Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Uploaded by
Ricah Delos Reyes RubricoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Uploaded by
Ricah Delos Reyes RubricoCopyright:
Available Formats
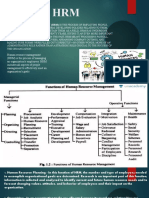
Chapter 9: Human Resource Management – Getting the Right People for Managerial
Success
9.1 Strategic Human Resource Management
The third factor that influences org’s ability to successfully implement strategy is human
resource practices
HR Practices : consist of all the activities that organizations use to manage their human capital,
including staffing, performance management, learning and development programs, and
compensation
Human Resouce management (HRM) : the process of planning for, attracting, developing, and
retaining an effective workforce
Strategic human resource management: the process of designing and implementing systems of
policies and practices that align an organization’s human capital with its strategic objectives.
Strategic HRM (SHRM) mobilizes necessary human and social capital.
● Human capital: the economic or productive potential of employee
knowledge, experience, and actions → stems from employee
competencies
● Social capital: the economic or productive potential of strong, trusting,
and cooperative relationships → stems from reciprocity, knowledge,
and capabilities embedded in informal connections and personal
relationships
Strategic HR Planning -Strategic human resource planning consists of developing a systematic,
comprehensive strategy for
(a) understanding current employee needs and
(b) predicting future employee needs.
Understanding current employee needs - To plan for the future, you must understand the
present-what today's staffing picture looks like. This requires that you do a job analysis first and
from that write a job description and a job specification.
Predicting Future Employee Needs - means you have to become knowledgeable about the
staffing the organization might need and the likely sources for that staffing.
9.2 Recruitment and Selection: Putting the Right People into the Right Jobs
Recruiting : the process of locating and attracting qualified applicants for job openings.
Internal recruiting : making people already employed by the organization aware of job
openings
External recruiting : attracting job applicants from outside the organization
Q: Which External Recruiting Methods Work Best?
Selection : the process of screening job applicants and choosing the best candidate for a
position.
3 types of selection checks include background information, interviews, and
employment tests,
1. Background information → education, work experience,certifications, citizenship
2. Interviews
a. unstructured interview : they gather information about a job candidate without the use
of a fixed set of questions or a systematic scoring procedure
b. situational interview : a structured interview in which raters ask applicants how they
would behave in hypothetical job situations
c. Behavioral-description interviews : a structured interview in which raters explore
applicants’ job-related past behavior
3. Employment tests : the standardized devices oroganizations use to measure specific skills,
abilities, traits, and other tendencies
a. Ability tests
b. Performance tests
c. Personality tests
d. Integrity tests
e. Drug and alcohol tests
f. Criminal and financial background checks
9.3 Managing an Effective Workforce: Compensation and Benefits
Compensation has three parts: (1) wages or salaries, (2) incentives, and (3) benefits.
1. Base pay : consists of the basic wage or salary paid employees in exchange for doing their jobs
2. Incentives- commissions, bonuses, profit-sharing plans, stock options
3. Benefits : nonmonetary forms of compensation designed to enrich the lives of all employees in
the organization, paid fully or in part by the organization.
9.4 Onboarding and Learning and Development
Onboarding (aka employee socialization) : the programs designed to integrate and
transition employees into new jobs and organizations through familiarization with
corporate policies, procedures, cultures, and politics, and clarification of work-role
expectations and responsibilities
Positive onboarding
Negative onboarding
9.5 Performance Management
Performance management: a set of processes and managerial behaviors that involve defining,
monitoring, measuring, evaluating, and providing consequences for performance expectations
Steps for performance management
1. Define performance
2. Monitor and evaluate performance
3. Review performance
4. Provide consequences
Performance appraisal: a management process that consists of 1) assessing employees’
performance and 2) providing them with feedback
Objective appraisals : based on facts and often numerical
Subjective appraisals : based on a manage’s perceptions of an employee’s traits or behaviors
9.6 Managing Promotions, Transfers, Disciplining, and Dismissals
Promotion : moving an employee to a higher-level position; the most obvious way to recognize
a person’s superior performance; factors to consider:
Fairness - step up must be deserved
Discrimination - shouldn’t be discriminated on basis of sexual orientation, gender,
ethnicity, etc
Others’ resentements
Transfer : is the movement of an employee to a different job with similar responsibility
Poorly performing employees may be given a warning or a reprimand and then disciplined
(temproary removal like suspension or demoted by having part of responsibilities and pay taken
away)
Dismissals have 3 categories: layoffs, downsizing, firings
● Layoffs : when a person has been dismissed temporarily and may be recalled when economic
conditions improve
● Downsizing: a permanent dismissal
● Firing: the persona was permanently dismissed for cause
Exit interview : a formal conversation between a representative from the organization and a
departing employee to find out why he or she is leaving and to learn about potential problems
in the organization
Non Disparagement agreement : a contract between two parties prohibiting both parties from
criticizing each other
Employment at will : the governing principle of employment in the great majority of states, it
means that anyone can be dismissed at any time for any reason, or for no reason at all
9.7 The Legal Requirements of Human Resource Management
1. Labor Relations
● National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) : enforces procedures whereby employees may vore to
have a union and for collective bargaining
2. Compensation and Benefitd
● Social Security Act of 1935 : establishes the US retirement system
● Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938
3. Health and Safety
● Occupational Safety and Health Ac t:
4. Equal Emmployment Opportunity
● Equal Employment Opportunity Commission :
5. Workplace Discrimination
● Workplace dscrimination :
Adverse impact :
Disparate treatment:
Affirmative action :
Sexual harassment :
Bullying :
9.8 Labor-Management Issues
Labor unions: organizations of employees formed to protect and advance their members
interests by bargaining with management over job-related issues
Union security clause : part of the labor-management agreement that states that
employees who receive union benefits must join the union, or at least pay dues to it
Right-to-work laws : stautes that prohibit employees from being required to join a union as a
condition of employment
Two-tier wage contracts : new employees are paid less or receive fewer benefits than veteran
employees have
Cost-of-living adjustment clause :during the period of the contract ties future wage increases to
inceases in cost of living as measured by US Bureau of labor Statistics
Givebacks : the union agrees to give up previous wage or benefit gains in return for something
else
Grievance : complaint by an employee that a manager has violated the terms of the labor
management agreement
Mediation: the process by which a neutral third party listens to both sides, make
suggestions, and encourages them to agree on a solution
Arbitration : the process in which a neutral third party, arbitrator, listens to both parties in a
dispute and makes a decision that the parties have agreed will be binding on them
You might also like
- 1.1 Female Dating ArchetypesDocument22 pages1.1 Female Dating ArchetypesSon Burnyoaz0% (1)
- Experiment No: 1 Self-Concept Questionnaire: Aim of The ExperimentDocument4 pagesExperiment No: 1 Self-Concept Questionnaire: Aim of The ExperimentPooja varma40% (5)
- Human Resource Management NotesDocument34 pagesHuman Resource Management NotesRana Sajid81% (21)
- Disorganized Infant Attachment Strategies and HelpDocument19 pagesDisorganized Infant Attachment Strategies and HelpMilos VuckovicNo ratings yet
- BLDR - Why Should Anyone Be Led by YouDocument14 pagesBLDR - Why Should Anyone Be Led by Youanvs69No ratings yet
- The Social Psychology of Love and Attraction PDFDocument9 pagesThe Social Psychology of Love and Attraction PDFmiriam100% (1)
- Bullying EssayDocument3 pagesBullying EssayIkhwan SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Reframing The Situation PDFDocument3 pagesExercise - Reframing The Situation PDFOltNo ratings yet
- MPA - Labor Management RelationsDocument65 pagesMPA - Labor Management RelationsReina Chiara Garcia MagcamitNo ratings yet
- Uts PresentationDocument13 pagesUts PresentationJennylyn Angela PatarataNo ratings yet
- Iat2 - Part BDocument9 pagesIat2 - Part BJEMILDA GNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Personnel ManagementDocument10 pagesLecture 3. Personnel ManagementAnonymous DgPsK0oQNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENTClifford Jay CalihatNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument54 pagesHRMAhsan ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Functions of HRMDocument3 pagesFunctions of HRMlanoox100% (1)
- A Project Report On Financial Ratio Annalysis Dharwad Milk Project Report Bec Bagalkot MbaDocument44 pagesA Project Report On Financial Ratio Annalysis Dharwad Milk Project Report Bec Bagalkot Mbaqari saibNo ratings yet
- Functions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Document16 pagesFunctions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Mittal SahabNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management ASSIGNMENT 1 AND 2 ANSWER SHEETDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Management ASSIGNMENT 1 AND 2 ANSWER SHEETarifNo ratings yet
- Functions of Human Resource Management1Document7 pagesFunctions of Human Resource Management1Marvee ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1ST UnitDocument11 pages1ST UnitAswin P SubhashNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 DirectDocument18 pagesMODULE 2 DirectRakesh RakiNo ratings yet
- Staffing: 1.2 ImportanceDocument9 pagesStaffing: 1.2 ImportanceBrent JamesNo ratings yet
- Staffing Chester Dela CruzDocument32 pagesStaffing Chester Dela CruzangeloNo ratings yet
- Staffing The Engineering Organization (Chapter 5)Document32 pagesStaffing The Engineering Organization (Chapter 5)fajarillokaren13No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Study MaterialDocument28 pagesHuman Resource Management Study MaterialArun Kumar100% (1)
- Staffing: Definition: According To Koontz and O'DonnellDocument8 pagesStaffing: Definition: According To Koontz and O'DonnellNajeeb khanNo ratings yet
- 1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1Document35 pages1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1JNo ratings yet
- 12 Business Studies CH 06 StaffingDocument9 pages12 Business Studies CH 06 StaffingKumar PreetamNo ratings yet
- HRM CapsuleDocument61 pagesHRM CapsuleNupur Agarwal Jain100% (2)
- Objectives and Functions of HRM: ChallengingDocument78 pagesObjectives and Functions of HRM: ChallengingRanjana KejariwalNo ratings yet
- 1.recruitment SelectionDocument46 pages1.recruitment Selectionbetcy georgeNo ratings yet
- Management SDM CHAPTER 14Document2 pagesManagement SDM CHAPTER 14Afrodinda IntanNo ratings yet
- Important Questions From Module 1Document8 pagesImportant Questions From Module 1naomiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document6 pagesChapter 6rajsoni9424700No ratings yet
- QA Personnel Mangement Long QuestionDocument10 pagesQA Personnel Mangement Long QuestionSanjeev PokharelNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Management Information SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Resources Management Information SystemPrajay KhNo ratings yet
- Ohsc Assignment 7Document6 pagesOhsc Assignment 7Kumar MangalamNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Human Resource Management: 3. Job AnalysisDocument12 pagesNature and Scope of Human Resource Management: 3. Job AnalysisSankar RajagopalNo ratings yet
- #6 StaffingDocument25 pages#6 StaffingJoanna Garcia100% (1)
- Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument29 pagesStaffing The Engineering OrganizationMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Semester II - HRM-Role and Functions: Welcome Online Learning Management SystemDocument89 pagesSemester II - HRM-Role and Functions: Welcome Online Learning Management SystemAkhil diwaseNo ratings yet
- RecruitmentDocument13 pagesRecruitmenttrisha.bbastudent21.13819No ratings yet
- ManagementDocument2 pagesManagementRasel SarderNo ratings yet
- Bus-101. ch-8Document16 pagesBus-101. ch-8Roynok Khan BadhonNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Management NotesDocument22 pagesHuman Resources Management Notessameerahmadkhan130No ratings yet
- Ques - What Is HRM? Describe Evaluation of HRM and Its Components?Document10 pagesQues - What Is HRM? Describe Evaluation of HRM and Its Components?Aniket SinghNo ratings yet
- BBA 2nd Year AzharDocument16 pagesBBA 2nd Year AzharRose DallyNo ratings yet
- Steps in Selection ProcessDocument33 pagesSteps in Selection ProcessJawad RasheedNo ratings yet
- MGT Chapter FourDocument8 pagesMGT Chapter Fourmillode dadoNo ratings yet
- Intr MGMT Chapter Five and SixDocument16 pagesIntr MGMT Chapter Five and SixAYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Staffing 5.1 DefinitionDocument9 pagesChapter Five Staffing 5.1 DefinitionMagarsa BedasaNo ratings yet
- Universitry of Mysore: C-1: AssignmentDocument10 pagesUniversitry of Mysore: C-1: AssignmentVenkateshNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Staffing: 6 MarksDocument11 pagesChapter - 6 Staffing: 6 MarksManan SuchakNo ratings yet
- Fiches HRDocument11 pagesFiches HRElisa PanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management: Unit:Ii Management ProcessDocument58 pagesNursing Management: Unit:Ii Management Processbemina jaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 StaffingDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 6 StaffingMercyNo ratings yet
- Managing Human Resources: Chapter # 12Document17 pagesManaging Human Resources: Chapter # 12Malaika Maryam CNo ratings yet
- (Anuran Bordoloi) Solved Question Bank - HRMDocument112 pages(Anuran Bordoloi) Solved Question Bank - HRMAnuran BordoloiNo ratings yet
- BTS 07Document21 pagesBTS 07Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- CH 6 StaffingDocument4 pagesCH 6 StaffingRONTECH GAMERSNo ratings yet
- DisciplineDocument8 pagesDisciplineBrindaaubeelauckNo ratings yet
- CH 13 and 14 Summary - Faiz AttaqiDocument7 pagesCH 13 and 14 Summary - Faiz AttaqiFaiz AttaqiNo ratings yet
- Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument32 pagesStaffing The Engineering OrganizationAbegail Ada Calayo MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Internal Assignment No:-1 Paper Title: - Human Resurece Management MBA: - 204Document14 pagesInternal Assignment No:-1 Paper Title: - Human Resurece Management MBA: - 204ashokj1984No ratings yet
- Recruitment in BanksDocument69 pagesRecruitment in BanksMrinmayi NaikNo ratings yet
- Seeking and Attracting The Right Kind of People To Apply For A Job in An OrganizationDocument13 pagesSeeking and Attracting The Right Kind of People To Apply For A Job in An OrganizationDivya TammineediNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument15 pagesHRMMittal SahabNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 3 - Q4 - W3Document3 pagesDLL - Science 3 - Q4 - W3Ricah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W3Document4 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W3Ricah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Teal and Yellow Modern Human Resource Transformation PresentationDocument10 pagesTeal and Yellow Modern Human Resource Transformation PresentationRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MTB 1 Q1Document4 pagesLesson Plan MTB 1 Q1Ricah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Libas Elementary SchoolDocument1 pageLibas Elementary SchoolRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Task 4-Chapter 9-Human Resource ManagementDocument11 pagesTask 4-Chapter 9-Human Resource ManagementRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- April ActivitiesDocument1 pageApril ActivitiesRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesFinancial ManagementRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q3 - W8Document3 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q3 - W8Ricah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Phil IriDocument2 pagesPhil IriRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Guidance Narrative ReportDocument7 pagesGuidance Narrative ReportRicah Delos Reyes RubricoNo ratings yet
- Cme451: Personality Development: Self-Awareness and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesCme451: Personality Development: Self-Awareness and DevelopmentRadhakrishna NayakNo ratings yet
- 13 Trait, Trait Theory - in The Encyclopedia of Cross-Cultural PsychologyDocument3 pages13 Trait, Trait Theory - in The Encyclopedia of Cross-Cultural PsychologyEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Lontok: Good Day Everyone. I Hope You Are All Doing Great. Well, Since EveryoneDocument3 pagesLontok: Good Day Everyone. I Hope You Are All Doing Great. Well, Since EveryoneRobert GarlandNo ratings yet
- A Study Conducted by Laguador and AgenaDocument1 pageA Study Conducted by Laguador and AgenalorieferpaloganNo ratings yet
- PMGT 402 103 W15 LeadershipDocument61 pagesPMGT 402 103 W15 LeadershiplovemashokoNo ratings yet
- Language BarriersDocument2 pagesLanguage BarriersLeandre Jasmine ReyesNo ratings yet
- M3 PB02 PPT Social InteractionDocument30 pagesM3 PB02 PPT Social InteractionIqbalNo ratings yet
- Thinking Styles QuizDocument4 pagesThinking Styles Quizezzaki.hanane4No ratings yet
- Personal Mastery and Mental ModelDocument14 pagesPersonal Mastery and Mental Modelseokyung2021No ratings yet
- Organizational Skills: Keterampilan BerorganisasiDocument13 pagesOrganizational Skills: Keterampilan BerorganisasiMohd NajibNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthprintDocument18 pagesMental HealthprintKyla AngelleNo ratings yet
- Eagly and Johannesen Schmidt 2001Document31 pagesEagly and Johannesen Schmidt 2001Grace GarnerNo ratings yet
- Leadership PDFDocument252 pagesLeadership PDFaboubakr soultanNo ratings yet
- Family IntroDocument23 pagesFamily IntroSADIA SOHAILNo ratings yet
- Selected People'S Attitude Towards Debit and Credit Card in Silang, CaviteDocument8 pagesSelected People'S Attitude Towards Debit and Credit Card in Silang, CaviteYvonne BerdosNo ratings yet
- DUE: NOVEMBER 10, 2020: Defining The Self: Personal and Developmental Perspectives On Self and IdentityDocument9 pagesDUE: NOVEMBER 10, 2020: Defining The Self: Personal and Developmental Perspectives On Self and IdentityMichaela Elaine MonteNo ratings yet
- Integrative Paper On Traits and Learning Theories of PersonalityDocument2 pagesIntegrative Paper On Traits and Learning Theories of PersonalityAbdel-aziz MasjirilNo ratings yet
- Erpat-2 0Document43 pagesErpat-2 0fob offNo ratings yet
- M e Research PaperDocument5 pagesM e Research Paperapi-607357733No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Organizational CultureDocument3 pagesChapter 16 Organizational CultureDuy LevineNo ratings yet
- Yu Lori Joy B. Bsa 2c Gs ActivityDocument3 pagesYu Lori Joy B. Bsa 2c Gs ActivityRea Del Valle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cultivation TheoryDocument5 pagesCultivation TheoryahmadhaamedrahmaniNo ratings yet