Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parliament Part 1 @upscplanner
Parliament Part 1 @upscplanner
Uploaded by
RohitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parliament Part 1 @upscplanner
Parliament Part 1 @upscplanner
Uploaded by
RohitCopyright:
Available Formats
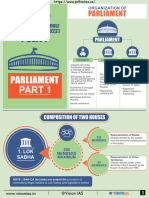
ORGANIZATION OF
PARLIAMENT
QUICK REVISION MODULE
(UPSC PRELIMS 2024)
POLITY PARLIAMENT
PRESIDENT LOK SABHA RAJYA SABHA
- Integral part of the
Parliament (though not
a member of either
House of Parliament).
- Also called as - Also called as
PARLIAMENT
- Bill passed by both Lower House Upper House
houses cannot become (First Chamber or (Second Chamber or
law without the Presi- Popular House House of Elders or
dent’s assent
or House of the
PART 1
Council of state).
-Summons & prorogue People).
Represent
both the Houses, Represents state’s interest in
-Dissolves the Lok Sabha people’s will. Parliament.
-Addresses both the
Houses,
-Issues ordinances
COMPOSITION OF TWO HOUSES
Representation of States:
530 Directly elected by the people
MEMBERS from the territorial constituencies
in the states
550
1. LOK MEMBERS
SABHA MAXIMUM Representation of Union
Territories:
20 Directly elected under union
MEMBERS territories (direct election to the
house of people) act 1965
NOTE: 104th CA Act does not extend the provision of
nominating Anglo Indians to Lok Sabha and legislative bodies
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 1
Representation of States:
• Elected by the elected members of state legis-
lative assemblies by proportional representation
by single transferable vote
• Seats in states according to population
238
MEMBERS Representation of Union Territories:
• Indirectly elected by members of an electoral
college specially constituted for the purpose.
2. RAJYA 250
• Out of the 9 union territories, only three
MEMBERS
SABHA MAXIMUM
(Delhi, Puducherry and Jammu & Kashmir)
have representation in Rajya Sabha.
Nominated Members:
12 Nominated by president from people who have
MEMBERS special knowledge or practical experience in
art, literature, science and social service.
Constitution ensures that there is uniformity of representation in two respects:
1. Between the different state.
TERRITORIAL
2. Between the different constituencies in the same state
CONSTITUENCIES
Note: This provision does not apply to a state having a population of less
than 6 millions.
After every census, a readjustment is to be made in:
READJUSTMENT • allocation of seats in the Lok Sabha to the states,
AFTER EACH • division of each state into territorial constituencies.
CENSUS Parliament is empowered to determine the authority (Delimitation
SYSTEM OF
Commission) and the manner in which it is to be made.
ELECTIONS TO
LOK SABHA RESERVATION
OF SEATS FOR
Constitution provides for the reservation of seats for SCs & STs in
the Lok Sabha on the basis of population ratio. Extended by 104th
SCS AND STS
CA Act 2020 till 25th January, 2030 (which was expiring in 2020).
FIRST-PAST- Constitution has adopted:
THE-POST • System of territorial representation (First-past-the-post system} for elections
SYSTEM to Lok Sabha
DURATION OF TWO HOUSES
LOK SABHA RAJYA SABHA
• Non continuing chamber as it dissolve in every five years • Continuing chamber as 1/3rd members retire every
• Term of 5 years second year (eligible for re-election and renomination)
• President dissolves Lok Sabha and this cannot be • Permanent body and not subject to dissolution
challenged in a court of law. • Term of office of members is not fixed by Constitution
• Term of the Lok Sabha can be extended during National and it is left to the Parliament.
emergency for 1 year at a time for any length of time. • Representation of the People Act (RPA) 1951 provides
• Extension cannot continue beyond a period of 6 the term of a member to be 6 years.
• RPA 1951 empowers President to curtail term of members.
months after the emergency has ceased to operate.
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 2
MEMBERSHIP OF PARLIAMENT
DISQUALIFICATIONS
QUALIFICATIONS
• Citizen of India. • Holds any office of profit under Union or state.
• Make and subscribe to an oath or affirm- • Unsound mind and stands so declared by a
ation before the person authorised by the ACCORDING TO court.
election commission for this purpose. CONSTITUTION • Undischarged insolvent.
• Rajya Sabha: Not less than 30 years of age. • Not a citizen of India or voluntarily acquired the
• Lok Sabha: Not less than 25 years of age. citizenship of a foreign state or is under any
• Possess other qualifications prescribed by acknowledgement of allegiance to a foreign state.
Parliament.
• Disqualified under any law made by Parliament.
DISQUALIFICATIONS
• Found guilty of certain
QUALIFICATIONS election offences.
• Registered as an elector for a parliamentary • Convicted for any offence
constituency. resulting in imprisonment for 2 or more years. (Not
• For Rajya Sabha, member can be an elector valid for preventive detention law).
from any state. • Failed to lodge an account of his
• Member of a SC or ST in any state or UT, if he ACCORDING TO election expenses.
wants to contest a seat reserved for them. RPA 1951 • Any interest in government contracts,
• SC or ST can also contest a seat not reserved works or services.
for them. • Be a director or managing agent nor hold an
office of profit in a corporation in which the
government has at least 25% share.
• Dismissed from government
service for corruption or disloyalty to the State.
• Convicted for promoting enmity
DISQUALIFICATION ON between different groups or for the offence of
GROUND OF DEFECTION bribery.
• Punished for preaching and
• 10th Schedule of Constitution
practising social crimes such as untouchability,
• Final decision by the Chairman in the case
of Rajya Sabha and Speaker in the case of dowry and sati.
Lok Sabha (and not by the president of India) • Note: President’s decision is final on the question
• Decision is subject to judicial review (kihoto on any of the above disqualifications with opinion
Hollohan case 1992).
of the election commission.
Voluntary gives up the membership
1 of the political party on whose ticket he
Any independently elected
is elected to the House; 3 member joins any political party
Votes or abstains from voting in the
2 House contrary to any direction given Any nominated member joins any
by his political party; 4 political party after the expiry of six months
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 3
VACATING OF SEATS
According to RPA 1951,
• If elected to both the Houses, he must intimate within 10 days in desired House. In default, his seat
in Rajya Sabha becomes vacant.
1. DOUBLE • If a sitting member of one House and elected to other House, first House seat becomes vacant.
MEMBERSHIP • If a person is elected to two seats in a House, he should exercise his option for one. Otherwise,
both seats become vacant.
• If a person is elected for both Parliament and state legislature, his seat in Parliament becomes
vacant if he does not resign his seat in the state legislature within 14 days.
2. DISQUALIFI- • As specified in the Constitution.
CATION • Disqualification on the grounds of defection (10th Schedule).
• By writing to Chairman of Rajya Sabha or Speaker of Lok Sabha.
3. RESIGNATION • Chairman/ Speaker may not accept the resignation if he is satisfied that it is not voluntary or genuine.
• Member absent from all its meetings for a period of 60 days without house’s permission.
4. ABSENCE • 60 days does not include any period during which House is prorogued or adjourned.
Members vacate seat if :
• Election is declared void by the court
5. OTHER CASES • Expelled by the House
• Becomes President or Vice President or governor
Note: Constitution lays down no procedure to declare the election void. This matter is dealt by RPA
1951 which enables the high court to declare an election void and he can also appeal to the
To uphold the sovereignty and integrity of India
• President or some
person appointed by him for
this purpose
OATH OR
AFFIRMATION • MP cannot vote and To bear true faith and allegiance to the
participate in the proceedings Constitution of India
BY MP without taking oath and also
can not enjoy parliamentary
privileges and
immunities. To faithfully discharge the duty upon
which he is about to enter
SALARIES AND ALLOWANCES
Salaries and allowances of the
Salaries, Allowances No provision of pension Speaker and Deputy Speaker and the
Determined by and Pension of in Constitution, however Chairman and Deputy Chairman are
Parliament Members of Parliament Parliament has provided charged on the Consolidated Fund of India
Act, 1954 pension to the members. and are not subject to annual vote of
Parliament.
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 4
PRESIDING OFFICERS OF PARLIAMENT
LOK SABHA
SPEAKER OF LOK SABHA
• Elected by the Lok Sabha from amongst its members.
• Date of election fixed by President.
• Vacate his office in three cases:
1. ceases to be a member of Lok Sabha;
2. resigns by writing to the Deputy Speaker;
3. removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all then members of the Lok Sabha.
Such a resolution can be moved only after giving 14 days’ advance notice.
ELECTION • While removal is under consideration, speaker cannot preside at the sitting of the House,
AND TENURE however can speak and take part in the proceedings of the House and vote in the first instance.
• On dissolution of Lok Sabha, Speaker does not vacate his office and continues till the newly-
elected Lok Sabha meets.
• Speaker and the Deputy speaker do not make and subscribe any separate oath or affirmation.
• Provisions of Speaker and Deputy speaker originated from Government of India Act of 1919
(Montague-Chelmsford Reforms).
• Head of the Lok Sabha, and its representative.
• Guardian of powers and privileges of the members, the House and its committees.
ROLE OF • Principal spokesman of the House, and his decision in all Parliamentary matters is final.
SPEAKER • Chairman of the Business Advisory Committee, the Rules Committee and the General
Purpose Committee.
• Constitution of India,
SOURCE OF • Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business of Lok Sabha
POWERS • Parliamentary Conventions (residuary powers that are unwritten or unspecified in the Rules).
• Maintains order and decorum in the House.
• Final interpreter of the provisions of Constitution, Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business of Lok
Sabha, and parliamentary precedents, within the House.
• Adjourns the House or suspends the meeting in absence of a quorum.
• Casting vote in the case of a tie.
POWERS AND • Presides over a joint setting summoned by President
• Allow a ‘secret’ sitting of the House at the request of Leader of House.
FUNCTIONS OF • Decides whether a bill is a money bill or not and this decision is final.
SPEAKER • Decides the questions of disqualification under 10th Schedule. This decision is subject to judicial
review
• Acts as the ex-officio chairman of the Indian Parliamentary Group and conference of presiding officers
of legislative bodies in the country.
• Appoints the chairman of all the parliamentary committees of the Lok Sabha and supervises their
functioning.
• Provided with a security of tenure.
• Removed only by a resolution passed by the Lok Sabha by a special majority. Motion of removal need
support of at least 50 members.
• Salaries and allowances are fixed by Parliament and charged on Consolidated Fund of India.
INDEPENDENCE • His work and conduct cannot be discussed and criticised in the Lok Sabha except on a substantive
AND motion.
IMPARTIALITY • His powers of regulating procedure or conducting business or maintaining order in the House are not
subject to the jurisdiction of any Court.
• Placed at seventh rank, along with the Chief Justice of India.
• Speaker does not resign from the membership of his party on his election to the exalted office.
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 5
SPEAKER PRO TEM PANEL OF CHAIRPERSONS OF LOK SABHA DEPUTY SPEAKER OF LOK SABHA
• Nominated under the Rules of Lok Sabha. • Elected by the Lok Sabha itself from
• Temporary office.
amongst its members.
• President appoints a member of the Lok • Speaker nominates from amongst the
• Date of election fixed by the Speaker.
Sabha as the Speaker Pro Tem. members a panel of not more than 10 • Performs the duties of the Speaker’s
• Usually, the seniormost member. chairpersons. office when it is vacant or absent.
• President adminsters oath to Speaker • Any of them can preside over the House in • Presides over the joint sitting, in case the
the absence of the Speaker or the Deputy Speaker absent.
Pro Tem.
Speaker. • Not subordinate to the Speaker but
• Presides over the first sitting of the directly responsible to the House.
• Holds office until a new panel of
newly elected Lok Sabha. • Whenever appointed as a member of a
chairpersons is nominated.
• Administer oath to the new members. parliamentary committee, he automatically
• House can determine any person as a
• Enables the House to elect the new becomes its chairman.
speaker if no member of panel of
Speaker and ceases his office after new chairpersons is present. • Since the 11th Lok Sabha, consensus that
speaker elected. • They cannot preside over the House, when the Speaker comes from the ruling party
the office of the Speaker or the Deputy and Deputy Speaker goes to the main
opposition party.
Speaker is vacant then President appoints • Casting vote in the case of a tie
any member as a Speaker for the purpose. • Vacancy of Deputy speaker in 3 cases:
• 1. ceases to be a member of Lok Sabha;
• 2. Resigns by writing to the Speaker;
• 3. Removed by a resolution passed by a
majority of all the then members of the Lok
Sabha. Such a resolution can be moved
only after giving 14 days’ advance notice.
RAJYA SABHA
• Vice-president of India is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
• Presiding officer of the Rajya Sabha.
CHAIRMAN • Removed from his office only if removed from the office of the Vice-President.
OF RAJYA • Chairman is not a member of the House.
SABHA • Chairman also cannot vote in the first instance and has a casting vote in case of tie.
• Speaker has two special powers which are not enjoyed by the Chairman:
1. Speaker decides on money bill and his decision is final.
2. Speaker presides over a joint sitting.
• Elected by the Rajya Sabha itself from amongst its members.
DEPUTY • Not subordinate to the Chairman but directly responsible to the Rajya Sabha.
CHAIRMAN • Vacates office in any of three cases:
OF RAJYA 1. ceases to be a member of the Rajya Sabha;
SABHA 2. resigns by writing to the Chairman;
3. removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all the then members of the
Rajya Sabha. Such a resolution can be moved only after giving 14 days’ advance
notice.
PANEL
OF VICE-
CHAIR- • Nominated under the Rules of Rajya Sabha.
PERSONS • Chairman nominates from amongst the members a panel of vice-chairpersons.
OF RAJYA • Any one of them can preside over the House in the absence of the Chairman or the
SABHA Deputy Chairman.
• Each House of Parliament has separate secretarial staff of its own.
SECRETARIAT • Recruitment and service conditions regulated by Parliament.
OF • Headed by a secretary-general (permanent officer) appointed by the presiding
PARLIAMENT officer of the House.
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 6
LEADER IN PARLIAMENT
LEADER OF THE LEADER OF THE HOUSE
OPPOSITION IN BOTH HOUSES WHIP (LoH) IN BOTH HOUSES
• Provide a constructive criticism of the • Neither mentioned in • Exercises direct influence on the
policies of the government and to Constitution nor in the Rules of the conduct of business.
provide an alternative government. House nor in a Parliamentary • Not mentioned in the Constitution
• Leader of the largest Opposition party Statute. of India
having not less than 1/10th seats of • Based on the conventions of the • Mentioned under the Rules of
the total strength of the House. parliamentary government. Houses.
• Not mentioned in the Constitution • Both ruling or Opposition party has its • Prime minister, if he is a member of
of India own whip in the Parliament. the Lok Sabha.
• Mentioned under Parliamentary • Serve as an assistant floor leader. • Minister who is a member of the Lok
Statute • Responsibility of ensuring the Sabha and nominated by the Prime
• Accorded statutory recognition in attendance of his party members and Minister.
1977. securing their support. • ‘Leader of the House’ in the Rajya
• Regulates and monitors their Sabha is a minister who is a member
• Salary, allowances and other facilities
of the Rajya Sabha and nominated by
equivalent to cabinet minister. behaviour in the Parliament.
the prime minister.
• First time recognised in 1969. • Members are supposed to follow the
• Can also nominate a deputy leader of
• USA: ‘Minority leader’. directives given by the whip.
the House.
• Britain: ‘Shadow Cabinet’. Otherwise, disciplinary action
• USA: ‘Majority Leader’
can be taken.
SESSIONS OF PARLIAMENT Adjournment
• Suspends the work in a sitting for a specified time, which may be
TERMINATION OF SESSION
Summoning hours, days or weeks.
• Done by presiding officer of the House.
• President summons each House of
Adjournment Sine Die
Parliament to meet. • Terminating a sitting of Parliament for an indefinite period.
• Maximum gap between two sessions of • Adjourned without naming a day for reassembly.
• Done by presiding officer of the House.
Parliament cannot be more than 6 months.
• Does not affect the bills or any other business pending.
• There are usually 3 sessions in a year
Prorogation
o Budget Session (February to May); • Terminates a sitting and session of the House.
o Monsoon Session (July to September); • Done by the President.
• Does not affect the bills or any other business pending.
o Winter Session (November to December). • All pending notices lapse on prorogation and fresh notices have to be
• ‘Session’ of Parliament: period spanning given form the next session.
between the first sitting of a House and its Dissolution
• Ends the very life of the existing House and a new House is
prorogation. constituted after general elections are held.
• Recess: period spanning between the • Only the Lok Sabha is subject to dissolution.
• By way of Automatic dissolution (expiry of tenure) or whenever
prorogation of a House and its reassembly
• President decides to dissolve the House.
in a new session. • Dissolution is irrevocable
• All business including bills, motions, resolutions, notices, petitions
and so on pending before Lok Sabha or its committees lapse
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 7
QUORUM LANGUAGE IN
Minimum number of VOTING IN
PARLIAMENT
members required to be • Constitution has declare HOUSE
present in the House before it Hindi and English to be the All matters at any sitting of
can transact any business. languages for transacting either House or joint sitting of
It is 1/10th of the total number business in the Parliament both the Houses decided by a
of members in each House • Presiding officer can permit a majority of votes of the
including the presiding officer. member to address the House members present and voting,
If no quorum, then presiding in his mother-tongue. excluding the presiding officer.
officer either adjourn the • Official Languages Act 1963 Presiding officer of a House
House or suspend the allowed English to be caste vote in the case of an
meeting until there is continued along equality of votes.
a quorum. with Hindi.
RIGHTS OF
MINISTERS AND
ATTORNEY GENERAL
LAME-DUCK
• In addition to members of a
SESSION House, every minister and the
• Last session of the existing attorney general of India have the
Lok Sabha, after a new Lok right to speak and take part in the
Sabha has been elected. proceedings of either House, any joint
• Lame-ducks: members of sitting of both the Houses and any
the committee of Parliament of which he
existing Lok Sabha who could is a member, without
not get re-elected to the new being entitled to vote.
Lok Sabha • A minister can participate in the
proceedings of a House, of
which he is not a
member.
LAPSING OF BILLS ON DISSOLUTION
BILL THAT LAPSE BILL THAT DOES NOT LAPSE
• A bill not passed by the two Houses and if the president has
notified the holding of a joint sitting before the dissolution of
• A bill pending in the Lok Sabha lapses Lok Sabha.
(whether originating in the Lok Sabha or • A bill pending in the Rajya Sabha but not passed by the Lok
transmitted to it by the Rajya Sabha). Sabha does not lapse.
• A bill passed by the Lok Sabha but pending • A bill passed by both Houses but pending assent of the
president does not lapse.
in the Rajya Sabha lapses.
• A bill passed by both Houses but returned by the president
for reconsideration of Houses does not lapse.
www.visionias.in Vision IAS 8
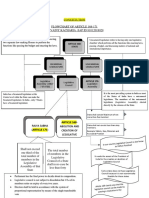
ARTICLES RELATED TO PARLIAMENT
OFFICERS OF
PARLIAMENT
GENERAL DISQUALIFICATIONS
A-89. The Chairman and Deputy Chairman of the OF MEMBERS
Council of States
A-79. Constitution of Parliament A-90. Vacation and resignation of, and removal from, the
office of Deputy Chairman A-101. Vacation of seats
A-80. Composition of the Council of States
A-91. Power of the Deputy Chairman or other person to A-102. Disqualifications
A-81. Composition of the House of the
perform the duties of the office of, or to act as, Chairman for membership
People A-103. Decision on questions
A-92. The Chairman or the Deputy Chairman not to
A-82. Readjustment after each census as to disqualifications of
preside while a resolution for his removal from office is
A-83. Duration of Houses of Parliament under consideration members
A-84. Qualification for membership of A-93. The Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the House of A-104. Penalty for sitting and
Parliament the People voting before making oath or
A-85. Sessions of Parliament, prorogation A-94. Vacation and resignation of, and removal from, the affirmation under Article 99 or
and dissolution offices of Speaker and Deputy Speaker when not qualified or when
A-86. Right of President to address and A-95. Power of the Deputy Speaker or other person to disqualified
send messages to Houses perform the duties of the office of, or to act as, Speaker
A-96. The Speaker or the Deputy Speaker not to preside
A-87. Special address by the President
while a resolution for his removal from office is under
A-88. Rights of Ministers and Attorney-
consideration
General as respects Houses A-97. Salaries and allowances of the Chairman and
Deputy Chairman and the Speaker and Deputy Speaker
A-98. Secretariat of Parliament
IMPORTANT CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT ACT (CAA)
• Extend reservation for SC and ST to Lok
Sabha and legislative bodies.
Froze the allocation Froze the allocation • Not extending the provision of
of seats till the year of seats till the year nominating Anglo Indians to Lok Sabha
2000 at the 1971 level. 2026 at the 1971 level. and legislative bodies
42nd CAA, 84th CAA, 104th CAA,
1976 2001 2020:
61st CAA, 87th CAA,
1988 2003
Voting age reduced Provided for the delimitation of constituencies on
from 21 to 18 years. the basis of 2001 census and not 1991 Census.
FOR DETAILED ENQUIRY, PLEASE CALL:
9
Vision IAS
www.visionias.in GUWAHATI
You might also like
- The 2016 Presidential Election-An Abundance of ControversiesDocument20 pagesThe 2016 Presidential Election-An Abundance of ControversiesHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- B.J. Thomas - Intermediate VocabularyDocument125 pagesB.J. Thomas - Intermediate VocabularyKlaudia R.92% (12)
- 20th CenturyDocument513 pages20th CenturyeclecticOTANo ratings yet
- 1950sDocument364 pages1950sfelipe-restum100% (1)
- Table of Quorum in ConstitutionDocument3 pagesTable of Quorum in ConstitutionAbigail Talosig BarandinoNo ratings yet
- Delegated LegislationDocument13 pagesDelegated LegislationrituNo ratings yet
- Nicolas-Lewis v. COMELECDocument2 pagesNicolas-Lewis v. COMELECVince MontealtoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Parliamentary CommitteesDocument16 pagesPresentation On Parliamentary Committeesposhita8singlaNo ratings yet
- The Union LegislatureDocument4 pagesThe Union LegislatureSukti Basu PaulNo ratings yet
- Ancient History - Sunya Prelims2024Notes KING R QUEEN PDocument115 pagesAncient History - Sunya Prelims2024Notes KING R QUEEN PRohitNo ratings yet
- 1500+ Nigerian Current Affairs Past Questions and Answers For Job Interviews & Aptitude TestsDocument35 pages1500+ Nigerian Current Affairs Past Questions and Answers For Job Interviews & Aptitude TestsSulyman Lukman OluwatoyinNo ratings yet
- List of 143 Chartered Cities in TheDocument6 pagesList of 143 Chartered Cities in Thejoshe_medNo ratings yet
- Parliament Part - 1Document9 pagesParliament Part - 1Aviral AkshatNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Jan-2024Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 29-Jan-2024aaryanandhasanu22No ratings yet
- Malaysia: Mary Jane Rose San Pedro Franzel Arenas Dave Lipayon Vannesa TanghalDocument22 pagesMalaysia: Mary Jane Rose San Pedro Franzel Arenas Dave Lipayon Vannesa TanghalMerceditas PlamerasNo ratings yet
- La Martiniere Girls' College: Class Viii AssignmentDocument12 pagesLa Martiniere Girls' College: Class Viii AssignmentPalakNo ratings yet
- Composition of Parliament by Nisha Rani 11 DDocument13 pagesComposition of Parliament by Nisha Rani 11 DNaisaNo ratings yet
- The Union ParliamentDocument39 pagesThe Union ParliamentDhruv MantriNo ratings yet
- Senate: Both The Senate and The House of Representatives Should Be Able ToDocument3 pagesSenate: Both The Senate and The House of Representatives Should Be Able ToEvan PavonNo ratings yet
- Important Points Class: X Sub: History & Civics Ls. 1 The Union ParliamentDocument4 pagesImportant Points Class: X Sub: History & Civics Ls. 1 The Union ParliamentAvangapuram JyothiNo ratings yet
- THE PARLIAMENT - Composition, Functions and FeaturesDocument10 pagesTHE PARLIAMENT - Composition, Functions and Featuresu2201151No ratings yet
- Complete Constituion Notes of Unit 2,3 and 4Document87 pagesComplete Constituion Notes of Unit 2,3 and 4Jitendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Parliament 1Document81 pagesParliament 1Abhimanyu RathodNo ratings yet
- Union LegislatureDocument49 pagesUnion LegislaturenosheenNo ratings yet
- Amendment of ConstitutionDocument1 pageAmendment of Constitutionznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Comparative Government UM LAW PERIOD 2Document13 pagesComparative Government UM LAW PERIOD 2laynamartensNo ratings yet
- L6 Legislatures - MC - Prelims - 2024 - 2 - Lyst9157Document12 pagesL6 Legislatures - MC - Prelims - 2024 - 2 - Lyst9157jankitkhareNo ratings yet
- Third MeetingDocument2 pagesThird Meetingcyrene rufoNo ratings yet
- Legislature TableDocument2 pagesLegislature Tableʀᴏɴ ᴄᴜɴᴀɴᴀɴ (ᜇᜓᜈ᜔ ᜃᜒᜈᜈᜌ)No ratings yet
- SURESH Full English Materials PDFDocument67 pagesSURESH Full English Materials PDFHari KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Article 6 HandoutDocument5 pagesArticle 6 HandoutJAVIER, Reinnier Jhiro C.No ratings yet
- ParliamentDocument14 pagesParliamentMOHD FAIZAN ALINo ratings yet
- Lesson - 11 Parliament of India: SummaryDocument4 pagesLesson - 11 Parliament of India: SummarySuvam DasNo ratings yet
- Abolition and Creation of Legislative Council Vidhan ParishadDocument2 pagesAbolition and Creation of Legislative Council Vidhan ParishadMansi KachariaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart 180622Document54 pagesComparison Chart 180622adithi gurkarNo ratings yet
- 5 Legislative BranchDocument25 pages5 Legislative BranchDannero Spotify ACCNo ratings yet
- The Union Parliament - NotesDocument11 pagesThe Union Parliament - NotesShubhendu KambleNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Usa and India - LegislatureDocument7 pagesComparative Study of Usa and India - LegislatureYoganjana SinghNo ratings yet
- Polity 2Document91 pagesPolity 2shqtkxh2No ratings yet
- Safari - 27-Nov-2023 at 4:14 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 27-Nov-2023 at 4:14 PMrishabh1907singhNo ratings yet
- Judiciary BranchDocument13 pagesJudiciary BranchDILGR3MED MANILABAYNo ratings yet
- LegislaturesDocument89 pagesLegislaturesFoundation IASNo ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument1 pageSubjective Questions: Short Answer Type QuestionsIbadul BariNo ratings yet
- Module IV - Parliament and Organs of GovernmentDocument19 pagesModule IV - Parliament and Organs of GovernmentKARTHIK MNo ratings yet
- Written Report (PhilGov)Document2 pagesWritten Report (PhilGov)Alano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Rajya Sabha: Arpita Sharma ClassesDocument14 pagesRajya Sabha: Arpita Sharma ClassesHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The Representation of Peoples Act 1Document9 pagesSalient Features of The Representation of Peoples Act 1vinamraNo ratings yet
- Polity Ebook IIDocument22 pagesPolity Ebook IIAjinkyaNo ratings yet
- PPT2Document105 pagesPPT2anahitagujral09876No ratings yet
- Parliament SlideShareDocument9 pagesParliament SlideShareRidhi SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan: The Local Government System in Pakistan Country Profile 2017-18Document5 pagesPakistan: The Local Government System in Pakistan Country Profile 2017-18SajidAliNo ratings yet
- The Parliament of IndiaDocument17 pagesThe Parliament of IndiaAbhijeet BhosaleNo ratings yet
- 14 - The State LegislatureDocument6 pages14 - The State LegislatureSahilNo ratings yet
- Ssee Unit 02Document41 pagesSsee Unit 02NayanNo ratings yet
- Parliament of IndiaDocument15 pagesParliament of IndiasruthymolsNo ratings yet
- Federal Governmet of PakistanDocument1 pageFederal Governmet of PakistanAhmed NasirNo ratings yet
- On Powers of Parliment of IndiaDocument17 pagesOn Powers of Parliment of Indiacifax83051No ratings yet
- Parliament: Kerala Legislative AssemblyDocument23 pagesParliament: Kerala Legislative Assemblyemil perumattomNo ratings yet
- India: The Local Government System in India Country Profile 2017-18Document7 pagesIndia: The Local Government System in India Country Profile 2017-18Suresh TirumalaNo ratings yet
- Class11 SST Ch-5Document18 pagesClass11 SST Ch-5Mudassir AkhterNo ratings yet
- Transcript Pre FinalsDocument21 pagesTranscript Pre FinalsVincent TanNo ratings yet
- Daily News Simplified - DNS NotesDocument14 pagesDaily News Simplified - DNS NotesTanuNo ratings yet
- 12 - The Union LegislatureDocument9 pages12 - The Union LegislatureSahil100% (4)
- The State LegislatureDocument8 pagesThe State LegislatureGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Parliament-Testbook NotesDocument10 pagesParliament-Testbook Notesrajhp54321No ratings yet
- Bicameralism&TopicsRelated To LegislatieOrgan - 230719Document13 pagesBicameralism&TopicsRelated To LegislatieOrgan - 230719Abhinandan AnandNo ratings yet
- House of Commons of CanadaDocument16 pagesHouse of Commons of CanadaAjay BharadvajNo ratings yet
- THE Legislative Branch: A Bill Becomes A LawDocument1 pageTHE Legislative Branch: A Bill Becomes A LawSebastian MichaelsonNo ratings yet
- ZRO Kolkata Rally Notification Soldier Technical Nursing Assistant 2024-25Document18 pagesZRO Kolkata Rally Notification Soldier Technical Nursing Assistant 2024-25RohitNo ratings yet
- Towards Freedom and Partition @upscplannerDocument12 pagesTowards Freedom and Partition @upscplannerRohitNo ratings yet
- L1 M.A.2 EthnomethodologyDocument4 pagesL1 M.A.2 EthnomethodologyRohitNo ratings yet
- Appraisal District Director's ManualDocument48 pagesAppraisal District Director's ManualcutmytaxesNo ratings yet
- Candidate Information SheetDocument6 pagesCandidate Information SheetAryan RahejaNo ratings yet
- Board of ElectionsDocument2 pagesBoard of ElectionsDaveNo ratings yet
- Sunrise Movement Dallas 2021 Endorsements Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesSunrise Movement Dallas 2021 Endorsements Press ReleaseBrendan BaumNo ratings yet
- Teo NEWDocument6 pagesTeo NEWMM GenicsNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For American Government Institutions and Policies 16th by WilsonDocument37 pagesTest Bank For American Government Institutions and Policies 16th by Wilsonvaultedsacristya7a11100% (26)
- Getting To Yes Learn To Negotiate Well Everything Is Based On NegotiationsDocument9 pagesGetting To Yes Learn To Negotiate Well Everything Is Based On NegotiationsLovre AnticNo ratings yet
- 25 Social Weather Assoc Vs ComelecDocument18 pages25 Social Weather Assoc Vs ComelecIshNo ratings yet
- Akbayan V. HRETDocument7 pagesAkbayan V. HRETCris Lloyd Alferez0% (1)
- American Democracy and Computer-Mediated Communication: A Case Study in MinnesotaDocument142 pagesAmerican Democracy and Computer-Mediated Communication: A Case Study in MinnesotaScott VorhNo ratings yet
- Donald Trump Personal Financial Disclosure (May 16, 2016)Document104 pagesDonald Trump Personal Financial Disclosure (May 16, 2016)Dank DrizzlerNo ratings yet
- Akshay ADocument36 pagesAkshay ASubrahmanya Sringeri0% (1)
- Ap Final Report PollpulseDocument35 pagesAp Final Report PollpulsesrihaasiniNo ratings yet
- Reynato Baytan v. ComelecDocument2 pagesReynato Baytan v. Comelecching113No ratings yet
- Daniel Crowe, General Election QuestionnaireDocument13 pagesDaniel Crowe, General Election QuestionnaireStatesman JournalNo ratings yet
- Kalyan Sir - Historical Background of The Indian ConstitutionDocument17 pagesKalyan Sir - Historical Background of The Indian ConstitutionSuresh Surya0% (1)
- Election Review - CCCVIIDocument1 pageElection Review - CCCVIIAnonymous Qn8AvWvxNo ratings yet
- Form 6Document6 pagesForm 6kaderseikh786No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law 1 Case DigestsDocument12 pagesConstitutional Law 1 Case DigestsAnonymous tCW5nDRONo ratings yet
- Thesun 2009-07-08 Page06 NG Accepts Property Agent OfferDocument1 pageThesun 2009-07-08 Page06 NG Accepts Property Agent OfferImpulsive collectorNo ratings yet
- Geeta RWA Rules and Bye LawsDocument27 pagesGeeta RWA Rules and Bye Lawsmahipalsharma302021No ratings yet
- American Democracy Now 4th Edition Harrison Test Bank 1Document25 pagesAmerican Democracy Now 4th Edition Harrison Test Bank 1jeffrey100% (34)