Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HALF WAVE RECTIFIER Class Notes
Uploaded by
RAJASHEKHAROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HALF WAVE RECTIFIER Class Notes
Uploaded by
RAJASHEKHARCopyright:
Available Formats
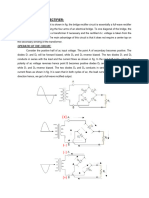
HALF WAVE RECTIFIER:
This rectifier circuit consists of resistive load, rectifying element, i.e. p-n junctin diode,
and the source of a.c. voltage, all connected in series.
The circuit diagram is shown in fig.
To obtain the desired d.c. voltage across the load, the a.c. voltage is applied to rectifier
circuit using suitable step up or step down transformer, mostly a step down one, with
necessary turns ratio.
The input voltage to the half-wave rectifier circuit shown in the fig. is a sinusoidal a.c.
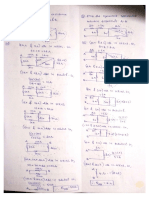
voltage, having a frequency which is the supply frequency, 50Hz given by, e s=Esmsinωt.
With ω=2πf and f=supply frequency.
OPERATION OF THE CIRCUIT:
During the positive half cylcle of input a.c voltage, terminal (A) becomes positive with
respect to terminal (B). The diode is forward biased and the current flows in the circuit in the
clockwise direction, as shown in the fig. This current is also flowing through the load resistance
RL hence denoted as iL (load current.)
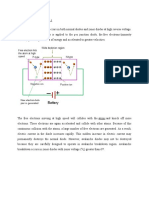
During negative half cycle when terminal (A) is negative with respect to terminal (B),
diode becomes reverse biased. Hence no current flows in the circuit as shown in fig. Thus the
circuit current, which is also the load current, is in the form of half sincusoidal pulses. The load
voltage, being the product of load current and load resistance, will also be in the form of half
sinusoidal pulses. The different waveforms are illustrated in fig.
You might also like
- Lecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)Document7 pagesLecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectificationDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectificationMohammad alhaboob2030No ratings yet
- RECTIFIERSDocument3 pagesRECTIFIERSmehakNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical by FarhanaDocument28 pagesBasic Electrical by FarhanaEr Rouf UlAlam BhatNo ratings yet
- Non-Sinusoidal OscillatorsDocument7 pagesNon-Sinusoidal OscillatorslekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Applications of PN Junction Diode PDFDocument8 pagesApplications of PN Junction Diode PDFZain Ul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4Altaher Bushra AdamNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Diode Applications & TransistorsDocument24 pagesElectronics - Diode Applications & TransistorsA B ShindeNo ratings yet
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDocument18 pagesيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDocument18 pagesيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- Module1 NotesDocument30 pagesModule1 Notesswarupa.23iseNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Inductors Capacitors and Alternating Current CircuitsDocument42 pagesBab 2 Inductors Capacitors and Alternating Current CircuitsVimal SaravananNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Ele PDFDocument38 pagesModule 2 Ele PDFRif RizNo ratings yet
- Solution of Current in R-L-C Series CircuitsDocument9 pagesSolution of Current in R-L-C Series CircuitsDIVYANSH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Diode Applications: Rectifier CircuitsDocument7 pagesDiode Applications: Rectifier Circuitseric labordoNo ratings yet
- Project Report On RectifierDocument10 pagesProject Report On RectifierHArsh90% (10)
- Unit - V InvertersDocument11 pagesUnit - V InvertersSukhpal SinghNo ratings yet
- BESCK104C 204C IEC Module1 NotesDocument24 pagesBESCK104C 204C IEC Module1 Notesblehbo100% (1)
- Full Wave PDFDocument2 pagesFull Wave PDFDonald Trump69No ratings yet
- Ch1 AC CurrentDocument23 pagesCh1 AC CurrentAhmed ElayanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices: Can You Recall?Document40 pagesSemiconductor Devices: Can You Recall?RAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- P-N Junction As A RectifierDocument3 pagesP-N Junction As A RectifierNouman RiazNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-10 at 7.08.51 PMDocument26 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-10 at 7.08.51 PMNiranjan N SNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeDocument13 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeCatalina ZelayaNo ratings yet
- 3 A RLCDocument10 pages3 A RLCsuresh krishnanNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - ADocument30 pagesAC-DC Converter - ABishnuNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Diode Circuit ApplicationsDocument31 pagesChapter Five Diode Circuit Applicationsfouad abdNo ratings yet
- Rectifier and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRectifier and Power SupplyNani NaniNo ratings yet
- 1208 EEC MIcroprojectDocument16 pages1208 EEC MIcroprojectDibyas Sanjay DubeyNo ratings yet
- CyclocovertersDocument4 pagesCyclocovertersAlfredNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Electronic Systems and DesignDocument23 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Electronic Systems and DesignNoel TeporaNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - Single PhaseDocument30 pagesAC-DC Converter - Single Phasebishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 Phasor RepresentationDocument57 pagesChapter One: 1.1 Phasor RepresentationMohamad AbdulghaniNo ratings yet
- Concept of A. C. CircuitsDocument11 pagesConcept of A. C. CircuitsAbhishekNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- FoEEE (Q & A)Document59 pagesFoEEE (Q & A)Cr SamiNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Half Wave Controlled RectifierpdfDocument14 pagesSingle Phase Half Wave Controlled RectifierpdfRîtzî Saxena92% (37)
- Inverter PDFDocument84 pagesInverter PDFVenkedesh RNo ratings yet
- Step-Down Cycloconverter Explained - Electrical ConceptsDocument5 pagesStep-Down Cycloconverter Explained - Electrical ConceptsMohammad HamamdNo ratings yet
- Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument27 pagesSingle Phase AC Circuitskali hembramNo ratings yet
- Rectifier 1rectifier Investigatory ProjectDocument4 pagesRectifier 1rectifier Investigatory ProjectcapvermaNo ratings yet
- I-9 Power CircuitDocument7 pagesI-9 Power Circuitsulatt.nandar.mdyNo ratings yet
- S1. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier - Principle of OperationDocument7 pagesS1. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier - Principle of OperationVicNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors CH14 Part 4Document14 pagesSemiconductors CH14 Part 4Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIIDocument3 pagesAssignment IIIAnandRajNo ratings yet
- Wa0017.Document45 pagesWa0017.Chintu ChintuNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Slides (Part II)Document22 pagesSemiconductor Slides (Part II)Nishant MehlaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Voltage Source Inverters: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Voltage Source Inverters: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 AC NetworksDocument70 pagesCh.2 AC NetworksaattishNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 Elec NotesDocument29 pagesModule - 1 Elec Notesswarupa.23iseNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDocument10 pagesSingle Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDeepu Chinna75% (4)
- Full Wave RectifierDocument25 pagesFull Wave RectifierSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Inverters: Seminar by Supervised byDocument45 pagesSingle-Phase Inverters: Seminar by Supervised bynoor deenNo ratings yet
- دايود ريكتفايرDocument7 pagesدايود ريكتفايرalamryzhra62No ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - Multi PhaseDocument39 pagesAC-DC Converter - Multi Phasebishnu prasad muniNo ratings yet
- AC-DC Converter - DDocument39 pagesAC-DC Converter - DBishnu100% (1)
- Capítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsDocument49 pagesCapítulo 1 Basic Concepts - em - InglêsPaulinha BezerraNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- New Doc 2017-08-21 - 1Document8 pagesNew Doc 2017-08-21 - 1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 2Document2 pagesIot Test 2RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 1Document7 pagesIot Test 1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- BRIDGE FWR Class NotesDocument2 pagesBRIDGE FWR Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Micro W A VE Solid State DevicesDocument7 pagesUnit Iii Micro W A VE Solid State DevicesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 1.1Document2 pagesIot Test 1.1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Mwe Unit 3part 3Document24 pagesMwe Unit 3part 3RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- 1 (11 Files Merged)Document11 pages1 (11 Files Merged)RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument1 pageBJTRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- 1 (11 Files Merged)Document11 pages1 (11 Files Merged)RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument46 pagesUnit VRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownDocument2 pagesAvalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownDocument2 pagesAvalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Pre PHDDocument16 pagesMathematics Pre PHDRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet