Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Problems - STRESS Sem 2 2023-2024
Uploaded by
Xavier Lervine0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesPractice Problems - STRESS Sem 2 2023-2024
Uploaded by
Xavier LervineCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
KNJ1083
SOLID MECHANICS 1
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
SEMESTER 2 2023/2024
DR NOOR HISYAM NOOR MOHAMED
CHAPTER 1 - STRESS
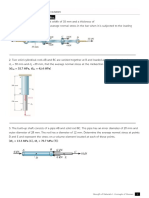
Q1
• The block is subjected to a compressive force of 2 kN.
Determine the average normal and average shear stress
developed in the wood fibers that are oriented along section
a–a at 30° with the axis of the block.
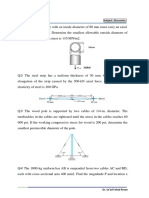
Q2
a) If P = 20 kN, determine the average
shear stress developed in the pins at A
and C. The pins are subjected to
double shear as shown, and each has a
diameter of 18 mm.
b) Determine the maximum magnitude P
of the load the beam will support if
the average shear stress in each pin is
not to allowed to exceed 60 MPa. All
pins are subjected to double shear as
shown, and each has a diameter of 18
mm.
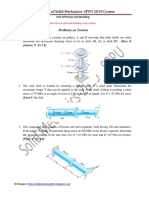
Q3
• Determine the largest load P that can be a applied to the frame
without causing either the average normal stress or the
average shear stress at section a–a to exceed and ,respectively.
Member CB has a square cross section of 25 mm on each side.
Q4
a) The three steel wires are used to support the
load. If the wires have an allowable tensile
stress of sallow = 165 MPa, determine the
required diameter of each wire if the applied
load is P = 6 kN.
b) The three steel wires are used to support the
load. If the wires have an allowable tensile
stress of sallow = 165 MPa and wire AB has a
diameter of 6 mm, BC has a diameter of 5 mm,
and BD has a diameter of 7 mm, determine the
greatest force P that can be applied before one
of the wires fails.
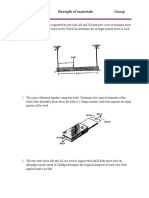
Q5
• The rods AB and CD are made of steel having a failure tensile
stress of sfail = 510 MPa. Using a factor of safety F.S = 1.75
for tension, determine their smallest diameter so that they
can support the load shown. The beam is assumed to be pin
connected at A and C.
- THE END -
You might also like
- Mukavemet Bolum 1 ProblemlerDocument4 pagesMukavemet Bolum 1 ProblemlerVanessa TanamasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityFrom EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 (Allowable Stress)Document5 pagesTugas 1 (Allowable Stress)WAHYU DWI LESTARINo ratings yet
- Chapter I-Stress: (66.7 Kpa, 115 Kpa)Document5 pagesChapter I-Stress: (66.7 Kpa, 115 Kpa)Irem DolekNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Mechanical stress problemsDocument7 pagesMechanical stress problemsDhenil ManubatNo ratings yet
- STRESS AND STRAIN CALCULATIONSDocument3 pagesSTRESS AND STRAIN CALCULATIONSSaketh BoggavarapuNo ratings yet
- 80 Mpa And: Allowed 500 Kpa, JointDocument3 pages80 Mpa And: Allowed 500 Kpa, JointJames TheeNo ratings yet
- Bolted Connection ModuleDocument5 pagesBolted Connection ModuleMakolNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Stress1 PDFDocument18 pagesConcepts of Stress1 PDFCarl Malone Lotivio LorillaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Taller #5 Esfuerzo Permisible. Diseño de Conexiones SimplesDocument6 pages5.2 Taller #5 Esfuerzo Permisible. Diseño de Conexiones SimplesCamilo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ans. σ = 70 psi; τ = 40.4 psi: ExercisesDocument2 pagesAns. σ = 70 psi; τ = 40.4 psi: ExercisesJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- MD1 Chapter1Document8 pagesMD1 Chapter1JH PerlasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsIsabelle LunaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NieNo ratings yet
- Draw The SFD BMDDocument12 pagesDraw The SFD BMDAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Document87 pagesLecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Cha Castillo100% (1)
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NieNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument12 pagesHydraulicsMugiwara Sparrow0% (1)
- Problem Sets Strength of Materials 1Document3 pagesProblem Sets Strength of Materials 1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Determine minimum diameters of rods under stress limitsDocument1 pageDetermine minimum diameters of rods under stress limitsAbdullrahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strength CalculationsDocument21 pagesStress and Strength CalculationsMidas Troy VictorNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses and Strains PDFDocument2 pagesSimple Stresses and Strains PDFSai Krishna SK100% (1)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaNo ratings yet
- Homework Mechanics of MaterialsDocument25 pagesHomework Mechanics of MaterialsAhlam EsamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Assig PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Assig PDFAnas Asif100% (1)
- PROBLEM SET: Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesPROBLEM SET: Strength of MaterialsMichael David CaparazNo ratings yet
- For Printing Bolted ConnectionDocument10 pagesFor Printing Bolted ConnectionLouvern Jake Dosono Reyes67% (3)
- Homework 1Document5 pagesHomework 1danietronico100% (1)
- CE224 MDB - Module 1: StressDocument8 pagesCE224 MDB - Module 1: Stressaileen eustaquioNo ratings yet
- MD Course Sheet 1: Joint Design ProblemsDocument2 pagesMD Course Sheet 1: Joint Design ProblemsMUuhammed FikiNo ratings yet
- Determine Properties of Materials Under StressDocument5 pagesDetermine Properties of Materials Under StressLelouch BlacknightsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Assgn-1Document6 pagesB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1sonawanepmsNo ratings yet
- CE22S CE BSC 232b Activity 1 StressDocument2 pagesCE22S CE BSC 232b Activity 1 StressJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Problem Set SolutionsDocument9 pagesMechanics of Materials Problem Set SolutionsDare DevilNo ratings yet
- Strengths of MaterialsDocument4 pagesStrengths of Materialsanna juarezNo ratings yet
- prac prob PSADDocument10 pagesprac prob PSADjeannechoiashNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetChristian RigonNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Course OverviewDocument20 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Course OverviewJullian Paul GregorioNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainDocument4 pagesMechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainYogeswaranNo ratings yet
- Cve224 Homework 1Document5 pagesCve224 Homework 1Deniz GüneşNo ratings yet
- Amd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017Document5 pagesAmd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017rip111176No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Group AssignmentDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Group Assignmentasmera gangulNo ratings yet
- Strength of Mat.l AssignmentDocument3 pagesStrength of Mat.l Assignmentasmera gangulNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1Olavo DélcioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDenver Nieveras0% (1)
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocument5 pagesScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Practical Problems ME302 Fall 2015 Chapters 1-4Document2 pagesPractical Problems ME302 Fall 2015 Chapters 1-4tevin sessa100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering TutorialsDocument6 pagesMechanical Engineering Tutorialsrip111176No ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics WorksheetDocument3 pagesSolid Mechanics WorksheetLoure ShakkeNo ratings yet
- Normal Stress Stress: Simple StressesDocument24 pagesNormal Stress Stress: Simple StressesJake Tuwa MiguelNo ratings yet
- Design strength of steel connectionsDocument9 pagesDesign strength of steel connectionsCrisnico PeligrinoNo ratings yet