Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trans Dust To Kiln
Uploaded by
chenghongwei2008Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trans Dust To Kiln
Uploaded by
chenghongwei2008Copyright:
Available Formats
Item
Transportation of raw materials Application process
for input into kiln Raw material process
For a kiln with preheater, such as SP or NSP, mixed raw materials are transported to the
top of the preheater and then fed into the system. When the SP kiln was developed, air
Background compression transpotation by a Quinion pump was initially adopted. Because of great
pressure loss, high power consumption rate, and frequent compressor faults, however, a
more reliable and efficient method was expected.
Compressed air transportation was replaced with mechanical transportation such as a
combination of bucket elevator (BE) and air slider (AS).
Two or three Bes are installed up to the top of the preheater. Raw materials are lifted to
the top by changing the Bes and fed into the preheater through the AS.
BE has small no-load power because of its structure and AS is a means of transportation
using the self weight of powder. Therefore, this method can reduce power consumption
greatly compared with air compression delivery.
Air compression transportation used to cause great fan power loss because of large
volume of compressed air flowing into the system with raw materials. Mechanical
transportation can minimize the air inflow.
The initial BE used a short-link chain that caused many problems of abrasion or
elongation. A plate-type chain reduced these problems greatly and achieved the current
high reliability.
As of 1996, 72 systems use mechanical transportation and two systems use air
compression transportation in Japan.
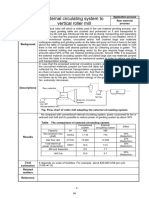
Combination of BE and AS Guided-discharge Preheater
Descriptions bucket elevator
Dust
collector
Air slider
Blower
Powder
To kiln
Mechanical transportation reduced power consumption by even 80%, although depending
Results
on the distance of transportation.
Cost Bucket elevator (2 units): About 1.4 million US$ [1US$=¥110]
estimation (For a kiln having a capacity of 3000 t/d)
Related
matters
Reference
-9-
75
You might also like
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Volume-2. Design and Manufacturing of Hydraulic CylindersDocument53 pagesVolume-2. Design and Manufacturing of Hydraulic CylindersQ.S. Khan96% (49)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Design of BlowerDocument18 pagesDesign of BlowerNipun K GajjarNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Maintenance ChecklistDocument2 pagesControl Valve Maintenance Checklisttrija_mr67% (6)
- FASSI F40B каталог деталей PDFDocument35 pagesFASSI F40B каталог деталей PDFSergeyNo ratings yet
- Cswip 3.2 PPDocument106 pagesCswip 3.2 PPMusa Çelik100% (1)
- Livchak ASHRAE Journal Chilled Beam & DOASDocument10 pagesLivchak ASHRAE Journal Chilled Beam & DOAS윤병택No ratings yet
- Hd465-7eo SM Sen01081-08 PDFDocument1,613 pagesHd465-7eo SM Sen01081-08 PDFJorge Rodolfo Yanez EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Setting Cement PlugsDocument8 pagesGuidelines For Setting Cement PlugsHassan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling Piping Systems: Chapter C14Document28 pagesAsh Handling Piping Systems: Chapter C14abhilash nairNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling Systen in A Power PlantDocument33 pagesAsh Handling Systen in A Power PlantScyrucs Singh100% (1)
- Air or Pneumatic ConveyorDocument36 pagesAir or Pneumatic ConveyorAshish Sharma100% (2)
- Engineering Letter: PneumaticconveyingDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: PneumaticconveyingMangatur SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshFrom EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling SystemsDocument32 pagesAsh Handling Systemsamit14326367% (9)
- AR-200 Operating Manual Revision 1Document133 pagesAR-200 Operating Manual Revision 1Paola de LeonNo ratings yet
- FE 3300 The Use of Fans in Pneumatic ConveyingDocument4 pagesFE 3300 The Use of Fans in Pneumatic ConveyingAvery OppegardNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling SystemDocument26 pagesAsh Handling SystemAnku PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Compressed Air Energy StorageDocument5 pagesCompressed Air Energy StorageDr-Aditya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Song Hau 1 Thermal Power Plant (2X600Mw) : Document Submission Status: For ConstructionDocument20 pagesSong Hau 1 Thermal Power Plant (2X600Mw) : Document Submission Status: For ConstructionMinh Hoang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Designing Pneumatic Conveying Systems: Cover StoryDocument11 pagesDesigning Pneumatic Conveying Systems: Cover StoryGhasem Bashiri100% (2)
- Compressed Air Energy StorageDocument29 pagesCompressed Air Energy StorageharshaNo ratings yet
- Materials Transfer: Types of Pneumatic Conveying & Design ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesMaterials Transfer: Types of Pneumatic Conveying & Design ConsiderationsRosa María Córdova100% (1)
- Efficient Pneumatic ConveyingDocument14 pagesEfficient Pneumatic Conveying설동하100% (2)
- A Primer On Dense Phase Pneumatic Conveying SystemsDocument7 pagesA Primer On Dense Phase Pneumatic Conveying Systemspneucon100% (1)
- Dense Phase Pneumatic ConveyingDocument0 pagesDense Phase Pneumatic Conveyingheroj83No ratings yet
- A Transcritical CO2 Turbine-CompressorDocument8 pagesA Transcritical CO2 Turbine-CompressorjoseNo ratings yet
- Occ 2 Final 00130Document3 pagesOcc 2 Final 00130VijayNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Conveying - GJ74, HauckDocument6 pagesPneumatic Conveying - GJ74, Hauckjfejfe100% (1)
- Compressed Air Production Using Vehicle SuspensorDocument28 pagesCompressed Air Production Using Vehicle SuspensorJyotishk MalviyaNo ratings yet
- A2P: Airslide To Pump Fly Ash Handling SystemDocument4 pagesA2P: Airslide To Pump Fly Ash Handling SystemVikas SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Summer 1998 Outside The Loop Newsletter For Geothermal Heat Pump Designers and InstallersDocument8 pagesSummer 1998 Outside The Loop Newsletter For Geothermal Heat Pump Designers and InstallersOutside the Loop Newsletter - GEO-HEAT CENTERNo ratings yet
- WWW - Nol Tec - Com Documents Pdfs Answers To Eight Common QuestionsDocument6 pagesWWW - Nol Tec - Com Documents Pdfs Answers To Eight Common QuestionsIaponaira de Abreu100% (1)
- ED3300Document4 pagesED3300Mohamed Tahoun100% (1)
- Group 6Document18 pagesGroup 6cyndrilla453No ratings yet
- Submitted byDocument62 pagesSubmitted byRameez AhmadNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2Document28 pagesSeminar 2Dilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Aeration PaperDocument11 pagesAeration PapersehonoNo ratings yet
- Boiler Soot-Blowing in Power Plants - Compressed Air Best PracticesDocument8 pagesBoiler Soot-Blowing in Power Plants - Compressed Air Best PracticesRoland NicolasNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Cooling Water SystemDocument3 pagesAuxiliary Cooling Water SystemBrijesh SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of A Regenerative Blower For EVA Suit VentilationDocument18 pagesDesign and Development of A Regenerative Blower For EVA Suit VentilationBrahimABDNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method For Improving Aerostat Endurance Using Microprocessor Controlled Feedtube (Patent Applied)Document7 pagesA Novel Method For Improving Aerostat Endurance Using Microprocessor Controlled Feedtube (Patent Applied)Harsh WaniNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic ConveyingDocument6 pagesPneumatic Conveyingsudhirm16100% (1)
- Conveying: E A. Zenz and D. F. Othmer, "Pneumatic and Hydraulic Conveying," Chapter 10, FluidizaDocument18 pagesConveying: E A. Zenz and D. F. Othmer, "Pneumatic and Hydraulic Conveying," Chapter 10, Fluidizavalerio.garibay100% (1)
- Diameter RatioDocument10 pagesDiameter RatioDavid Fransiskus SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pneu Conveyor 1Document17 pagesJurnal Pneu Conveyor 1Zulfahmi AmriNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis of Power Recovery Systems For Cabin Exhaust AirDocument8 pagesDesign Analysis of Power Recovery Systems For Cabin Exhaust AirJoe shankerNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Conveying Spreadsheet-ContentDocument27 pagesPneumatic Conveying Spreadsheet-Contentaladdin4dNo ratings yet
- Calculation Cooling Compressors: January 2016Document11 pagesCalculation Cooling Compressors: January 2016RIDONo ratings yet
- Calculation Cooling Compressors: January 2016Document11 pagesCalculation Cooling Compressors: January 2016RIDONo ratings yet
- Air Slide DKE292 Ch18Document36 pagesAir Slide DKE292 Ch18RICARDOALEXBORGESNo ratings yet
- Innovatory Conveying Systems: 2004 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument16 pagesInnovatory Conveying Systems: 2004 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights ReservedGustavo Hernandez100% (1)
- Nyb - El-09 PDFDocument4 pagesNyb - El-09 PDFtylerstearnsNo ratings yet
- Steady State OptimizationDocument12 pagesSteady State OptimizationMuhammad Haris HamayunNo ratings yet
- Study Into Electrically Shaft Driven Air Cycle Machines: Conference PaperDocument10 pagesStudy Into Electrically Shaft Driven Air Cycle Machines: Conference PaperAhmedNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Design Upload (Sem1 2023 New)Document75 pagesPneumatic Design Upload (Sem1 2023 New)dat54636No ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Air Classification ofDocument7 pagesThe Feasibility of Air Classification ofmshah222No ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: FansandblowersforcombustionprocessDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: Fansandblowersforcombustionprocessnedduc20No ratings yet
- Fuel FiringDocument39 pagesFuel Firingnetygen1No ratings yet
- Minimising The Air Demand of Micro-Hydro Impulse Turbines Incounter Pressure OperationDocument8 pagesMinimising The Air Demand of Micro-Hydro Impulse Turbines Incounter Pressure Operationdeepakverma33546No ratings yet
- A Reverse Brayton Cycle Mine Refrigeration System: DL Millar Laurentian University, CanadaDocument18 pagesA Reverse Brayton Cycle Mine Refrigeration System: DL Millar Laurentian University, Canadajbloggs2007No ratings yet
- Air Movers For Dilute-Phase Pneumatic Conveying PDFDocument7 pagesAir Movers For Dilute-Phase Pneumatic Conveying PDFBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- 3222experience of Implementing Clyde Bergemann Technologies of Ash Removal PDFDocument3 pages3222experience of Implementing Clyde Bergemann Technologies of Ash Removal PDFKARTHIKEYANNo ratings yet
- RP 1742. Experimental Methodology and Results For Heat Gains From Various Office EquipmentDocument14 pagesRP 1742. Experimental Methodology and Results For Heat Gains From Various Office EquipmentEduardoNo ratings yet
- Castable - Tancbor 4Document1 pageCastable - Tancbor 4chenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Castable - Ancbor 3Document1 pageCastable - Ancbor 3chenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Castable - Ancbor 1Document1 pageCastable - Ancbor 1chenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Intermiten Charging of Elctrical CollectorDocument1 pageIntermiten Charging of Elctrical Collectorchenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- TMEIC Cement Industry Brochure - A4Document24 pagesTMEIC Cement Industry Brochure - A4chenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- New Suspension Burding SystemDocument1 pageNew Suspension Burding Systemchenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Vertical Roller Mill ECSDocument1 pageVertical Roller Mill ECSchenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Raw Material FinenessDocument1 pageRaw Material Finenesschenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Vertical Roller Mill For Raw MaterialsDocument1 pageVertical Roller Mill For Raw Materialschenghongwei2008No ratings yet
- Built Tough: High HeadDocument3 pagesBuilt Tough: High HeadDodyNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts List KuhnDocument3 pagesSpare Parts List KuhnthaisswiestNo ratings yet
- Coal NEW CHECKLIST Coal MillDocument9 pagesCoal NEW CHECKLIST Coal MillanilNo ratings yet
- Parshall FlumeDocument2 pagesParshall FlumeuvozoneNo ratings yet
- Jig DesignDocument23 pagesJig DesignЦырен ЖалсаповNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: Amclyde Model 60 Crane Serial Number Bp5318Document181 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual: Amclyde Model 60 Crane Serial Number Bp5318Luis Chan ChanNo ratings yet
- Valves Objective QuestionsDocument4 pagesValves Objective QuestionszhangyiliNo ratings yet
- CV of Eya - ARAFATDocument2 pagesCV of Eya - ARAFATESK ChannelNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet 1137 19Document210 pagesSpreadsheet 1137 19SanteBrucoliNo ratings yet
- Material For Fibre Optic Lines PDFDocument21 pagesMaterial For Fibre Optic Lines PDFWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: Families BW 190 BW 250 BW 360 BW 460 BW 750Document124 pagesInstallation Manual: Families BW 190 BW 250 BW 360 BW 460 BW 750Sam Running BearNo ratings yet
- Continuous Beam Analysis Beam:: 2 Span 1 Span 2 Beam Data L H BDocument31 pagesContinuous Beam Analysis Beam:: 2 Span 1 Span 2 Beam Data L H BMadushike JayawickramaNo ratings yet
- Trabafo Final de Ingles TecnicoDocument19 pagesTrabafo Final de Ingles TecnicoLuis GarciaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 31451: DEP 31.38.01.15-Gen Class 31451, Rev. G Page 1 of 13Document13 pagesCLASS 31451: DEP 31.38.01.15-Gen Class 31451, Rev. G Page 1 of 13SaguesoNo ratings yet
- CARD LOCK RETAINER 265 - DataSheetDocument2 pagesCARD LOCK RETAINER 265 - DataSheetSCRIBD DOCSNo ratings yet
- WC Manifold: Jeevan Bhar Ka Saath..Document2 pagesWC Manifold: Jeevan Bhar Ka Saath..arjun 11No ratings yet
- April 2024 - PSAD 17Document2 pagesApril 2024 - PSAD 17rando12345No ratings yet
- SS-3002 Series: Drop in LavatoryDocument1 pageSS-3002 Series: Drop in LavatoryerrenmayNo ratings yet
- Lenntech: Engineering Drawing PacketDocument7 pagesLenntech: Engineering Drawing PacketjazaibNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga Rucika Fitting uPVCDocument4 pagesDaftar Harga Rucika Fitting uPVCSurya NirmanaNo ratings yet
- Process Sheet: Part No.: Hub 1500629 (Annexure 1 To PCP 1500629E CP-08)Document5 pagesProcess Sheet: Part No.: Hub 1500629 (Annexure 1 To PCP 1500629E CP-08)Suraj RawatNo ratings yet
- (Template) U3A Review QuestionsDocument3 pages(Template) U3A Review QuestionsnahvimohaddasehNo ratings yet
- Macchinedacaffe'Automatica Automaticcoffeemachines: de Longhi Ecam23210Document20 pagesMacchinedacaffe'Automatica Automaticcoffeemachines: de Longhi Ecam23210Alessandro Capitani FilhoNo ratings yet