Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EM1 Electrostatics
Uploaded by
pencymosothwaneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EM1 Electrostatics
Uploaded by
pencymosothwaneCopyright:
Available Formats
1
ELECTROSTATICS [Static Electricity].
Static electricity refers to charge that is not moving i.e. stationary charge.
An insulator can be charged electrically by rubbing it while a conductor cannot.
Types Of Charge
There are two types of charge. These are Positive [+] and Negative [-].
The SI unit of charge is the Coulomb (C)
Negative charge is acquired if excess electrons are gained and positive charge is gained if
electrons are lost.
NB: Positive charge arises as a result of a deficiency of electrons.
All charges obey The Law Of Electric Charges which states that “like charges repel and
unlike charges attract”
Electric charges can exist independent of each other.
Electrostatic Charging
Methods of electrostatic charging include (i) Charging through contact
(ii) Charging through induction
Charging Through Contact
When a polythene rod is rubbed with a cloth it becomes negatively charged. Electrons flow from
the piece of cloth into the polythene rod. As a result the cloth attains a positive charge.
On the other hand an acetate rod becomes positively charged when rubbed with a piece of cloth.
Electrons flow out of the acetate rod into the cloth which then becomes negatively charged.
The rods and cloths described above became charge through contact.
Charging through induction
Charging through induction can be achieved in two ways- by earthing as well as through
separation of charges.
NOTES: Static Electricity leemok productions 2011©
2
Charging through separation of charge.
This can be illustrated by placing two metal spheres A and B next to each other so that they are
in contact.
A charged strip is then brought close to the metal spheres, but not touching them.
This causes a separation of charges in the two spheres. All negative charges are attracted from
sphere A to B.
On being separated, the two spheres are found to be ;
A- Positively charged
B- Negatively charged
NOTES: Static Electricity leemok productions 2011©
3
Charging through earthing
A charged strip is brought close to a neutrally charged metal sphere. See (a) below.
This causes a separation of charge within the sphere itself. See (b) below.
Earthing the sphere causes the negative charge to be repelled by the strip to the ground. See (c)
above.
This leaves the sphere with a net positive charge. See (d )above.
Detecting Charge
Charge can be detected through the use of a Gold Leaf Electroscope.
When a charged object is brought close to the metal cap, the gold leaf deflects upwards. This
happens because both the stem and the leaf have the same charge and as such repel each other.
To find out the nature of the charge on the object; the electroscope has to be charged first.i.e only
a charged electroscope can be used to detect the type of charge in an object.
NOTES: Static Electricity leemok productions 2011©
4
Discharging
Discharging refers to the loss of excess charge.
It takes place through contact or ionization. Dangers of ionization are minimized by earthing.
Lightning Conductor
As clouds move overhead they gain a negative charge. When excess charge has been
accumulated in the cloud it is discharged to the ground through ionization. This is called
lightning. Lightning is dangerous and it’s effects can be minimized through the use of a
Lightning Conductor. A lightning conductor discharges a cloud before it discharges on its own.
The lightning conductor should be made from a good conductor of electricity and it should be
taller than the structure it is protecting. When clouds move through the sky they acquire a
negative charge. As they pass above the lightning conductor they induce a positive charge in the
spikes at the tip of the lightning conductor.
NOTES: Static Electricity leemok productions 2011©
5
Since charge accumulates at sharp points, the positive charge at the tip of the spikes is large
enough to ionize the air molecules around them by attracting electrons from them. These
electrons are repelled down the lightning conductor to the ground.. The resulting positive ions
are attracted by the negatively charged cloud.
Thus an electric wind of positively charged particles moves from the spikes to the cloud where
they neutralize its negative charged.
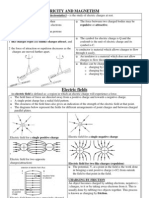
Electric Fields
The electric field is a region in which a charged particle exerts its electric force. Electric fields
are illustrated with the help of electric field lines which begin at the positive charge and end at
the negative charge.
Field around single charges.
Field between simmilar charges.
Field between 2 unlike charges.
Field between 2 positively charged plates.
NOTES: Static Electricity leemok productions 2011©
You might also like
- EM2 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesEM2 ElectrostaticsNathan TvascorNo ratings yet
- EM1 - Electrostatics 1Document3 pagesEM1 - Electrostatics 1Kimberly MojeNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Document33 pagesElectric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Maryam MehekNo ratings yet
- Phy CHP 1 NotesDocument33 pagesPhy CHP 1 Notesayaan ahmedNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Static ElectricityDocument82 pages10.1 Static ElectricityHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument82 pagesStatic ElectricityMadiha ShakilNo ratings yet
- CXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesCXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and Magnetismdela278% (9)
- ElectrostaticsDocument87 pagesElectrostaticsart angelNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Lesson 1 PDFDocument85 pagesQ3 - Lesson 1 PDFTimothy Francisco100% (1)
- ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesElectrostaticsjelvatro56No ratings yet
- Electric Charges Physics SSS 1Document14 pagesElectric Charges Physics SSS 1aliutunde3495No ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and Magnetismkhrisannmiller12No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Electro: StaticsDocument26 pagesElectrostatics Electro: StaticsHomok NokiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GP2Document40 pagesLesson 1 GP2lovlegin diongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument30 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionImaduddin SharafiNo ratings yet
- Basu ElectrostaticsDocument12 pagesBasu Electrostaticskedari PawarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics SS1Document6 pagesElectrostatics SS1OlusolaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS (Week 1)Document4 pagesELECTROSTATICS (Week 1)Philip MooreNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesElectrostaticsmelissaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeDocument19 pagesElectrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeManishKumarNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document20 pagesGeneral Physics 2christine isabel mendozaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument42 pagesElectric Charges and FieldKunal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Charging ProcessesDocument23 pagesDifferent Types of Charging ProcessesRiah VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Unit 2 Note - 07-08-14E.CDocument35 pagesG-10 Physics Unit 2 Note - 07-08-14E.CEmnet SolomonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument3 pagesReviewer in PhysicsBeatrice MararacNo ratings yet
- Explanation For ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesExplanation For Electrostaticsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Physics: Electric ChargesDocument8 pagesPhysics: Electric Charges23maabNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument37 pagesElectric Forces and Electric FieldsJennifer Magango100% (1)
- M3 Training NotesDocument64 pagesM3 Training NotessushilNo ratings yet
- Lectrure 1 (Electric Charge and Coulomb Law)Document15 pagesLectrure 1 (Electric Charge and Coulomb Law)mohidchishty6No ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive ChargeDocument6 pagesELECTROSTATICS 1 - Form 1 Physics Notes: Positive Chargecatherine SitatiNo ratings yet
- Physics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismDocument10 pagesPhysics Section D-Electricity and MagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics CH1 Part - 1Document24 pagesElectrostatics CH1 Part - 1Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrificationDocument10 pagesElectrificationjeremiah341harry0No ratings yet
- 1.9 Electrostatics (I)Document13 pages1.9 Electrostatics (I)Ferdnard WanjalaNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument16 pagesElectricitypatrick omonyNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Force TheoryDocument15 pagesElectrostatic Force TheoryRaviShankarDubeyNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Physics Notes Chapter 13 AjkDocument3 pages10th Class Physics Notes Chapter 13 AjkAsher KabirNo ratings yet
- Sourav Physics ProjectsDocument16 pagesSourav Physics ProjectsT VpNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsDocument27 pagesStatic Electricity: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsSajayanKSNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electric CircuitsDocument54 pagesTopic 2 Electric CircuitsMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Charging by InductionDocument10 pagesCharging by Inductionjuvy な.No ratings yet
- Sph4u Solutions (Unit 3)Document101 pagesSph4u Solutions (Unit 3)Voormila Nithiananda100% (1)
- HSSRPTR - Class 3-Electric Charges and Fields Class 1Document4 pagesHSSRPTR - Class 3-Electric Charges and Fields Class 1itsquitenNo ratings yet
- GP2 Q3W1Document24 pagesGP2 Q3W1DonggadongNo ratings yet
- 17 Static ElectricyDocument26 pages17 Static ElectricyDoraemonNo ratings yet
- Notes ElectricityDocument17 pagesNotes ElectricityPinki NegiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 All Electricity CambridgeDocument22 pagesUnit 3 All Electricity CambridgeAbdullah MostafaNo ratings yet
- G12 General Physics 2 Q3W1Document10 pagesG12 General Physics 2 Q3W1Aleyah Pangcoga Hadji OmarNo ratings yet
- AP CH 15-TeacherDocument36 pagesAP CH 15-TeacherOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Charge and It's Properties: NegativeDocument5 pagesCharge and It's Properties: Negativepusa123No ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities - Free Exam AcademyDocument19 pagesElectrical Quantities - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document12 pagesLec 1Kainat MusawarNo ratings yet
- EGM Fields - ClassconnectDocument118 pagesEGM Fields - Classconnectzia.mudassir2No ratings yet
- Class Viii LN-15 SummaryDocument9 pagesClass Viii LN-15 Summarysiddharthkvia321No ratings yet
- Static Electricity - Lesson NoteDocument8 pagesStatic Electricity - Lesson Noteyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument12 pagesStatic Electricityslm8749No ratings yet
- Children's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09Document15 pagesChapter 09Martin WolffeNo ratings yet
- Nvfsa30dc24v PDFDocument2 pagesNvfsa30dc24v PDFModathir BushraNo ratings yet
- Photonic-Crystal Fibers: Philip St.J. Russell, Member, IEEEDocument21 pagesPhotonic-Crystal Fibers: Philip St.J. Russell, Member, IEEESebastian Soto PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Imp. Derivations For XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesImp. Derivations For XII PhysicsJethiya SyckoNo ratings yet
- Ix-Film Datasheet PDFDocument12 pagesIx-Film Datasheet PDFalettristeNo ratings yet
- Physics Olympiad Syl Lab UsDocument3 pagesPhysics Olympiad Syl Lab UsMohammad ArikNo ratings yet
- Smith Chart PDFDocument49 pagesSmith Chart PDFKarthik DevarajanNo ratings yet
- Gate 2022 Online Test Series EeDocument7 pagesGate 2022 Online Test Series EeShaik ShaikNo ratings yet
- 14-SAMSS-534 Oh TransformerDocument8 pages14-SAMSS-534 Oh TransformerHatemS.MashaGbehNo ratings yet
- HV Ac Series: Resonant Test SystemsDocument4 pagesHV Ac Series: Resonant Test SystemsAlejandro Maturano100% (2)
- Electronics and Communication Engineering: Department ofDocument39 pagesElectronics and Communication Engineering: Department ofMohit MeenaNo ratings yet
- USM AME Advance Manufacturing EngineeringDocument16 pagesUSM AME Advance Manufacturing EngineeringRajesh RajendranNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 March 2015 TO Is 7098 (Part 2) : 2011 Specification For Crosslinked Polyethylene Insulated Thermoplastic Sheathed CablesDocument3 pagesAmendment No. 1 March 2015 TO Is 7098 (Part 2) : 2011 Specification For Crosslinked Polyethylene Insulated Thermoplastic Sheathed CablesVatsalNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Performance Task (3 Quarter)Document2 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Performance Task (3 Quarter)christie villaNo ratings yet
- Science 4 PPT Q3 - Heat Transfer Week 3Document72 pagesScience 4 PPT Q3 - Heat Transfer Week 3Jennifer CastroNo ratings yet
- Theory of Irregular Impedance Waveguides, Generalised Method of Separation of Variables - Zaginaylov Et Al (MMET 2014)Document6 pagesTheory of Irregular Impedance Waveguides, Generalised Method of Separation of Variables - Zaginaylov Et Al (MMET 2014)dpshepherdNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Pravat Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manualdinuarslan86% (7)
- Center of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Document19 pagesCenter of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Sador YonasNo ratings yet
- Emr/Esr/Epr Spectroscopy For Characterization of NanomaterialsDocument183 pagesEmr/Esr/Epr Spectroscopy For Characterization of NanomaterialsRajendraNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 6-1Document13 pagesAssignment No. 6-1JOSEFCARLMIKHAIL GEMINIANONo ratings yet
- Electroventilatoare CatalogDocument58 pagesElectroventilatoare CataloggeorgeNo ratings yet
- SS3 Physics WAVE NATURE OF MATTER - PassnownowDocument6 pagesSS3 Physics WAVE NATURE OF MATTER - PassnownowsunliasNo ratings yet
- 13.1 H-Plane Sectoral Horn: 13.1.1 Aperture FieldsDocument17 pages13.1 H-Plane Sectoral Horn: 13.1.1 Aperture FieldsErick Morocho CarrionNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification: IEC TS 62153-4-1Document21 pagesTechnical Specification: IEC TS 62153-4-1S.V.SubrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- 303E CR Mini Hydraulic Excavator Electrical System PDFDocument27 pages303E CR Mini Hydraulic Excavator Electrical System PDFMichael Krol0% (1)
- SRI986 Electro-Pneumatic Positioner: Product SpecificationsDocument16 pagesSRI986 Electro-Pneumatic Positioner: Product Specificationsherysyam1980No ratings yet
- Laser PPT 2Document22 pagesLaser PPT 2Akhil SainiNo ratings yet
- Waves: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument46 pagesWaves: Theory and Exercise BookletVikram AadiNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument24 pagesPhysics XIPavithra PrakashNo ratings yet