah123No ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1enginerrmohamedsalah123No ratings yet
- The KNX Journal 2024Document58 pagesThe KNX Journal 2024enginerrmohamedsalah123No ratings yet