Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amendment of Constitution
Amendment of Constitution
Uploaded by
znx5fdtkkjOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amendment of Constitution
Amendment of Constitution
Uploaded by
znx5fdtkkjCopyright:
Available Formats
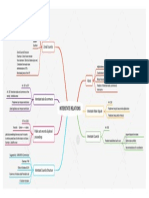
Power of parliament to ammend
constitution
Art. 368 part xx
Cannot ammend the provisions which form
★ keshavanand Bharati case the basic feature of the constitution
1973
Bill introduced -
only in parliament , not in SL
Minister or private member ( anyone )
Passed in each house - special majority
No joint sitting if disagreement
★ procedure for amendment
Federal features - Does not require prior permission of the
ratified by Legislatures of half of states by president
simple majority
Majority of the members of the house
President - MUST give his asscent Neither withhold nor return present at voting
Bill becomes act after asscent
Simple majority
Special majority
★ types
Special majority of the parliament and
ratification of half of SL
Establishment of New states
Formation of new states by altering areas ,
boundaries
Abolition / creation - LC
Second schedule
Amendment of Quorum in parliament
constitution Salaries and allowances - MP
Rules of procedure - P
Privileges of parliament , members and
committees
English language
Simple majority
No. Puisne judges in sc
Conferring more judiction power to sc
Official language
Citizenship - acquisition and termination
Elections - P , SL
Delimitation of constituencies
Union territories
5th schedule & 6 th schedule
Majority of toatal membership of each
house & majority of 2/3 members of each
house present at voting
Req, only at 3rd reading
Special majority
FR, DPSP , all other which not coverd before
Federal structure of polity
President election and its manner
Extent of executive power of union and
states
Special majority
No time limit - SC , HC
with in which state should give their
consent to bill Legislative powers - centre and states
GST
Any lists in 7th schedule
Representation of states in parliament
Parliament power to ammend constitution
You might also like
- 06-01-0001-INF-001 Cube Transportation and Handling Guidelines (Marked) - 1Document40 pages06-01-0001-INF-001 Cube Transportation and Handling Guidelines (Marked) - 1Luis Marín DíazNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Manajemen Logistik & Rantai PasokDocument30 pagesCase Study: Manajemen Logistik & Rantai PasokDede AtmokoNo ratings yet
- Business Combinations and Consolidations - Steven M. BraggDocument69 pagesBusiness Combinations and Consolidations - Steven M. BraggIbrahimDaasNo ratings yet
- Legislative Branch: Dewan Rakyat & Dewan NegaraDocument29 pagesLegislative Branch: Dewan Rakyat & Dewan NegaragaiaoNo ratings yet
- Sami HOUARBI - Codingame - (Scala) - PHP - #1-82088Document25 pagesSami HOUARBI - Codingame - (Scala) - PHP - #1-82088methnani chaima100% (2)
- L7 Executive - MC - Prelims - 2024 - 1 - Lyst9440Document7 pagesL7 Executive - MC - Prelims - 2024 - 1 - Lyst9440jankitkhareNo ratings yet
- Body Nature Appoint Ed by Members Office Term / Reappointment Removal Reports Special NotesDocument4 pagesBody Nature Appoint Ed by Members Office Term / Reappointment Removal Reports Special NotesPrynkaNo ratings yet
- 14 - The State LegislatureDocument6 pages14 - The State LegislatureSahilNo ratings yet
- Mindmaps 210607114739 PDFDocument3 pagesMindmaps 210607114739 PDFSatyanarayana BokamNo ratings yet
- Parliament Part - 1Document9 pagesParliament Part - 1Aviral AkshatNo ratings yet
- rd2 Poli OutlineDocument37 pagesrd2 Poli OutlinejefftafNo ratings yet
- Amendment + Basic Structure NotesDocument3 pagesAmendment + Basic Structure NotesSaloni YadavNo ratings yet
- 2 GS-2Document19 pages2 GS-2Rajat Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 5 Legislative BranchDocument25 pages5 Legislative BranchDannero Spotify ACCNo ratings yet
- Features of ConstitutionDocument1 pageFeatures of Constitutionznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- SKETCHY Notes - StatCon (Finals Only)Document33 pagesSKETCHY Notes - StatCon (Finals Only)Angela Bianca MiraNo ratings yet
- Interstate Relations: Zonal CouncilsDocument1 pageInterstate Relations: Zonal CouncilsVijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Amendment NewDocument29 pagesEighteenth Amendment NewRabia JavedNo ratings yet
- Table of Quorum in ConstitutionDocument3 pagesTable of Quorum in ConstitutionAbigail Talosig BarandinoNo ratings yet
- Separature of PowerDocument3 pagesSeparature of PowerbastiNo ratings yet
- Duuaunausdui: The Union ParliamentDocument15 pagesDuuaunausdui: The Union Parliamentsarah prakashNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Bodies PDFDocument13 pagesConstitutional Bodies PDFVip TopNo ratings yet
- L6 Legislatures - MC - Prelims - 2024 - 2 - Lyst9157Document12 pagesL6 Legislatures - MC - Prelims - 2024 - 2 - Lyst9157jankitkhareNo ratings yet
- Procedure of Amendment of The ConstitutionDocument3 pagesProcedure of Amendment of The ConstitutionSakshamNo ratings yet
- Concept of GovernmentDocument14 pagesConcept of GovernmentdyesaNo ratings yet
- One Pager Pdfresizer - Com-Pdf-ResizeDocument2 pagesOne Pager Pdfresizer - Com-Pdf-Resize29sfw4rvjmNo ratings yet
- ExecDocument2 pagesExecHemsley Battikin Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- 10civ UDocument14 pages10civ UJikan KamuraNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3: State GovernmentDocument14 pagesUnit - 3: State GovernmentkvinothscetNo ratings yet
- GovernorDocument9 pagesGovernorSuyash BhosaleNo ratings yet
- VOWIAS - Vision - PreTest-02-SummaryDocument20 pagesVOWIAS - Vision - PreTest-02-Summaryrahul kumarNo ratings yet
- AmendmentDocument12 pagesAmendmentShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Amendment NewDocument24 pagesEighteenth Amendment Newconfidential fourNo ratings yet
- Article VI (6) of The Philippine Constitution ReviewerDocument4 pagesArticle VI (6) of The Philippine Constitution ReviewerMigoy DANo ratings yet
- Trancription Art 6Document17 pagesTrancription Art 6Rafael AbedesNo ratings yet
- Legal Studies Unit 4 PDFDocument7 pagesLegal Studies Unit 4 PDFabdullahi mohamedNo ratings yet
- J&K Act 2019Document11 pagesJ&K Act 2019Rahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Legislative Department: Legislative Power Power To Propose, Enact, Amend and Repeal LawsDocument4 pagesLegislative Department: Legislative Power Power To Propose, Enact, Amend and Repeal LawsArn DCNo ratings yet
- Legislative Branch Quiz Study GuideDocument2 pagesLegislative Branch Quiz Study Guideapi-259307817No ratings yet
- Difference Between Unicameral and Bicameral LegislatureDocument8 pagesDifference Between Unicameral and Bicameral Legislatureashley brownNo ratings yet
- Types of Amendments in Indian Constitution Indian Polity NotesDocument2 pagesTypes of Amendments in Indian Constitution Indian Polity NotesShiv KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.3 US Senate, House of Representatives, Congress and JudiciaryDocument3 pages3.3 US Senate, House of Representatives, Congress and JudiciarySohailNo ratings yet
- L3 Magna Carta Mains 2023Document25 pagesL3 Magna Carta Mains 2023vamshiNo ratings yet
- Timor Leste System of GovernmentDocument2 pagesTimor Leste System of GovernmentvitoderNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Amendment & Historical PerspectivesDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Amendment & Historical PerspectivesShruti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Government in The States State LegislatureDocument12 pagesGovernment in The States State LegislaturegrsrikNo ratings yet
- Except To The Extent Reserved To The People by The Provision OnDocument11 pagesExcept To The Extent Reserved To The People by The Provision OnDaphne BarceNo ratings yet
- Article ViDocument11 pagesArticle ViJessa Mae CutarraNo ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument1 pageSubjective Questions: Short Answer Type QuestionsIbadul BariNo ratings yet
- Bueno, Kier Benedict Joseph S. SS10/A2Document1 pageBueno, Kier Benedict Joseph S. SS10/A2Jp Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Law - RevisionDocument6 pagesLaw - RevisionKotoko IrieNo ratings yet
- Union LegislatureDocument49 pagesUnion LegislaturenosheenNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Indian Constitution - UPSC Polity Notes - Rau's IASDocument19 pagesSalient Features of Indian Constitution - UPSC Polity Notes - Rau's IASaashirwad701No ratings yet
- Written Report (PhilGov)Document2 pagesWritten Report (PhilGov)Alano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Parliament Part 1 @upscplannerDocument9 pagesParliament Part 1 @upscplannerRohitNo ratings yet
- Welcome!: Episode 01Document19 pagesWelcome!: Episode 01Hhnnn BbbnnNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionsDocument25 pagesConstitutionsifatima9852No ratings yet
- Amendment To ConstitutionDocument6 pagesAmendment To ConstitutionPalakNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document1 pageModule 6Reian TubisNo ratings yet
- Consti 1 - Art. VI-VIII MATRIXDocument9 pagesConsti 1 - Art. VI-VIII MATRIXCaryl TinaeNo ratings yet
- Constitution Lecture 5 105393851Document23 pagesConstitution Lecture 5 105393851Himanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Constitution As A Living DocumentDocument10 pagesConstitution As A Living DocumentKashvi YadavNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument3 pagesUntitled NotebookPath NaruenatNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 2Document14 pagesUnit-5 2znx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Features of ConstitutionDocument1 pageFeatures of Constitutionznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Basic StructureDocument1 pageBasic Structureznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Coral Reef - WikipediaDocument35 pagesCoral Reef - Wikipediaznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- Pundan SinghDocument93 pagesPundan Singhznx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- It Is Required To Design A Helical Compression Spring Subjected To Maximum Force of 245Document4 pagesIt Is Required To Design A Helical Compression Spring Subjected To Maximum Force of 245Satish JangraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214509520300905 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2214509520300905 MainIngedemy EducacionNo ratings yet
- Accounting - QuizDocument3 pagesAccounting - QuizAmelynieNo ratings yet
- CJV30 Mechanical Drawing Supplement Version D500388 Ver.2.3b PDFDocument7 pagesCJV30 Mechanical Drawing Supplement Version D500388 Ver.2.3b PDFaigarsNo ratings yet
- Shores Motel LetterDocument4 pagesShores Motel Letteral_crespoNo ratings yet
- Polymers and Its TypesDocument9 pagesPolymers and Its TypesZarnain khanNo ratings yet
- 29 Exhaust Gas TurbochargerDocument79 pages29 Exhaust Gas TurbochargerYuri Duri50% (2)
- Panther VDocument4 pagesPanther VFelipe Fantinel100% (1)
- p91 PDFDocument1 pagep91 PDFpenelopegerhardNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Doc Amol Donerao Final ProjectDocument91 pagesHyundai Doc Amol Donerao Final ProjectamoldoneraoNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk (2017) Claimed ''AI Will Be The Best or Worst Thing Ever For Humanity''. Student's Name: University: Course: Tutor: DateDocument7 pagesElon Musk (2017) Claimed ''AI Will Be The Best or Worst Thing Ever For Humanity''. Student's Name: University: Course: Tutor: DateOle Sarbabi Meleji EvansNo ratings yet
- Fargo DTC550 Service Manual PDFDocument614 pagesFargo DTC550 Service Manual PDFnelutuanv-1No ratings yet
- ISO 4427-5 2007 (E) - Character PDF Document PDFDocument12 pagesISO 4427-5 2007 (E) - Character PDF Document PDFgustavoNo ratings yet
- Rational Choice Theory Module1Document2 pagesRational Choice Theory Module1Tam Gerald Calzado80% (5)
- PLDT v. City of Bacolod, G.R. No. 149179, July 15, 2005Document7 pagesPLDT v. City of Bacolod, G.R. No. 149179, July 15, 2005JamieNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Lecture DepreciationDocument20 pagesEngineering Economy Lecture DepreciationMuhammadMahmoudAbdelNabyNo ratings yet
- Vendor QualificationDocument2 pagesVendor QualificationDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- The Bridge, March 20, 2014Document24 pagesThe Bridge, March 20, 2014The BridgeNo ratings yet
- 8510 - LM-80 XLamp XP-G2 Rev 9Document54 pages8510 - LM-80 XLamp XP-G2 Rev 9Amr AbdelmoatamadNo ratings yet
- E-283 (2) Gondi 930K PDFDocument1 pageE-283 (2) Gondi 930K PDFLuis Manuel CastilloNo ratings yet
- TUV India Training Academy - Online Training Calendar - Uptill 3oth Sept 2023Document9 pagesTUV India Training Academy - Online Training Calendar - Uptill 3oth Sept 2023Janarthanan LaxmananNo ratings yet
- CMS Cash Pooling 072013Document88 pagesCMS Cash Pooling 072013malvert91No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument22 pagesAssignmentVishnupriya Sunil100% (1)
- Lifting GuideDocument59 pagesLifting GuideAnandababuNo ratings yet
- SW Radio PDFDocument5 pagesSW Radio PDFAhmed BoubakerNo ratings yet