Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Midterm 2
Practice Midterm 2
Uploaded by
venzonguyen9Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practice Midterm 2
Practice Midterm 2
Uploaded by
venzonguyen9Copyright:
Available Formats
HSS 1100 Practice Mid Term (2)
Multiple Choice
1. A Mantoux test would be used to determine the cell mediated immunity for what
bacteria?
a) Syphilis
b) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
c) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d) Vibrio cholerae
2. Which of the following gram-positive bacilli is not a spore forming rod?
a) Bacillus anthracis
b) Clostridium botulinum
c) Bacillus cereus
d) Corynebacterium diphtheriae
e) Both B and C
3. The condition known as gangrene is caused by what bacteria?
a) Clostridium tetani
b) Clostridium perfringens
c) Shigellae
d) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
4. Which of the following protozoa does not cause the diarrhea in humans?
a) Entamoeba histolytica
b) Plasmodium ovale
c) Giardia lamblia
d) Plasmodium gondii
e) Both B and D
5. Which of the following Cestodes is associated with beef?
a) Taenia solium
b) Diphyllobothrium latum
c) Taenia saginata
d) Trichinella spiralis
6. If an individual presented with a cutaneous fungal infection, where would you
expect the infection to be isolated?
a) Skin, hair, and mucous membranes
b) Arteries, veins, and capillaries
c) Bone, muscle, subcutaneous tissue
d) Skin, hair, and nails
7. Which parasite has host consisting of dolphins, porpoises, and whales?
a) Anisakis simplex
b) Herringworm
c) Enterobius vermicularis
d) Pinworms
e) Both A and D
f) Both A and B
g) Both B and C
8. While doing your rounds at a walk in clinic, you notice a young man in the
waiting room who has a grotesque grinning expression on his face. Rather then
being appalled by the expression, you knew the young man may be infected with:
a) Listeria monocytogenes
b) Bacillus cereus
c) Clostridium tetani
d) Clostridium difficile
9. The neurotoxin created by Clostridium botulinum blocks the release of what
neurotransmitter?
a) Acetylcholine
b) Dopamine
c) GABA
d) Serotonin
10. In Helicobacter pylori, what is the purpose of urease?
a) To destroy the lining of the stomach
b) To decrease the production of mucous
c) To increase the pH locally in the stomach
d) To decrease the pH locally in the stomach
11. Which of the following microorganisms are not able to ferment lactose?
a) Salmonella typhi
b) Shigellae
c) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d) Enterobacter sakazakii
e) a and b
f) a, b and c
g) all of the above
12. Which microorganism is the major cause of “traveller’s diarrhea”?
a) Campylobacter coli
b) Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
c) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
d) Salmonella typhi
e) a and b
f) a, b and c
g) all of the above
13. This microorganism is very risky to Cystic Fibrosis patients:
a) Vibrio cholerae
b) Campylobacter jejuni
c) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d) Pseudomonas cepacia
e) a and b
f) a, b, c and d
g) b and c only
h) c and d only
i) all of the above
14. The microorganism responsible for whooping cough can be classified under:
a) Spirochetes
b) Mycobacteria
c) Gram negative bacilli
d) Nematodes
e) None of the above
15. A dermal induration that is 5 – 9mm would indicate
a) A positive tuberculin test
b) A diagnostic active tuberculin infection
c) A doubtful tuberculin test
d) A negative tuberculin test
e) a and b
16. Which microorganism uses a vector other than itself to transmit an infection?
a) Leptospira interrogans
b) Borrelia burgdoferi
c) Shcistosoma
d) Anisakis simplex
e) All of the above
17. Which antigen is only found on motile enteric bacteria?
a) O
b) K
c) H
d) none of the above
18. Bloody stools is an indicator of what stage of disease by an enteric bacterium?
a) Diarrhea with or without systemic invasion
b) Diarrhea with invasion of intestinal epithelial cells
c) Diarrhea with invasion of lymph nodes and bloodstream
d) a and b
e) b and c
f) all of the above
1. List the four levels of fungal infections.
2. Distinguish between Pseudomonas cepaciae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
3. Describe the stages of a syphilis infection.
You might also like
- Quiz MicrobiologyDocument65 pagesQuiz MicrobiologyMedShare98% (51)
- Cameron - Visceral Sensory Neuroscience-Interoception - 0195136012Document372 pagesCameron - Visceral Sensory Neuroscience-Interoception - 0195136012Lilith100% (1)
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument7 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyChen JoshetteNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument52 pagesMicrobiologyhema100% (1)
- Quiz Public HealthDocument26 pagesQuiz Public HealthMedShare89% (27)
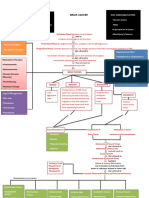
- Brain Cancer Concept MapDocument3 pagesBrain Cancer Concept MapIced Coffee100% (4)
- T&L MicroDocument78 pagesT&L MicroIdris IdenyiNo ratings yet
- Q.P. Code: 526066Document2 pagesQ.P. Code: 526066Vandamme S WillishNo ratings yet
- HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE Udann DPPDocument13 pagesHUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE Udann DPPArnold WILLIAMSNo ratings yet
- Class IX - Human Diseases - 20-08-22 OnlineDocument7 pagesClass IX - Human Diseases - 20-08-22 Onlineavijayprasad2207No ratings yet
- Tuv BacteriologyDocument8 pagesTuv BacteriologyArunadeviNo ratings yet
- Al Neelain University Faculty of Medicine Level Three (Batch 13) MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesAl Neelain University Faculty of Medicine Level Three (Batch 13) MicrobiologyMuawia AbdelrahimNo ratings yet
- Ws-2-Why Do We Fall IllDocument6 pagesWs-2-Why Do We Fall Illphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Micro MCQ All PDFDocument60 pagesMicro MCQ All PDFragulNo ratings yet
- Paper I MCQ 'S MicrobiologyDocument66 pagesPaper I MCQ 'S MicrobiologyMadhu RauniyarNo ratings yet
- Micro StaphyloccocusDocument28 pagesMicro Staphyloccocus9500810259 67No ratings yet
- Q.P. Code: 526066Document8 pagesQ.P. Code: 526066Riya CassandriyaNo ratings yet
- Document 32Document13 pagesDocument 32silvanerahkayeNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument20 pagesMicrobiologySarah JaneNo ratings yet
- MCQ - May, 2015Document7 pagesMCQ - May, 2015ahmed nasser100% (1)
- Entomology QuestionsDocument6 pagesEntomology QuestionsJøňäthan J BàñdaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Science (Ntse) Some Common Diseases M.M:30Document6 pagesAssignment-3 Science (Ntse) Some Common Diseases M.M:30CHAKSHU CHAKSHUNo ratings yet
- 2018 MycologyDocument15 pages2018 MycologySAMMY100% (1)
- MICROBIOLOGY Exam 2020Document8 pagesMICROBIOLOGY Exam 2020christinejoanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper of Microbiology and Infection ControlDocument5 pagesQuestion Paper of Microbiology and Infection ControlMelbin W MNo ratings yet
- Week 14 CD QUIZ 21Document2 pagesWeek 14 CD QUIZ 21tina santiagoNo ratings yet
- DPP - Human Health & Disease by Seep PahujaDocument11 pagesDPP - Human Health & Disease by Seep PahujamilanbhongadeNo ratings yet
- T&L Vol.2a 2Document38 pagesT&L Vol.2a 2Idris IdenyiNo ratings yet
- Bacterio Part2 YtDocument76 pagesBacterio Part2 YtHarshitha CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28Document14 pagesChapter 28ram sunderNo ratings yet
- MB115 2020 Final Exam 2020Document26 pagesMB115 2020 Final Exam 2020Milimo MweembaNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 Combined PacopDocument103 pagesMod 6 Combined PacopJacosby WorcestershireNo ratings yet
- Microbio PDFDocument17 pagesMicrobio PDFHernandez IanNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia Trachomatis and Other Chlamydia SPP - MCQ On Chlamydia SPP InfectionsDocument8 pagesChlamydia Trachomatis and Other Chlamydia SPP - MCQ On Chlamydia SPP InfectionsGhaith AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - A - 2012 PDFDocument12 pagesFinal Exam - A - 2012 PDFShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- 1.d 2.d 3.a 4.c 5.a 6.c 7.c 8d. 9.d 10. B: Answer Key For MCQ MicrobiologyDocument9 pages1.d 2.d 3.a 4.c 5.a 6.c 7.c 8d. 9.d 10. B: Answer Key For MCQ Microbiologymenah ayyashNo ratings yet
- Unknown 9Document3 pagesUnknown 9Adam Ayman MukahalNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic DiversityDocument2 pagesProkaryotic DiversityHadia SaeedNo ratings yet
- Midterm QuestionsDocument4 pagesMidterm QuestionsNaNo ratings yet
- Basic Bacteriology McqsDocument25 pagesBasic Bacteriology Mcqshassan qureshi100% (1)
- SAMPLE Exam 3 Winter 2020 PDF (1) Microbiology PSUDocument8 pagesSAMPLE Exam 3 Winter 2020 PDF (1) Microbiology PSULESLI RODRIGUEZ BENDEZUNo ratings yet
- (INFECTIOUS) تجميعة سنواتDocument71 pages(INFECTIOUS) تجميعة سنواتمحمدا الهادي الشارفNo ratings yet
- MIZ 332 Final Exam.Document11 pagesMIZ 332 Final Exam.kalasa roydNo ratings yet
- Assignment 21Document5 pagesAssignment 21Not AvailableNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 MicroDocument7 pagesLec 7 Microa.drioicheNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Infection Control For Health Professionals 6Th Edition Lee Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesMicrobiology and Infection Control For Health Professionals 6Th Edition Lee Test Bank Full Chapter PDFemilymorrowjmtafrqcdn100% (11)
- Chapter 26Document7 pagesChapter 26ram sunderNo ratings yet
- Lpws Pathology Test SeriesDocument6 pagesLpws Pathology Test SeriesYasirMukhtarNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Ii MCQ:: Prepared By: Srey Viso, Pharmd Medical Biologist & Microbiology, DMM For Pharmacy ClassDocument21 pagesBacteriology Ii MCQ:: Prepared By: Srey Viso, Pharmd Medical Biologist & Microbiology, DMM For Pharmacy ClassPiseth VichhekaNo ratings yet
- Question SetDocument140 pagesQuestion SetPiyush Ranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Para MCQDocument13 pagesPara MCQAbby Siervo100% (2)
- XII Standard - Microbiology Model Question Paper: Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks:150Document7 pagesXII Standard - Microbiology Model Question Paper: Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks:150guruyasNo ratings yet
- 28.3, Why Do We Fall Ill Ncert MCQDocument5 pages28.3, Why Do We Fall Ill Ncert MCQHimmat NahariaNo ratings yet
- (Answers) Diarrhea I McqsDocument9 pages(Answers) Diarrhea I McqsKero amgedNo ratings yet
- Human HeailthDocument25 pagesHuman HeailthAnmol KudalNo ratings yet
- Clostridial Diseases of AnimalsFrom EverandClostridial Diseases of AnimalsFrancisco A. UzalNo ratings yet
- COVID 1984: The Pandemic, The Great Reset and the New World Order: A comprehensive and evidence-based investigation of the Covid-19 crisis, including data, facts, backgrounds, forecasts and solutionsFrom EverandCOVID 1984: The Pandemic, The Great Reset and the New World Order: A comprehensive and evidence-based investigation of the Covid-19 crisis, including data, facts, backgrounds, forecasts and solutionsNo ratings yet
- Child Care What If Child Becomes Sick FlowchartDocument1 pageChild Care What If Child Becomes Sick FlowcharthmareidNo ratings yet
- DR Leny - The Importance of Exercise in Weight ManagementDocument42 pagesDR Leny - The Importance of Exercise in Weight ManagementlilaNo ratings yet
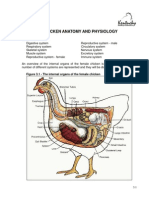
- Chicken AnatomyDocument24 pagesChicken Anatomybrianmore10No ratings yet
- КRОК 2 explained pedDocument41 pagesКRОК 2 explained pedAimeeNo ratings yet
- Daftar Kode Icd XDocument2 pagesDaftar Kode Icd Xpoli mcuNo ratings yet
- G7-G10 Module-4Document16 pagesG7-G10 Module-4Jaddie LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Computer Analysis of Computed Tomography Scans of The Lung: A SurveyDocument21 pagesComputer Analysis of Computed Tomography Scans of The Lung: A SurveyariefNo ratings yet
- Urology Resident Handbook3380 PDFDocument65 pagesUrology Resident Handbook3380 PDFKeserovic AdmirNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPEarlKristofferdeGuiaNo ratings yet
- List of Norwegian WordsDocument12 pagesList of Norwegian WordsSankar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges: College of NursingDocument1 pagePines City Colleges: College of NursingJoy Erica LeoNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Le Hoai Anh, Risks and Challenges To Transgender People in Vietnam and Suggestions, Vietnam Social Sciences, No. 5 (163), 2014, 28-39Document12 pagesNguyen Le Hoai Anh, Risks and Challenges To Transgender People in Vietnam and Suggestions, Vietnam Social Sciences, No. 5 (163), 2014, 28-39Dương ThanhNo ratings yet
- I Consenso Latinoamericano de Ojo Seco Síndrome de Disfunción LagrimalDocument37 pagesI Consenso Latinoamericano de Ojo Seco Síndrome de Disfunción LagrimalPriscila Verduzco MartínezNo ratings yet
- Controlled Tooth Movement To Correct An Iatrogenic Problem: Case ReportDocument8 pagesControlled Tooth Movement To Correct An Iatrogenic Problem: Case ReportElla GolikNo ratings yet
- Fox News: Watch TVDocument27 pagesFox News: Watch TVJoao WerleyNo ratings yet
- 01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFDocument26 pages01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFawinsyNo ratings yet
- Tara DohertyDocument4 pagesTara Dohertydylanmore1223No ratings yet
- Aesthetic, Breast 2001 PDFDocument124 pagesAesthetic, Breast 2001 PDFAhmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Sri Ramachandra University SRMC & Ri Department OF Obstetrics AND Gynaecology List OF Equipments AND Instruments (AS PER Mci)Document6 pagesSri Ramachandra University SRMC & Ri Department OF Obstetrics AND Gynaecology List OF Equipments AND Instruments (AS PER Mci)ValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Manifestations of Eating Disorders PDFDocument11 pagesEndocrine Manifestations of Eating Disorders PDFJaime GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Ancylostoma DuodenaleDocument5 pagesAncylostoma Duodenalegrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Malabsorption Syndrome1Document46 pagesNutrition in Malabsorption Syndrome1Hera Dwi P100% (1)
- 10 Facts About Healthcare in The PhilippinesDocument10 pages10 Facts About Healthcare in The PhilippinesJohnpaolo EscotoNo ratings yet
- APHNI Proceeding 2021Document9 pagesAPHNI Proceeding 2021Muhammad Faza ZhafranNo ratings yet
- Noushad RT-PCR TEST REPORT 2Document2 pagesNoushad RT-PCR TEST REPORT 2kabirNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation CriteriaDocument3 pagesCase Presentation CriteriaDavid MatthewNo ratings yet
- AyurvasthraDocument7 pagesAyurvasthraVineesha VikramNo ratings yet
- Blood Everywhere: A Case Study in BloodDocument2 pagesBlood Everywhere: A Case Study in BloodAbdullahNo ratings yet