Professional Documents
Culture Documents
hoetzsch-ESSAY-The Baltic States, Germany and Russia-1931
hoetzsch-ESSAY-The Baltic States, Germany and Russia-1931
Uploaded by
epsteynCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
hoetzsch-ESSAY-The Baltic States, Germany and Russia-1931
hoetzsch-ESSAY-The Baltic States, Germany and Russia-1931
Uploaded by
epsteynCopyright:
Available Formats
© FOREIGN
AFFAIRS
The Baltic States, Germany and Russia
Author(s): Otto Hoetzsch
Source: Foreign Affairs, Vol. 10, No. 1 (Oct., 1931), pp. 120-133
Published by: Council on Foreign Relations
Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/20030413 .
Accessed: 10/06/2014 01:33
Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions of Use, available at .
http://www.jstor.org/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp
.
JSTOR is a not-for-profit service that helps scholars, researchers, and students discover, use, and build upon a wide range of
content in a trusted digital archive. We use information technology and tools to increase productivity and facilitate new forms
of scholarship. For more information about JSTOR, please contact support@jstor.org.
Council on Foreign Relations is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Foreign
Affairs.
STOR
http://www.jstor.org
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
T H E BALTIC
THE BALTIC STATES,
STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND
RUSSIA
RUSSIA
By Otto Hoetzsch
By Otto Hoetzsch
ON APRIL 23,
APRIL 23, 1908,
1908, Germany, Russia, Russia, DenmarkDenmark and and
Germany,
1 BSWeden
Sweden concluded
concluded the the so-called
so-called "Baltic
“Baltic Agreement,”
by which those those four four states,
states, all themAgreement,"
all ofof them with Baltic
Baltic
by which with
littorals, mutually
littorals, mutually
guaranteed the existing
the existing status
status of this
of this sea
sea and
and
guaranteed
its coasts. The attitude of the two smaller
its coasts. The attitude of the two smaller states was purely states was purely
defensive. Nor
defensive. Norwaswasthat thatofof thethe two
two largerones ones aggressive, though
owing toto their
their extensive
extensivearea area and hinterland aggressive,
larger
andhinterland theywere though
were bringing
owing they bringing
forwardall
forward all possible pressuretoto strengthen their their respectiveBaltic Baltic
possible pressure strengthen respective
coastlines. In the case
coastlines. In the case of Germany of Germany this pressure was
this pressure was not of any not of any
great moment, for, for, in in addition
addition toto her her coastline
coastline extending from from
great moment,
Flensburg totoMemel,Memel, she she hadhad another
another outlet
outlet on on extending
the North
the North Sea. Sea.
Flensburg
But for
But for Russia Russia the Baltic was of much
the Baltic was of much greater concern and greater concern and
importance. Her territory extended, it is true, from Libau asas far far
importance. Her territory extended, it is true, from Libau
north asasTornea
north Tornea and and thusthus embraced
embraced aa very considerable
considerable part ofof
very part
the entire
the entireBaltic
Baltic coast.
coast.But But itit included
included two two "bottle-necks,"
“bottle-necks,” the the
Gulf of Finland and the
Gulf of Finland and the Gulf of Bothnia.Gulf of Bothnia. Indeed, for Russia
Indeed, for Russia the the
entireBaltic
entire Baltic coast
coastwas was inin the the nature
nature ofof aa bottle-neck,
bottle-neck, aa fact fact
which made itself felt in various ways. For
which made itself felt in various ways. For the Baltic is nothing the Baltic is nothing
butbut anan inland
inland sea,sea,veryvery inadequately and and indirectly connected connected
inadequately indirectly
with the
with theocean
ocean byaa third third bottle-neck,
bottle-neck, the the Sound,
Sound,between betweenDen Den
by
markand
mark and Sweden.
Sweden. Andbehind
And behind this thisnarrow
narrowcoastline
coastlineonon aa remote remote
inland sea
inland sea extended
extended the the vast
vast territories
territories ofof the theRussian
Russian Empire.
Empire.
These geographic considerations which
These geographic considerations which were so important were so important bebe
fore the
fore thewarwar hold
hold good inin every every respect asas far far asas concerns
concerns the the
good respect
stateswhich
states which today touch touch the theBaltic.
Baltic.Due Due toto the thedefeat
defeat andand disdis
today
solution ofof the
solution theRussian
Russian Empire, togetherwith with the the peace treaties
treaties
Empire, together peace
ofofBrest-Litovsk
Brest-Litovsk and and ofofVersailles,
Versailles, and and due due toto the the emergence
emergenceofof
the theory of the right of national
the theory of the right of national self-determination, self-determination, there are
there are
nownow twice
twice asas many ofof them them asaswhen when the theBaltic
Baltic agreementwas was
many agreement
signed:Finland,
Finland, the the Soviet
Soviet Union,
Union, Estonia,
Estonia,Latvia,Latvia, Lithuania
Lithuania
signed:
(with Memel), Poland
(with Memel),
Poland (Danzig), Germany, Denmark Denmark and and
(Danzig), Germany,
Sweden. The
Sweden. Thename name"border
“borderstates"states”whichwhichhas hascomecome toto bebe applied
applied
generally toto Finland,
Finland,Estonia,
Estonia,Latvia Latvia and and also
also toto Lithuania
Lithuania isis
generally
very fitting, since it denotes not only their “geopolitical” char
very fitting, since it denotes not only their "geopolitical"
char
acterbut
acter but also
also their
their problematicand and precarious situation situation among
among
problematic precarious
theBaltic
the Balticstates
states inin general.Thus Thus some
somedefinite
definite groupings become become
general. groupings
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES,
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND RUSSIA
RUSSIA 121
121
discernible: there
discernible: there are
areDenmark
Denmark andand Sweden,
Sweden,with with their
their former
former
situation hardlymodified;
situation modified; there
there are
are the
the new
new "border
“border states;"
states;”
hardly
there is
there is thethe new
new Polish state,
Polish state, now
now an
an ascendant Baltic Power;
ascendant Baltic Power;
and finally there remain Germany and Russia, with
and finally there remain Germany and Russia, with their main their main
3
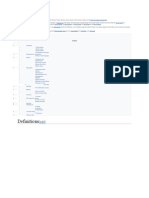
50 100 200 MILES
I0Q 200 300 KILOMETERS
Il1 K lb A K ID
larva
Dorpaiy
)
i D vi ns k/
\7
r/vilna
idensk
Gcfynia- Katbowitz fine
Bialystok
other railroads x y
1
Warsaw,
2,5
tendencies and
tendencies andneeds
needs still
still the
the same
sameand,
and, inin their
theirnature
nature asasGreat
Great
Powers, still bringing the same pressure to
Powers, still bringing the same pressure to bear on the Baltic bear on the Baltic
coast with
coast with itsits river-mouths
river-mouthsand andharbors.
harbors.
The situation
The situation existing today is regulated by the Treaty ofof
11 existing today is regulated by the Treaty
Versailles
Versailles and by Russia’s peace
and by Russia's peace treaties treatieswith
withEstonia
Estonia (February
(February
11Articles
Articles 87-93,
87-93, 99-108,
99--108, inin some
some respects also
also 109-114
109-1 14 and
and 116-117.
respects 116-117.
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
122
122 FOREIGN AFFAIRS
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
2,2, 1920),
1920), Lithuania
Lithuania (July 12,
(July
12, 1920),
1920), Latvia
Latvia (August 11,
(August
11, 1920),
1920),
Finland (October
Finland (October 14, 14, 1920)
1920) and
andPoland
Poland (October
(October 12, 12, 1920,
1920, and
and
March 18, 1921). To these
March 18,1921). To these treaties treaties must
must further be added the
further be added the settlesettle
mentofof the
ment theAland
Aland question,with withwhich
whichthe
theCouncil
Council ofofthe
the League
question, League
ofofNations
Nations hadhad toto deal.
deal.Sweden
Sweden demanded
demandedaa plebiscite regarding
plebiscite regarding
this groupofof islands,
this islands, which
which isisofof great importancetoto her, her, but
but the
the
group great importance
Council awarded them to Finland, subject to
Council awarded them to Finland, subject to certain guarantees. certain guarantees.
ItI twas
was atat the
the expense
expense ofof Germanyand
Germany
andRussia,
Russia, then,
then, that
that the
the
post-war reorganization was was effected.
effected. ItIt rested,
rested,soso far
far asas the
thevicvic
post-war reorganization
torious Western
torious Western Powers Powers were
were able to have their
able to have their way, way, onon the
the ideaidea
of the French barriere. In other words, the two
of the French barri?re. In other words, the two great nations, the great nations, the
Germansand
Germans and the
theRussians,
Russians,were weretoto bebe permanently separated by
permanently separated by
aa chain
chain ofof states
stateswhich
which on on account
account ofof theirtheir small
small size
size could
could bebe
expected always toto remain remain dependent on on the
theWestern
Western Powers.
Powers.
expected always dependent
The question remained
The remained asas totowhether
whether England and andFrance
France were were
question England
toto act
act asas aa unit
unit inin dealingwithwith this
this situation,
situation,ororwhether
whether there there
dealing
might perhaps be separate spheres of influence, so so that
that England
might perhaps be separate spheres of influence, England
could exert her power along the
could exert her power along the coast, in Riga and coast, in Riga and Tallinn
Tallinn
(Revel), and France hers mainly in
(Revel), and France hers mainly
inPoland.
Poland.
The
The new
new independent Baltic states
states established in in this
thismanner
manner
independent Baltic established
between 1917 and 1921 were threatened
between 1917 and 1921 were threatened by Bolshevism; by Bolshevism; but
but theythey
proved strong enough to hold their own own against it. it. They have have
proved strong enough to hold their against They
developed considerably and and exist
exist today asas small small oror medium
medium
developed considerably today
sized democracies,
sized democracies, largely agrarian and and ofof aa constitutional
constitutional and and
largely agrarian
parliamentarycharacter.character. What are their individual
What are their individual traits? What traits? What
parliamentary
isis their
theirattitude
attitude oror "orientation"
“orientation” in in foreign politics?And
foreign politics?
Andwhat what isis
the attitude
the attitude ofof Germanyand andRussia
Russia towards
towards them
them and and towards
towards
Germany
the new
the new situation
situation on on the
theBaltic
Baltic in
in general?First First ofof all
allwewemust
must
general?
give some
some ideaideaofof their
their size
size and
and population:
give population:
Population asas
Population
Area in
Area in estimated 1929
estimated 1929 Density per
Density per
squaremiles
square miles oror1930
1930 squaremue
square mile
Finland ...................... ............................. 2 6
Finland. 149*926 U9,9 6 3, 34,°47
3*634,047 24
24
Estonia ...................................................
Estonia. 18,362 18,362 1,115,000
1,115,000
61
61
Latvia ........................ .............................
Latvia. 25,00025,000 1,900,045 {a}
1,900,045 (a)
76
j6
Lithuania................... .............................
Lithuania. 21,489 21,489 2,340,038 109
109
2,340,038
Memel .................... .............................
Memel. 1,026
1,026
146,000
146,000 143
143
Poland .....................................................
Poland. i49>958149,958 30,737,448 205
205
(a)1930
1930 census
censusfigure
figure
3?>737>448
(<*)
Here wewehave,
Here have, then,
then, four
four small
small states
statesand and one
one that
that can
canbebe called
called
medium-sized oror even
medium-sized even large, /.i. e.,e. yPoland,
Poland,which
which protrudes into into
large, protrudes
the Baltic
the Baltic area
area with
with aa coastal strip barely forty miles
coastal strip barely forty miles long. long.
Finland’s inhabitants
Finland's inhabitants are are partly ofofFinnish
Finnish (89
(89 percent) and and
partly percent)
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES,
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND RUSSIA
RUSSIA 123
123
partly of Swedish (11 percent) descent. It is an an agrarian democ democ
partly of Swedish (11 percent) descent. It is agrarian
racy, the great
racy, the great majority
majority of
of the
the farms
farms being small
small or
or of
of medium
medium
being
size. Its
size. Its industry isis insignificant, the thenumber
numberofofworkers
workers amount
amount
industry insignificant,
ing toto only aboutabout 150,000;
150,000; but but its its commerce
commerce isis important, the the
ing only important,
principal exports being butter and lumber. One of the essential
principal exports being butter and lumber. One of the essential
problems with withwhich
which ititmust must cope cope isis the
the questionhow how farfar itit can
can
question
live by means of its own grain crops, which
ive by means of its own grain crops, which have to be raised on
f>roblems
have to be raised on
very poor soil, for on this depends in part how it is to maintain its its
very poor soil, for on this depends in part how it is to maintain
independence.Finland'sFinland’s cultural
cultural achievements
achievementshave have beenbeenmost most
independence.
remarkable:asas far
remarkable: far asas civilization
civilization and and culture
culture are are concerned
concerned itit
might bebe aa nation
nation ofofwesternwestern Europe.Alike Alike towards
towardswhat what isis
might Europe.
Swedish and
Swedish andwhat
what isisRussian
Russian the theFinnish
Finnish people observe observe aa con con
people
sistently negative attitude. attitude.But But that that only serves
serves toto accentuate
accentuate
sistently negative only
their isolation,
their isolation, unable
unable asas they are are toto build
build up aa well-organized
they up well-organized
moderneconomic
modern economic structure
structurewith withan anextensive
extensive industryand andaa large
industry large
middle class,
middle class, due due toto the
the fact
fact that
that the
the enormous
enormous Russian
Russian hinterland
hinterland
isisno
no longer open toto them
longer open
themfor for lucrative
lucrativeeconomic
economic exploitationasas itit
exploitation
used totobebebefore
used before the thewar.war.
To Finland
To Finland foreign trade trade isisaavital
vital question.The The greater partofof
foreign question. greater part
her imports she receives from
her imports she receives from Germany; next come Germany; next come the the imports
imports
from England, amounting to half the
from England, amounting to half the value of Germany's. Then value of Germany’s. Then
follow those
follow those from
from the theUnited
UnitedStates,
States,Sweden,
Sweden,etc. etc. Soviet
Soviet Russia,
Russia,
Finland’s
Finland's nearest
nearest neighbor, is
is far
far down,
down,
in
in eighth place. In
In
neighbor, eighth place.
1930 imports from Germany amounted
1930 imports from Germany amounted in value to 1,935,000,000 in value to 1,935,000,000
Finnishmarks,
Finnish marks, and and imports from fromRussia
Russia toto only 131,000,000
131,000,000
imports only
Finnishmarks.
Finnish marks.AsAs for for exports, first first place isis held
held by England
exports, place by England
(2,103,000,000 Finnish marks),
(2,103,000,000 Finnish marks), with Germany
with Germany and the
and theUnited
United
States following
States following in that order.
in that order. Russia Russia is sixth, taking
is sixth, taking Finnish Finnish
goods toto thethevalue
value ofof only 243,000,000
243,000,000Finnish Finnishmarks.
marks.
goods only
These figures become
These become intelligible only ifif viewed viewed against the the
figures intelligible only against
background ofofFinland's
Finland’s general social social structure.
structure. Although the the
background general
countryhas has alwaysbeen been largely composed ofof small smallAlthough
and medium
and medium
country always largely composed
sized farms,
sized farms, the the Social
SocialDemocratic
Democratic Party has hasbeen
been astonishingly
Party astonishingly
large ever
ever since
since universal
universal suffragewas was introduced.
introduced.Out Out ofof 200
200
large suffrage
representatives in in the
the present parliament there there are
are 66
66 Social
Social
representatives present parliament
Democrats, asas comparedwith
Democrats, with 59 59 Agrarians, 4242 Conservatives
Conservatives
compared Agrarians,
and 21
and 21Swedes.
Swedes.ThisThis fact,
fact, that
that there
there isisaa largeSocialSocialDemocratic
Democratic
large
Party in in aa country almost
almost wholly agrarian, indicates an insecure
an insecure
Party country wholly agrarian, indicates
and even dangerous agrarian system. The
and even dangerous agrarian system. The agrarian reform carriedagrarian reform carried
out as far back as twenty years ago has resulted in the rise ofofaa
out as far back as twenty years ago has resulted in the rise
group ofof small
smallfarmers
farmerswhose
whose lot lot isis far
far from
from satisfactory;nor norhas
has
group satisfactory;
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
124
I24 FOREIGN AFFAIRS
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
itit decisively
decisively improved the
improved
the condition
condition ofof the
the numerous
numerous small
small
tenant-farmers.
tenant-farmers.
That isis why the
That theFinnish
Finnish internal
internal political situation situation isis really
why political really
less stable than
less stable than it appears it appears to be. A
to be. A country country depending so so
depending
largely on on commerce
commerce and and shipping has has ofof course
course been been hithit by
largely shipping by
the present economic
the economic crisis, crisis, and and the the uncertainty ofof the the political
present uncertainty political
situation has
situation has thereby been been augmented. Simultaneously the the
thereby augmented. Simultaneously
prevalent antagonism towards towards communism
communism has has increased.
increased.The The
prevalent antagonism
attitude ofof the
attitude the farmers,
farmers, born born ofof economic
economicdistressdistress and and hatred
hatred
ofof communism,
communism, has has found
found its its expression in
expression
in the
the curious
curious Lappo
Lappo
movement,aa religious-agrarian movement
movement,
movement ofof anan ultra-conserva
ultra-conserva
religious-agrarian
tivecharacter.
tive character.In In 1930
1930 itit grew toto large proportionsand andwas wason on the
the
grew large proportions
verge of carrying out a Fascist coup d'etat, but it has now been
verge of carrying out a Fascist coup d'?tat, but it has now been
repressed under the influence of President Svinhufvud,aa states states
repressed under the influence of President Svinhufvud,
man
man of of ability and moderation. Neither the economic
the economic nor the nor the
ability and moderation. Neither
political tension,
tension, however,
however, has has definitely been been eased.
eased. Indeed,
Indeed,
political definitely
Russia’s agrarian policy and
Russia's and various
various aggressive movements movements onon
agrarian policy aggressive
Finland’s part have brought the
Finland's part have brought the antagonism of the two antagonism of the twocountries
countries
to
to a a dangerous point. It is therefore quite natural that Finland
dangerous point. It is therefore quite natural that Finland
should always emphasize the
should the fact
fact that
that she she isis aamember
member ofof the the
always emphasize
League ofofNations
Nationsand and turnturn itit toto profitable account,account, especially asas
League profitable especially
anassurance
an assuranceofof territorial
territorial integrity and of financial aid in case
case ofof
integrity and of financial aid in
war.
war.
So far,
So far,Finland
Finlandhas hasnot not succeeded
succeeded inin strengtheningher her position
strengthening position
in foreign affairs by association with
in foreign affairs by association with other states. With other states. With themore
the more
southern
southern Baltic
Baltic states
states she
she has has practically nothing in common.
in common.
practically nothing
She feels
She feelsherself
herself barred
barred from from Sweden
Sweden and the
and the so-called "Scandi
so-called “ Scandi
navian orientation"
navian orientation” by the the domestic
domestic opposition toto the the Swedish
Swedish
by opposition
minorityand and by the theAland
Aland question,as aswell
wellasas by the the fact
fact that
that
minority by question, by
Sweden
Sweden makes
makes no overtures
no overtures and
and prefers to
to play a a passive role
r?le in in
prefers play passive
European politics.The The sentiments
sentiments of the Finnish
of the Finnish people as aa people as
European politics.
whole are
whole are inclined
inclined toto turn turn strongly in in favor
favorofof Germany,which which isis
strongly Germany,
natural
natural as
as aa result of the intimate
result of the intimate and extensive and extensive commercial
commercial
relations existingbetween
relations between the the twotwo countries.
countries. They admire admire Eng
existing They Eng
land. But
land. But towards
towards Soviet Soviet RussiaRussia their their attitude
attitude isis thoroughly
thoroughly
hostile, nor is the general antagonism lessened
hostile, nor is the general antagonism
lessened by the the fact
fact that
that
by
they have
have not not relinquished their their claimclaim toto the the neighboring
they relinquished
autonomousSoviet
autonomous Soviet RepublicofofKarelia Kareliawith 250,000neighboring
with250,000 inhabitants,
inhabitants,
Republic
which though itit isisnow
which now part ofof Soviet Soviet Russia
Russia belongs racially toto
though part belongs racially
Finland.
Finland. Russia Russia means
means to
to keep it
it for
for the sake
the sake ofof access
access toto thethe
keep
Arctic Ocean.
Arctic Ocean.
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES,
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND RUSSIA
RUSSIA 125
125
Estoniaand
Estonia andLatvia
Latvia can canbebedealtdealtwithwithmore more briefly.These These two two
briefly.
countries
countries were
were fashioned
fashioned out
out of
of the
the three
three Russian
Russian governments
governments
ofofEstonia,
Estonia,LivoniaLivonia and andKurland,
Kurland, in inwhich
which large landowners
large
landownersofof
ancientGerman
ancient German lineageformed formed the the rulingclass,class,withwith the thebulkbulkofof
lineage ruling
the populationLatvian
the Latvian in in the
the south
south and andEstonian
Estonian in in the
thenorth.
north.
population
This
This class
class of landed proprietors
of landed proprietors used
used to
to furnish
furnish the
the Russian
Russian Gov
Gov
ernment with countless officers and
ernment with countless officers and officials. The Latvians, officials. The Latvians, oror
Letts,form
Letts, form part ofof the theLithuanian
Lithuaniangroup, group,whereas
whereas the theEstonians
Estonians
part
are Finno-Ugrians. When
are When these these territories
territorieswere were reorganized into into
Finno-Ugrians. reorganized
two
two independent states the old economic
states the old economic and social and social structure
structure
independent
went toto pieces.The
went The greatGerman German landowners
landownerswere were expropriated,
pieces. great expropriated,
and todayLatvia
and Latvia and and Estonia
Estonia are are agrarian democracies.
democracies. The The
today agrarian
consequences of this agrarian revolution
consequences of this agrarian revolution have been accentuated
have been accentuated
by the separation of the two two countries
countries from from the the vastvastRussian
Russian
by the separation of the
hinterland.
hinterland.
Estonia, which for the past two years has had the lowest living
Estonia, which for the past two years has had the lowest living
costs
costs in in Europe, isisaa country
countryofof small smallfarms.
farms. Its Its industry (mainly
Europe, industry (mainly
paper) isis insignificant, and and itsits exports consistconsist mainlyofof lumber lumber
paper) insignificant, exports mainly
and butter.
and butter. Foreign trade, trade, however,
however, shows shows the the influence
influence ofof the the
Foreign
economic depression, havingdecreased
economic decreased during the the pastyear year by
depression, having during past by
almost fifty percent. Germanystands
almost standsfirstfirst on
on the
the list
listofof countries
countries
fifty percent. Germany
exporting totoEstonia,
Estonia, beingfollowed followed bythe theUnited
UnitedStates,
States,RussiaRussia
exporting being by
and England. AsAsfar
and far asas exports are areconcerned,
concerned, England isis the thebestbest
England. exports England
customer, though the figures for Germany
customer, though the figures for Germany are only slightly lower. are only slightly lower.
Thus, wewehave
Thus, haveherehere again the thecurious
curiousfact fact that
thatRussia,
Russia, the thenearest
nearest
again
neighbor, occupies only the thirdororan an even
even lower
lower place, whereas whereas
neighbor, occupies only the third place,
twomore
two moredistant
distant countries,
countries, Germanyand and England,are are far
farmoremore
Germany England,
importantand and are
are ininactive
active competitionwith witheacheachother.
other. Despite
important competition Despite
Estonia’s small
Estonia's small population the the governmenthas
government
hasminorities
minorities toto deal
deal
population
with, the
with, theGermans,
Germans, numbering 18,000, 18,000, beingthe themost
most important.
numbering being important.
ItI tmust
must bebe conceded
conceded that that thethe problem ofofminorities,
problem
minorities,which which isisofof
such great importance
such great importance throughout Eastern Europe, has found aa
throughout Eastern Europe, has found
satisfactory and and promising solution in
solution in Estonia Estonia in the form ofof
in the form
satisfactory promising
cultural autonomy.
cultural autonomy.
Latvia isis another
Latvia another state
state in inwhich
which therethere isis aa curious
curious balance
balanceofof
power between
between Agrarians and and Socialists.
Socialists. WeWe find find here,
here, too,too, the the
power Agrarians
results
results of anof an agrarian revolution, far-reaching social
revolution, far-reaching social and national
and national
changes, aa ruling agrarianclass
changes, ruling class ofof small
small landowners
landowners struggling with
struggling
with aa
powerful social social democracy, the the loss
loss ofof anan artificially developed
powerful democracy, artificially developed
large-scale industry in Riga and Libau, some some industryon on aa small
small
large-scale industry in Riga and Libau, industry
orormedium
medium scale, scale, also
also some
some commerce,
commerce, for forwhich
which Riga and and the the
Riga
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
n6
126 FOREIGN AFFAIRS
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
Gulfofof Riga offer
Gulf offer excellent facilities.The
excellent export facilities. economiccrisis
The economic crisis
Riga export
very painfullyin
feltvery
isisfelt painfully
Latvia, although ititmust
inLatvia,
although
added that
mustbebeadded the
that the
little not in
state’s stability isisnot
littlestate's anyway
in any way endangered.In In the matter
thematter
stability endangered.
imports, Germany stands
ofof imports, Germany
first, followed
standsfirst,
by
Poland, England,
followed byPoland,
England,
Russia and
Russia and the Unitedthe United States. As far as exports
States. As far as exports and and foreign
foreign
marketsare
markets concerned, what
are concerned, whathas hasbeen saidofofEstonia
been said holds good
Estoniaholds
here,
here,
too.
too. The separation from the Russian
The separation from the Russian hinterland hinterland feltgood
isis felt here
here
even more
even than elsewhere,
more than Russia’s
result ofofRussia's
elsewhere, particularly asas aa result
particularly
commerce,which
monopolization ofof foreign commerce, interferes
which seriously interferes
monopolization foreign seriously
with the development
with the development of Riga.
of Riga. In
In Latvia,
Latvia, too, there
too, there are
are minori
minori
ties, including 73,000 Germans who play an important
ties, including 73,000 Germans who play an important part in the
part in the
Latvian Parliament
Latvian Parliament and who are turning their cultural
and who are turning their cultural attain attain
ments in aa country
use in
ments toto good use which isis still
countrywhich deficient in
stilldeficient such
in such
good
matters.
matters.
Both countrieshave
Both countries have aa scanty population, and and the increase isis
the increase
scanty population,
slow; there isis plentyofof land,
slow; there land,but resources are
natural resources
butnatural poor.The
arepoor. The
plenty
civilization
civilization of of both
both is
is that
that ofof Western
Western Europe, and
and the
the “ orienta
"orienta
Europe,
tion" culture asas they possess isis in
such culture
tion” ofof such in the direction ofof the
the direction the
they possess
west. Whether they will
west. Whether will prove maintain aa complete
able toto maintain
prove able
they complete
existenceofof their
existence own remains
theirown whichputs
seen, which
remains totobebe seen, them in
puts them in aa
different category from Finland
different category from Finland where there where there can
can bebe no
no doubt
doubt on on
this point. I t will naturally be asked whether they might not
this point. It will naturally be asked whether they might not
combine into
combine intoaa single stronger Differences in
state.Differences
stronger state. in language and and
single language
stand in
nationality stand in the way,and
theway, there isis aa further
and there difference in
further difference in
nationality
the “orientation”
the "orientation" of the foreign policies of the
of the foreign policies of the two countries. two countries.
To Estonia, its
To Estonia, relation totoRussia
its relation Russia isis by far the
by far themostmost important
important
factor; Latvia, on
factor; totoLatvia, on the otherhand,
theother Lithuania and
hand,Lithuania Poland are
andPoland are
also important.
also important. It
It will
will be
be remembered
remembered that
that by the
the Peace
Peace ofof Riga,
by Riga,
mentioned,the
alreadymentioned, thedistrict Vilnawas
districtofofVilna included in
was included in the Polish
thePolish
already
territory, bringing the thePolish frontier up
Polish frontier up toto the Dvina, so
theDvina, that
so that
territory, bringing
three-quarters of Latvia’s southern frontier borderson Lithuania,
onLithuania,
three-quarters of Latvia's southern frontier borders
and the
and the remainingquarter quarter on Poland.
onPoland.
remaining
The importanceofof these
The these two small countries
two small borderingon
countries bordering the
on the
importance
Baltic self-evident for
Baltic isis self-evident for geographical reasons.reasons. This This was was im im
geographical
demonstratedon
pressively demonstrated on the occasionofof the
theoccasion decennial jubilee
thedecennial
pressively ? — which, by the way, isaa real fleet? —jubilee
ofof the Latviannavy
theLatvian navy which, by the way, is real fleet by the
by the
Estonian,Finnish,
presence ofofEstonian, German,Danish
Finnish,German, Danishand Polish war
andPolish war
presence
wellasas byones
ships, asaswell ones from Norway, Englandand
fromNorway, France. NoNo
andFrance.
ships, by England
invitation
invitation waswas sent
sent to
to the
the Russian
Russian navy
navy
to
to bebe represented.
represented.
In Lithuania the
InLithuania situation isismore
the situation complicated. The
more complicated. Lithua
The Lithua
nians are
nians the opinion that
are ofof the that their still incomplete;they
state isis still
theirstate they
opinion incomplete;
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES,
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND RUSSIA
RUSSIA 127
127
vigorously maintain their their claim
claim toto the
the territory
territory ofofVilna,
Vilna,which
which
vigorously maintain
was taken
was taken awayaway from
from them
them by Poland Poland with with the
the final
final silent
silent
by
consent of the League of Nations.
consent of the League of Nations. One of the One of the most
most dangerous
dangerous
factors in
factors in the
the general situation
situation ofofEastern
Eastern Europe isis that that the
the
general Europe?
Vilna question has
Vilna has not
not been
been settled
settled toto this
this day —neither
neither by
question day by
formal decision
formal decision of
of the
the League, nor
nor on
on the
the basis
basis of
of national
national self-
self
League,
determination.For
determination. For Vilna
Vilna isis atat the
the root
root ofofLithuania's
Lithuania’s generally
generally
hostile attitude
hostile attitude towards
towardsPoland,
Poland,which which in in turn
turn exerts
exertsaa decisive
decisive
influence on
influence on the
the conditions
conditionsand and tendencies
tendenciesofof thetheBaltic
Baltic states
states inin
general.
general.
The Lithuanians,
The Lithuanians, too, too, like
like the
the other
other peoples described,
described, have have
peoples
gone through an agrarian revolution. Agriculture isis the
gone through an agrarian revolution. Agriculture
thedominat
dominat
ing interest.
interest. They cultivate
cultivate grainand andflax,
flax, raise
raise cattle
cattleandand export
ing They grain export
lumber. Industry isis practically non-existent.
lumber. non-existent.AsAs far far asas foreign
Industry practically foreign
trade isis concerned,
trade concerned, Germany isismost most important totoLithuania Lithuania in in
Germany important
every respect, furnishing nearly one-half of all imports and taking
every respect, furnishing nearly one-half of all imports and taking
three-fifths ofof the
three-fifths the exports;
exports; other
other countries
countries followfollow aa long way way
long
behind. Russia (which, of course, does not
behind. Russia (which, of course, does not directly adjoin Lithu directly adjoin Lithu
ania, being separated from it by the Polish territory of Vilna)
ania, being separated from it by the Polish territory of Vilna)
figures on on thethe list
listwith
with only aavery veryminute
minutepercentage.
percentage.
figures only
The political situation of
The political situation of Lithuania has Lithuania has not
not yet quieted down
yet quieted down
and is still far from stable. The strong
and is still far from stable. The strong anti-Bolshevist anti-Bolshevist tendencies
tendencies
ofof the
the agricultural democracies
agricultural
democracies ofof the the other
other border
border states
states here
here
assumes aa half-Fascist
assumes half-Fascist character;
character; ititwas wasmost
most pronounced under under
pronounced
Valdemaras’s dictatorship,but
Valdemaras's buthas
hasnotnot really changedmuch mucheveneven
dictatorship, really changed
since the
since thefall
fall ofof that
that undoubtedlyable able statesman.
statesman.In In aaword,
word, thethe
undoubtedly
political regime isis similar similar toto Poland's
Poland’s pseudo-Fascism under under
political r?gime pseudo-Fascism
Marshal Pilsudski.
Marshal Pilsudski.
The internal
The internal political situation
situation isis further
further complicated by the the
political complicated by
fact that
fact that the
the country
country isisRoman
RomanCatholic
Catholic (90 (90 percent), and and that
that
percent),
theChristian
the ChristianDemocrats
Democratswho who comprise the theclerical
clericalparty
partyare arevery
very
comprise
strong. I t was really the clergy who brought about Lithuania’s
strong. It was really the clergy who brought about Lithuania's
national regeneration,yet
national yet their
their attitude
attitude towards
towards the the prevailing
regeneration, prevailing
Fascist regime is hostile;
Fascist r?gime is hostile; moreover, moreover, the government
the government has hasnotnotasasyet
yet
succeeded in
succeeded in arriving
arrivingatat aa completeagreementagreementwith with thetheVatican,
Vatican.
complete
To the disturbed
To the disturbed situation situation in
in general must
must therefore be added
therefore be added an an
general
incessant strife between
incessant strife between government government and clergy, and
and clergy, and between between
Lithuania and
Lithuania and thetheVatican.
Vatican.This This conflict
conflict isis ofofgreat
great importance,
importance,
because
because the the Christian
Christian Democrats
Democrats incline
incline to
to seek
seek an understanding
an
understanding
withPoland
with Poland over over thetheVilna
Vilna question,
question,with with aa viewview toto creating aa
creating
united front
united front against Russia. Russia. On On the the other
other hand hand the the Fascist
Fascist
against
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
128
128 FOREIGN AFFAIRS
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
Government and
Government and the
the parties supporting itithave haveentered
entered into
into ties
ties
parties supporting
withRussia
with Russia toto aa degreeunknown
unknown in in any other
other ofof the
the border
border
degree any
states. The Soviet peace treaty with Lithuania was
states. The Soviet peace treaty with Lithuania was followed on followed on
September 28, 28, 1926
1926 by aa pactofof non-aggression and and neutrality
September by pact non-aggression neutrality
whichwas
which wasrenewed
renewed May 6, 1931. Indeed, Lithuania might almost
May 6,1931. Indeed, Lithuania might almost
be regarded
be regarded as
as Russia’s ally.
Russia's ally.
The inclination
The inclination toto come
come into
into close
close relations
relationswith
withRussia
Russia are,
are,
however, adversely affected
however,
affected by two two circumstances.
circumstances.First, First, asas alal
adversely by
ready mentioned,Lithuania Lithuania isis not not contiguous totoRussia, Russia, being
ready mentioned, contiguous being
separated from from itit by aa broad broad strip ofofLatvian Latvian and andPolish
Polish terri terri
separated by strip
tory; secondly, Lithuania's
Lithuania’s access access toto the the Baltic
Baltic Sea Sea isis too too in in
tory; secondly,
considerable toto serve
considerable serve the theRussian
Russian hinterland.
hinterland.Lithuania's
Lithuania’s own own
share of
share of that that coast
coast is really restricted
is really restricted to
to the district of Polangen,
the district of Polangen,
butbut this
thishas
hasbeenbeen increased
increased towardtoward the the south
south by the the separationofof
by separation
the district
the district ofofMemelMemel from from Germany,with with the the result
result thatthat the the
Germany,
length ofof thetheLithuanian
Lithuanian coastlinecoastlinehas hasbeen been doubled.
doubled. ItItwill will bebe
length
remembered that
remembered thatwhen when this thiswaswasdone done theretherewas was aa proviso and and
proviso
guarantee
guarantee
that the district should be
that the district should be under autonomous under autonomous (/.
(/. e.,e.,
German) administration,
German)
administration, asas stipulated in in the
theMemel
Memel Statute Statute
stipulated
dated March 14, 1924,
14,1924, and and as
as finally sanctioned by the Council of
dated March finally sanctioned by the Council of
Ambassadors on
on May 8, 1924. We shall not enter into details re
Ambassadors May 8, 1924. We shall not enter into details re
garding the the complicated form formofof governmentbestowed bestowed upon the the
garding complicated government upon
district
district ofof Memel
Memel at
at that
that time.
time. Suffice
Suffice it
it to
to say
say
that
that it
it is
is of
of so
so
intricate a nature,
intricate a nature, and Lithuaniaand Lithuania pays so little regard to the
pays so little regard to the
provisions for for autonomous
autonomous rights, that, that, justasas in in the
the case
case ofof the the
provisions rights, just
Vilnaquestion
Vilna questionbetweenbetween Lithuania
Lithuania and andPoland,
Poland, the theMemel
Memel ques ques
tion has remained
tion has remained to
to this
this day the
the subject ofof endless quarrels
endless quarrels be be
day subject
tween Germany
tween Germany and Lithuania,
and Lithuania, as the League
as the League of Nations of Nations well
well
remembers.There
remembers. There can can bebe nono doubtdoubt that that this thisMemel
Memel question,
question,
affecting as it does the status of the river’s mouth and the port of
affecting as it does the status of the river's mouth and the port of
Memel, isis aa highly important factor
Memel, factor in in thethe generalBaltic Baltic situa situa
highly important general
tion,
tion,
so
so much
much so
so that there has been considerable discussion ofof
that there has been considerable discussion
ways and andmeans
means toto bring about about aa definitive
definitive agreement
agreementbetween between
ways bring
Germany and Lithuania.Such Such projectsdo donot notexclude
exclude considera
considera
Germany and Lithuania. projects
tion of the questions of the Corridor
tion of the questions of the Corridor and Danzig. and Danzig.
AtAt this
this pointweweare
point
are brought face
brought
facetoto face
facewithwith the the powerful r?le
powerful
role
which Poland
which Poland plays in in the
the Baltic
Baltic question.
question. ItItwould would bebe out out ofof
plays
place totodescribe
describePolandPolandatatasasmuch much lengthasas the theother
other countries,
countries,
place length
for she
for she isisnot
not really aaBaltic Baltic state.
state.HerHer seacoast
seacoast measures
measures only
really only
forty miles, and and even
even this thismeager
meager access access toto the the sea
sea she
she owesowes toto
forty miles,
thepeace
the peace treaty,
treaty,which which created
created the the anomalous
anomalous entity ofofDanzig Danzig
entity
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES,
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND RUSSIA
RUSSIA 129
129
? —aa state
statewhich
which isis toto belong and and thenthen again isisnot not toto belong toto
belong again belong
Poland,
Poland, which iswhich is to
to be united
be united to
to Poland and
Poland and neverthelessnevertheless isis toto
remain intrinsically
remain intrinsically independent and autonomous.
autonomous. Such
Such a solua solu
independent and
tion could
tion could have
have permanence only ififPoland Poland showed showed the the utmost
utmost
permanence only
good will; it is intolerable to Germany,because because itit involves
involves the the
good will; it is intolerable to Germany,
loss of territory that is unquestionably
loss of territory that is unquestionably German.
German.
What itit isismost
What most important toto pointout out inin thethe present connec connec
important point present
tion, however, is that Poland, as a glance at the map will show,
tion, however, is that Poland, as a glance at the map will show,
extends
extends to to the
thewest
west around
around partofof the the territoryofof Danzig, up toto
part territory Danzig, up
the Baltic, and that in this
the Baltic, and that in this outlying part outlying part ofofher her territoryPoland Poland
territory
has developed a port of her own, which she
has developed a port of her own, which she is determined to make, is determined to make,
by hook ororcrook,
crook, her her principal porton on the
theBaltic.
Baltic.Not Notmoremore thanthan
by hook principal port
three years ago, Gdynia, which has since
three years ago, Gdynia, which has since acquired such notoriety,acquired such notoriety,
was aamiserable
was miserable fishing village with with aa few fewhundred
hundred inhabitants.
inhabitants.
fishing village
Today, itit isis aa rapidly growing town townwith with all allmodern
modern improve
Today, rapidly growing improve
mentsand
ments and an anultra-modern
ultra-modern port.This This port, in in itself
itselfaa dangerous
port. port, dangerous
competitor of Danzig, isisdestined destined byPoland Poland toto bebe aa permanent
competitor of Danzig, by permanent
and integral partofofher
and hereconomic
economiclife. life.Evidence
Evidenceofof this this isisfound
found in in
integral part
the important railroad
the railroadnow nowunderunder construction
construction from from Kattowitz
Kattowitz
important
northwards toto Gdynia,ofofwhich
northwards which only aa short short section
section isis still
stillun un
Gdynia, only
finished. In the spring of 1931 this whole
finished. In the spring of 1931 this whole railroad was taken over railroad was taken over
byaa French company,aa railway loan loan beingfloatedfloated in inFrance
France for for
by French company, railway being
the purpose. The
the The crux crux ofof the
thematter
matter isis that that thisthis south-to-north
south-to-north
purpose.
pressure, bymeans meansofofwhich whichPoland,
Poland, aidedaided byFrance, France, tends tends toto
pressure, by by
establish direct connections with the
establish direct connections with the nations of the west and nations of the west and toto
figure asas aaGreat
GreatPower,Power, breaks
breaks the the east-and-west
east-and-west connectionconnection ofof
figure
Germany proper with withEastEastPrussia,
Prussia, beyond the theVistula.
Vistula.Further
Further
Germany proper beyond
more,
more, PolandPoland is brought
is brought into conflict with
into conflict with Germany Germany through
through
Gdynia’s competition with with Konigsberg, formerly the the Baltic
Baltic
Gdynia's K?nigsberg,
terminus ofcompetition
terminus of the
theGerman
German line line ofof communication
communicationformerly
southward
southward toto
Odessa, via Prostken, Bialystok,
Odessa, via Prostken, Bialystok, Brest-Litovsk,
Brest-Li to vsk, Rovno,
Rovno, Kasatyn
Kasatyn
and Shmerinka.
and Shmerinka.The The strategic advantages ofof the the Kattowitz
Kattowitz-
strategic advantages
Gdynia line line are
are self-evident,
self-evident, asas regards the the supply ofofwar warma ma
Gdynia regards supply
terials byFrance
terials Franceboth bothtotoPoland
Polandand andtotoRumania.
Rumania.And Andon on thethesea,
sea,
by
from Cherbourg,LeLeHavre
from Havre and andCalais,
Calais, through the theNorth
North Sea, Sea,
Cherbourg, through
andaround
and around the the Skagerrack into intothetheBaltic
Balticand and toto Gdynia,France, France,
Skagerrack Gdynia,
Poland’s ally, isisnot
Poland's notconfronted
confronted by anynaval navalPower Powerwhich which isisher her
ally, by any
equal. TheThe French
French navy isis superior toto the thenavies
naviesofofall all the
theother
other
equal. navy superior
countries along that
countries that coast,
coast,and and thethePolish
Polish navy, small smallasas itit isis in in
along navy,
itself, means something in combination
itself, means something in combination with it. with it.
Thus the
Thus the picture today isis totallydifferent different from from thatthat ofof 1914.
1914.
picture today totally
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
130
i3o FOREIGN AFFAIRS
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
Several new
Several new Baltic
Baltic states
states have
have been
been called
called into
into being atat thethe
being
expense of Russia and and Germany, and and although they are are inin
expense of Russia Germany, although they
dependent they cannotcannot dodo without
without those
those twotwo Great
Great Powers.
Powers.
dependent they
Russia has
Russia haslost
lost almost
almostall
allher
herformer
formercoast
coastonon the
theBaltic,
Baltic, retaining
retaining
merely the
the small
small bit
bit extending from
fromNarva
Narva toto Leningrad and and
merely extending Leningrad
thenceaa short
thence shortdistance
distance towards
towards the
thenorthwest,
northwest,onon the
the innermost
innermost
recessofof the
recess theGulf
GulfofofFinland.
Finland. Germany’sBaltic Balticcoastline
coastlinehas hasbeen
been
Germany's
broken in two by the Polish wedge, and she
broken in two by the Polish wedge, and she has also lost the dishas also lost the dis
trictofofMemel.
trict Memel. Poland
Poland isis takingher her placeasas one
oneofof the
the principal
taking place principal
Baltic Powers. The position of Sweden
Baltic Powers. The position of Sweden and Denmark and Denmark remains
remains the
the
same, but they are pondering over these changes
same, but they are pondering over these changes and wondering and wondering
about the
about thefinal
final outcome.
outcome.
This
This new
new situation
situation has hasbeen
been created
created by the the policy ofof England
by policy England
and France since the war. I t was generally
and France since the war. It was generally believed, believed, asas already
already
stated, that
stated, that England would would establish
establish permanent bases bases in in the
the
England permanent
north,
north,
and
and France
France in
in Poland. England,
Poland. England, however,
however,
has
has shown
shown an
an
increasing lack lack ofof interest
interest in in the
the Baltic.
Baltic. So So long asas Russia
Russia rere
increasing long
mainsasasweak
mains weakasas sheshe isis today these
theseborderland
borderland territories
territoriesare arenotnot
today
ofof so
somuch
much importance toto England.Under
importance England.
Under presentconditions
present
conditionsher her
principal interest
interest inin them
them isis commercial:
commercial:Finnish,
Finnish,Estonian
Estonian and and
principal
Latvian exports, especially dairy products, are
Latvian are the
thevery
very things
exports, especially dairy products, things
England needs toto import.The The ties
ties between
betweenFrance
France andand Poland
Poland
England needs import.
are stronger. On
are On the
thewhole,
whole, however,
however, France
Francehas hasbeen
been less
less active
active
stronger.
politically in in the
theBaltic
Baltic countries
countries thanthan isis usually supposed.
politically usually supposed.
One need
One need only recall
recall the
thediscussions
discussions before
before the
the League ofofNaNa
only League
tions toto realize
tions realize that
that there
therehas
hasbeen
beennono permanentand
and satisfactory
permanent satisfactory
solution ofof the
solution the Baltic
Baltic problem, especially atat itsitsmost
most sensitive
sensitive
? — Vilna, Memel problem, especially
points and Danzig. The future depends
Vilna, Memel and Danzig. The future depends almost almost
points
entirelyon onwhat
whatbecomes
becomes ofofRussia.
Russia.This
This has
hasan an importantbear bear
entirely important
ing on
on the
the pertinent questionwhether
whether the
theBaltic
Balticstates,
states,after
afterhav
hav
ing pertinent question
ing been
been atomized
atomized andand endowed
endowed with
with independent organizations
ing independent organizations
ofof their
theirown,
own,oughtnot not somehow
somehow toto come
come together again,soso that that
ought together again,
?— inin the Herbert Spencer? —differentiation
the language ofofHerbert differentiation could could bebe
language Spencer
followed once
followed oncemore
more by integration. Signsmay maybebe seenseen pointing in in
by integration. Signs pointing
that direction
that direction both inboth in the
the field of commercial
field of commercial policy policy and
and in
in the
the
narrowerfield
narrower fieldofof foreign politics.AA customs
customsunion unionexists
exists between
between
foreign politics.
Estonia
Estonia and Latvia,
and Latvia, even
even though so far it has not
so far it has not borne any borne any
though
practical results. Commercial agreements agreements are are inin force
force between
between
practical results. Commercial
Latvia and Lithuania,
Latvia and Lithuania, between Estonia and
between Estonia and Lithuania, Lithuania, and bebe
and
"
tween Finland and
tween Finland and Estonia. Estonia. In addition to the so-called
In addition to the so-called “Baltic
Baltic
Clause,”
Clause,"
some
some of
of these
these agreements contain
contain also
also the
the so-called
so-called
agreements
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES,
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
GERMANY AND
AND RUSSIA
RUSSIA 13 1
131
“FinnishClause,"
"Finnish Clause,” /.i. e.,
e., the
the stipulation that
thatRussia
Russia shall
shall not
not bebe
stipulation
entitled
entitled to
to demand any
demand any special special favors
favors which
which the
the Baltic
Baltic states
states may
may
concede toto one
concede one another.
another.The
The same
same applies toto the
the commercial
commercial
applies
treatiesofof these
treaties these states
stateswith
with Germanyand andwithwithPoland,
Poland, and
and this
this
Germany
so-called "Baltic
so-called “Baltic Clause"
Clause” keeps the thewayway openopen forfor aa customs
customs
keeps ?
? — if that is unattainable
union or
or unattainable — for
for trade
trade preference in the
union if that is preference in the
sense of the Geneva discussions
sense of the Geneva discussions and and aa regional agreement at least
at least
regional agreement
between
between Latvia Latvia and Estonia,
and Estonia, with
with the possible
the possible inclusion ofof
inclusion
Finland.
Finland.
Butall
But all this
this taken
taken together isis onlyaavery verysmall
small stepon on the
theroad
road
together only step
leadingtoto thetheconsolidation
consolidationand andunion
unionofof these
thesesmall
smallstates.
states.ItIthas
has
leading
been frequently suggested in in the
the press
press that
that ifif theyunited
united in in aa
been frequently suggested they
“BalticBloc"
"Baltic Bloc” theywouldwouldhavehavegreater
greaterpower,
power, e.g., e. g.,atatGeneva,
Geneva,
they
than they can exercise separately. But the practical outcome ofof
than they can exercise separately. But the practical outcome
numerous talks,
numerous talks, visits,
visits, newspaper
newspaper articles
articles andand conferences
conferences bebe
tween their
tween their representatives has has been
been absolutely nil. nil.Natural
Natural
representatives absolutely
conditions have
conditions have preventedprevented the formation
the formation of of a a block of
block of border border
states under Polish leadership, because Finland
states under Polish leadership, because Finland lies in a totally lies in a totally
different sphere, while
different while for for Estonia
Estonia and and Latvia
Latvia the the Russian
Russian
sphere,
colossus is more
more important. These difficulties in
in the way ofof rap
the way rap
colossus is important. These difficulties
prochement have have been
been rendered
rendered unsurmountable
unsurmoun table owing toto the the
prochement owing
Polish-Lithuanian
Polish-Lithuanian conflict over Vilna. There are influences atat
conflict over Vilna. There are influences
work, directed especially by political groups closely associated
work, directed especially by political groups closely associated
with
with the theRoman
RomanCatholic
CatholicChurch,
Church,whichwhichaim aim atat aa reconciliation
reconciliation
between Poland and
between Poland and Lithuania, Lithuania, but so far results
but so far results have have beenbeen
negligible. The relations between Lithuania Lithuania and and Poland
Poland seem seem
negligible. The relations between
fixed
fixed onon an
an unsatisfactory basis,
basis, and
and are
are aa real danger
real danger to
to the
the
unsatisfactory
peace of Europe. Poland herself is weakened,
peace of Europe. Poland herself is weakened, both politically and
both politically and
ethically, by the situation, notwithstanding the the fact
fact that
that she
she isis
ethically, by the situation, notwithstanding
in actual
in actual possession ofofVilna: Vilna:nonoone one can
can take
takeVilna Vilna away
away from from
possession
Poland byforce.
Poland force.
by
Thus aa would-be
Thus would-be architect
architect ofof aa Baltic
Baltic BlocBlocwould would have have toto
choose between a Bloc
choose between a Bloc without Poland,without Poland, a Bloc under
a Bloc under Polish Polish
hegemony and aa Bloc including Russia and under her leadership.
hegemony and Bloc including Russia and under her leadership.
Oneneed
One need saysay nothingmore more toto show
show the the incompatibilityofof these these
nothing incompatibility
political ideas.
ideas.NorNor hashas the
theso-called
so-calledLitvinov
LitvinovPact Pactofof February 9,9,
political February
1929, in
1929, inwhich,
which, under
underRussia's
Russia’s leadership, the the Baltic
Baltic states ofof
states
leadership,
Finland, Estonia,
Finland, Estonia,Latvia,
Latvia,Lithuania
Lithuania and andPoland,
Poland, together with with
together
Rumania, mutually pledged themselves to
to the Kellogg Treaty,
Rumania, mutually pledged themselves the Kellogg Treaty,
madeaamore
made more intimate
intimateassociation
association any anymore
more likely.
likely.
The states
The statesdescribed,
described,after after all,
all, in
innonoway
wayformform aa homogeneous
homogeneous
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
132
132
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
FOREIGN AFFAIRS
group. The natural groups are: Finland-Sweden-Denmark in in the
the
group. The natural groups are: Finland-Sweden-Denmark
north; Estonia-Latvia-Lithuania in
north; Estonia-Latvia-Lithuania
in the
the south;
south;Poland
Poland on on the
the way
way
to becoming aaGreat
to GreatPower;
Power;and and the
the two
twodefeated
defeatedGreat
GreatPowers,
Powers,
becoming
Germany andRussia,
and Russia, each
eachdetermined
determined toto retain
retain their
their influence
influence
Germany
over the Baltic and the Baltic question. This
over the Baltic and the Baltic question. This division would be division would be
more apparent even
more even today but but for
for the
the fact
fact that
that the the Soviet
Soviet
apparent today
monopoly ofof foreign commerce commercemakes makes ititvery
verydifficult
difficult toto establish
establish
monopoly foreign
aa really close close association
association between
between Russia
Russia andand other
other states
states and,
and,
really
onon the the other
other hand,
hand, because
because the the interests
interestsofof the
the Baltic
Baltic states
states inin
agricultural exports are are inin violent
violent conflict
conflict with
with thethe agrarian
agricultural exports agrarian
commercial policy ofof Germany.
commercial policy Germany.
ItI t isisaaprecarious
precarious situation.
situation.The TheBaltic
Balticstates
statesare
are endeavoring in
endeavoring
in
every way to secure and consolidate their independence. Nowhere
every way to secure and consolidate their independence. Nowhere
in Germany isis there
in Germany there the
the slightest tendency toto advocate
advocate the the con
con
slightest tendency
quest ofof them them by force,
force, nor
norwould
would this
this indeed
indeed bebe possible. The The
quest by possible.
same holds
same holds good for for Russia;
Russia; sheshe has
has nono desire
desire atat the
the present
good present
moment toto see
moment see the
the existing condition
conditionofof things changed.Denmark Denmark
existing things changed.
and,above
and,
above all,
all, Sweden,
Sweden, are are observinganan essentiallydefensive defensive atat
observing essentially
titude asas spectators, although ititmust
titude must bebe added
added that that Sweden
Sweden isis
spectators, although
very
very
much
much onon her
her guard against Bolshevism
Bolshevism and
and is
is worrying
guard against worrying
about it. We have already stated
about it.We have already stated why it has not been why it has not been possible so
so
possible
far to effect a Finnish-Swedish
far to effect a Finnish-Swedish rapprochement, which on
which on some some
countswould
counts would seem natural. rapprochement,
seem sosonatural.
Let usus return
Let return now now totoourour pointofof departure, the theBaltic
Baltic Agree
point departure, Agree
ment of 1908.
ment of 1908. Would Would it be possible, as things are
it be possible, as things are today, to today, to renew
renew
it, thus assuring the safety of the states
it, thus assuring the safety of the states adjoining the Baltic? adjoining the Baltic?
One can
One can raise
raise thethe question but but notnot answer
answer it. it.However,
However, itit isis
question
enough toto bring itit forward
forward in in order
order toto indicate
indicate the the direction
direction in in
enough bring
which
which an
an accord must be sought. The old points
accord must be sought. The old points of view remain of view remain
the same.
the same. NoNo one one isis going toto assail
assail the the rightofof the the smaller
smallerBaltic
Baltic
going right
states toto the
states the independencewhich which theyhave have attained.
attained.But But itit also
also
independence they
remains aa fact
remains fact ofof undiminished
undiminished importance that that Germany and and
importance Germany
Russia, the largest Baltic Powers, cannot
Russia, the largest Baltic Powers, cannot do without coasts and
do without coasts and
harbors. There is, as already
harbors. There is, as already mentioned, mentioned, this difference
this difference between between
thetwo
the two:-.Germany sufferssuffersfrom
from smartingwounds wounds (Danzig,Memel), Memel),
Germany smarting (Danzig,
while Russia
while Russia has been has been cut
cut off from the Baltic almost
off from the Baltic almost completely. completely.
NoNo oneone cancan saysay that
that either
either Germany oror Russia
Germany
Russia has has brought
brought
influence toto bear
influence bear onon the
theBaltic
Balticstates
statestoto change the the existing situasitua
change existing
tion during
tion during the the ten
ten years since the termination of the war.
war. Ger
Ger
years since the termination of the
many’s relations
relations with withLithuania,
Lithuania,Latvia Latvia and andEstonia
Estonia are are good,
many's
and quite satisfactory from
and from the the economic
economic point ofof view. view.good,The
The
quite satisfactory point
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
BALTIC STATES, GERMANY
BALTIC STATES, RUSSIA
AND RUSSIA
GERMANY AND 133
133
fundamental between democracy and
fundamental opposition between Bolshevism
and Bolshevism
opposition democracy
separates these border states from Russia. But this has not pre
separates these border states from Russia. But this has not pre
vented the
vented relations, especially (as
establishment ofof political relations,
the establishment (as
political especially
noted) between
alreadynoted) Russia and
between Russia but also
Lithuania,but
andLithuania, between
also between
already
Russia and
Russia and?
Estoniaand
andEstonia lesser degree? —Latvia.
— toto aa lesser Between
Latvia.Between
degree
Finland and
Finland andRussia, true, there
Russia, itit isis true, toleration or
mutual toleration
there isis nonomutual or
cooperation.
cooperation.
really ought toto bebe possible, nonomatter
ItI t really ought possible,
matterhow how deeplyrooted
deeply
rootedallall
these differences and conflicts are, to stabilize
these differences and conflicts are, to stabilize the relations be the relations be
tween the
tween states adjoining the
the states the Baltic, cannot bebe
even ifif they cannot
Baltic, even
adjoining they
brought into harmonious
intoharmonious collaboration. But, of course, more im
collaboration. But, of course, more im
brought
portant than than even Finnish-Russian relations
theFinnish-Russian
even the relationshave have been and
been and
portant
must remain the
must remain betweenPoland
relations between
the relations Poland and and Germany.This This
Germany.
German-Polish question is
is aa problem by itself. The Powers of
German-Polish question problem by itself. The Powers of
Western Europe, and especially France, can
Western Europe, and especially France, can best promote general best promote general
peace and security in northeastern Europe by refraining from
peace and security in northeastern Europe by refraining from
using the countries involved asas the the wrestling-ground for their
for their
using the countries involved wrestling-ground
world rivalries. Until this happens it will be
world rivalries. Until this happens it will be quite impossible to quite impossible to
propose any constructive plan for
anyconstructive solutionofof the
the solution
for the the problem ofof
propose plan problem
the BalticSea
theBaltic and the
Sea and coast.
Baltic coast.
theBaltic
This content downloaded from 62.122.77.73 on Tue, 10 Jun 2014 01:33:35 AM
All use subject to JSTOR Terms and Conditions
You might also like
- The Law of The SeaDocument65 pagesThe Law of The SeaNur Iman100% (1)
- Congo Primary Sources - King LeopoldDocument4 pagesCongo Primary Sources - King Leopoldapi-285230022No ratings yet
- Americanah by Chimamanda Ngozi AdichieDocument19 pagesAmericanah by Chimamanda Ngozi AdichieRandom House of Canada35% (31)
- Julius Caesar - Gallic War Bilingual - 10 First PagesDocument12 pagesJulius Caesar - Gallic War Bilingual - 10 First PagesTyrex: Psychedelics & Self-improvementNo ratings yet
- Literature Analysis of No Name WomanDocument3 pagesLiterature Analysis of No Name WomankaiaceegeesNo ratings yet
- Setting Up Payroll For Oracle Cash Management IntegrationDocument6 pagesSetting Up Payroll For Oracle Cash Management Integrationmohammedsalah89No ratings yet
- The Pacific Problem, 1924Document27 pagesThe Pacific Problem, 1924JapanAirRaids100% (1)
- Vertigo TestDocument6 pagesVertigo Testalam saroorNo ratings yet
- Carpenter, Rhys - The Greek Penetration of The Black SeaDocument12 pagesCarpenter, Rhys - The Greek Penetration of The Black SeapharetimaNo ratings yet
- BR Kapoor V State of Tamil NaduDocument13 pagesBR Kapoor V State of Tamil Naduagrawalabinas83% (6)
- Maritime Defense For The Baltic StatesDocument10 pagesMaritime Defense For The Baltic StatesThe Atlantic Council100% (1)
- SEO Services Contract Template Free Microsoft WordDocument12 pagesSEO Services Contract Template Free Microsoft WordDanz HolandezNo ratings yet
- Aluminium FormworkDocument14 pagesAluminium FormworkebinVettuchirayil100% (6)
- History of Greece Ernst CurtiusDocument500 pagesHistory of Greece Ernst CurtiusBlackbeard73100% (1)
- Drainage de BrazilDocument5 pagesDrainage de BrazilDoct shafiqNo ratings yet
- MV Wilhelm GustloffDocument2 pagesMV Wilhelm GustloffNadia AminNo ratings yet
- Fishing Grounds of The Gulf of Maine by Rich, Walter H.Document113 pagesFishing Grounds of The Gulf of Maine by Rich, Walter H.Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Osor - Blecic - Kavur - M. - 2015 - Povezanost - PespekDocument272 pagesOsor - Blecic - Kavur - M. - 2015 - Povezanost - PespekVito Benvin Kaštelanić100% (1)
- Age of the Third Arcon: Adventures of Stag Captain Wurtheim: Age of the Third Arcon, #4From EverandAge of the Third Arcon: Adventures of Stag Captain Wurtheim: Age of the Third Arcon, #4No ratings yet
- Baltic SeaDocument16 pagesBaltic SeaAlex KibalionNo ratings yet
- Future Malaysia NewspaperDocument2 pagesFuture Malaysia NewspaperNursyahidah SafwanaNo ratings yet
- United States v. Bevans, 16 U.S. 157 (1818)Document35 pagesUnited States v. Bevans, 16 U.S. 157 (1818)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- The Facts of The Disaster and RelatedDocument36 pagesThe Facts of The Disaster and RelatedthestorydotieNo ratings yet
- R Times: in This Issue Middle East Door Ajar Living Amid The Atoms Who Shall Open The Tomb? After Darkness - LightDocument16 pagesR Times: in This Issue Middle East Door Ajar Living Amid The Atoms Who Shall Open The Tomb? After Darkness - LightDaniel PintoNo ratings yet
- A Succinct View of the Importance and Practicability of Forming a Ship Canal across the Isthmus of PanamaFrom EverandA Succinct View of the Importance and Practicability of Forming a Ship Canal across the Isthmus of PanamaNo ratings yet
- 1956 WarDocument7 pages1956 WarTito HassanNo ratings yet
- A Narrative of the Shipwreck, Captivity and Sufferings of Horace Holden and Benj. H. Nute Who were cast away in the American ship Mentor, on the Pelew Islands, in the year 1832; and for two years afterwards were subjected to unheard of sufferings among the barbarous inhabitants of Lord North's islandFrom EverandA Narrative of the Shipwreck, Captivity and Sufferings of Horace Holden and Benj. H. Nute Who were cast away in the American ship Mentor, on the Pelew Islands, in the year 1832; and for two years afterwards were subjected to unheard of sufferings among the barbarous inhabitants of Lord North's islandNo ratings yet
- LacusCurtius - Strabo's Geography - Book III Chapter 3Document10 pagesLacusCurtius - Strabo's Geography - Book III Chapter 3A Miguel Simão LealNo ratings yet
- MDP 39015027795890 30 1631727211Document1 pageMDP 39015027795890 30 1631727211almasNo ratings yet
- smolka-ESSAY-Soviet Strategy in The Arctic-1938Document8 pagessmolka-ESSAY-Soviet Strategy in The Arctic-1938epsteynNo ratings yet
- Baumann Schernewskijellyfish JCC2012Document13 pagesBaumann Schernewskijellyfish JCC2012VICTOR ADI WINATANo ratings yet
- The London GazetteDocument1 pageThe London GazetteCristian BotozisNo ratings yet
- How The Greeks Sailed Into The Black SeaDocument6 pagesHow The Greeks Sailed Into The Black Seaonr100% (1)
- BalseaDocument18 pagesBalseailieciprianNo ratings yet
- Fortune: The Fortunates. Islands and The SystemDocument50 pagesFortune: The Fortunates. Islands and The SystemAlberto VieiraNo ratings yet
- Practical Phases of Caribbean DominationDocument12 pagesPractical Phases of Caribbean DominationDany FernandesNo ratings yet
- Telders Case 2023 Brackfish Is ServedDocument6 pagesTelders Case 2023 Brackfish Is ServedBuda ZoltaNo ratings yet
- Jmse-09-00038 Cross-Shore Profile Evolution After An Extreme ErosionDocument15 pagesJmse-09-00038 Cross-Shore Profile Evolution After An Extreme ErosionNojus DekerisNo ratings yet
- Text of Munich Agreement For Original DocumentDocument4 pagesText of Munich Agreement For Original DocumentYi CaiNo ratings yet
- JIA Acct of HRSBGHDocument129 pagesJIA Acct of HRSBGHDr. ShaharilNo ratings yet
- News BBC 14 March 2015 CyclonDocument3 pagesNews BBC 14 March 2015 CyclonOrne llaNo ratings yet
- 1hzvohwwhu: (Xurshdq 0dulwlph +hulwdjhDocument10 pages1hzvohwwhu: (Xurshdq 0dulwlph +hulwdjhRoberto SchellenbergerNo ratings yet
- VoglerThompson ImplicationsMaritimeSecurity Mar15Document9 pagesVoglerThompson ImplicationsMaritimeSecurity Mar15vosvos kamilNo ratings yet
- Publshed To Web A - 410-900 Who Were The Hastingas 410-900Document28 pagesPublshed To Web A - 410-900 Who Were The Hastingas 410-900S DNo ratings yet
- The Gulf and Inland Waters The Navy in the Civil War. Volume 3.From EverandThe Gulf and Inland Waters The Navy in the Civil War. Volume 3.No ratings yet
- Rumania in 1900 - Benger Gottlieb, London, 1900Document323 pagesRumania in 1900 - Benger Gottlieb, London, 1900PrometheusNo ratings yet
- The Friend or Advocate of Truth PDFDocument697 pagesThe Friend or Advocate of Truth PDFvesshawaiiNo ratings yet
- Battle Creek, Mich., Third-Day, January NumberDocument8 pagesBattle Creek, Mich., Third-Day, January NumberamnonbpdNo ratings yet
- VIEIRA, Alberto (2002) : RecomendaçõesDocument51 pagesVIEIRA, Alberto (2002) : RecomendaçõesAlberto VieiraNo ratings yet
- Mythology and ReligionDocument23 pagesMythology and ReligionkpestylidasNo ratings yet
- Discoveries and Surveys in New Guinea and the D'Entrecasteaux IslandsFrom EverandDiscoveries and Surveys in New Guinea and the D'Entrecasteaux IslandsNo ratings yet
- Kendall1981 PDFDocument32 pagesKendall1981 PDFAnonymous ujOX1ELNo ratings yet
- Complete War CommentariesDocument105 pagesComplete War CommentariesAndy NunezNo ratings yet
- High Seas. This Was The Settled Position Till About 19: Points To RememberDocument3 pagesHigh Seas. This Was The Settled Position Till About 19: Points To RememberAzwad Abrur KolinchNo ratings yet
- Between Isolation and The World: Hvar and The Islands of DalmatiaDocument3 pagesBetween Isolation and The World: Hvar and The Islands of DalmatiaFlorian BieberNo ratings yet
- Caso Estudo-Rostock-Alemanha PDFDocument16 pagesCaso Estudo-Rostock-Alemanha PDFGogo1111No ratings yet
- Read Online Textbook Epsilon 1 Primo Corso Di Analisi Matematica Michiel Bertsch Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument22 pagesRead Online Textbook Epsilon 1 Primo Corso Di Analisi Matematica Michiel Bertsch Ebook All Chapter PDFrebecca.norris656100% (5)
- Voyages From Asia To America, For Completing The Discoveries of The North West Coast of America. To Which Is Prefixed, A Summary of The Voyages Made by The Russians On The Frozen SDocument144 pagesVoyages From Asia To America, For Completing The Discoveries of The North West Coast of America. To Which Is Prefixed, A Summary of The Voyages Made by The Russians On The Frozen Sfortross1812No ratings yet
- The Delimitation of Marine Spaces Between States With Opposite or Adjacent CoastsDocument76 pagesThe Delimitation of Marine Spaces Between States With Opposite or Adjacent CoastsNguyễn Trương Quốc HưngNo ratings yet
- The Territorial Temptation A Siren Song at SeaDocument23 pagesThe Territorial Temptation A Siren Song at SeaNguyễn Trương Quốc HưngNo ratings yet
- Oxman - The Territorial TemptationDocument22 pagesOxman - The Territorial TemptationSourabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Archipelago OF Sea: Problems and Perspectives: Concept in The Law THEDocument72 pagesThe Archipelago OF Sea: Problems and Perspectives: Concept in The Law THEChen-En SungNo ratings yet
- 20,000 Leagues Under The Sea: Jules VerneDocument280 pages20,000 Leagues Under The Sea: Jules VerneJoshua Michael Taylor MieritzNo ratings yet
- Maldives Islands DividedDocument7 pagesMaldives Islands DividedXINKIANGNo ratings yet
- Ure v. Coffman, 60 U.S. 56 (1857)Document8 pagesUre v. Coffman, 60 U.S. 56 (1857)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- The Standards of Weights and Measures ActDocument8 pagesThe Standards of Weights and Measures Actvikasnehra9999No ratings yet
- Audit Reporting For Going Concern PDFDocument33 pagesAudit Reporting For Going Concern PDFclarensia100% (1)
- Assignment - Hero Motocorp LTD - SHRM - Debasis RoutDocument2 pagesAssignment - Hero Motocorp LTD - SHRM - Debasis RoutAvishek BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- ISDN - Partnership Agreement SampleDocument9 pagesISDN - Partnership Agreement SampleMaxine Nicole BacarezaNo ratings yet
- Thank God Acknowledgement ThesisDocument7 pagesThank God Acknowledgement Thesispzblktgld100% (2)
- Sustainibility Stories Recycling of Ppe KitsDocument9 pagesSustainibility Stories Recycling of Ppe KitsSandesh SanNo ratings yet
- Departmental Accomplishment Report: Annual Return of Income Tax Withheld On Compensation (PHILECO)Document2 pagesDepartmental Accomplishment Report: Annual Return of Income Tax Withheld On Compensation (PHILECO)AdyNo ratings yet
- MDA Legislative Report Elk 2022Document3 pagesMDA Legislative Report Elk 2022inforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Ntu - Hss - Hp8002 - 1213ss02 - Course OutlineDocument4 pagesNtu - Hss - Hp8002 - 1213ss02 - Course OutlineMing EnNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 4 The Stove Is in The KitchenDocument7 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 4 The Stove Is in The KitchenSiti ZamillahNo ratings yet
- Letter To SponsorDocument11 pagesLetter To SponsorJeremiah Miko LepasanaNo ratings yet
- Advice To A Young Man Upon First Going To OxfordIn Ten Letters, From An Uncle To His Nephew by Berens, EdwardDocument37 pagesAdvice To A Young Man Upon First Going To OxfordIn Ten Letters, From An Uncle To His Nephew by Berens, EdwardGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Da FunkDocument4 pagesDa FunkJames L. KelleyNo ratings yet
- Grant Neal v. CSU Pueblo Et. Al.Document90 pagesGrant Neal v. CSU Pueblo Et. Al.Michael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- Neetu's Project PDFDocument14 pagesNeetu's Project PDFAkhil rayanaveniNo ratings yet
- 3 Verb Assignment - EditedDocument5 pages3 Verb Assignment - EditedNishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- NCR T-274-WD 041724Document27 pagesNCR T-274-WD 041724jazzleNo ratings yet
- ILO JudgementsDocument28 pagesILO JudgementsArshima RNo ratings yet
- Rivera-Feliciano Et Al v. Acevedo-Vila Et Al - Document No. 19Document7 pagesRivera-Feliciano Et Al v. Acevedo-Vila Et Al - Document No. 19Justia.com100% (1)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument5 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeoplewajeehNo ratings yet
- MQP Ans 04Document3 pagesMQP Ans 04vision xeroxNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learnt From Security Analysis-100Document8 pagesLessons Learnt From Security Analysis-100ravi_405No ratings yet