Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCQ On Poentiometry
Uploaded by
gehanhefina8040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesOriginal Title
MCQ on poentiometry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesMCQ On Poentiometry
Uploaded by
gehanhefina804Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
MCQ on poentiometry
1. The electrode potentials are calculated by
A. Ilkovic equation B. Nernst equation C. Randles equation
D. Ohm's law
2. The electrochemical analysis, in which the current is measured by
keeping potential constant is
A. Potentiometric titration B. Coductometric titrations
C . Amperometric titrations D. Voltammetry
3. All of the following statements are correct regarding
potentiometric titrations, except
(A) They are suitable for colored or turbid reactions
(B) The emf of the cell is zero at the equivalence point
(C) These are not suitable for analysis of dilute solutions less than 0.001M
(D) Liquid junction potentials will not influence the study
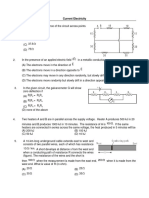
4. In an electrolytic cell, metal passes in to ions at
(A) Cathode (B) Anode (C) Salt bridge (B) No oxidation or reduction
5. The expressions valid in potentiometry are
(A) E Cell =E ERE - E ISE (B) E Cell =E ISE – E ERE + E J
(C) E ISE =E IRE – E membrane (D) E ISE =E IRE – E J
6. An electrode has the standard electrode potential as +2.50V. The
electrode will be
(A) P,S (B) Q,R (C) P,R (D) Q,
7. Standard hydrogen electrode
(A) Can’t be easily prepared (B) Doesn’t go reduction
(C) Indicator electrode (D) All of the above
8. The electrochemical analysis which measures the current generated
at the electrode in an ionic solution by application of potential is
known as
9. Calculate logarithm of the equilibrium constant of following redox
cell
(A) 10 (B) 15 (C) 20 (D) 30
10. Voltammetry belongs to the group of electrochemical analysis of
(A) Steady-state methods (B) Transient methods
(C) Controlled potential methods (D) Charge transfer by migration
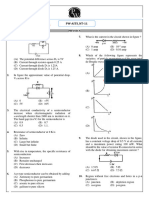
11. Select the true statements regarding glass electrode.
(A) Q (B) R (C) P,S (D) P,Q
12. Ion-selective potentiometry involves
(A) Measurement of electrode potential at zero current
(B) Measurement of electrode potential as a function of volume of titrant at
zero current
(C) Measurement of current as a function of volume of titrant at constant
potential difference
(D) Addition or deletion of analyte to null the potential difference at zero
current
.13
You might also like
- AE04 SolDocument126 pagesAE04 Solbaig79No ratings yet
- Material Science 79 Important MCQ PDFDocument13 pagesMaterial Science 79 Important MCQ PDFNandakumar Reddy0% (1)
- Electronics Engineering Test QuestionDocument28 pagesElectronics Engineering Test Questionkimnuj17No ratings yet
- In Electrical Electronic MeasurementDocument29 pagesIn Electrical Electronic Measurementsiddhartha bharadwajNo ratings yet
- Q07 - Harris QCA 7e-Ch 17Document3 pagesQ07 - Harris QCA 7e-Ch 17anooshNo ratings yet
- 12 and 14 Phy Q-BankDocument21 pages12 and 14 Phy Q-BankCharmiNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 45 QuestionsDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity 45 Questionsajiyasingh232000No ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2022 Dato Mansor P2 AnswerDocument16 pagesTrialstpm 2022 Dato Mansor P2 AnswerASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument17 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Class 12 P. T 2Document7 pagesClass 12 P. T 2Adhvai Senthil kumarNo ratings yet
- 100 Most Imp Question For Jee MainsDocument23 pages100 Most Imp Question For Jee MainsgopinadhNo ratings yet
- 12 - Physics Question Paper (Pre-Board Ii)Document7 pages12 - Physics Question Paper (Pre-Board Ii)VaniceWhilderNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument16 pagesCurrent ElectricityNavya RastogiNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - LDA - 1Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity - LDA - 1Ayushmaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper Set-1Document10 pagesCbse Paper Set-1maheshsoni10051982No ratings yet
- Most Expected Questions-2023Document28 pagesMost Expected Questions-2023Tytyuih FuiottibNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question Bank - 2 Subject: - Engineering ChemistryDocument18 pagesMultiple Choice Question Bank - 2 Subject: - Engineering ChemistryJitendra BaravkarNo ratings yet
- QP Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP Xii PhysicsSufiyan BelimNo ratings yet
- Typical Questions & AnswersDocument32 pagesTypical Questions & AnswersJatin GaurNo ratings yet
- MCQ-Diodes and TransistorsDocument102 pagesMCQ-Diodes and Transistorsaksaltaf913774% (23)
- JTO Telecom 2009Document28 pagesJTO Telecom 2009jeevanNo ratings yet
- Click Here To Join: PW-AITS - NT-11Document12 pagesClick Here To Join: PW-AITS - NT-11Shekhar JainNo ratings yet
- Fund - Elect DE52.Document355 pagesFund - Elect DE52.atashi baran mohantyNo ratings yet
- Semi ConductorDocument4 pagesSemi ConductorSchrodinger's CatNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering by Pawan Chandani Sir 1679927943592-UnlockDocument27 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering by Pawan Chandani Sir 1679927943592-UnlockSunnu MauryaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mains-Narayana Question Paper For Specific TopicsDocument11 pagesMains-Narayana Question Paper For Specific Topics10C-sai sachin adithya .Mk-TNo ratings yet
- 005 Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 03Document11 pages005 Xii Phy Sample Question Paper 03Upendra MandalNo ratings yet
- AE04 Sol PDFDocument126 pagesAE04 Sol PDFarunachelamNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1Document11 pages12 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 1aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors - DPP 02Document3 pagesSemiconductors - DPP 02mv7602456No ratings yet
- Physics XII QP Set 1Document10 pagesPhysics XII QP Set 1meme MachineNo ratings yet
- MCQ Ch14 - D21 Feb 2022Document27 pagesMCQ Ch14 - D21 Feb 2022Arun ShankarNo ratings yet
- Csec Electrical and Electronic TechnolohyDocument9 pagesCsec Electrical and Electronic TechnolohyDanel67% (9)
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument18 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersGyan BardeNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 - All Seniors - Cbse Board - Physics (Selected Topics) Q.paper (01.02.2024)Document8 pages2023-24 - All Seniors - Cbse Board - Physics (Selected Topics) Q.paper (01.02.2024)pravchoo2006No ratings yet
- Cblephpl 12Document6 pagesCblephpl 12Harishni ArulvasagamNo ratings yet
- 8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023Document11 pages8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023EMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- SEMI CONDUCTOR-schoolDocument2 pagesSEMI CONDUCTOR-schoolCLT ISHAANNo ratings yet
- Xii QP Physics VSTDocument5 pagesXii QP Physics VSTkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- Objective Que - of EeeDocument149 pagesObjective Que - of EeeNikhil Pareek100% (2)
- Circuitrix EventDocument6 pagesCircuitrix EventNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Advances in Quantum Electronics: Volume 3From EverandAdvances in Quantum Electronics: Volume 3D. W. GoodwinNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)