Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screenshot 2024-01-23 at 18.20.55
Uploaded by
wfffs7bcr4Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screenshot 2024-01-23 at 18.20.55
Uploaded by
wfffs7bcr4Copyright:
Available Formats
SELECTED PROBLEMS
PHYSICS EXAM PREPARATION
WORK, ENERGY, AND POWER
Copyright: © Dian Sandi Pratama, S.Pd., M.Si
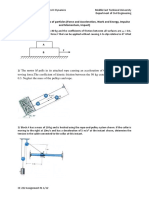
1. A car with a mass of 1,200 kg moves from point A to point B, then to point C as in Figure
below.
Determine:
a. The potential energy at B and C with respect to reference point A
b. The change in potential energy when the car moves from B to C
2. A diver weighing 640 N jumps from a tower plank
which has a height of 10 m from the water surface.
If the jumper pushes skateboard so that it leaves the
board with an initial speed of 2 m/s. determine:
a. The speed of the jumper when it is at a height of
5 m above the surface water
b. Touching the water surface
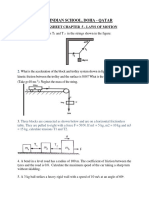
3. A block with a mass of 2 kg is initially released from the top of a curved plane in the shape of
a quarter circle with radius R. Then the block slides on a flat plane and stops at B which is 3 m
from the starting point of the flat plane A.
If the curved plane is smooth, the force friction between the block and the plane is 8 N, then R
is ...
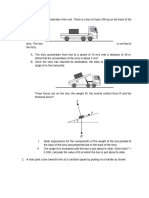
4. A solid ball with a mass of 4 kg is placed at the end of the cupboard, then pushed horizontally
so that its speed is 2 m/s2 when it leaves the top edge of the cupboard as shown in the figure
below.
Work, Energy, and Power (© Dian Sandi Pratama.2023-2024)
If the gravitational acceleration g is 10 m/s, the mechanical energy of a particle when an object
is at a height of 1 m from the ground is ...
5. Look at the image below!
A roller coaster is launched from point A with no initial speed at a height of 12 m from the
reference point. If the Earth's gravitational acceleration is 10 m/s2, and the speed of the roller
coaster at point B is 10 m/s, determine the height of point B (hB) from the reference point!
6. Suppose a car has a mass of 8,500 kg and has an emphasized power output to the wheels
of 115 kW (around 100 HP). The emphasizer claims that it has constant acceleration over the
range of 5 m/s2 – 35 m/s2. Determine the time the car should take under ideal conditions to
accelerate from 15 m/s2 to a speed of 55 ms-1!
7. Prove that the work formula can be considered as changes in kinetic energy in terms of
Newton's laws of motion!
8. The first car has twice the mass of the second car, but its kinetic energy is only half that of the
second car. When both cars increase their speed by 5 m/s, their kinetic energy becomes the
same. What is the initial speed of the two cars?
9. A car of mass m has an engine of power P. If the effect of friction is small, then prove that the
minimum time required for the car to reach speed v from rest is 𝑡 = !
10. Fill in the energy storage table below with the appropriate answers!
Work, Energy, and Power (© Dian Sandi Pratama.2023-2024)
You might also like
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Work, Energy and Power Cambridge OLDocument14 pagesWork, Energy and Power Cambridge OLSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Plates 1Document3 pagesPlates 1Rowel Gonzaga GulleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 8Document3 pagesTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- CE222 Problem Set 2Document12 pagesCE222 Problem Set 2Mehmet ArasNo ratings yet
- 6B Physics - WPEDocument3 pages6B Physics - WPEDanielle MullingsNo ratings yet
- Tordillo Engineering Review Center Mechanical Engineering Review Engineering MechanicsDocument7 pagesTordillo Engineering Review Center Mechanical Engineering Review Engineering MechanicsEymann JalaNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Document5 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Unit V - Unid End Questions - EMDocument6 pagesUnit V - Unid End Questions - EMNaresh JonnaNo ratings yet
- CL4Document2 pagesCL4Harvey BautistaNo ratings yet
- (Physics) AnswersDocument15 pages(Physics) AnswersLoraine Rose EstivaNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerDocument3 pages2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerBEN CHILUFYANo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Test 2 NDocument1 pageGrade 12 Physics Test 2 NAmanNo ratings yet
- 逢甲大學 修課班別: 航二甲 姓名: 座號: 應用力學 (二) Homework #3Document3 pages逢甲大學 修課班別: 航二甲 姓名: 座號: 應用力學 (二) Homework #3李傑No ratings yet
- BM Q3 REVIEW-QuestionsDocument5 pagesBM Q3 REVIEW-QuestionshuangzhouexportNo ratings yet
- (Ans) Newtons Second Law WSDocument1 page(Ans) Newtons Second Law WSnisalielisha rodrigoNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument7 pagesMomentumSaberNo ratings yet
- Exercise For Final Physics 10thDocument3 pagesExercise For Final Physics 10thWilsen JeftaNo ratings yet
- Take Home QuizdynamicsDocument3 pagesTake Home QuizdynamicsRazexaLNo ratings yet
- Question MechanicsDocument5 pagesQuestion MechanicsZahid IbkNo ratings yet
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarDocument12 pagesF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarAndre BocoNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Worksheet 1Document5 pagesWork Energy Worksheet 1TheOnesNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2Document12 pagesAssignment #2Deniz GüneşNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions: Energy (Grade 11 Level)Document11 pagesExam Questions: Energy (Grade 11 Level)Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- ProbSet Impulse-Momentum PDFDocument1 pageProbSet Impulse-Momentum PDFcriscab12345No ratings yet
- Assignment 0910 Spring Set2Document3 pagesAssignment 0910 Spring Set2Sarp Yiğit ŞirinNo ratings yet
- Mechanics AssignmentDocument1 pageMechanics AssignmentruukiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination PhysicsDocument2 pagesMidterm Examination PhysicsKirk Daniel ObregonNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument5 pagesWorkRoriel Hernandez BenamirNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument34 pagesWork Energy PowerYesha NorraineNo ratings yet
- SwerdwsDocument4 pagesSwerdwsTú ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Take Home Assig-Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesTake Home Assig-Wps OfficeMakame AliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 QuestionDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 QuestionJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- M1 Chap-5 Supporting MaterialDocument19 pagesM1 Chap-5 Supporting MaterialRocketNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 6: (A 1.547 m/s2, T 60 N) 4Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 6: (A 1.547 m/s2, T 60 N) 4Aashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam For Review 2019Document2 pagesMechanics Exam For Review 2019John Derick LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics TutorialDocument23 pagesMechanics TutorialDipesh PanditNo ratings yet
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- 2 Energy, Power, Work #2Document5 pages2 Energy, Power, Work #2Lil homieNo ratings yet
- Newton S Laws Ex1Document3 pagesNewton S Laws Ex1Ahmed ZakiNo ratings yet
- Physical Universe 13th Edition Krauskopf Test BankDocument14 pagesPhysical Universe 13th Edition Krauskopf Test BankMarkJonesqsmzj100% (14)
- Conservation Laws ReviewDocument6 pagesConservation Laws ReviewAnanya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- DinmjgDocument10 pagesDinmjghaker linkisNo ratings yet
- Work/Energy Practice Problems: For Q1 OnlyDocument4 pagesWork/Energy Practice Problems: For Q1 Only(25) Sena GuzelsevdiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4 - QuestionDocument5 pagesTutorial Chapter 4 - QuestionNilofer NisaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01Document2 pagesProblem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01Benedick Jayson P. Marti100% (1)
- WS - 6 DT PreparationDocument4 pagesWS - 6 DT PreparationNathanael Anthony Haposan PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Ee2233 - Tutorial 01Document3 pagesEe2233 - Tutorial 01Aneel NaickerNo ratings yet
- Momentum NpteDocument30 pagesMomentum NptediliniNo ratings yet
- (25745) 6. Forces CfE Questions 2Document7 pages(25745) 6. Forces CfE Questions 2Emmanuel KiptooNo ratings yet
- (UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestDocument14 pages(UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestMon Belle AmourNo ratings yet
- QUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1Document26 pagesQUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1AicelleNo ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum Problem SetDocument4 pagesEnergy and Momentum Problem SetPranjal DhamNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work and PowerDocument47 pagesEnergy, Work and PowerMaria BhaijiNo ratings yet
- Conservacion de La EnergiaDocument4 pagesConservacion de La EnergiaDaniel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument2 pagesProblemsAnagha NandaNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion - Worksheet NewDocument3 pagesLaws of Motion - Worksheet Newzoombs1223No ratings yet
- HPhys Unit 09 Packet CFPM 2012Document12 pagesHPhys Unit 09 Packet CFPM 2012Kelly O'Shea100% (3)
- Problem Set No. 3Document14 pagesProblem Set No. 3Arazo, Oliver B.No ratings yet
- BVAA Valve User Issue 13 PDFDocument88 pagesBVAA Valve User Issue 13 PDFrakacyuNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Rock PropertiesDocument40 pagesReservoir Rock PropertiesAhmed Bubaker100% (1)
- (42!10!1) NPTEL - Safety in CryogenicsDocument42 pages(42!10!1) NPTEL - Safety in CryogenicsSouresh PalNo ratings yet
- MSCE 509-106-Deep Beams Using Strut and Tie ModelsDocument26 pagesMSCE 509-106-Deep Beams Using Strut and Tie ModelsOtep TimusNo ratings yet
- HVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Document26 pagesHVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Sam Wing Hong50% (2)
- XD248 Temperature Controller SettingDocument2 pagesXD248 Temperature Controller SettingKan Chee LiangNo ratings yet
- Lab # 3 Analysis of Uniform and Non Uniform Quantization of Speech Signals (U-Law and A-Law)Document13 pagesLab # 3 Analysis of Uniform and Non Uniform Quantization of Speech Signals (U-Law and A-Law)zain islamNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Laboratory Sample Preparation For Fibre Reinforced SandsDocument11 pagesAssessment of Laboratory Sample Preparation For Fibre Reinforced SandsPinak RayNo ratings yet
- Cae Analysis and Structure Optimization Design of Injection Mold For Charge Upper Cover IJERTV8IS110007Document4 pagesCae Analysis and Structure Optimization Design of Injection Mold For Charge Upper Cover IJERTV8IS110007mubarakNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Calculation of Wind Loads For BuiDocument11 pagesPart 3 Calculation of Wind Loads For BuiAica M. AtendidoNo ratings yet
- Fenner-Dunlop Conveyor Problems & SolutionsDocument18 pagesFenner-Dunlop Conveyor Problems & Solutionsmickey262010No ratings yet
- MODULE 6 - Linear Equations of The First OrderDocument7 pagesMODULE 6 - Linear Equations of The First OrderKNARF FRANKNo ratings yet
- Warm UpDocument6 pagesWarm UpAnanthCJayanNo ratings yet
- Extending Our Assessments: Homework and TestingDocument22 pagesExtending Our Assessments: Homework and TestingRyan HoganNo ratings yet
- A Biomechanical Analysis of Rowing (CrossFit Journal)Document7 pagesA Biomechanical Analysis of Rowing (CrossFit Journal)AnaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical Model - Student NotesDocument36 pagesQuantum Mechanical Model - Student NotesMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document19 pagesChapter 01Stefan SalvatorNo ratings yet
- CE211F-18 FW#2 Angular Measurement by Tape - 2CE-3Document8 pagesCE211F-18 FW#2 Angular Measurement by Tape - 2CE-3Bea BachillerNo ratings yet
- Grade 80 Percent of WoodDocument4 pagesGrade 80 Percent of WoodChris John Q. TeñidoNo ratings yet
- SAFE VerificationDocument7 pagesSAFE VerificationRahul AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Endeavor-Gilbarco MEADocument2 pagesEndeavor-Gilbarco MEAgilbarcomarketing123100% (3)
- Chapter - 1 CSEET Clocks Questions and Basic ConceptsDocument3 pagesChapter - 1 CSEET Clocks Questions and Basic ConceptsKalpana SureshNo ratings yet
- P1-Training Report-Gulzad PDFDocument223 pagesP1-Training Report-Gulzad PDFeldhoseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Metrology by Waldemar Nawrocki (2015)Document287 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Metrology by Waldemar Nawrocki (2015)Vallik TadNo ratings yet
- Magnetostrictive MaterialsDocument11 pagesMagnetostrictive MaterialsrenukaceNo ratings yet
- Sci5 - Q3 - Melc11Document26 pagesSci5 - Q3 - Melc11Pauline Erika CagampangNo ratings yet
- Primary Checkpoint - Science (0846) October 2016 Paper 1 PDFDocument20 pagesPrimary Checkpoint - Science (0846) October 2016 Paper 1 PDFdinakarc88% (8)
- Wenya, Li .Numerical Simulation of Friction Welding Processes Based On ABAQUS EnvironmentDocument10 pagesWenya, Li .Numerical Simulation of Friction Welding Processes Based On ABAQUS EnvironmentRadinal Fernandez SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Fine Tuned UniverseDocument36 pagesFine Tuned Universeiryll78e2100% (3)
- Guide To Better GuardingDocument20 pagesGuide To Better GuardingLew MingNo ratings yet