Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Center Virtualization
Uploaded by
michoel.ahmaad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesData Center Virtualization
Uploaded by
michoel.ahmaadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
What is Data Center
Virtualization?
Data center virtualization is the transfer of physical data
centers into digital data centers (i.e., virtual) using a cloud
software platform, enabling companies to remotely access
information and applications.
Why has data center virtualization
emerged?
Historically, data centers have been kept and managed in a physical
state from one central location; however, developments in cloud
computing and an increased demand for flexible IT solutions have led
to emergent technologies that literally transform the traditional data
center.
How does data center virtualization
work?
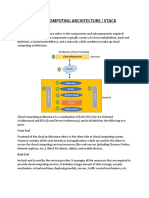
Data center virtualization is the process of creating a virtual server—
sometimes called a software defined data center (SDCC)—from
traditional, physical servers. The process abstracts physical hardware
by mimicking its processors, operating system, and other resources
with help from a hypervisor. A hypervisor is a software that creates
and manages a virtual machine (VM) that, in this process, helps align
communication with a central processing unit (CPU). Typically, data
center virtualization results in one or several cloud infrastructures, an
interconnected system of virtualized hardware, and other digital
components.
How are virtualized data centers
managed?
Virtualized data center platforms can be managed from a central
physical location (private cloud) or a remote third-party location (public
cloud), or any combination of both (hybrid cloud). On-site virtualized
servers are deployed, managed, and protected by private or in-house
teams. Alternatively, third-party servers are operated in remote data
centers by another service provider who offers cloud infrastructure
solutions to many different organizations and companies based on set
fees or a consumption-based (i.e., pay for what you use) model.
What are the benefits of data
center virtualization?
Virtual data center design offers a variety of benefits for IT specialists
and end users alike.
Scalability: Unlike physical servers, which need extensive and, at
times, expensive sourcing and time management, virtual data centers
are relatively simple, quick, and inexpensive to set up. They can be
added in response to rapid rises in demand for processing and other
resources, or downsized when they are no longer necessary—
something that is not possible with metal servers.
Enhanced functionality: Virtualized resources decentralize the
notion of the modern office. Before virtualization, everything from
common tasks and daily interactions to in-depth analytics and data
storage happened at the server level and could only be accessed from
one location. Virtualized resources can be accessed from anywhere
with a strong enough Internet connection. For example, employees
can access data and other applications from remote locations, making
productivity possible outside the office. Virtualized servers also enable
versatile collaboration and sharing opportunities through cloud-based
applications like video conferencing, word processing, and other
content creation tools.
Cost savings: Data center virtualization eliminates the higher
management and maintenance associated with physical servers,
which are typically outsourced to third-party providers. And unlike their
physical counterparts, virtual servers are often offered as part of a
consumption-based model, meaning companies only pay for what
they use. By contrast, whether physical servers are used or not,
companies still incur costs for their maintenance. And the additional
functionality that virtualized data centers offer can reduce other
business expenses like travel costs.
You might also like
- Cloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersDocument38 pagesCloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersPraveen Madupu100% (1)
- Ferrari 328 Microplex ECU TestingDocument18 pagesFerrari 328 Microplex ECU Testingcesareconto100% (1)
- Azure LearningDocument16 pagesAzure Learningshailesh bhatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computingliuliming100% (3)
- Cloud Computing Assignment-1 (Virtualization)Document18 pagesCloud Computing Assignment-1 (Virtualization)DarshpreetKaurNo ratings yet
- f5 Bip Ip DNS 302 Specialist Exam 1685189109Document52 pagesf5 Bip Ip DNS 302 Specialist Exam 1685189109M. J. A. EmpreendimentosNo ratings yet
- Cortex-M4 Part1Document65 pagesCortex-M4 Part1shaliniNo ratings yet
- Basics of Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesBasics of Cloud ComputingAtharvaNo ratings yet
- How To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationFrom EverandHow To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationNo ratings yet
- Berghof Automation Handbuch Display-Steuerung DC1103 enDocument58 pagesBerghof Automation Handbuch Display-Steuerung DC1103 enwilsonNo ratings yet
- Docu97010 - Dell EMC Unity Family 5.0.2.0.5.009 Release Notes PDFDocument156 pagesDocu97010 - Dell EMC Unity Family 5.0.2.0.5.009 Release Notes PDFemcviltNo ratings yet
- Desktop Transformation - Steps For Migration To Virtual Desktop InfrastructureDocument6 pagesDesktop Transformation - Steps For Migration To Virtual Desktop InfrastructureIpswitchWhatsUpGold2No ratings yet
- TITAN NP 1.0 Release NotesDocument13 pagesTITAN NP 1.0 Release NotesTi UkraineNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Research PaperDocument11 pagesCloud Computing Research PaperPracheta BansalNo ratings yet
- Blue Prism - Solution Design Overview - 0Document27 pagesBlue Prism - Solution Design Overview - 0kishore50% (2)
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingsweetgirlieNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCADocument48 pagesCloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCAPvlsowjanya100% (4)
- Cloud TechnologyDocument23 pagesCloud TechnologypallaviNo ratings yet
- ONTAP AFF ArrayDocument28 pagesONTAP AFF ArraycresmakNo ratings yet
- Cloud MigrationDocument20 pagesCloud MigrationOlaonipekun GbeminiyiNo ratings yet
- 22 12 2022 506814215Document113 pages22 12 2022 506814215abizer safdariNo ratings yet
- Virtual DesktopDocument18 pagesVirtual DesktopAbhinavreddy BNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Cloud Virtualization TechnologyDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Cloud Virtualization TechnologyYonesH gurUngNo ratings yet
- Virtualization CloudComputingDocument2 pagesVirtualization CloudComputingkasimNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Building Cloud NetworkDocument11 pagesUnit 3 Building Cloud Networksushil@irdNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Business PerspectiveDocument23 pagesCh02 Business PerspectivesaadNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFDocument16 pagesNetwork Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFelvisNo ratings yet
- Ibm CloudDocument7 pagesIbm CloudDivya GNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Management (IM) : Systems Management Network Management Storage Management Hewlett-PackardDocument10 pagesInfrastructure Management (IM) : Systems Management Network Management Storage Management Hewlett-Packardanoopsingh83No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Viva Question & AnswerDocument9 pagesCloud Computing Viva Question & AnswerxiomiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesCloud ComputingAvik BachharNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1Document30 pagesACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1tanishNo ratings yet
- CC 104 Information Management Tuesday and Friday 12.30 - 3.00 (Vilas, Leo Jade Suello, Llenes, John Claude G, Lauren, Adrian, Lao, Ma. Lorene B.)Document12 pagesCC 104 Information Management Tuesday and Friday 12.30 - 3.00 (Vilas, Leo Jade Suello, Llenes, John Claude G, Lauren, Adrian, Lao, Ma. Lorene B.)Glenzy Aleah Joy ParedesNo ratings yet
- Types of Virtualization: Autonomic ComputingDocument6 pagesTypes of Virtualization: Autonomic ComputingjattniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDocument11 pagesCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AUDocument11 pagesCloud Computing AUTHANGA DURAINo ratings yet
- Virtualization AssigDocument29 pagesVirtualization AssigMishal FathimaNo ratings yet
- Student Manual # 06 Cloud Computing 101Document18 pagesStudent Manual # 06 Cloud Computing 101Manish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingRyan FabianNo ratings yet
- Idc Iview Transcript: Automated, Standardized, and Private Cloud ManagementDocument5 pagesIdc Iview Transcript: Automated, Standardized, and Private Cloud ManagementSundar KannanNo ratings yet
- What Is VirtualizationDocument7 pagesWhat Is Virtualization88awscloudNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCloud ComputingRo TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Virtualization in Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesVirtualization in Cloud Computing2028110No ratings yet
- Olusola Martins CSC 103 AssignmentDocument13 pagesOlusola Martins CSC 103 Assignmentadeloyeheritage1No ratings yet
- Virtualization Concept: Definition-And-Solutions - HTMLDocument10 pagesVirtualization Concept: Definition-And-Solutions - HTMLIlsha McpheeNo ratings yet
- Citrix Guide To Desktop Virtual Is at IonDocument10 pagesCitrix Guide To Desktop Virtual Is at Ionjsumar04No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureFrom EverandCloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Infrastructure: Vmware Special EditionDocument6 pagesSoftware-Defined Infrastructure: Vmware Special EditionJav ierNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Client Virtualization Strategy White Paper - FinalDocument12 pagesMicrosoft Client Virtualization Strategy White Paper - FinalPavan Krishna ONo ratings yet
- WP 1 Virtual IzationDocument8 pagesWP 1 Virtual Izationmmoizuddin1251No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionDocument12 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionAditi SudhirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Moaaz BederNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CCDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CCHAFIZ AMEENUDDINNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingZinzy MNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit2Document37 pagesCloud Computing Unit2Bella SNo ratings yet
- Information Communication TechnologyDocument8 pagesInformation Communication TechnologyMalik KhawarNo ratings yet
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing and TypesDocument3 pagesVirtualization in Cloud Computing and TypesDolkar YangkyiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing PresentationDocument17 pagesCloud Computing PresentationCielo MarzanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 03-135191-007 M. Raza SiddiqueDocument9 pagesAssignment-1 03-135191-007 M. Raza SiddiqueRaza SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Cloud Infrastructure and Security NotesDocument13 pagesCloud Infrastructure and Security Notesisha gaonkarNo ratings yet
- L11 Virtualization 17062021 030456pmDocument9 pagesL11 Virtualization 17062021 030456pmSehar AliNo ratings yet
- CC Lab FileDocument42 pagesCC Lab FileRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- Virtualization in Cloud ComputingDocument74 pagesVirtualization in Cloud Computingtoon townNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Cloud Computing.Document25 pagesSeminar Report On Cloud Computing.Rahul Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Arun PaperDocument3 pagesArun Paperrohan vNo ratings yet
- 2 Cloud HostingDocument2 pages2 Cloud HostingSantanuNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- R2017 - OOAD - UNIT-5 UpdDocument30 pagesR2017 - OOAD - UNIT-5 UpdE L A N G ONo ratings yet
- MECSOL PAKISTAN - Tplink Schneider (06 NOVEMBER)Document2 pagesMECSOL PAKISTAN - Tplink Schneider (06 NOVEMBER)sultanhusssainNo ratings yet
- Product Id: Vgapatterneu: VGA Video Test Pattern Signal GeneratorDocument3 pagesProduct Id: Vgapatterneu: VGA Video Test Pattern Signal Generatorgarcia5No ratings yet
- OBE Based Course - Outline - LCA Fall 2017Document3 pagesOBE Based Course - Outline - LCA Fall 2017Tehseen HussainNo ratings yet
- Hirschmann Easy - Industrial Standard Solutions - Original - 110315Document8 pagesHirschmann Easy - Industrial Standard Solutions - Original - 110315Manuel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tvs Apache RTR 180 Service Manual PDFDocument3 pagesTvs Apache RTR 180 Service Manual PDFRodrigo Castro Orjuela100% (1)
- Acer MPC PriceListDocument8 pagesAcer MPC PriceListRaymondNo ratings yet
- Mpi Assignment Solution1Document15 pagesMpi Assignment Solution1alkesh.eng0% (1)
- CR - Operation Manual PDFDocument4 pagesCR - Operation Manual PDFPhong Nguyen0% (1)
- Old Linux Course ModulesDocument562 pagesOld Linux Course Modulesvasan nanguneriNo ratings yet
- Elite Software HandbookDocument70 pagesElite Software HandbookShaik Bepari JakeerNo ratings yet
- Simple ESR Meter Circuit Homemade Circuit ProjectsDocument6 pagesSimple ESR Meter Circuit Homemade Circuit ProjectsreynielNo ratings yet
- 3042 - New ABARS Related Products For Improved Disaster Recovery EffectivenessDocument32 pages3042 - New ABARS Related Products For Improved Disaster Recovery Effectivenessgborja8881331No ratings yet
- Embedded Systems An Integrated Approach - (PG 55 - 67)Document13 pagesEmbedded Systems An Integrated Approach - (PG 55 - 67)anjul0% (1)
- Chapter 10: Device Discovery, Management, and MaintenanceDocument59 pagesChapter 10: Device Discovery, Management, and MaintenanceevamNo ratings yet
- Hitachi White Paper Accelerated Flash StorageDocument30 pagesHitachi White Paper Accelerated Flash StorageMark HinkleNo ratings yet
- ICM Configuration: IP Contact Center Enterprise (IPCCE) v1.0Document39 pagesICM Configuration: IP Contact Center Enterprise (IPCCE) v1.0Kuldeep TiwariNo ratings yet
- SafeNet Sentinel End User GuideDocument24 pagesSafeNet Sentinel End User Guidelgskumar2010No ratings yet
- Cassandra 12Document214 pagesCassandra 12rohitsamaNo ratings yet
- Dm00105879 Description of Stm32f4 Hal and LL Drivers StmicroelectronicsDocument2,173 pagesDm00105879 Description of Stm32f4 Hal and LL Drivers StmicroelectronicsMetehan TuranNo ratings yet
- BX11 Technical Manual en v1.4Document100 pagesBX11 Technical Manual en v1.4Alaeddin Ben Hammed100% (1)
- Lab Puppet FirewallDocument5 pagesLab Puppet FirewallDSunte WilsonNo ratings yet