Professional Documents
Culture Documents
REF 3 MATH EE
Uploaded by
Jevan SoberanoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
REF 3 MATH EE
Uploaded by
Jevan SoberanoCopyright:
Available Formats
BEERS ELECTRICAL ENG’G REFRESHER EXAM 3 MATH
Instruction: Select the correct answer for each of the following
questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the box
corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet
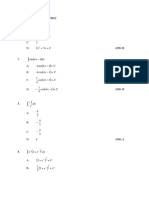
B. X = C1 ()
3 4t
4
e + C2
1 4t
4
e ()
provided.
C. X = C1 ()
1 4t
3
e + C2
2
e ()
3 −3t
() ()
Strictly no erasures allowed. Use pencil no. 1 only.
NOTE: Whenever you come across a caret (^) sign, it means 2 2t 1 6t
D. X = C1 e + C2 e
exponentiation. 1 2
1. Determine the locus represented by |z – 2| = 3. 13. Compute the value of “b” if A and B are perpendicular
A. circle* C. parabola A = 2i + bj + k B = 4i − 2 j − 2k
B. ellipse D. hyperbola
A. 2 C. 4
B. 3* D. 5
2. Find i .
−1 + i 14. The divergence of F = 2 xy i + 2 x zj − xyzk
2 2
A. 2i C.
2
A. 4 y − xy
2
C. 2 y − xy * 2
1+ i
B. 2( −1 + i) D. * B. xy D. 2 y i − xyk 2
15. Calculate the divergence of (x,xy,z)
3. One of the roots of i1/3 is _____.
A. x-1 C. x+2 *
B. 0 D. 2
3 1 1 3
A. − + i* C. − + i
2 2 2 2 16. Calculate the curl of (x,xy,y)
1 3 3 1 A. (0,0,y+1)* C. (0,x,y+1)
B. + i D. + i
2 2 2 2 B. (0,0,0) D. (0,x,z)
4. Evaluate log(2+i) 17. Div(gradA)
A. 0.349+0.202j* C. 0.439+0.345j A. Jacobian C. laplacian*
B. 0.325-0.567j D. 0.349-0.345j B. Curl D. gradient
18. What is the laplacian of f(x,y,z)=x2+y2?
5. Evaluate log(-2+3i) A. 0 C. 2x
A. 0.3 + j1.364 C. -0.87 – j2.331 B. 4* D. 2y
B. -0.3 - j1.364 D. 0.557 + j0.938*
19. Transform (2,3,4) to spherical coordinates
6. The sum of all the elements in the main diagonal of a square A. (5.38,48,56.3°) C. (5.38,82°,56.3°)
matrix is called: B. (5.38,42°,56.3°)* D. (5.38,67.4°,59.3°)
A. Trace* C. Cofactor
B. Determinant D. Rank 20. What is the normal to the surface xy3z2=4 at the point (-1,-1, 2)?
A. −4i −12 j + 4k * C. −1 i − 3 j + 1 k
7. Evaluate log(-2) 11 11 11
A. 0.3 + j1.364* C. -0.87 – j2.331 B. −1 i + 4 j + 1 k D. 4i + 12 j − 4k
B. -0.3 - j1.364 D. 0.87 + j2.331 11 11 11
8. Find the acute angles between the two planes 2x – y + z = 8 and 21. One term of a Fourier series in cosine form is 10cos40πt. Write
x + y + 2z – 11 = 0. it in exponential form.
A. 30 deg C. 60 deg* A. 5e j40 t C. 10e − j40 t
B. 45 deg D. 40 deg
B. 5e j40 t + 5e − j40 t * D. 10e j40 t
9. What is the inverse of the matrix A?
22. A circuit consist of an inductance of 0.05 Henry, a resistance of
20 ohms, a condenser of capacitance 100 microfarads, and an
− cos sin
A= emf of 100 volts. Find the current when t=0, i=0 and q=0.
− sin cos A. 2e−200t sin 200t C. 5e−200t sin 400t *
− cos sin − cos − sin
−200 t
B. 2e sin 400t D. 5e−200t sin 200t
A. C. *
sin cos sin cos
23. The evolute of a hyperbola is a _____.
sin − cos A. Lemniscate of Bernoulli C. Lame curve *
B. D. none of the above
sin cos B. Limacon of Pascal D. Hyperboloid
24. What are the values of x for which the series
12 15 𝑥3 𝑥5 𝑥7
10. Determine the adjoint of the matrix 𝑥− + − + ⋯ converges?
−28 19 3! 5! 7!
A. 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 C. 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
19 12 −59 −44
A. C.
B. −1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 1 * D. All values of x
−28 −15 −28 −15
25. A 10 ohms resistance R and a 1.0 henry inductance L are in
−19 14 19 −15
B. 28 −12 D. * series. An AC voltage e(t) = 100sin 377t is applied across the
28 12 series circuit. The applicable differential equation is:
di
Ri + L = e ( t )
11. Determine the Wronskian of two differentiable functions f and g dt
. Solve for the particular solution (without the complimentary
A. fg’-gf’* C.f’+g’ solution) to the differential equation, and determine the
B. f’g-g’f D. f’g’-fg amplitude of the resulting sinusoidal current i(t).
12. The general solution of the system X’=AX for A =
8 −3 A. 0.352 C. 0.265 *
is B. 0.325 D. 0.625
16 −8
A. X =C
1 4
()
3 4t
e +C
2 4
()
1 −4 t
e *
26. Bacteria grow in a culture at a rate proportional to the amount
present. Initially, 300 strands of the bacteria are in the culture
BEERS: 0932 3288053/0945 5663113 1
BEERS ELECTRICAL ENG’G REFRESHER EXAM 3 MATH
and after two hours that number has grown by 20 percent. Find 38. It is given that complex number Z1 and Z2, satisfy z1 = 2 |z1 | =
the time needed for the bacteria to double its initial size.
A. 6.7 hours C. 7.6 hours * 2and z2 = 3 |z1 | = 2|z2 | = 3If the included angle of their vector
B. 4.3 hours D. 3.4 hours z1 + z2
is 60O, then ?
z1 − z2
27. A body at a temperature of 50°F is placed outdoors where the
temperature is 100°F. If after 5 minutes, the temperature of the 145 133 √√145133
7
body is 60°F; find how long it will take the body to reach a A. C. *
7 7 7
temperature of 75°F and the temperature of the body after 20
minutes. 120 127
B. D.
A. 13.6 min, 97.5 °F C. 19.5 min, 97.5 °F 7 7
B. 15.5 min, 79.5 °F * D. 16.9 min, 79.5 °F
39. Two equations having the same solution set is said to be:
28. The velocity of a body is given by v(t) = sin(𝜋𝑡), where the A. Independent C. Consistent
velocity is given in meters/seconds/ and t is given in seconds. B. Dependent* D. Inconsistent
The distance covered in meters between t = ¼ and ½ seconds
is close to 40. Which of the following functions is homogeneous?
A. -0.2251
B. 0.2251 *
C. 1.2251
D. 1 A. x siny C. log x 2y ( )
C.
dy -x
B. exy D. x 2 + y2 *
29. The graphs of the solutions to = are
dx y
A. straight lines C. circles* é 1 1 3 ù
ê ú
B. parabolas D. hyperbolas 41. The matrix A = ê 5 2 6 ú is:
ê -2 -1 -3 ú
ë û
dy A. Nilpotent of degree 2 C. Nilpotent of degree 3*
30. The linear differential equation of the form + Py = Q can be
dx B. Involutory D. Idempotent
made exact by:
A. substituting y=vx é cosa sina ù
B. multiplying both sides by the integrating factor* 42. The matrix A = ê ú is:
ë - sina cosa û
C. partial integration
A. symmetric C. orthogonal*
D. partial differentiation B. periodic of period 1 D. periodic of period 2
E.
31. Solve the integrating factor of the equation 43. Which of the following matrices is not invertible?
( )
2 y - 4x dx + xdy = 0 .
2 é
A. ê 1 1 ú
ù é
C. ê -1 -1 ú
ù
A. 1/x C. e x
2
ë 0 1 û ë -1 2 û
é ù é ù
D. ê 2 -2 ú
B. x2* D. 2x3
B. ê 2 3 ú *
ë 4 6 û ë 1 1 û
32. Determine the integrating factor of the differential equation
( ) ( )
y x + y +1 dx + x x + 3y + 2 dy = 0 . 44. Find the orthogonal trajectories to the family of curves
A. x C. xy
x 2 + y2 = c .
B. y* D. y2
A. y = cx 2 C. x 2 + 2y2 = c
dy B. y = x + c D. y = cx *
33. The differential equation + P(x)y = Q(x)yn with n=1 is:
dx
A. Bernoulli type C. Variable separable* 45. In case a differential equation has the form
B. Linear Type D. Homogeneous M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0 and M, N have the same degree of
homogeneity, then a change in variable z=y/x will make the
dy equation solvable using
34. Classify the following differential equation: e x + 3y = x 2y
dx A. Exact method C. Variable separable*
A. Separable and not linear B. Linear type D. Bernoulli equation
B. Both separable and linear*
C. Linear and not separable 46. The power series expansion for sinx is:
¥ ¥
xj 2j+1
å å ( -1) (2j + 1)! *
D. Neither separable nor linear j x
A. C.
j!
j=0 j=0
35. The partial differential equation
¥ ¥
∂2 z ∂2 z
å( )
x2j
åa x
j
- 5 =0 B. -1 D. j
j
∂x2 ∂y2 j=0 (2j)! j=0
is classified as
A. elliptic
B. parabolic
C. hyperbolic *
D. none of the above ( )
47. The equation of the form 1- x 2 y"- 2xy'+ p(p +1)y = 0 is called:
A. Ricatti’s equation C. Euler’s equation
2− j
36. Find the principal root of z = (1 + j) B. Legendre’s equation* D. Bessel’s equation
A. z = 1.4900 + j4.1257 * C. z = 4.1257 + j1.4900 48. The wave equation is an instance of a class of equations called
B. z = 1.4900 − j4.1257 D. z = 4.1257 − j1.4900 _____partial differential equations.
A. Parabolic C. Elliptic
37. Which of the following is not the root of 4
−16 B. Hyperbolic* D. Cyclic
3 49. Which of the following differential equations is nonlinear?
j j
A. 2e 4 C. 2e 4 d2y d2x
3
A. + w 2y = sinx C. -x y =5
−j j dx 2 dx 2
B. 2e 4 D. 2e 5 *
d3y dy d2y dy
B. x3 + 5x + 6y = ex D. +y + 2y = x *
3 dx 2 dx
dx dx
BEERS: 0932 3288053/0945 5663113 2
BEERS ELECTRICAL ENG’G REFRESHER EXAM 3 MATH
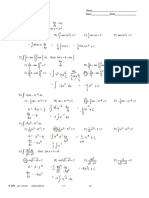
50. Determine the integrating factor of the differential equation 51 −99 −93 51 −99 −39
B. A = 26 −32 −125 D. A = 26 −23 −125
y'- 3tanx × y = 1.
A. sin3x C. cos3x*
3
B. sec x D. cot3x −42 150 291 −42 150 219
51. A body cools in air of constant temperature Tm=20C. If the
temperature of the body changes from 100C to 60C in 20 60. Find the eigenvalues of the matrix shown
minutes, determine how much more time it will need for the 5 7 0 0
temperature to fall to 30C. −3 −5 0 0
A. 60 min. C. 20 min. A=
B. 40 min.* D. 10 min. 0 0 −2 1
0 0 0 −2
z10 + 1
52. Evaluate lim . A. -2 of multiplicity one, 2 of multiplicity three
z®i z 6 + 1
B. 2 of multiplicity one, 2 of multiplicity three
A. 3/4 C. 3/5 C. -2 of multiplicity three, 2 of multiplicity one *
B. 4/3 D. 5/3* D. 2 of multiplicity three, -2 of multiplicity one
53. Determine the particular solution of the following differential π/2 4cosθ
equation y ( ) + 2y ''+ y = 3sin ( t ) − 5cos ( t ) . ρ3 dρdθ
4
61. Solve
0 2
3 5
A. y p = − t 2 sin ( t ) + t 2 cos ( t ) * A. 10π * C. 10
8 8 B. 20π D. 20
3 5
B. y p = − t 3 sin ( t ) + t 3 cos ( t )
8 8 62. For what values of a are A = ai − 2j + k and A = 2ai + aj − 4k
3 2 5 A. 2, -1 * C. 1, 3
C. y p = − t sin ( t ) − t 2 cos ( t ) B. 2, 1 D. 4, 5
8 8
3 3 5 A = 2i + aj + k
D. y p = − t sin ( t ) − t 3 cos ( t ) 63. Determine the value of a so that and
8 8 B = 4i − 2j − 2k are perpendicular.
A. 2 C. 3 *
54. Solve: y '''− 6 y ''+ 2 y '+ 36y = 0 B. 1 D. 0
A. y = C1e 4x + e −2x C2 cos
( )
2x + C3 sin ( 2x ) 64. The following forces act on a particle P: F1 = 2i + 3j − 5k ,
B. y = C1e −2x + e 4x C2 cos ( 2x ) + C3 sin ( 2x ) F2 = −5i + j + 3k , F3 = i − 2j + 4k , and F4 = 4i − 3j − 2k pounds.
C. y = C1e + e C2 cos ( 2x ) + C3 sin ( 2x ) *
−2x 4x Find the magnitude of the resultant.
8 6
A. C.
4x
D. y = C1e + e −2x
C cos ( 2x ) + C3 sin ( 2x ) 7 5*
2 B. D.
55. A cone-shaped paper cup is being filled with water at the rate of 65. Find the angle between A = 2i + 2j − k and A = 6i − 3j + 2k
3 cubic centimeters per second. The height of the cup is 10
centimeters and the radius of the base is 5 centimeters. How fast A. 63 C. 79 *
is the water level rising when the level is 4 centimeters? B. 36 D. 97
A. 3 2 C. 3 4 *
B. 2 3 D. 4 3 66. Find the angle with the vectors A = 3i − 6j + 2k makes with
coordinate axes.
56. Evaluate the integral . A. 65, 149, 73 * C. 45, 129, 27
+ πi B. 55, 109, 37 D. 35, 139, 72
cos ( z ) dz
− πi 67. Find the volume of the parallelepiped whose edge are presented
A. -23.097 C. -23.097i by A = 2i − 3j + 4k , B = i + 2j − k and C = 3i − j + 2k
B. +23.097 D. +23.097i * A. 6 C. 5
B. 7 * D. 4
57. What are the eigenvalues of orthogonal matrix?
A. Real
68. Find the area of parallelogram having diagonals A = 3i + j − 2k
B. Purely Imaginary or Zero
C. Real or Complex conjugate pairs and an absolute value of 1 * and B = i − 3j + 4k
D. None of the Above
A. 5 2 C. 5
58. What are the eigenvalues of Hermitian matrix? B. 5 3 * D. 5 5
A. Real *
B. Purely Imaginary or Zero 69. The Laplace transform is an operation that transforms a function
C. Real or Complex conjugate pairs and have an absolute value of _________ to a function of _________.
of 1
D. None of the Above A. time domain ; frequency domain*
B. frequency domain ; time domain
11 12 13 C.continuous ; discrete
59. What is the adjoint of Matrix A = −10 9 2 ? D.discrete ; continuous
6 −3 5
ex
70. What is the power series of about x=0?
51 −99 − 93 51 219 − 93
1 − x
A. A = 62 −23 −152 * C. A = 62 −152 −23
5 2 8 3 5 2 8 3
A. 1 − 2x + x − x + ... C. 2x − x + x − ...
−24 105 219 105 −24 −99 2 3 2 3
BEERS: 0932 3288053/0945 5663113 3
BEERS ELECTRICAL ENG’G REFRESHER EXAM 3 MATH
5 8 5 8 1
81. Find the inverse z-transform of X ( z ) =
2 3 2 3
` B. 1 + 2x + x + x + ... * D. 2x + x + x + ... z 2
2 3 2 3 −1
1 + 3z + 2z −2
n n n n
A. 3 ( −2 ) u ( n) + ( −1) u(n) C. 2 ( −2 ) u ( n) – ( −1) u ( n ) *
2s − 18
n n n n
71. Find the inverse Laplace transform of as a function of x. B. ( −2 ) u ( n) – 2 ( −1) u ( n ) D. ( −2 ) u ( n ) + ( −1) u ( n )
s2 + 9
A. 2cos3x − sin3x C. 3cos3x − 2sin3x
6
B. 2cos3x − 6sin3x * D. 6cos3x − 3sin3x 82. Determine the coefficient of x in the Taylor series expansion
x3 x5 x 7
about x = 0 for f ( x ) = sin x ( ).
2
x - + - + ... A. 0 C. 1/120
72. What are the values of x for which the series 3! 5! 7! B. -1/6 * D. 1/6
converges?
83. Determine the order and degree, respectively, of the differential
A. 0 £ x £ 2 C. 0 < x < 2 𝑑4 𝑏
5
𝑑𝑏 10
equation 5 ( ) +( ) + 𝑏7 − 𝑏5 = 𝑝
B. -1£ x £ 1 * D. All values of x 𝑑𝑝4 𝑑𝑝
A. 1,10 C. 4,5*
73. Find the derivative of the series B. 5,4 D. 10,1
A. cos x C. sin x
84. What is the general solution of the differential equation
B. – cos x D. – sin x* dy 1+ cos 2y
= ?
dx 1- cos 2x
8 2 A. tan y - cot x =C* C. tan y + cot y =C
74. Evaluate 6Γ 5Γ B. tan x - cot y =C D. tan x + cot y =C
3 3
A. 1/3 C. 1
85. A function g(x,y) is homogeneous of degree n if g(tx,ty)=t ng(x,y)
B. 2/3 D. 4/3* for all t. Determine the degree of the function f(x,y)= x +
ysin(x/y)^2.
75. Consider the Fourier Series (of period 10) representing
A. 1* C. 2
f ( x ) = 3x 6 − 2x 2 , −5 x 5 , f ( x + 10 ) = f ( x ) . Which statement B. 3 D. 4
below is true?
A. The Fourier series is a cosine series. * 86. What is the degree of the homogeneous function
B. The Fourier series is a sine series. f(x,y)=xe^(x/y)sqrt(x^2+y^2)
C. The Fourier series is neither a cosine or sine series. A. 2* C. 1
D. The Fourier series does not have Fourier series because it is B. 3 D. 4
not periodic.
E. 87. Determine the integrating factor of the differential equation y’ +
(4/x) y=x4
A. lnx4
1 C. x
76. Evaluate: L
−1
( )
B. x4* D. ex
s3 s2 + 1
88. Solve the first linear differential equation y’-2xy=x.
A. t cost − 1 C. t cost − 2 A. y=cex^2 -0.5 * C. y=ce-x^2 -0.5
1 2 1 2 B. y=cex^2 +-0.5 D. y=ce-x^2 +0.5
B. t + cos t − 1 * D. t − sint − 1
2 2
89. Which of the following is a solution to the differential equation
77. One term of a Fourier series in cosine form is 10cos 40πt .
Write it in exponential form. A. x(t)=3e-1 C. x(t)=2e-3t
− j40πt B. x(t)=-3/2 t2* D. x(t)=3t2
A. 5e j40πt C. 10e
B. 5e j40πt + 5e − j40πt * D. 10e j40πt 90. For the differential equation
𝑑𝑦
+ 5𝑦 = 0 with y(0)=1, the
𝑑𝑡
general solution is
sin3t 0tπ A. e5t C. 5e5t
78. What is the laplace transform of f ( t ) = -5t
0 tπ B. e-5t*
D. e√
A.
(
3 1 − e − πs ) C.
(
3 1 + e − πs )* 𝑑𝑦
91. if 𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥 + 2xy =
2𝑙𝑛𝑥
𝑥
, and y(1)=0, then what is y(e)?
2 2
s −9 s +9 A. e C. 1/e
B.
(
3 1− e − πs
) D.
3 (1 − s )
B. 1 D. 1/e2*
2
s2 + 9
𝑑𝑦 2
s +9 92. The solution of the differential equation 𝑑𝑥 + 2xy = 𝑒 −𝑥 with
y(0)=1 is
79. Find the Laplace transform of L t ( t − 2 )( t + 2 ) .
2 2
A. (1+x) 𝑒 +𝑥 C. y=(1-x) 𝑒 +𝑥
−𝑥 2 −𝑥 2
B. (1+x) 𝑒 * D. y=(1-x) 𝑒
4! 3! 3! 4!
A. − C. − *
s4 s2 s4 s2 93. The solution of dy/dx = y2 with initial value y (0) = 1 bounded in
the interval
4! 3! 3! 4! A. − ∞ ≤ x ≤ ∞ C. − ∞ ≤ x ≤ 1
B. + D. + B. x <1, x >1 * D. − 2 ≤ x ≤ 2
s4 s2 s4 s2
94. The solution to the differential equation f’’(x)+4f’(x)+4f(x)=0 is
1 A. f1(x) = e-2x C. f1(x) = e2x, f2(x) = e-2
80. Evaluate Γ − -2x
B. f1(x) = e , f2(x) = xe -2x*
D. f1(x) = e-2x, f2(x) = e-x
3
2 2 95. A spherical naphthalene ball exposed to the atmosphere loses
A. −3Γ * C. −2Γ volume at a rate proportional to its instantaneous surface area
3 3
due to evaporation. If the initial diameter of the ball is 2 cm and
3 3 the diameter reduces to 1 cm after 3 months, the ball completely
B. −3Γ D. −2Γ
2 2 evaporates in
A. 6 months* C. 9 months
BEERS: 0932 3288053/0945 5663113 4
BEERS ELECTRICAL ENG’G REFRESHER EXAM 3 MATH
B. 12 months D. infinite time 109. If A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order, then (AB′–
BA′) is a
96. A body originally at 60ºC cools down to 40ºC in 15 minutes when A. Skew symmetric matrix* C. Null matrix
kept in air at a temperature of 25ºC. What will be the temperature B. Symmetric matrix D. None of these
of the body at the end of 30 minutes?
A. 35.2º C C. 31.5º C 110. If z = 1 + i, what is z9 + z6 + z3 + 1 as a single complex number?
B. 28.7º C D. 15º C A. 5i - 2 B. 15+10i* C. 12+3i D. 3i – 2
𝑑𝑥 111. Which of the following matrices is Skew-Hermitian?
97. Solution of the differential equation 3y + 2𝑥 = 0 represents a
𝑑𝑡 4 1-3i 3𝑖 2+𝑖
family of A. ( ) C. ( )
1+3i 7 −2 + 𝑖 −𝑖
A. Ellipses* C. circles 1 1
B. Parabolas D. hyperbolas 𝑖 √3 2𝑖 √3𝑖
B. (1 2 2
1 ) D. ( 1 )∗
√3 𝑖 −√3
2 2 2
98. The partial differential equation that can be formed from z = ax
1 −1 0
+ by + ab has the form 112. Which of the following is an eigenvector of (0 1 1)
A. z = px + qy C. z = px + pq* 0 0 −1
B. z = px + qy + pq D. z = qy + pq 1 1 1 -1
A. [2] B. [ 2 ] ∗ C. [-2] D. [ 2 ]
99. Solve y(4) +8y”’ +24y” +32y’+16y=0 4 -4 -4 4
A. y=c1e2x+c2e2x+c3e2x+c4e2x
B. y=c1e-2x+c2e-2x+c3e-2x+c4e-2x 113. Matrix A has eigenvalues -2 and 1. Find the eigenvalues of the
C. y=c1e2x+c2xe2x+c3x2e2x+c4 x3e2x transpose of Matrix A.
D. y=c1e-2x+c2xe-2x+c3x2e-2x+c4 x3e-2x* A. -2,1* B. 2, -1 C. -1/2,1 D. ½, -1
100. Obtain the differential equation of the family of straight lines with 0 9 −12
slope and y-intercept equal, 114. The Matrix of (−9 0 20 )
A. y dy + (x+ 1) dx = 0 C. y dx + (x+ 1) dy = 0 12 −20 0
B. y dy - (x+ 1) dx = 0 D. y dx - (x+ 1) dy = 0* A. Skew symmetric matrix* C. Orthogonal
B. Symmetric matrix D. Unitary
101. A tank contains 400 liters of brine holding100kg of salt in
solution. Water containing 125 g of salt per liter flows in to the 1 -4
115. The adjoint matrix of [ ] is
tank at the rate of 12 liters per minute, and the mixture, kept 0 2
4 2 4 2
uniform by stirring, flows out at the same rate. Find the amount A. [ ] C. [ ]
0 1 0 1
of salt at the end of 90 minutes. 2 4 2 4
A. 53.36 kg* C. 53.63 kg B. [ ] D. [ ]*
1 0 0 1
B. 0 D. 65.33 kg
116. The matrix, that has an inverse is
A. [3 1] C. [5
102. A thermometer reading 18°C is brought into a room where the 2]
temperature is 70°C; 1 minute later the thermometer reading is 6 2 2 1
6 2
D. [8
31oC. Determine the thermometer reading 5 minutes after it is 2]
B. [ ]*
brought into the room; 9 3 4 1
A. 72.73 kg C. 27.23 kg
B. 23.27 kg D. 32.72 kg* 2 14 3 1
117. Evaluate the determinant: [1 5 -1 3]
103. Which of the following functions would have only odd powers of 1 -2 2 -3
x in its Taylor series expansion about the point x = 0? 3 -4 -3 -4
A. sin (x3)* C. sin (x2)
3 A. 489 B. 326* C. 389 D. 452
B. cos (x ) D. cos (x2)
1 -1 2 x
104. The infinite series converges to 118. If Matrix (2 1 3) is multiplied (y) is equal to zero, then
A. cos (x) B. sin (x) * C. sin h (x) D. ex 0 -1 1 z
x
cos θ sin θ matrix (y) is?
105. What is the inverse of the matrix A? A= ( )
sin θ cos θ z
A. 3 B. 1 C. 0* D. -2
A. (cos θ − sin θ) C. ( cos θ sin θ ) ∗
sin θ cos θ −sin θ cos θ
3 1 2
B. (−cos θ sin θ ) D. (cos θ sin θ 0 ) 119. if A=(-2 -1 0 ), What is the cofactor with the first row, second
sin θ cos θ 0 sin θ cos θ
0 2 -1
1 1 0 1 column element?
106. What is the rank of 𝑨= (3 1 1 -1 )? A. − [3 2 ] C. [3 2 ]
0 1 -1 1 0 -1 0 -1
2 0 1 -2 -2 -1 -2 0
B. [ ]* D. − [ ]*
A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3* 0 2 0 -1
2 3 120. Simplify the expression i1997 + i1999, where i is an imaginary.
107. If 𝐴 = (2 1 3) and B= (4 2), then A. 0* B. –I C. 1 + i* D. 1 – i
4 5 1
1 5
A. only AB is defined
B. AB and BA both are defined*
x+1 2x+1 3x+1
C. only BA is defined 121. Solve the equation ( 2x 4x+3 6x+3)=0
D. AB and BA both are not defined.
4x+1 6x+4 8x+4
0 0 5 A. 0, ½* B. 1, ½ C. 0, - D. ½, -½
108. The matrix A =(0 5 0) is a
5 0 0
A. scalar matrix C. diagonal matrix 122. Write in the form a + bi the expression i3217 – i427 + i18
B. unit matrix D. square matrix* A. 2i + 1 B. -1 + I C. 2i – 1* D. 1 + i
BEERS: 0932 3288053/0945 5663113 5
BEERS ELECTRICAL ENG’G REFRESHER EXAM 3 MATH
123. The expression 3 + 4i is a complex number. Compute its 142. Transform (2,3,4) to spherical coordinates
absolute value. A. (5.38,48,56.3°) C. (5.38,82°,56.3°)
A. 4 B. 5* C. 6 D. 7 B. (5.38,42°,56.3°)* D. (5.38,67.4°,59.3°)
124. Evaluate the value of √-10 x √-7 143. Evaluate log(2+i)
A. i B. -√70* C. √70 D. √17 A. 0.349+0.202j* C. 0.439+0.345j
B. 0.325-0.567j D. 0.349-0.345j
125. If A = 40ej120°, B = 20 ∠ -40°, C = 26.46 + j0, solve for A + B + C.
A. 27.7 ∠ 45° C. 30.8 ∠ 45°* 144. Evaluate log( ii )
B. 35.1 ∠ 45° D. 33.4 ∠ 45° A. 0.2079j C. -0.682j*
th
B. -0.0207j D. 0.702j
126. Find the principal 5 root of [50(cos 150° + jsin 150°)].
A. 1.9 + j1.1* C. 2.87 + j2.1 −1
B. 3.26 – j2.1 D. 2.25 – j1.2 145. Determine the Laplace transform of t 2
2 2
127. Consider the z-transform X(z) = 5z2 + 4z-1 + 3; 0 < | z| < ∝ . The 1 1
A. s C. s
2 2
inverse z-transform x[n] is
A. 5 δ[n + 2] + 3 δ[n] + 4 δ[n – 1]* 2
1 1
B. 5 δ[n – 2] + 3 δ[n] + 4 δ[n + 1] B. s *
2
D. 3s
2
C. 5 u[n + 2] + 3 u[n] + 4 u[n – 1]
D. 5 u[n – 2] + 3 u[n] + 4 u[n + 1] 146. Evaluate the Laplace transform of t
128. k divided by s2 + k2 is the inverse laplace transform of
3 3
A. cos kt B. sin kt* C. ekt D. 1.0 A. s
2
C. 2s *
2
129. The laplace transform of cos wt is, 1 1
B. 2s D. s
2 2
A. s / (s2 + w2)* C. w / (s + w)
B. w / (s2 + w2) D. s / (s + w)
−4 −3 −1
130. Find the laplace transform of [ 2 / (s + 1) ] – [ 4 / (s + 3) ]. 147. Given the matrix A = 2 1 1 find the matrix
A. 2e-t – 4e-3t* C. e-2t – e-3t
B. e-2t + e-3t D. (2e-t) (1 – 2e-3t) 4 −2 4
4 I − 4 A − A2 + A3
131. Determine the inverse laplace transform of I(s) = 200 / (s2 – 50s
1 2 −1 1 2 3
+ 10625) 2 3 4
A. I(s) = 2e-25t sin 100t* C. I(s) = 2e-25t cos 100t A. c. 1 −1 2
B. I(s) = 2te-25t sin 100t D. I(s) = 2te-25t cos 100t 1 1 2 4 1 2
1 2 −1
132. The inverse laplace transform of s / ( s2 + w2 ) 2 0 4
A. sin wt B. w C. ewt D. cos wt*
B. D. 0 *
−3 1 5
133. The inverse laplace transform of ( 2s – 18 ) / ( s2 + 9 )
A. 2 cos x – sin 3x C. 3 cos 2x – 2 sin 6x 148. Determine the interval of convergence for the given power
B. 2 cos 3x – 6 sin 3x* D. 6 cos x – 3 sin 2x
series n x
n2 n
n =1 3
134. Determine the inverse laplace transform of 1 / ( 4s2 – 8s ).
A. −2 x 3 C. −2 x 2 *
A. ¼ et sinh t* C. ¼ et cosh t
B. ½ e2t sinh t D. ½ e2t cosh t B. −1 x 1 D. −3 x 3
135. The Laplace transform of the function sin2 2t is 1
A. (1/2s)-s/[2(s2+16)] * C. s/(s2+16) 149. What is the power series of the 2
2
B. (1/s)-s/(s +4) D. s/(s2+4) 1 + 2x
2n
136. The Inverse Laplace transform of 1/(S2+S) is x ( −2) n
A. n =0 C. 2 n
A. 1+e^t C. 1-e^-t* n =0 x
B. 1-e^t D. 1+e^-t
n 2n n n
B. ( −2) x * D. ( −1) x
137. The Laplace transform of a function f(t) is 1/s^2(s+1). The n=0 n =0
function f(t) is
A. t-1+e^t* C. -1-e^+t* 150. The divergence of F = 2 xy i + 2 x zj − xyzk
2 2
B. t+1+e^t D. 2t+e^t
A. 4 y − xy C. 2 y − xy *
2 2
D. 2 y i − xyk
138. Find the general solution of the non-homogeneous differential 2
B. xy
equation y”-y’-2y=5sin3x
A. y=c1e-x+c2e2x-11/26 sin 3x+3/26 cos 3x*
B. y=c1e-x+c2e2x-11/26 sin 3x-3/26 cos3x “Never lose hope. Storms make people
C. y=c1e-x-c2e2x-11/26 sin 3x+3/26 cos3x
D. y=c1e-x+c2e2x+11/26 sin 3x+3/26 cos3x stronger and never last forever.”
139. Evaluate log(-2+3i)
~ Roy T. Bennett
A. 0.3 + j1.364 C. -0.87 – j2.331
B. -0.3 - j1.364 D. 0.557 + j0.938*
140. Find the differential equation of the family of parabolas having
their vertices at the origin and their foci on the y-axis
A. xy '+ 2 y = 0 C. xy '− 2 y = 0 *
B. y '− 2xy + y = 0 D.
ì8 t < 2
141. Determine the Laplace transform of the function f(t) = í
ï6 t > 2
î
A. (8-2es)/s C. (8s-e-s)/s
B. (2-8e-s) D. (8-2e-s)/s*
BEERS: 0932 3288053/0945 5663113 6
You might also like
- Mathematics 1983 Paper 2Document9 pagesMathematics 1983 Paper 2api-3826629No ratings yet
- QnA SM025 TRIAL2Document7 pagesQnA SM025 TRIAL2Nur HananiNo ratings yet
- Certc: Mathematics Refresher 2Document4 pagesCertc: Mathematics Refresher 2Hary Kriz100% (1)
- IYGB Paper E For C1Document6 pagesIYGB Paper E For C1Sherine El-NakkadyNo ratings yet
- Roots of cubic equation x3 – 6x – 3 = 0Document33 pagesRoots of cubic equation x3 – 6x – 3 = 0Joel James Gomez EvangelioNo ratings yet
- P4 June 2022 Model AnswersDocument10 pagesP4 June 2022 Model AnswersNot.DXcr GaMeRNo ratings yet
- YCT Capacitance NEET JEE Questions PracticeDocument152 pagesYCT Capacitance NEET JEE Questions Practicetechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- E-Math Level 4 Sec 4 Headstart Programme SolutionsDocument9 pagesE-Math Level 4 Sec 4 Headstart Programme SolutionsWei Ting ChuiNo ratings yet
- SBTET Online Exam Papers for Engineering Mathematics IIDocument3 pagesSBTET Online Exam Papers for Engineering Mathematics IIJghhhsh JsjsjjsNo ratings yet
- Bothra MecDocument12 pagesBothra MecAnirudha ThakurNo ratings yet
- 1678679579phpoW87Yv PDFDocument11 pages1678679579phpoW87Yv PDFTORIN RAJAN100% (1)
- TS Ipe 2023 7Document15 pagesTS Ipe 2023 7bharathbharath6824No ratings yet
- D2test2 With SolutionsDocument5 pagesD2test2 With SolutionsDangalira KamwanjaNo ratings yet
- Test 11m Full Maths Test Latest Pattern Test 2Document5 pagesTest 11m Full Maths Test Latest Pattern Test 2Hardik ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Cal s2Document5 pagesCal s2api-489918644No ratings yet
- Question+Bank MOD+++Indefinite by+MC+SirDocument20 pagesQuestion+Bank MOD+++Indefinite by+MC+SirHemendra PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiaryDocument6 pagesIygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced Subsidiarymohammad haniNo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiaryDocument6 pagesIygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiarySherine El-NakkadyNo ratings yet
- HSC 2013 March MathsDocument4 pagesHSC 2013 March MathsArchana KumbharNo ratings yet
- Math 173: Iff. FDocument3 pagesMath 173: Iff. Frtgersergtgr trghgrwthtrtehNo ratings yet
- MATH 183: L-1/T - 21N AME Date: 16/01/2017Document6 pagesMATH 183: L-1/T - 21N AME Date: 16/01/2017akib ajadNo ratings yet
- TS-IPE-2020-7Document16 pagesTS-IPE-2020-799210041290No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration Reviewer For PrelimsDocument3 pagesSolid Mensuration Reviewer For PrelimsFlorence GonzalezNo ratings yet
- General Quiz (1-) 12th ABCDDocument5 pagesGeneral Quiz (1-) 12th ABCDRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- P-Star P0-P9 - PaperDocument20 pagesP-Star P0-P9 - Paperkumarharshit8705No ratings yet
- Old P4 Mock ExamDocument12 pagesOld P4 Mock ExamNot.DXcr GaMeRNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document3 pagesExercise 1ANo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiaryDocument7 pagesIygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiarySherine El-NakkadyNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Form 5 Monthly Test July 2009Document4 pagesAdd Maths Form 5 Monthly Test July 2009Bid Hassan67% (3)
- IYGB GCE Mathematics MP1 Advanced Level Practice Paper ZDocument6 pagesIYGB GCE Mathematics MP1 Advanced Level Practice Paper ZAhmed Taha RazinNo ratings yet
- BC Practice Test 3Document7 pagesBC Practice Test 3Tim JonesNo ratings yet
- Special Products and FactoringDocument4 pagesSpecial Products and FactoringRD BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1: Multiple ChoiceDocument1 pageAlgebra 1: Multiple ChoiceTrina Ritchell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ellipseregular 2Document4 pagesEllipseregular 2Nibha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1988 Paper 2Document11 pagesMathematics 1988 Paper 2api-3826629No ratings yet
- Aaron Casey - CALN02E - Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesAaron Casey - CALN02E - Midterm ExamAaron CaseyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - June-2019-Question-Paper-21Document16 pagesIGCSE - June-2019-Question-Paper-21Arturo PizarroNo ratings yet
- Giải toán tối ưu hóa đề bài toán họcDocument4 pagesGiải toán tối ưu hóa đề bài toán họcmai4ka-1No ratings yet
- BOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION JUNIOR INTER MATHEMATICS PAPER - I (A) MODEL PAPER (ENGLISH VERSIONDocument2 pagesBOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION JUNIOR INTER MATHEMATICS PAPER - I (A) MODEL PAPER (ENGLISH VERSIONPrudhvi VudaNo ratings yet
- HSC 2015 October MathsDocument4 pagesHSC 2015 October MathsMehul GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Maximum Time: 40 Min. DPP No.: 46 (Jee-Advanced)Document2 pagesMaximum Time: 40 Min. DPP No.: 46 (Jee-Advanced)rishabh sNo ratings yet
- SI N D IA: Jee Advanced Sample Paper - 2019 Sample Paper 2 Mathematics Part-I QuestionsDocument3 pagesSI N D IA: Jee Advanced Sample Paper - 2019 Sample Paper 2 Mathematics Part-I QuestionsMudit KumarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Mathematical FormulaeDocument15 pagesQuadratic Equation Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Mathematical FormulaeRishwin Singh Sinda a/l Karamjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Model Exam 2022 S.SDocument9 pagesModel Exam 2022 S.STesfamichael FufaNo ratings yet
- 4037 s08 QP 2Document8 pages4037 s08 QP 2Khurram Ahmed100% (1)
- SelfStudys Document (4) .Document6 pagesSelfStudys Document (4) .Hari prakarsh NimiNo ratings yet
- Random MathsDocument15 pagesRandom MathsHillaryNo ratings yet
- Ts Jrinter 2022 Maths1a emDocument3 pagesTs Jrinter 2022 Maths1a emsaiamsh0024No ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document3 pagesExercise 4ANo ratings yet
- Advanced Math Problems No AnswerDocument6 pagesAdvanced Math Problems No Answermuelmar jan maraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Additional Mathematics 0606/13Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Additional Mathematics 0606/13hang yinNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument10 pagesKinematicsMř ĆøøŁ AkhìŁNo ratings yet
- Elementary Mathematics QuestionDocument2 pagesElementary Mathematics QuestionSANTOSH4176No ratings yet
- 2nd Week AssessmentDocument4 pages2nd Week AssessmentJay Mark CayonteNo ratings yet
- MCQ 4A Ch3 Quad Equations in 1 UnknownDocument4 pagesMCQ 4A Ch3 Quad Equations in 1 Unknownangela.ok.auNo ratings yet
- IB QuestionbankDocument1 pageIB QuestionbankFortNite KIDNo ratings yet
- Soal Kelas X - GenapDocument9 pagesSoal Kelas X - GenapAfhita Intan NursetyatiNo ratings yet
- Xercise: Multiple Correct (Objective Questions)Document1 pageXercise: Multiple Correct (Objective Questions)Avirup RayNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- REF 2 SCIENCES EE - Answer keyDocument4 pagesREF 2 SCIENCES EE - Answer keyJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- REF 1 EEDocument4 pagesREF 1 EEJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- REF 1 SCIENCES EE Take HomeDocument10 pagesREF 1 SCIENCES EE Take HomeJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- REF 1 EEDocument4 pagesREF 1 EEJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Ee Terms-ObjectivesDocument28 pagesEe Terms-ObjectivesZendrick MaltoNo ratings yet
- Ee Transformers HandoutsDocument3 pagesEe Transformers HandoutsJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Ee Control Systems HandoutsDocument1 pageEe Control Systems HandoutsJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Ee Synchronous Motors HandoutsDocument1 pageEe Synchronous Motors HandoutsJevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Hermite PolynomialsDocument6 pagesHermite PolynomialsJhon Bladimir Caicedo PortillaNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesDifferential EquationsCarswel Hidalgo HornedoNo ratings yet
- W4 1.3 Inverse FunctionsDocument6 pagesW4 1.3 Inverse FunctionsbidarihassanNo ratings yet
- 0607 Worksheet10Document2 pages0607 Worksheet10minati0830No ratings yet
- Lo2 Algebric EquationDocument5 pagesLo2 Algebric EquationMohamed Suhoothi Abdul CareemNo ratings yet
- Topological Vector SpacesDocument5 pagesTopological Vector SpacestestNo ratings yet
- 2011 Pre-Calc Slides Section 3.3Document26 pages2011 Pre-Calc Slides Section 3.3RKO Al SubaieNo ratings yet
- An Example of A Non-Linear Differential Equation: R. C. DailedaDocument3 pagesAn Example of A Non-Linear Differential Equation: R. C. Dailedavasanth9046No ratings yet
- Code: D3 Kcet - 2021 Test Paper With Answer Key (HELD ON SATURDAY 28-08-2021)Document10 pagesCode: D3 Kcet - 2021 Test Paper With Answer Key (HELD ON SATURDAY 28-08-2021)Ryan AahilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Linear TransformationsDocument64 pagesChapter 3 - Linear TransformationsChristopherNo ratings yet
- A First Course in Functional Analysis Theory and ApplicationsDocument487 pagesA First Course in Functional Analysis Theory and Applicationsسعدالدين مالك الرفاعي عبدالرحمن100% (2)
- Higher Order Derivatives of The Inverse Function - Version 2Document6 pagesHigher Order Derivatives of The Inverse Function - Version 2andrej_liptajNo ratings yet
- 3 Continuity and Definition of The Derivative: Math 180 WorksheetsDocument4 pages3 Continuity and Definition of The Derivative: Math 180 WorksheetsDeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Midterm Exam For Math For Econ Fall2021Document13 pagesAnswer Key To Midterm Exam For Math For Econ Fall2021Experimental BeXNo ratings yet
- MIT6 003F11 Lec05 PDFDocument52 pagesMIT6 003F11 Lec05 PDFMunir KadernaniNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document56 pagesCH 6francisco.guerra.ingNo ratings yet
- Rational Expressions and Rational Equations: 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Problem Recognition ExercisesDocument66 pagesRational Expressions and Rational Equations: 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Problem Recognition Exercisesfr2nc1sNo ratings yet
- Maths Matrix 2Document25 pagesMaths Matrix 2andyrobin058No ratings yet
- Fourier Analysis: N N FX A A X B X Period F P P PDocument2 pagesFourier Analysis: N N FX A A X B X Period F P P PJustin ContrerasNo ratings yet
- 20ma201 - Mod 3 Fsv-Tutorial 6Document2 pages20ma201 - Mod 3 Fsv-Tutorial 6Sanjay Pandi.SNo ratings yet
- AVP Week 3Document69 pagesAVP Week 3Dee-vhine Gee Raposas-RabutNo ratings yet
- Binary OperationDocument9 pagesBinary Operationhare ram hare ram hare krishna hare raaam .....No ratings yet
- Differentiation of Inverse Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument11 pagesDifferentiation of Inverse Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsChainarong TaepanichNo ratings yet
- Cis For Eed, Ted, EledDocument25 pagesCis For Eed, Ted, Eledbilawal khanNo ratings yet
- Improper Integrals ExplainedDocument16 pagesImproper Integrals ExplainedFreddie P. Kido Jr.No ratings yet
- L8 - Discrete Cosine TransformDocument17 pagesL8 - Discrete Cosine Transformmanikchillal08No ratings yet
- Vector Norms and Matrix NormsDocument42 pagesVector Norms and Matrix NormsLucky DeltaNo ratings yet
- Calculus on Surfaces ExplainedDocument16 pagesCalculus on Surfaces ExplainedTattuuArapovaNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivatives, Jacobian and GraphsDocument10 pagesPartial Derivatives, Jacobian and GraphssrinidhiNo ratings yet
- Updated Question Bank 1 LinearDocument11 pagesUpdated Question Bank 1 Linearguptarishabh5480No ratings yet