Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 RC PHASE SHIFT OSCILLATOR USING TRANSISTORS
Uploaded by
damasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 RC PHASE SHIFT OSCILLATOR USING TRANSISTORS
Uploaded by
damasCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab manual
DAR ES SALAAM INSTITUTE OF
TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS
ENGINEERING
ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS LAB
Lab Manual
MODULE: ETU 07121
MODULE NAME: PRACTICAL ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
CLASS: BENG21-ETE-G1&2
EXPERIMRNT 04: RC PHASE SHIFT OSCILLATOR USING TRANSISTORS
TASK:
1) DESIGN AND SIMULATION USING PROTEUS SOTWARE
2) TESTING IN THE HARDWARE LABORATORY
SUBMISSION:
Dept of ETE, DARA ES SALAAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Page 1
Lab manual
RC PHASE SHIFT OSCILATOR USING TRANSISTORS
AIM: To calculate the frequency of the RC phase shift oscillator & to measure the phase
angles at different RC sections.
APPARATUS:
1. Transistor BC107
2. Resistors: 10KΩ -3Nos
8KΩ or 10KΩ
22KΩ
1.2KΩ
100KΩ
3. Capacitors: 0.001µf – 3 Nos
10µF – 2Nos
1µf
4. Regulated power Supply
5. CRO
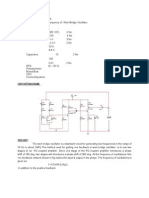
THEORY:
RC-Phase shift Oscillator has a CE amplifier followed by three sections of RC phase
shift feedback Networks the output of the last stage is return to the input of the amplifier. The
values of R and C are chosen such that the phase shift of each RC section is 60º.Thus The RC
ladder network produces a total phase shift of 180º between its input and output voltage for
the given frequencies. Since CE Amplifier produces 180 º phases shift the total phase shift from
the base of the transistor around the circuit and back to the base will be exactly 360º or
0º. This satisfies the Barkhausen condition for sustaining oscillations and total loop gain of this
circuit is greater than or equal to 1, this condition used to generate the sinusoidal oscillations.
The frequency of oscillations of RC-Phase Shift Oscillator is,
f= -----------
2RC* √6
Dept of ETE, DARA ES SALAAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Page 2
Lab manual
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
PROCEDURE:
1. Make the connection as per the circuit diagram as shown above.
2. Observe the output signal and note down the output amplitude and time period (Td).
3. Calculate the frequency of oscillations theoretically and verify it practically (f=1/Td).
4. Calculate the phase shift at each RC section by measuring the time shifts (Tp) between
the final waveform and the waveform at that section by using the below formula.
OBSERVATIONS:
THEORITICAL CALCULATIONS: R = 10KΩ, C = 0.001 μf
1
f= ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐ =
2RC* √6
PRACTICAL CALCULATIONS:
Td =
1
f = ‐‐‐‐‐
Td
Tp1
(1). θ 1= ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐*3600 =
Td
Dept of ETE, DARA ES SALAAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Page 3
Lab manual
Tp2
(2). θ 2 = ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐ * 3600 =
Td
Tp3
(3). θ 3= ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐ *3600 =
Td
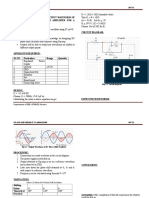
MODEL WAVE FORMS:
OUT PUT WAVE FORM :
OUT PUT WAVE FORM : θ = 600
OUT PUT WAVE FORM : θ = 1200
OUT PUT WAVE FORM : θ = 180
Dept of ETE, DARA ES SALAAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Page 4
Lab manual
RESULT: The frequency of RC phase shift oscillator is calculated and the phase shift at
different RC sections is noted.
FT = FP =
VIVA QUESTIONS:
1. What are the conditions of oscillations?
2. Give the formula for frequency of oscillations?
3. What is the total phase shift produce by the RC ladder network?
4. Whether the oscillator is positive feedback or negative feedback?
5. What are the types of oscillators?
6. What is the gain of RC phase shift oscillator?
7. What is the difference between damped oscillations undamped oscillations?
8. What are the applications of RC oscillations?
9. How many resistors and capacitors are used in RC phase shift network
10. How the Barkhausen criterion is satisfied in RC phase shift oscillator
REDRAW THE CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Dept of ETE, DARA ES SALAAM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Page 5
You might also like
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator Circuit AnalysisDocument3 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator Circuit Analysisskmrajkumar100% (2)
- Eca Lab-Min PDFDocument87 pagesEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eca Lab-Manual PDFDocument87 pagesEca Lab-Manual PDFdedoga9086No ratings yet
- lab_manualDocument38 pageslab_manualsivaNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge Oscillator FrequencyDocument6 pagesWein Bridge Oscillator Frequencyinspectornaresh100% (1)
- 2 TWO STAGE RC COUPLED AMPLIFIERDocument7 pages2 TWO STAGE RC COUPLED AMPLIFIERdamasNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator Design and VerificationDocument3 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator Design and VerificationpoojaNo ratings yet
- 3.RC Phase ShiftDocument3 pages3.RC Phase ShiftpoojaNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument3 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillatoreseses100% (1)
- 5 HARTELY OSCILLATORDocument4 pages5 HARTELY OSCILLATORdamasNo ratings yet
- 6 RC Phase ShiftDocument6 pages6 RC Phase ShiftengineerluvNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument68 pagesPDC Lab Manualnama varapuNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument4 pagesRC Phase Shift OscillatorReddyvari Venugopal67% (3)
- Expt 4 RC Phase Shift Oscillator (2020)Document4 pagesExpt 4 RC Phase Shift Oscillator (2020)samarthNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits LatestDocument69 pagesElectronic Circuits LatestSai SadiqNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Engineering: Department ofDocument39 pagesElectronics and Communication Engineering: Department ofMohit MeenaNo ratings yet
- Build transistor RC phase shift oscillator circuitDocument4 pagesBuild transistor RC phase shift oscillator circuitmanojkumar9No ratings yet
- AEC Exp 4 ManualDocument4 pagesAEC Exp 4 ManualChandrahasa reddy ENo ratings yet
- 3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsDocument11 pages3.transient Analysis of Series RL, RC CircuitsshubhamNo ratings yet
- Analog Assignment FinalprintDocument20 pagesAnalog Assignment FinalprintAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument71 pagesPDC Lab Manualswapnadeepika100% (3)
- Analog Electronics LAB ManualDocument52 pagesAnalog Electronics LAB ManualPrahlad ReddyNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave Shaping: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument0 pagesLinear Wave Shaping: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringanishadandaNo ratings yet
- 120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab RecordDocument51 pages120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab Recordpappu singhNo ratings yet
- REC 752 Lab ManualDocument10 pagesREC 752 Lab ManualManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- I C and Pulse and Digital Circuits LabvbDocument81 pagesI C and Pulse and Digital Circuits LabvbGarry MehrokNo ratings yet
- 1.RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1.RC CircuitsNaveen ChNo ratings yet
- Elec Circuits Lab- Self & Mutual Inductance, Resonance, Power TransferDocument39 pagesElec Circuits Lab- Self & Mutual Inductance, Resonance, Power TransferTomy JulieNo ratings yet
- Lab02 OscillatorDocument4 pagesLab02 OscillatorYenlyn TanNo ratings yet
- Pulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual PDFDocument61 pagesPulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual PDFKarunakar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- Pulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual 3Document61 pagesPulse & Digital Circuits Lab Manual 3Suda KrishnarjunaraoNo ratings yet
- Oscillator ManualDocument22 pagesOscillator ManualckooipgNo ratings yet
- ELEN 214 Lab Manual 7-1Document7 pagesELEN 214 Lab Manual 7-1Ratnesh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- ECLDocument65 pagesECLAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Hartley OscillatorDocument3 pagesExperiment No.1: Hartley OscillatorBhadresh RenukaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab Updated 1Document63 pagesPDC Lab Updated 1deepa reddyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual FOR Lab Course EL 491 Electronics Circuit Design LaboratoryDocument15 pagesLaboratory Manual FOR Lab Course EL 491 Electronics Circuit Design LaboratoryNaushad AlamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report on Integrator and Differentiator CircuitDocument22 pagesLaboratory Report on Integrator and Differentiator CircuitHrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits (Lic'S) Laboratory Manual: Iii / Iv B.E (Ece), I - SemesterDocument52 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits (Lic'S) Laboratory Manual: Iii / Iv B.E (Ece), I - SemesterArun JyothiNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 - OscillatorDocument6 pagesExp 6 - OscillatorJanica Rheanne JapsayNo ratings yet
- Gate Driver For N-Channel Mosfet: Experiment 6Document34 pagesGate Driver For N-Channel Mosfet: Experiment 6Noona MigleiNo ratings yet
- 6.RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument4 pages6.RC Phase Shift OscillatorManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Lic Lab Manual 7Document6 pagesLic Lab Manual 7Vijayakumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus RequiredDocument44 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus Requiredvkdkris75% (4)
- Electronic Circuits & Logic Design Laboratory ManualDocument61 pagesElectronic Circuits & Logic Design Laboratory ManualSrihari Y.sNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Lab ManualDocument60 pagesAnalog Communication Lab Manualjsingh19No ratings yet
- Expt - 7 :transistorized Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesExpt - 7 :transistorized Astable Multivibratorsamarth100% (1)
- Analog Communication ManualDocument50 pagesAnalog Communication Manualgowrav_hassanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EC II Format 2Document53 pagesLab Manual EC II Format 2nishavs100% (1)
- AnalogIntegratedCircuts LAB MANUAL by Prabhu Kumar SurarapuDocument80 pagesAnalogIntegratedCircuts LAB MANUAL by Prabhu Kumar Surarapuprabhu4scribdNo ratings yet
- CS Lab ManualDocument28 pagesCS Lab Manualkcop111No ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual in PDFDocument56 pagesCs Lab Manual in PDFvasukonetiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Cover SheetDocument15 pagesLaboratory Report Cover SheetPreet PatelNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave Shaping-Integrator and DifferentiatorDocument5 pagesLinear Wave Shaping-Integrator and DifferentiatorManjot Kaur0% (1)
- Electrical Circuits LabDocument64 pagesElectrical Circuits LabraveendrababupNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 3 SINGLE TUNED VOLTAGE AMPLIFIERDocument4 pages3 SINGLE TUNED VOLTAGE AMPLIFIERdamasNo ratings yet
- TVET Nigeria PDFDocument17 pagesTVET Nigeria PDFChristine MwauraNo ratings yet
- Project Manager Skills Improve Construction PerformanceDocument34 pagesProject Manager Skills Improve Construction Performancebediraz8402No ratings yet
- Free Computer Training Certificate TemplateDocument1 pageFree Computer Training Certificate TemplatedamasNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document1 pageTest 1damasNo ratings yet
- TA7358APGDocument9 pagesTA7358APGdexterconexion1312No ratings yet
- Kamran Shafqat: Linux Infrastructure EngineerDocument3 pagesKamran Shafqat: Linux Infrastructure EngineerIqbal ReshiNo ratings yet
- CableFree FOR3 - Full Outdoor Microwave Radio DatasheetDocument3 pagesCableFree FOR3 - Full Outdoor Microwave Radio DatasheetNaison KapisNo ratings yet
- SVX Troubleshooting GuideDocument24 pagesSVX Troubleshooting Guidemk saravananNo ratings yet
- Oracle Linux 7 Oracle Database 12c Installation GuideDocument11 pagesOracle Linux 7 Oracle Database 12c Installation GuideChristiam NiñoNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversitypatelNo ratings yet
- The Inexpensive Starting Block Force Plate For SprintersDocument5 pagesThe Inexpensive Starting Block Force Plate For SprintersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PAM8610 Audio Stereo Amplifier Module Pinout, Features, Specs & DatasheetDocument5 pagesPAM8610 Audio Stereo Amplifier Module Pinout, Features, Specs & DatasheetGerardo MediabillaNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument4 pagesData ProcessingKwonyoongmaoNo ratings yet
- Huawei NE05E NE08E Series Router Product BrochureDocument9 pagesHuawei NE05E NE08E Series Router Product Brochuredesconocido_esNo ratings yet
- 5c713810f3f1f-Canon Ir400i PLDocument4 pages5c713810f3f1f-Canon Ir400i PLvon arvin gregorioNo ratings yet
- Got-F900 To Got1000Document142 pagesGot-F900 To Got1000albeertoNo ratings yet
- Internet and Open Source Q&ADocument10 pagesInternet and Open Source Q&AriscomputersirNo ratings yet
- IOT Using Arduino IDE to Monitor Temperature and HumidityDocument20 pagesIOT Using Arduino IDE to Monitor Temperature and HumidityPrabir dasNo ratings yet
- Intelligent instrumentation: Smart vs intelligent sensorsDocument40 pagesIntelligent instrumentation: Smart vs intelligent sensorstesfaye meberateNo ratings yet
- PCC CS 302 3rd InternalDocument1 pagePCC CS 302 3rd InternalGargiMemorial cseNo ratings yet
- Student Discussion Board (PHP) PDFDocument54 pagesStudent Discussion Board (PHP) PDFAman Kumar ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- CTM Quick Guide For DevsDocument1 pageCTM Quick Guide For DevsAlessia RamvelNo ratings yet
- Se Lab ManualDocument43 pagesSe Lab Manualgunu guptaNo ratings yet
- SJ-20161215135501-001-ZXA10 C300&C350&C320 (V2.1.0) Product at A Glance - 738099 PDFDocument19 pagesSJ-20161215135501-001-ZXA10 C300&C350&C320 (V2.1.0) Product at A Glance - 738099 PDFRonaldo YoupLoadNo ratings yet
- Black Box ManualDocument57 pagesBlack Box ManualДмитрий ЧеNo ratings yet
- Ne01 Scto Electrical / Electronics & TelecommunicationDocument4 pagesNe01 Scto Electrical / Electronics & TelecommunicationvivekNo ratings yet
- Manage Network SynchronizationDocument43 pagesManage Network SynchronizationHung Tran100% (3)
- A100K10602 Alphacom XE User GuideDocument119 pagesA100K10602 Alphacom XE User GuideAlberto R PerezNo ratings yet
- CS546 Parallel Processing Fall 1999, Dr. Xian-He Sun Exam #1 (October 28, 1999)Document5 pagesCS546 Parallel Processing Fall 1999, Dr. Xian-He Sun Exam #1 (October 28, 1999)JameelAhmadNo ratings yet
- MM Goods Movements With The Batch-Input InterfaceDocument11 pagesMM Goods Movements With The Batch-Input InterfaceSilva Silva0% (1)
- CV Adrian Irimescu en 2013Document4 pagesCV Adrian Irimescu en 2013iri_iri_aNo ratings yet
- IBM M A S Q R (1.0) : Aximo Utomation Cripts Uick EferenceDocument2 pagesIBM M A S Q R (1.0) : Aximo Utomation Cripts Uick EferenceVishnu VickyNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: EC303: September 22 2020Document35 pagesDigital Signal Processing: EC303: September 22 2020V Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- BTT SKR V1.4 Instruction ManualDocument12 pagesBTT SKR V1.4 Instruction ManualMaruf HasanNo ratings yet