Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UN Conventions
Uploaded by
aanjnay12340 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesOriginal Title
UN Conventions (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesUN Conventions
Uploaded by
aanjnay1234Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
UN Conventions
● The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
(UNCLOS)
○ It is an international agreement that establishes guidelines for
businesses, the environment, and the management of marine
natural resources.
○ UNCLOS became effective in the year 1994 and later in the year
2016, UNCLOS was joined by 167 countries and the European
Union.
○ The International Tribunal for the Law of the
Sea(ITLOS)
■ It is an independent judicial body that adjudicates disputes arising out of the
convention (UNCLOS).
■ It was created by the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea which was signed
at Jamaica on the 10th of December 1982.
■ The convention became effective on 16th November 1994.
● The United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity
(UNCBD)
○ It is a United Nations treaty that is responsible for the
conservation of Biological Diversity around the world.
○ It is a multilateral treaty opened for signature at the Earth
Summit in Rio De Janeiro in 1992. It is a key document
regarding sustainable development.
○ 196 countries are a party to the CBD.
○ India is also a party to the Convention. India ratified it in 1994.
■ The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 was enacted for giving
effect to the provisions of the Convention.
■ To implement the provisions of the Act, the government
established the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) in
2003. The NBA is a statutory body.
● The Montreal Protocol
○ It is on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer is an
important Multilateral Agreement regulating the production,
consumption, and emissions of ozone-depleting substances
○ Signed in 1987
○ Came into force in 1989
○ The Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer
was signed in 1985 under which UN member countries
recognized the importance of curbing damage to the ozone
layer. As per the Convention’s provisions, countries agreed to
adopt the Montreal Protocol to further the goals of the Vienna
Convention.
○ It has been ratified by 197 Parties (196 member states of the
UN plus the EU) making it the first United Nations treaty to be
ratified by every country in the world.
○ India became a signatory to the Montreal Protocol in 1992.
○ The Kigali Agreement is an amendment to the Montreal
Protocol
■ The Kigali Amendment is the 8th amendment.
■ It happened during the 28th Meeting of Parties when the
197 member countries signed the agreement to amend
the Montreal Protocol.
■ It is so named because it happened in Kigali, the capital of
Rwanda in October 2016.
■ According to the terms of the Amendment, the signing
countries are expected to decrease the manufacture and
usage of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) by about 80-85%
from their baselines until 2045.
■ This will curb global warming (by arresting global average
temperature rise to 0.5 degrees Celsius) by the year 2100.
■ The agreement aims to phase down HFCs by reducing its
manufacture and consumption.
● UNCCD stands for United Nations Convention to Combat
Desertification.
○ Established in 1994, UNCCC is a sole legally binding
environment convention that links development and
environment to sustainable land management.
○ It became effective in 1996 after receiving 50 ratifications.
○ The 14th Conference of Parties (COP) to the UNCCD was held
in India in 2019.
■ The conference which was held in Greater Noida had the
theme, “Restore Land, Sustain Future”.
● The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate
Change(UNFCC)
○ In Rio de Janeiro in Brazil,1992
○ It came into force on 21st March 1994. It has been ratified by
197 countries and is called to have a near-universal
membership.
○ The latest, COP26, was scheduled to be held in Glasgow,
Scotland in November 2020, but was postponed due to the
COVID-19 pandemic.
● The Minamata Convention
○ The Minamata Convention on Mercury is an important
international treaty intended to protect health and the
environment from the adverse effects of mercury.
○ The Convention was signed in 2013 in Japan and entered into
force in 2017.
● Kyoto Protocol
○ It is an international treaty to reduce greenhouse gas
emissions.
○ Kyoto Protocol applies to 6 greenhouse gases; carbon dioxide,
methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons,
sulfur hexafluoride.
○ It is an extension to the 1992 UNFCCC.
○ It was adopted in Kyoto, Japan on 11 December 1997.
○ came into force on 16 February 2005.
○ India was exempted from legally binding commitments on
greenhouse gas emissions.
● The United Nations Conference on Environment and
Development (UNCED)
○ It is also known as the Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, Rio
Summit, Rio Conference, and Earth Summit (Portuguese:
ECO92), was a major United Nations conference held in Rio de
Janeiro (Brazil) from 3 to 14 June 1992.
○ 172 governments participated, with 116 sending their heads of
state or government.
○ The Rio Summit 1992 is also called the Earth Summit. This summit led to the
development of the following documents:
■ Rio Declaration on Environment and Development
■ Agenda 21
■ Forest Principles
○ The first document called the Rio Declaration, in short,
contained 27 principles that were supposed to guide countries
in future sustainable development. Agenda 21 is an action plan
concerning sustainable development, but it is non-binding. The
Forest Principles is formally called ‘Non-Legally Binding
Authoritative Statement of Principles for a Global Consensus on
the Management, Conservation and Sustainable Development
of All Types of Forests’. It makes many recommendations for
conservation and sustainable development forestry and is
non-binding.
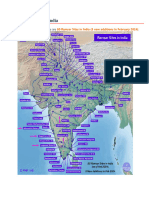
● Ramsar Convention
○ It is called the Convention on Wetlands
○ It was adopted in the city of Iran, Ramsar in 1971.
○ It came into force in 1975.
○
Sl. Name of Site State Location Date of Area
No. Declaration (in Sq.
km.)
1 Asan Conservation Reserve Uttarakhand 21.7.2020 4.444
2 Asthamudi Wetland Kerala 19.8.2002 614
3 Beas Conservation Reserve Punjab 26.9.2019 64.289
4 Bhitarkanika Mangroves Orissa 19.8.2002 650
5 Bhoj Wetlands Madhya Pradesh 19.8.2002 32.01
6 Chandertal Wetland Himachal 8.11.2005 0.49
Pradesh
7 Chilka Lake Orissa 1.10.1981 1165
8 Deepor Beel Assam 19.8.2002 40
9 East Kolkata Wetlands West Bengal 19.8.2002 125
10 Harike Lake Punjab 23.3.1990 41
11 Hokera Wetland Jammu and 8.11.2005 13.75
Kashmir
12 Kabartal Wetland Bihar 21.07.2020 26.20
13 Kanjli Lake Punjab 22.1.2002 1.83
14 Keoladeo Ghana NP Rajasthan 1.10.1981 28.73
15 Keshopur-Miani Community Punjab 26.9.2019 3.439
Reserve
16 Kolleru Lake Andhra Pradesh 19.8.2002 901
17 Loktak Lake Manipur 23.3.1990 266
18 Lonar Lake Maharashtra 22.7.2020 4.27
19 Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary Gujarat 24.09.2012 120
20 Nandur Madhameshwar Maharashtra 21.6.2019 14.37
21 Nangal Wildlife Sanctuary Punjab 26.9.2019 1.16
22 Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary Uttar Pradesh 19.9.2019 2.246
23 Parvati Agra Bird Sanctuary Uttar Pradesh 2.12.2019 7.22
24 Point Calimere Wildlife and Tamil Nadu 19.8.2002 385
Bird Sanctuary
25 Pong Dam Lake Himachal 19.8.2002 156.62
Pradesh
26 Renuka Wetland Himachal 8.11.2005 0.2
Pradesh
27 Ropar Lake Punjab 22.1.2002 13.65
28 Rudrasagar Lake Tripura 8.11.2005 2.4
29 Saman Bird Sanctuary Uttar Pradesh 2.12.2019 52.63
30 Samaspur Bird Sanctuary Uttar Pradesh 3.10.2019 79.94
31 Sambhar Lake Rajasthan 23.3.1990 240
32 Sandi Bird Sanctuary Uttar Pradesh 26.9.2019 30.85
33 Sarsai Nawar Jheel Uttar Pradesh 19.9.2019 16.13
34 Sasthamkotta Lake Kerala 19.8.2002 3.73
35 Sunderbans Wetland West Bengal 30.1.2019 4230
36 Surinsar-Mansar Lakes Jammu and 8.11.2005 3.5
Kashmir
37 Sur Sarovar Uttar Pradesh 21.8.2020 4.31
38 Tso Kar Wetland Complex Ladakh 17.11.2020 95.77
39 Tsomoriri Lake Jammu and 19.8.2002 120
Kashmir
40 Upper Ganga River Uttar Pradesh 8.11.2005 265.9
(Brijghat to Narora Stretch)
41 Vembanad Kol Wetland Kerala 19.8.2002 1512.5
42 Wular Lake Jammu & 23.3.1990 189
Kashmir
43 Bhindawas wildlife sanctuary Haryana 2021
44. Sultanpur National Park Haryana 2021
45 Thol Lake Wildlife Sanctuary Gujrat 2021
46 Wadhvana Wetland-[[ Gujrat 2021
You might also like
- Catfish Farmers HandbookDocument40 pagesCatfish Farmers HandbookHenry Odunlami100% (1)
- Absorption Chiller PDFDocument54 pagesAbsorption Chiller PDFmiraNo ratings yet
- Submarine Cables Protection and - Utpal Kumar Raha, Raju K. DDocument192 pagesSubmarine Cables Protection and - Utpal Kumar Raha, Raju K. DHuy Thông Nguyễn100% (2)
- Cauvery River Water DisputeDocument14 pagesCauvery River Water DisputeArhum KhanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Delight in ArchitectureDocument108 pagesThermal Delight in Architecturekyle100% (1)
- Before The National Green TribunalDocument20 pagesBefore The National Green TribunaladhiNo ratings yet
- Norway Clean Energy Invest ASDocument1 pageNorway Clean Energy Invest ASAserNo ratings yet
- Page 2 of 4 (Semi-Final Examination in TN@CT)Document4 pagesPage 2 of 4 (Semi-Final Examination in TN@CT)Alvin ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Greenhouse Production in Alberta 2002Document58 pagesCommercial Greenhouse Production in Alberta 2002Javiercm10No ratings yet
- Sand Stories: Surprising Truths about the Global Sand Crisis and the Quest for Sustainable SolutionsFrom EverandSand Stories: Surprising Truths about the Global Sand Crisis and the Quest for Sustainable SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Wetland Sites: Significance of WetlandsDocument5 pagesRamsar Wetland Sites: Significance of Wetlandsmadhu anvekarNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of India (Assignment Task)Document28 pagesWetlands of India (Assignment Task)Cryogen101 TheAssassinNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Site in IndiaDocument5 pagesRamsar Site in IndiaRana MondalNo ratings yet
- Forest and WL Acts, SriPKSharmaIFS (Retd)Document23 pagesForest and WL Acts, SriPKSharmaIFS (Retd)Shiv RamNo ratings yet
- Legal ProvisionsDocument18 pagesLegal ProvisionsNauraa JeenaNo ratings yet
- Treaties and Agreements PPSCDocument3 pagesTreaties and Agreements PPSCMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Environment LawDocument17 pagesEnvironment LawUtkarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Acfrogbpy5 Yw8xfdoyxesexpiizeaibt7 Kpab9sutak1s1stfo4n6pyxk4n R4oppjz6aa6che1fjothmmqfj04 Pxrfe0thdeg7wecs8vclwk Bnqpqtx3rt4v Unssa0hw8e347s3o1wubf2Document46 pagesAcfrogbpy5 Yw8xfdoyxesexpiizeaibt7 Kpab9sutak1s1stfo4n6pyxk4n R4oppjz6aa6che1fjothmmqfj04 Pxrfe0thdeg7wecs8vclwk Bnqpqtx3rt4v Unssa0hw8e347s3o1wubf2MJ ColumbresNo ratings yet
- 17 October 2020Document24 pages17 October 2020buntyhibuntyNo ratings yet
- Conventions: Govind TiwariDocument29 pagesConventions: Govind TiwariabcdefNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Convention1Document5 pagesRamsar Convention1DEEPAK VERMANo ratings yet
- Environment Studies - 12:00 PM, 5 February 2019Document8 pagesEnvironment Studies - 12:00 PM, 5 February 2019Niranjan PatilNo ratings yet
- PRATHAM CLAT Booster-10Document6 pagesPRATHAM CLAT Booster-10Arpan KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Both Government and Civil Society OrganisationsDocument8 pagesBoth Government and Civil Society OrganisationsPranksNo ratings yet
- Environment and Ecology 2022 CA (2021 Revision) - 221220 - 162012Document80 pagesEnvironment and Ecology 2022 CA (2021 Revision) - 221220 - 162012kavleen kourNo ratings yet
- Environmental Laws by IntenseDocument103 pagesEnvironmental Laws by IntenseKayrelle GuansingNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Sitesinindia2022Document8 pagesRamsar Sitesinindia2022Samrat MisraNo ratings yet
- ES 520: Environmental Policy and Planning: Masters in Environmental Science ProgramDocument29 pagesES 520: Environmental Policy and Planning: Masters in Environmental Science ProgramScarlet SudipraNo ratings yet
- IMP SummitsDocument1 pageIMP Summitsmaulik07No ratings yet
- District Survey Report For Gravel, Laterite, Red Soil and Savudu Cuddalore DistrictDocument49 pagesDistrict Survey Report For Gravel, Laterite, Red Soil and Savudu Cuddalore DistrictmehNo ratings yet
- December 2021 - EnglishDocument36 pagesDecember 2021 - EnglishPappoo KothariNo ratings yet
- 25 Year Environment Plan Annex3Document5 pages25 Year Environment Plan Annex3melesray2No ratings yet
- Environment Convention and ProtocolsDocument20 pagesEnvironment Convention and ProtocolsRaksha shanNo ratings yet
- Convenção de Ramsar Sobre Terras HúmidasDocument116 pagesConvenção de Ramsar Sobre Terras HúmidasBernabé Alexandre FondoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Laws and Regulations Disajikan Oleh Ridwan MahzunDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Laws and Regulations Disajikan Oleh Ridwan Mahzunnopri andiNo ratings yet
- Manual of Environemt Laws Inpaksitan: Pakistan Environmental Protection Act, 1997Document8 pagesManual of Environemt Laws Inpaksitan: Pakistan Environmental Protection Act, 1997Richard LongNo ratings yet
- Handbook 4: Integrating Wetland Conservation and Wise Use Into River Basin ManagementDocument45 pagesHandbook 4: Integrating Wetland Conservation and Wise Use Into River Basin ManagementDaisyNo ratings yet
- Convention On Wetland1Document3 pagesConvention On Wetland1drake12345No ratings yet
- Environment LegislationsDocument48 pagesEnvironment LegislationsHyma KavyaNo ratings yet
- Matsya Bharat April-June 2017Document8 pagesMatsya Bharat April-June 2017Saikat MajiNo ratings yet
- Environment Reckoner1 PDFDocument159 pagesEnvironment Reckoner1 PDFsony priya valluruNo ratings yet
- Ecology Current Affairs GKTODAYDocument5 pagesEcology Current Affairs GKTODAYGurpreet Sidhu0% (1)
- Ramsar Sites 2022Document46 pagesRamsar Sites 2022c2vivek_p1481No ratings yet
- North South University: Law of The Sea and International River LawDocument92 pagesNorth South University: Law of The Sea and International River LawSheikh vlogsNo ratings yet
- NEW AGE IAS BPSC 65th Crash Course: Major Conferences, Conventions & ProtocolsDocument6 pagesNEW AGE IAS BPSC 65th Crash Course: Major Conferences, Conventions & ProtocolsICS InstituteNo ratings yet
- Environmanetal Law Sneha KapoorDocument25 pagesEnvironmanetal Law Sneha KapoorSneha KapoorNo ratings yet
- Multilateral Environmental AgreementsDocument4 pagesMultilateral Environmental AgreementsNikhat HinaNo ratings yet
- World Wetland Day Celebration Report-2008: September 2016Document27 pagesWorld Wetland Day Celebration Report-2008: September 2016Jonel HernandezNo ratings yet
- December 2018 Current AffairsDocument34 pagesDecember 2018 Current AffairsMakNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Sites 2022 - 10228757 - 2022 - 08 - 22 - 03 - 51Document53 pagesRamsar Sites 2022 - 10228757 - 2022 - 08 - 22 - 03 - 51Koushik BiswasNo ratings yet
- MackieDocument5 pagesMackieMarvin kakindaNo ratings yet
- International Conventions On NRMDocument13 pagesInternational Conventions On NRMacharya.venishaNo ratings yet
- Before The Hon'Ble Supreme Court of Sindia Original Writ Jurisdiction Public Interest LitigationDocument17 pagesBefore The Hon'Ble Supreme Court of Sindia Original Writ Jurisdiction Public Interest LitigationVILJOEN AJITNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Convention: in India There 23 Sites Are There. in Ap Only One KollaruDocument2 pagesRamsar Convention: in India There 23 Sites Are There. in Ap Only One KollaruHearty AmarNo ratings yet
- Desire TO Learn: Environmental Conventions and ProtocolDocument27 pagesDesire TO Learn: Environmental Conventions and ProtocolKunal GautamNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Sites in IndiaDocument12 pagesRamsar Sites in IndiaUmesh PratapNo ratings yet
- 1766ADocument23 pages1766ABrijeshNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs PDF Plans: Help Us To Grow & Provide Quality ServiceDocument22 pagesCurrent Affairs PDF Plans: Help Us To Grow & Provide Quality ServiceRajpal Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Environment 365 Module 2022Document99 pagesEnvironment 365 Module 2022Ashish RaiNo ratings yet
- International Environmental Law: Dr. Raju KDDocument21 pagesInternational Environmental Law: Dr. Raju KDRaju KDNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument17 pagesAcid RainVenkat PalaganiNo ratings yet
- Sydenham College of Commerce and EconomicsDocument30 pagesSydenham College of Commerce and EconomicssaniyaprashantkNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Sites in IndiaDocument21 pagesRamsar Sites in Indianaziakhankhan17No ratings yet
- Environmental Law RadhaDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Law RadharadhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Forest Act 2002Document93 pagesForest Act 2002TFS CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- ACOPS Yearbook 1986-87: Advisory Committee on Pollution of the Sea, LondonFrom EverandACOPS Yearbook 1986-87: Advisory Committee on Pollution of the Sea, LondonAdvisory Committee on PollutioNo ratings yet
- Ca 4 68Document18 pagesCa 4 68aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Summits 2021-22Document3 pagesSummits 2021-22aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Legal - 2Document5 pagesLegal - 2aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Science 1Document4 pagesScience 1aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Election and Representation Part 2Document37 pagesElection and Representation Part 2aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- PU Mock 5 - QDocument8 pagesPU Mock 5 - Qaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Mock PU-1 2023 - QDocument9 pagesMock PU-1 2023 - Qaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- CLAT 2023 Current Affairs Repository QuestionsDocument172 pagesCLAT 2023 Current Affairs Repository Questionsaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Ashiq Sulthan V State of KeralaDocument6 pagesAshiq Sulthan V State of Keralaaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- The Law and The LawyersDocument21 pagesThe Law and The Lawyersaanjnay1234No ratings yet
- TP 2019 6 SCC 512 518 Aanjnay1234 Gmailcom 20240302 073410 1 7Document7 pagesTP 2019 6 SCC 512 518 Aanjnay1234 Gmailcom 20240302 073410 1 7aanjnay1234No ratings yet
- Lecture-12 Practice-3Document5 pagesLecture-12 Practice-3Muhammad ZainNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Lisa Henthorne, Buddy BoysenDocument11 pagesDesalination: Lisa Henthorne, Buddy Boysenmona aminNo ratings yet
- Circular 24-BPS Model United Nations 2022Document1 pageCircular 24-BPS Model United Nations 2022King VictoryNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - 5 - Unit HydrographDocument8 pagesUnit 3 - 5 - Unit Hydrographtom meeteiNo ratings yet
- VALVESDocument19 pagesVALVESArie amNo ratings yet
- Sentence Structures in Writing Task 2Document12 pagesSentence Structures in Writing Task 2Jewel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Act 16Document1 pageAct 16Jaja MarquezNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs: Energy Crisis in PakistanDocument10 pagesCurrent Affairs: Energy Crisis in PakistanArsalan Khan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Analyses On Kashmir Tourism SiteDocument15 pagesSustainability Analyses On Kashmir Tourism SiteAbir HasanNo ratings yet
- Asia-Pacific Network For Sustainable Forest Management and RehabilitationDocument14 pagesAsia-Pacific Network For Sustainable Forest Management and RehabilitationErin NatiaNo ratings yet
- The Drying of Lake Urmia As A Case of The "Aralism" Concept in Totalitarian SystemsDocument21 pagesThe Drying of Lake Urmia As A Case of The "Aralism" Concept in Totalitarian SystemsPremier PublishersNo ratings yet
- Planning and Design of Water Supply System For Zone - I of Village BorgaonDocument8 pagesPlanning and Design of Water Supply System For Zone - I of Village BorgaonLuisAtocheGanozaNo ratings yet
- Floor Finishes BCM 3Document29 pagesFloor Finishes BCM 3VarunNo ratings yet
- Bu 1 - Plumbing and SanitaryDocument12 pagesBu 1 - Plumbing and SanitarySharmaine Danica MarceloNo ratings yet
- Erythrina - Poeppigiana ICRAFDocument5 pagesErythrina - Poeppigiana ICRAFAndres TelloNo ratings yet
- Name: Nurul Shuhadah Binti Mohd Annuar STUDENT ID: 2018440816 Class: Bae6B Subject: Environmental Law (Law 573)Document5 pagesName: Nurul Shuhadah Binti Mohd Annuar STUDENT ID: 2018440816 Class: Bae6B Subject: Environmental Law (Law 573)nurul shuhadahNo ratings yet
- Guide To Artificial Perches For BirdsDocument9 pagesGuide To Artificial Perches For BirdsOmar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- World Green Building Council - KUNALDocument13 pagesWorld Green Building Council - KUNALkrishnadevuthale88No ratings yet
- Brochure Commerciale DGT UkDocument33 pagesBrochure Commerciale DGT UkRahayu HandayaniNo ratings yet
- New Techniques of Erosion Controls On Hill RoadsDocument25 pagesNew Techniques of Erosion Controls On Hill RoadsAyush GargNo ratings yet
- FIFA World Cup Qatar 2022™ Sustainability PolicyDocument1 pageFIFA World Cup Qatar 2022™ Sustainability PolicyVũ Nhật MinhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CirculationDocument21 pagesIntroduction To CirculationDisonaurNo ratings yet
- Training ProposalDocument2 pagesTraining ProposalJenny PabayoNo ratings yet
- Flyer EN Activated Carbon Filtration 2018-A4 PDFDocument2 pagesFlyer EN Activated Carbon Filtration 2018-A4 PDFMusawenkosi NcubeNo ratings yet