Professional Documents
Culture Documents
43) Fraud
Uploaded by
kasimranjhaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
43) Fraud
Uploaded by
kasimranjhaCopyright:
Available Formats
Fraud – ISA 240
Fraud is an intentional act by one or more individuals among management, those charged with
governance, employees or third parties, involving the use of deception to obtain an unjust or illegal
advantage.
Two types of Fraud
(1) Misappropriation of Assets
(2) Fraudulent financial reporting
NOTE: - There may be misstatement in the financial statements either due to ERROR or FRAUD.
FRAUD RISK FACTORS
Some factors which cast doubt that a person may be involved in fraud;
Fraud 1 By:- Haris Hanif
Director’s responsibilities related to FRAUD
Directors are primarily responsible for prevention and detection of fraud and responsibilities
include:-
- Implementing the effective system of control; reducing the opportunities of fraud and
increasing chances of detection of fraud (if any) and punishment to the people involved in
the fraud.
- Creating the culture of honesty, ethical behaviour.
NOTE:-
Audit committee should review these procedures to ensure they are in place and working
effectively.
Fraud and Internal Auditors
Internal auditors can help management fulfil their responsibilities in respect of fraud and error.
Typical functions the internal auditor can perform include:
• Testing the effectiveness of the internal controls at preventing and detecting fraud and error
and provide recommendations for improvements to the controls.
• Performing fraud investigations to:
– identify how the fraud was committed
– identify the extent of the fraud
– provide recommendations on how to prevent the fraud from happening again.
• Performing surprise asset counts to identify misappropriation.
The presence of an internal audit department may act as a deterrent to fraud in itself as there is a
greater chance of being discovered.
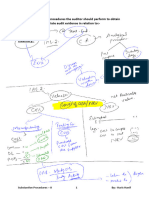
AUDITOR’S responsibilities related to FRAUD
Auditor has two responsibilities related to the fraud:-
(1) Assessment of risk of material misstatements due to fraud.
(2) Responding to the assessed risk
Fraud 2 By:- Haris Hanif
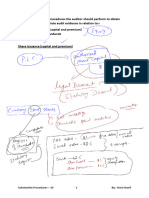
(1) Assessment of risk of material misstatements due to fraud.
Auditor should:-
- Obtain reasonable assurance that financial statements are free from material
misstatements, whether caused by error or fraud.
- Apply professional scepticism and remain alert to the possibility that fraud may take place.
- Consider the possibility of management override of controls
PROCEDURES:-
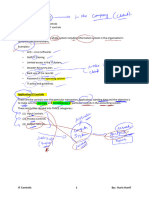
(2) Responding to the assessed risk
PROCEDURES:-
- Review journal entries to identify any manipulated figure
Focus on unusual activity
Any unauthorised recorded transaction
Any adjustments made at the end of the period.
- Review the management’s estimates
Evaluate the reasonableness of judgments and identify any bias.
Review any retrospective adjustments reflected in the prior year.
- Review any transaction outside the normal course of the business.
Fraud Reporting
Auditor should consider to report to the fraud to the appropriate channel:-
If fraud:-
- By the staff ---------------->
- By the management ---------------->
- By the BOD ---------------->
Fraud 3 By:- Haris Hanif
Written representation:-
Written representation should be taken from management related to the fraud:-
- Acknowledgment that management is responsible for prevention and detection of fraud.
- Management has disclosed to auditor the results of management’s fraud risk assessment.
- Management has disclosed to auditor any known/suspected fraud.
- Management has disclosed to auditor any allegation of fraud affecting the financial
statements.
Exam Focused
State the auditor’s responsibility in relation to the prevention and detection of fraud.
Auditor must conduct an audit in accordance with ISA 240 The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to
Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements and are responsible for obtaining reasonable assurance
that the financial statements taken as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether caused
by fraud or error.
In order to fulfil this responsibility, the auditor is required to identify and assess the risks of material
misstatement of the financial statements due to fraud.
They need to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the assessed risks of material
misstatement due to fraud, through designing and implementing appropriate responses. In addition,
the auditor must respond appropriately to fraud or suspected fraud identified during the audit.
When obtaining reasonable assurance, the auditor is responsible for maintaining professional
scepticism throughout the audit, considering the potential for management override of controls and
recognising the fact that audit procedures which are effective in detecting error may not be effective
in detecting fraud.
To ensure that the whole engagement team is aware of the risks and responsibilities for fraud and
error, ISAs require that a discussion is held within the team. For members not present at the
meeting, the audit engagement partner should determine which matters are to be communicated to
them.
If fraud is detected, the auditor must report this to management and those charged with
governance.
Fraud 4 By:- Haris Hanif
You might also like
- CHAPTER 3 - AudTheoDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 3 - AudTheoVicente, Liza Mae C.No ratings yet
- Financial Statements, Deals With An External Auditor's Responsibilities However, Both Internal andDocument11 pagesFinancial Statements, Deals With An External Auditor's Responsibilities However, Both Internal andDanisa NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Fraud From Study ManualDocument4 pagesFraud From Study ManualShajid HassanNo ratings yet
- Isa 240Document67 pagesIsa 240Darren LowNo ratings yet
- PrE1 Auditor's ResponsibityDocument17 pagesPrE1 Auditor's ResponsibityAbegail Kaye BiadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Risk of FraudDocument49 pagesChapter 2 The Risk of FraudcessbrightNo ratings yet
- PP FF Auditoria Clase 4Document173 pagesPP FF Auditoria Clase 4Tony amador gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Oliveros, Mark M. ACTYCY32S1-3 Year Accountancy ACCTG 026 - Auditing and Assurance: Specialized IndustriesDocument6 pagesOliveros, Mark M. ACTYCY32S1-3 Year Accountancy ACCTG 026 - Auditing and Assurance: Specialized IndustriesJessalyn DaneNo ratings yet
- 14considering The Risk of Frauds, ErrorsDocument8 pages14considering The Risk of Frauds, ErrorsIrish SanchezNo ratings yet
- Fraud in Audit-RevisedDocument6 pagesFraud in Audit-Revisedbehroz khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Auditors' ResponsibilityDocument51 pagesChapter 3 - Auditors' ResponsibilityddddddaaaaeeeeNo ratings yet
- Fraud, Laws and Regulations (ISA 240)Document8 pagesFraud, Laws and Regulations (ISA 240)I'j Chut MoHammadNo ratings yet
- P4 - Fraud and ErrorDocument19 pagesP4 - Fraud and ErrorHaNguyenNo ratings yet
- Fraud Risk Document With AppendixDocument17 pagesFraud Risk Document With AppendixNathalie PadillaNo ratings yet
- Sa 240Document2 pagesSa 240Azru KhanNo ratings yet
- Objective of An Audit (Narasi)Document4 pagesObjective of An Audit (Narasi)ayu dwinyNo ratings yet
- HO2-B - Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Part 2 (Risk Assessment)Document10 pagesHO2-B - Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Part 2 (Risk Assessment)Jaynalyn MonasterialNo ratings yet
- FRAUDDocument3 pagesFRAUDprincess manlangitNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th Edition Alvin A Arens Randal J Elder Mark S Beasley Chris e HoganDocument31 pagesSolution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th Edition Alvin A Arens Randal J Elder Mark S Beasley Chris e HoganMeredithFleminggztay100% (79)
- AT.0105 - Fraud Error and Non ComplianceDocument9 pagesAT.0105 - Fraud Error and Non ComplianceMaeNo ratings yet
- ISA 240 Audit ProjectDocument20 pagesISA 240 Audit ProjectKarina Indus KahwagiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory Chapter 3 and 4Document60 pagesAuditing Theory Chapter 3 and 4Cherryjane RuizNo ratings yet
- Auditor's Opinion and Report, Materiality, Missatement & FraudDocument6 pagesAuditor's Opinion and Report, Materiality, Missatement & Fraudgimata kochomataNo ratings yet
- ISA 240 Summary: The Auditor's Responsibilities Relating To Fraud in An Audit of Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesISA 240 Summary: The Auditor's Responsibilities Relating To Fraud in An Audit of Financial StatementsAnonymous XlHWbwyeq5100% (1)
- Auditing Theory 2Document13 pagesAuditing Theory 2Ceejay FrillarteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Auditing For FrauDocument37 pagesChapter 9 Auditing For FrauKeith Joanne SantiagoNo ratings yet
- At 9308Document11 pagesAt 9308omer 2 gerdNo ratings yet
- Fraud in Government - Prevention and DetectionDocument3 pagesFraud in Government - Prevention and DetectionKaye Garcia Hamid0% (1)
- Audit Lanjutan Fraud and Forensic InvestigationDocument37 pagesAudit Lanjutan Fraud and Forensic InvestigationYouJianNo ratings yet
- I. Definitions, Standards and PlanningDocument4 pagesI. Definitions, Standards and PlanninglauraoldkwNo ratings yet
- Important Files and DocumentDocument6 pagesImportant Files and Documentgazer beamNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th by ArensDocument32 pagesSolution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th by ArensMeredithFleminggztay99% (81)
- Identifying and Assessing The Risks of Material MisstatementDocument7 pagesIdentifying and Assessing The Risks of Material MisstatementRoseyy GalitNo ratings yet
- Audit RiskDocument17 pagesAudit RiskStephenly TongganoNo ratings yet
- Definitions: SA 240:the Auditor's Responsibility Related To Fraud in An Audit of Financial Statements (Revised)Document4 pagesDefinitions: SA 240:the Auditor's Responsibility Related To Fraud in An Audit of Financial Statements (Revised)Kunal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CH - 9 Assessing The Risk of Material MisstatementDocument14 pagesCH - 9 Assessing The Risk of Material MisstatementOmar C100% (1)
- ACH Guides Managing Fraud RiskDocument24 pagesACH Guides Managing Fraud RiskRafik BelkahlaNo ratings yet
- Course Hero 8Document2 pagesCourse Hero 8nhbNo ratings yet
- At.106.1 Fraud Error and Non Compliance My StudentsDocument9 pagesAt.106.1 Fraud Error and Non Compliance My StudentsLimuel NievoNo ratings yet
- Objectives and Scope of Financial Statement AuditDocument54 pagesObjectives and Scope of Financial Statement AuditKogilavani a/p ApadoreNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Chapter 2 - The Fundamental Concepts of AuditDocument21 pages2.1 Chapter 2 - The Fundamental Concepts of AuditĐức Qúach TrọngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Objective and Scope of Financial Statements Audit FinalDocument49 pagesLecture 2-Objective and Scope of Financial Statements Audit FinalKanageswary AnandanNo ratings yet
- Salosagcol CompilationDocument19 pagesSalosagcol CompilationJasmine Lim100% (1)
- Auditor'S ResponsibilityDocument28 pagesAuditor'S Responsibilityadarose romaresNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Responding To Fraud Risks: Concept Checks P. 281Document30 pagesAssessing and Responding To Fraud Risks: Concept Checks P. 281Eileen HUANGNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Audit RiskDocument9 pagesAssessment of Audit RiskAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Frauds and Errors in The Audit of Financial Statements: September 2016Document11 pagesFrauds and Errors in The Audit of Financial Statements: September 2016Iddy ShabaniNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80A - PSA 315 Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MisstatementDocument6 pagesLS 2.80A - PSA 315 Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MisstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- Fraud PDFDocument25 pagesFraud PDFNicole TondoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Auditor's ResponsibilityDocument28 pagesModule 4 - Auditor's ResponsibilityMAG MAG100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Auditor's ResponsibilityDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Auditor's ResponsibilityDemafilasan, Khyro Paul G.No ratings yet
- What Is FraudDocument8 pagesWhat Is FraudVeneranda AtriaNo ratings yet
- Objectives and Scope of Financial Statement AuditDocument57 pagesObjectives and Scope of Financial Statement AuditMAAN SHIN ANGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Auditors ResponsibilityDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Auditors ResponsibilityJay LloydNo ratings yet
- Group 3 PSA 240 SummaryDocument10 pagesGroup 3 PSA 240 SummaryAra Jane T. Pinili100% (1)
- At Lecture 5 - Fraud in An Audit of FS (FEU - Mkti)Document12 pagesAt Lecture 5 - Fraud in An Audit of FS (FEU - Mkti)markNo ratings yet
- At 04Document10 pagesAt 04Mitch PacienteNo ratings yet
- 22) Substantive Procedures - 3Document4 pages22) Substantive Procedures - 3kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 42) Analytical Procedures - IsA 520Document4 pages42) Analytical Procedures - IsA 520kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 41) Risk and Response Question KangarooDocument2 pages41) Risk and Response Question KangarookasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 56) EthicsDocument14 pages56) EthicskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 26) Substantive Procedures - 7Document4 pages26) Substantive Procedures - 7kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 40) Materiality - IsA 320Document4 pages40) Materiality - IsA 320kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 23) Substantive Procedures - 4 - Gooseberry CoDocument6 pages23) Substantive Procedures - 4 - Gooseberry CokasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 27) Substantive Procedures - 8Document4 pages27) Substantive Procedures - 8kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 29) Substantive Procedures - 10Document4 pages29) Substantive Procedures - 10kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 39) Understanding Client Entity and Its Environment - IsA 315Document2 pages39) Understanding Client Entity and Its Environment - IsA 315kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 34) Assertions Specific SubstantiveDocument4 pages34) Assertions Specific SubstantivekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 7) IT ControlsDocument2 pages7) IT ControlskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 19) Audit EvidenceDocument6 pages19) Audit EvidencekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 2) IntroductionDocument7 pages2) IntroductionkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 37) Audit Risk and Risk ResponseDocument5 pages37) Audit Risk and Risk ResponsekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 6) Inventory SystemDocument4 pages6) Inventory SystemkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 4) Internal ControlsDocument5 pages4) Internal ControlskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 3) AssuranceDocument7 pages3) AssurancekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F8 - AUDIT RISK by Alan Biju Palak ACCADocument5 pagesACCA F8 - AUDIT RISK by Alan Biju Palak ACCAkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- MGT 210Document19 pagesMGT 210FAYAZ AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Sobeys Integrated Accessibility Standards Policy OntarioDocument4 pagesSobeys Integrated Accessibility Standards Policy OntariohaloninenineNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Work-At-Home (WAH) Operations: Webinar SeriesDocument24 pagesBest Practices For Work-At-Home (WAH) Operations: Webinar SeriesHsekum AtpakNo ratings yet
- DIRECTION: Read The Statement Carefully and Choose The Answer That Best Described The Statement. Write Your Answer in Your Answer SheetDocument3 pagesDIRECTION: Read The Statement Carefully and Choose The Answer That Best Described The Statement. Write Your Answer in Your Answer SheetGenelita B. PomasinNo ratings yet
- Mercantile LawDocument10 pagesMercantile LawPreety SharmaNo ratings yet
- Part A ASEAN CG ScorecardDocument3 pagesPart A ASEAN CG ScorecardriskaNo ratings yet
- Purcari Wineries Public Company Limited: Report and Separate Financial StatementsDocument68 pagesPurcari Wineries Public Company Limited: Report and Separate Financial StatementsMihaela PulbereNo ratings yet
- Template Expense Report - With JobsDocument6 pagesTemplate Expense Report - With JobsLiz AnNo ratings yet
- Sy0 601 01Document17 pagesSy0 601 01SABRINA NUR AISHA AZAHARI100% (1)
- VW MAN Scania FormalDocument2 pagesVW MAN Scania FormallikeliberationNo ratings yet
- Cash Flows and Accrual Accounting in Predicting Future Cash FlowsDocument210 pagesCash Flows and Accrual Accounting in Predicting Future Cash FlowsNicolai AquinoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Concept of BankingDocument12 pages1.1 Concept of BankingsidharthNo ratings yet
- McLeod CH08Document46 pagesMcLeod CH08RichaMaehapsari CahKeraton100% (1)
- Strategic Cost Management - Management AccountingDocument5 pagesStrategic Cost Management - Management AccountingVanna AsensiNo ratings yet
- bài tập tổng hợp 1Document10 pagesbài tập tổng hợp 1Hoàng Bảo TrâmNo ratings yet
- Systemize Your BusinessDocument27 pagesSystemize Your BusinessvlaseNo ratings yet
- VINAYAK KONDAL AI & Finance Report CBRDocument7 pagesVINAYAK KONDAL AI & Finance Report CBRvinayakNo ratings yet
- EVA and Compensation Management at TCSDocument9 pagesEVA and Compensation Management at TCSioeuser100% (1)
- Corporate Governance of WiproDocument34 pagesCorporate Governance of WiproMohammad Imran100% (2)
- Lesson 4-7Document79 pagesLesson 4-7marivic franciscoNo ratings yet
- A Cross-Category Analysis of Shelf-Space Allocation, ProductDocument13 pagesA Cross-Category Analysis of Shelf-Space Allocation, ProductAnuradha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Selection of Strategies Revision NotesDocument5 pagesEvaluation and Selection of Strategies Revision NotesDave Dearing100% (1)
- Assignment On Case 1.1 and Case 1.2: Submitted ToDocument4 pagesAssignment On Case 1.1 and Case 1.2: Submitted ToEhsan AbirNo ratings yet
- GYM Financial ModelingDocument12 pagesGYM Financial ModelingDivyanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- MOU With DCB Bank 9may16Document10 pagesMOU With DCB Bank 9may16Sainik AddaNo ratings yet
- Material Costing - Theory & Practical Questions-3Document12 pagesMaterial Costing - Theory & Practical Questions-3sakshi.sinha56327No ratings yet
- Cost New Suggested IanDocument609 pagesCost New Suggested IanSuZan DhaMiNo ratings yet
- Afar 2 Module CH 13Document12 pagesAfar 2 Module CH 13Ella Mae TuratoNo ratings yet
- About APSCA D 021Document2 pagesAbout APSCA D 021VANo ratings yet
- SWAD 3D Printing Challenge GatewayDocument2 pagesSWAD 3D Printing Challenge GatewayMuhammad AdilNo ratings yet