Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Voie Descendante Rubrospinale
Uploaded by
JJOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Voie Descendante Rubrospinale
Uploaded by
JJCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 8/9/2021
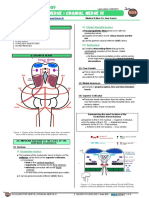
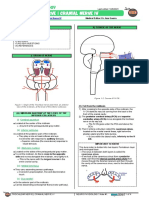
DESCENDING TRACTS – RUBROSPINAL TRACT
Neurology: Descending Tracts: Rubrospinal Tract Medical Editor: Dr. Sofia Suhada M. Uzir
OUTLINE II) THE STIMULUS
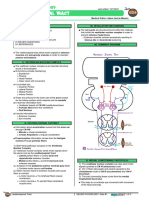
I) OVERVIEW (A) IMPULSE FROM CEREBRAL CORTEX
II) THE STIMULUS • Primary motor cortex
III) THE PATHWAY • Premotor cortex
IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS • Supplemental motor area
o Cortico-rubro fibers
V) REFERENCES Collateral fibers from the cerebral cortex to the red
nucleus which stimulates it
(B) FROM CEREBELLUM
I) OVERVIEW
● Concerns with proprioception
o Understand position of joints, muscles and tendons
within 3-dimensional space
o Globose and emboliform nuclei deep in the
cerebellum send fibers to the red nucleus
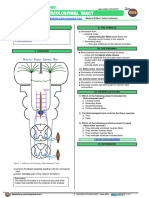
III) THE PATHWAY
● Red nuclei in the pons → rubrospinal tract descend and
decussate in the midbrain via ventral tegmental
decussation → continue descend and enter into lateral
while column (may even be intermixed with lateral
corticospinal tract) → give collaterals to the
anterior/ventral grey horns → stimulate alpha and gamma
motor neurons (in the grey horns) → flexion of the limb
(primarily upper limbs more than the lower limbs)
(1) Alpha motor neurons
● Contraction of extrafusal muscle fibers
● → shorten and lengthen muscle fibers
(2) Gama motor neurons
● Contraction of intrafusal muscle fibers
● → keep muscle spindles taut
Remember:
• Vestibular spinal tract + Pontine reticulospinal tract
→ Stimulate extensor muscles
• Rubrospinal tract and medullary reticulospinal tract
→ Stimulate flexor muscles
Figure 1 Pathway of rubrospinal tract
(A) FUNCTION
• Activating flexor muscles
o Both rubrospinal tract and medullary
reticulospinal tract stimulate the flexor muscles
o Pontine reticulospinal tract in particular, assist the
lateral corticospinal tract in stimulating the flexor
muscles, primarily in the upper limb whilst keeping
the lower limb intact
DESCENDING TRACTS – RUBROSPINAL TRACT NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 2
IV) REVIEW QUESTIONS
Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true concerning a. The rubrospinal tract helps in extension of the hands
rubrospinal tract? b. The red nuclei help in shorten and lengthen muscle
a. The pathway starts from the red nuclei fibers through the intrafusal muscle fibers
b. It is an ascending tract c. The medullary reticulospinal tract also helps in
c. It stimulates extensor muscle extension of the upper limbs
d. It decussates in the pons d. None of the above
Which of the following DOES NOT help in flexion CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
the upper limbs?
a. Rubrospinal tract V) REFERENCES
b. Medullary reticulospinal tract ● Paul Johns Clinical Neuroscience, Chapter 4 – Sensory and
motor pathways. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2014
c. Vestibular spinal tract
● Sabatine MS. Pocket Medicine: the Massachusetts General
d. All of the above Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine. Philadelphia: Wolters
Kluwer; 2020.
Regarding the gamma motor neurons ● Le T. First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020. 30th anniversary
edition: McGraw Hill; 2020.
a. It contracts the extrafusal muscle fibers ● Williams DA. Pance Prep Pearls. Middletown, DE: Kindle Direct
b. It shortens the muscle fibers Publishing Platform; 2020.
c. It lengthens the muscle fibers ● Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW. Current Medical
Diagnosis & Treatment 2018. New York: McGraw-Hill
d. It keeps the muscle spindles taut Education; 2017.
● Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL,
Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, Twentieth
Which of the following is correct regarding the Edition (Vol.1 & Vol.2). McGraw-Hill Education / Medical; 2018
stimulus of flexion of muscles? ● Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Anatomy & Physiology. Hoboken, NJ:
a. Primary motor cortex is not one of them Pearson; 2020.
● Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical Physiology.; 2017.
b. Supplemental motor area helps with decussation of ● Netter FH, Felten DL, Józefowicz Ralph F. Netter's Atlas of
reticulospinal tract Human Neuroscience. Teterboro, NJ: Icon Learning Systems; 2004.
c. The globose nuclei from cerebellum sends fibers to ● Netter FH. Atlas of Human Anatomy. Amsterdam: Elsevier;
2018.
the red nuclei ● Westover MB. Pocket Neurology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;
d. The fibers from the cerebellum will decussate at the 2016.
midbrain ● Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. Philadelphia,
PA: Elsevier; 2021.
Regarding cortico-rubro fibers
a. It gives collaterals to the red nuclei
b. It is from the cerebellum
c. It helps in stimulating extensor muscles of the upper
limb
d. None of the above
Which of the following center of impulse do not
originate from the cerebral cortex?
a. Primary motor cortex
b. Premotor cortex
c. Supplemental motor area
d. Emboliform nuclei
Regarding the function of the rubrospinal tract:
a. It helps in flexion of the upper limb more than the
lower limb
b. It helps in flexion, mainly in the lower limb
c. It helps in extension of the lower limb more than the
upper limb
d. It helps in extension, mainly in the upper limb
Regarding the decussation of the rubrospinal tract:
a. It happens in the medulla oblongata
b. It happens in the pons
c. It happens in the midbrain after sending impulse to
the muscles
d. It occurs in the midbrain via ventral tegmental
decussation
A patient is found to have left brain injury that
affects nerve fibers before the midbrain, which of
the following you expect that patient to show?
a. Weak/paralysis of the flexors of the hands on the left
side
b. Weak/paralysis of the extensor of the hands on the
right side
c. Both the extensors and flexors of the hands on the
left side will be affected
d. There is weakness/paralysis of flexor muscles of the
right hands
2 of 2 NEURO PHYSIOLOGY: Note #1. DESCENDING TRACTS – RUBROSPINAL TRACT
You might also like
- Carigie's Neuroanatomy of the RatFrom EverandCarigie's Neuroanatomy of the RatWolfgang ZemanNo ratings yet
- Voie Descendante Réticulospinale (Pontique)Document2 pagesVoie Descendante Réticulospinale (Pontique)JJNo ratings yet
- 100 - Neurology Physiology) Descending Tracts OverviewDocument3 pages100 - Neurology Physiology) Descending Tracts OverviewOsman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ultrastructure of the KidneyFrom EverandUltrastructure of the KidneyAlbert J. DaltonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Voie Descendante Réticulospinale (Médullaire)Document1 pageVoie Descendante Réticulospinale (Médullaire)JJNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal and Extra Pyramidal Tract1Document23 pagesPyramidal and Extra Pyramidal Tract1agudabelieveNo ratings yet
- 2 01 Peripheral Nerves and Spinal Cord EDITED Dra DoqueniaDocument31 pages2 01 Peripheral Nerves and Spinal Cord EDITED Dra DoqueniaCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- L 9 Anatomy, Nerves of The Lower Limb Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesL 9 Anatomy, Nerves of The Lower Limb Lecture Notesamrwheed9No ratings yet
- Voie Descendante VestibulospinaleDocument2 pagesVoie Descendante VestibulospinaleJJNo ratings yet
- 2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesDocument7 pages2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesstellaNo ratings yet
- OT1024 - 1S1L - Organization of The Nervous System-CompressedDocument14 pagesOT1024 - 1S1L - Organization of The Nervous System-CompressedRidz FNo ratings yet
- 094 - Neurology Physiology) Descending Tracts - Corticobulbar TractDocument3 pages094 - Neurology Physiology) Descending Tracts - Corticobulbar TractNikki Lin LiuNo ratings yet
- Slide Title Slide Number: Slide 2 Slide 3 Slide 4 Slide 5 Slide 6 Slide 7 Slide 8 Slide 9Document9 pagesSlide Title Slide Number: Slide 2 Slide 3 Slide 4 Slide 5 Slide 6 Slide 7 Slide 8 Slide 9MUHAMMAD AHMAD IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Spinal CordMai GaberNo ratings yet
- 4 BMC Lecture Spinal Cord (Autosaved)Document63 pages4 BMC Lecture Spinal Cord (Autosaved)Hoang Nhu NguyenNo ratings yet
- 084 - Neurology Physiology) Medulla Anatomy & FunctionDocument14 pages084 - Neurology Physiology) Medulla Anatomy & Functionice.bear.wolfoNo ratings yet
- NervexbsDocument4 pagesNervexbsDelfin UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord: Deswaty Furqonita, Ssi, MbiomedDocument22 pagesSpinal Cord: Deswaty Furqonita, Ssi, Mbiomedno lifeNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular Systemnaofumixeia24No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Histology Mock BoardsDocument29 pagesAnatomy and Histology Mock BoardsSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- PAS113 Block 2 NotesDocument41 pagesPAS113 Block 2 NotesAngela WuNo ratings yet
- Vagus Nerve Cranial Nerve X AtfDocument3 pagesVagus Nerve Cranial Nerve X AtfRishi VermaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Feb2021 Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20Document7 pagesNcert Feb2021 Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20Gufran AhmadNo ratings yet
- 115 - Neurology Physiology) Oculomotor Nerve - Cranial Nerve IIIDocument6 pages115 - Neurology Physiology) Oculomotor Nerve - Cranial Nerve IIIUssama MDNo ratings yet
- Pectoral Region and AxillaDocument25 pagesPectoral Region and AxillaSelva pandi100% (1)
- 14 CerebellumDocument26 pages14 CerebellumkaputostanleyNo ratings yet
- Lec5 TransesDocument10 pagesLec5 Transes4xwqm42hyrNo ratings yet
- 083 - Neurology Physiology) Pons Anatomy & FunctionDocument6 pages083 - Neurology Physiology) Pons Anatomy & Functionice.bear.wolfoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Class 11Document7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Class 11AlfaazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDocument6 pagesChapter 13: Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesthwisemanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution of Neural Coordination and Control Class 11Document17 pagesNcert Solution of Neural Coordination and Control Class 11Ayush DuttaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Back MusclesDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Back Musclesfatima wribagNo ratings yet
- Trochlear Nerve Cranial Nerve IV AtfDocument4 pagesTrochlear Nerve Cranial Nerve IV AtfRishi VermaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Spinal Cord: A. Cauda Equina B. Conus Medullaris C. Filum Terminale D. Foramen MagnumDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Spinal Cord: A. Cauda Equina B. Conus Medullaris C. Filum Terminale D. Foramen MagnumChelanie Vidad AndaweNo ratings yet
- Genral Motor Function, SC and Muscle SpindlesDocument41 pagesGenral Motor Function, SC and Muscle SpindlesnoufNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System 3rd Year Medicine Cerebellum & Basal GangliaDocument17 pagesCentral Nervous System 3rd Year Medicine Cerebellum & Basal GangliaGroup 14100% (1)
- HA L2 Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts, and Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesHA L2 Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts, and Lymphatic SystemljtorreslriejyNo ratings yet
- ,11,12 Muscles, Function, and Nerve Supply Slides.Document30 pages,11,12 Muscles, Function, and Nerve Supply Slides.hawazinNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument8 pagesSpinal CordCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Sample - Chapter - AnatomyDocument22 pagesSample - Chapter - AnatomyKumar KPNo ratings yet
- Lect. 50 Histology Review 2Document93 pagesLect. 50 Histology Review 2Mira ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb: Clinicoanatomical ProblemDocument100 pagesLower Limb: Clinicoanatomical ProblemsrisakthiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Neuroscience Trans03 TheMotorSystem (Part2)Document8 pages2023 Neuroscience Trans03 TheMotorSystem (Part2)Brionelle DumelodNo ratings yet
- ANA 6.01 General Somatic Afferents Dr. EsguerraDocument22 pagesANA 6.01 General Somatic Afferents Dr. EsguerraNinna Ricci San JuanNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Movement-Lecture Notes 20201Document47 pagesCoordination of Movement-Lecture Notes 20201Zobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bio101 SpinalCordDocument24 pagesBio101 SpinalCordDawnNo ratings yet
- Midtern LabDocument21 pagesMidtern LabJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- National NORCET Test-8Document108 pagesNational NORCET Test-8SHIVANIINo ratings yet
- (ANA) 4.04 Midgut and HindgutDocument18 pages(ANA) 4.04 Midgut and HindgutIzza Mari DeLeon LaurioNo ratings yet
- LAB Forearm and HandDocument15 pagesLAB Forearm and HandnanaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury IntroductionDocument243 pagesSpinal Cord Injury Introductionfahad100% (1)
- 13 Abdomen Part IDocument12 pages13 Abdomen Part IMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum-Rr - 1 (Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry)Document215 pagesCerebellum-Rr - 1 (Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry)REACT ATTRACTSNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous Sytem of HumanDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Nervous Sytem of HumanKharisulNo ratings yet
- NER4 and 5 NotesDocument11 pagesNER4 and 5 NotesjasminNo ratings yet
- 15 Peripheral Nervous InjuryDocument8 pages15 Peripheral Nervous Injury楊畯凱No ratings yet
- USMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewDocument767 pagesUSMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewMack LinfidioNo ratings yet
- 1-External Features of Spinal CordDocument24 pages1-External Features of Spinal Cordyaram3512No ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument9 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbjainilNo ratings yet
- Muring, Tirso PDocument2 pagesMuring, Tirso PMarielle RamesoNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts of Davao and Zamboanga CityDocument26 pagesArts and Crafts of Davao and Zamboanga CityCarmi C. Paciente0% (1)
- Ronak Shah 1210Document4 pagesRonak Shah 1210Ronak ShahNo ratings yet
- Resolution Honoring Hispanic Heritage MonthDocument6 pagesResolution Honoring Hispanic Heritage MonthMarkWarnerNo ratings yet
- Edarabia ADEC International Academic School 2015 2016 PDFDocument21 pagesEdarabia ADEC International Academic School 2015 2016 PDFEdarabia.comNo ratings yet
- Palladio Virtuel Exhibition - ArchDailyDocument5 pagesPalladio Virtuel Exhibition - ArchDailyrajyamgarNo ratings yet
- Online Railway PassesDocument23 pagesOnline Railway PassesSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation of Reservoir Causes and EffectsDocument33 pagesSedimentation of Reservoir Causes and Effects53 Hirole AadeshNo ratings yet
- Case-Smiths Occupational Therapy For Children and Adolescents - Ebook (Jane Clifford OBrien Heather Kuhaneck)Document1,597 pagesCase-Smiths Occupational Therapy For Children and Adolescents - Ebook (Jane Clifford OBrien Heather Kuhaneck)Anthony stark100% (9)
- Qualitative Research 2009 Keats 181 95Document16 pagesQualitative Research 2009 Keats 181 95Vratislav SlavíkNo ratings yet
- Actividad Individual InglesDocument3 pagesActividad Individual InglesLopez KeilyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Suheil PDFDocument9 pagesLesson 13 Suheil PDFrusilawati sallehNo ratings yet
- Tir 13 03 4 OttesonDocument21 pagesTir 13 03 4 OttesonTodd WeinsteinNo ratings yet
- Gcse EssaysDocument3 pagesGcse Essaysafabilalf100% (2)
- Reflections On Native Language Use in Adult ESL Classrooms: ResearchDocument11 pagesReflections On Native Language Use in Adult ESL Classrooms: ResearchJessieRealistaNo ratings yet
- Sample AcknowledgmentDocument4 pagesSample AcknowledgmentNishant GroverNo ratings yet
- SW Lesson Plan 7Document5 pagesSW Lesson Plan 7cammcbeanNo ratings yet
- IS2184 Information Systems ManagementDocument2 pagesIS2184 Information Systems ManagementMihirinie AbhayawardhanaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument12 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentDa dang100% (6)
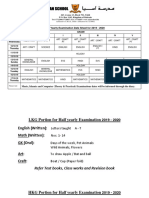
- Date Sheet and Portions of Half Yearly Exams For LKG To Grade 5 PDFDocument3 pagesDate Sheet and Portions of Half Yearly Exams For LKG To Grade 5 PDFManish KapriNo ratings yet
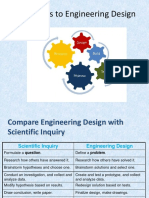
- Shift Gears To Engineering DesignDocument14 pagesShift Gears To Engineering DesignHamdan RamdanyNo ratings yet
- Rules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishDocument5 pagesRules of Subject Verb Agreement in Standard EnglishPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- DLLP - Simple Past Tense of The Verb REVISEDDocument9 pagesDLLP - Simple Past Tense of The Verb REVISEDChristine Joy Guillano CalluengNo ratings yet
- Assignment FP002 ORC Casanova GuadalupeDocument11 pagesAssignment FP002 ORC Casanova GuadalupeGuadalupe Elizabeth Casanova PérezNo ratings yet
- Notification DMHO West Godavari Staff Nurse Bio Statistician Other PostsDocument5 pagesNotification DMHO West Godavari Staff Nurse Bio Statistician Other PostsChakravaram Sai Bharath RajuNo ratings yet
- Hastings Dictionary of The Bible - One Volume Edition (1919)Document1,024 pagesHastings Dictionary of The Bible - One Volume Edition (1919)David Bailey100% (3)
- Recruitment Under Assam Skill Development Mission For APM IndustriesDocument1 pageRecruitment Under Assam Skill Development Mission For APM IndustriesNasim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Jin Jiang 2020 Tuition FeesDocument10 pagesJin Jiang 2020 Tuition FeesYuan LiNo ratings yet
- Nurses 05-2023Document81 pagesNurses 05-2023PRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- Скиллс 5Document2 pagesСкиллс 5LizzzikNo ratings yet