Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mock Assignment - Requirements - M D H S Gunathilake (E157016)
Uploaded by
Hasitha SanjayaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mock Assignment - Requirements - M D H S Gunathilake (E157016)
Uploaded by
Hasitha SanjayaCopyright:
Available Formats
Requirements
Requirement is a broad concept that defines any function, attribute, capability,
characteristic or quality of a system that gave value and advantage to a customer,
organization and internal or external stakeholders. Simply requirements fulfill the
expectations of users by implementing the software products. This can be known or
unknown, expected or unexpected or hidden from customer’s point of view. It mainly
used in development of the software/ system designing and also in system engineering
and enterprise engineering. Note that, requirements provide mutual understanding
between users and designers and describe the behavior of a system. The requirements
should adapt with the willingness of users or else the final outcome may cause many
failures. Further, identification of correct requirement is important to the initial stage of
system designing. Furthermore, requirements are categorized as business requirements,
user requirements and system requirements.
1. Business requirements
Business requirements describe why the organization carrying out the project/system. It
explores the benefits of the product which customer or organization expect to gain from
the final outcome. This covers the areas of problem statement, project vision, project
budget/ schedule/ resources, project objectives, scope statement, business process analysis
and stakeholder analysis. Project owner, stakeholder and project team create Business
Requirement Document (BRD) to examine business requirements. BRD is a living
document that maintain future requirements, updates and changes with all the practical
and measurable organization and customer expectations.
2. User requirements
User requirements to mean the high-level abstract requirements which describes what the
user does with the system or how user interact with the system. These requirements poses
as a primary inputs for the system requirement. Even, this express the services that the
system expected to provide to users and the limits to be implemented. Natural languages,
tables and diagrams are used to approach user requirements. The requirements need to be
identify clearly because different types of users use these in different ways. Client
managers, system end-users, client engineers, contractor mangers, system architects
usually interact with the user requirements. URD, the acronym of User Requirement
Document is a document that mentioned the introduction (project background, project
scope and objectives etc.), risks, assumptions, constraints, proposed system overview and
future business process. However, the users of user requirements are not familiar with
how the system will be implemented.
3. System requirements
M D H S Gunathilake (E157016) Requirements 1|Page
System requirements explain the details of what the system should do. System
requirements are concern with the system functions, services and operational limitations.
By the way, this is the part of a contract between the customer and system developers.
System end-users, client engineers, system architects are concern with the system
requirements. In addition, functional requirements, non- functional requirements, and
domain requirements are classified under the system requirement. This classification
based on the objective specificity which defines operational needs of the system to design
and develop and the traceability of requirements for the functional needs of the system.
Further, the documentation part of the functional and non- functional is called Software
Requirement Specification (SRS). SRS is the source that analysts use to communicate
requirement information in detail with system developers, testers and project
stakeholders.
a) Functional requirements
This explain services that the system should provide, how the system response to the
particular inputs and how the system react in different conditions. The inputs can be such
as addresses, names or calculations need for the system to work properly. And also
functional requirements defines what the system should not to do. Even, the statements or
goals that used to recognize the system behavior are called functional requirements.
Further, functional requirement describes a set of high-level requirements and consists set
of functions. Each high-level requirement collect data from users and dispatch data to
users. Note that the functions include input data set, output data set and processes which
require to obtain inputs from the outputs.
b) Non- functional requirements
Non-functional requirements express how the system should operate. The non-functional
requirements specify the characteristics and architecture of the system as a whole. The
main characteristics of the aforesaid requirements can be point out as performance,
usability, portability, security, scalability, reliability and maintainability. It is important to
achieve non-functional requirements without failures to meet successful outcome.
c) Domain requirements
Domain requirements can be functional requirement or non-functional requirement which
describes the expectations of a specific software, purpose or industry vertical.
Accordingly, the following example make clear view of the process of all types of
requirements.
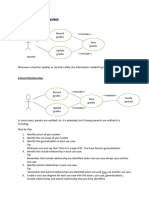
Example: Hospital Patient Management System
The information of patients and patient’s families are stored in the system. Patients are
judged and treated by doctors. Under the supervision of doctors, nurses are delivering
various treatments. Patients' appointments are handled by medical receptionists and all
the system related information setup and upkeep by the IT personnel, who is in charge of
the system. The medical ethics manager is responsible for ensuring that the system
complies with current patient-care ethical principles. Managers of health-care
M D H S Gunathilake (E157016) Requirements 2|Page
organizations are the persons who use the system to get management data. Medical
records personnel ensure that the system data can be retained and preserved, as well as
that adequate record-keeping practices are in place.
M D H S Gunathilake (E157016) Requirements 3|Page
You might also like
- 2019 Book EntertainmentScience PDFDocument879 pages2019 Book EntertainmentScience PDFFelipe MendesNo ratings yet
- Normalization Exercise Solutions PDFDocument10 pagesNormalization Exercise Solutions PDFHimasha100% (2)
- Requirements EngineeringDocument5 pagesRequirements EngineeringMaricar SucalditoNo ratings yet
- SRE Complete NotesDocument24 pagesSRE Complete NotesSana ArshadNo ratings yet
- By Khadak Budha Chhetri: Unit .2 Software RequirementsDocument7 pagesBy Khadak Budha Chhetri: Unit .2 Software RequirementskhadakNo ratings yet
- Positive Pay File Creation Using Payment Medium WorkbenchDocument19 pagesPositive Pay File Creation Using Payment Medium WorkbenchGaphur shaikNo ratings yet
- PV QCDocument1 pagePV QCrameshqcNo ratings yet
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Block Level SSN Insertion On Processor CoreDocument33 pagesLab2 Block Level SSN Insertion On Processor Corezys WdNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Requirements EngineeringDocument20 pagesLecture 7 - Requirements EngineeringAamerMAhmadNo ratings yet
- I. Company Analysis Short Profile of The CompanyDocument24 pagesI. Company Analysis Short Profile of The CompanyHannah Gonzales100% (3)
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Requirement Management1242Document18 pagesRequirement Management1242niyati25No ratings yet
- Pointwise Glyph Reference ManualDocument60 pagesPointwise Glyph Reference Manualrobin gongNo ratings yet
- All in One Reviewcustemize123Document51 pagesAll in One Reviewcustemize123Misgana TerefeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Types of Requirements 1Document9 pagesChapter Two Types of Requirements 1Yasin KorichoNo ratings yet
- Requirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Document17 pagesRequirement and Specifications: Chapter - 3Chandrashekhar KuriNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Melissa T. GuillermoDocument37 pagesPrepared By: Melissa T. GuillermomtguillermoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - SetDocument33 pagesUNIT 2 - Setrahul mNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document41 pagesUnit 2Kings GreysonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Requirement EngineeringDocument91 pagesChapter 3 - Requirement EngineeringDeeNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument21 pagesUnit IIm10k4tmgw5No ratings yet
- Requirement EngineeringDocument3 pagesRequirement Engineeringtrs smritiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Requirement-EngineeringDocument40 pagesUnit 4 Requirement-EngineeringMysto GanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document37 pagesUnit 2K BNo ratings yet
- SE - UNIT 2 CLG NotesDocument31 pagesSE - UNIT 2 CLG Notes4073 JOSEPH SAVIO PEREIRA100% (1)
- Requirements Engineering Process Course M2-2020 PDFDocument39 pagesRequirements Engineering Process Course M2-2020 PDFLionel Perin NAGUEU DJAMBONGNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Introduction To Software Requirements SpecificationDocument39 pagesChapter - 3 Introduction To Software Requirements Specificationabdulrahman abushanab0% (1)
- Software RequirementsDocument17 pagesSoftware RequirementsMeghnadhNo ratings yet
- Semester V: Title Software Engineering and Testing Code Hours 45 Credits 03 Faculty Dr. Pooja S.BDocument22 pagesSemester V: Title Software Engineering and Testing Code Hours 45 Credits 03 Faculty Dr. Pooja S.Brahul mNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4: Requirement EngineeringDocument45 pagesChapter-4: Requirement EngineeringarhumNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 OoseDocument67 pagesUnit-2 OoseRAMYA GNo ratings yet
- 004 SRS Software Requirements Terminology GuideDocument1 page004 SRS Software Requirements Terminology GuideWeyNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification On Book Shop Management SystemDocument5 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification On Book Shop Management SystemNachiket GawaliNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Requirement EngineeringDocument28 pagesUNIT-2 Requirement EngineeringAnuj MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Requirements Engineering Definition: RequirementsDocument15 pagesUnit 2 - Requirements Engineering Definition: RequirementsHema RaghuNo ratings yet
- 4.1requirement Engg P1Document26 pages4.1requirement Engg P1Usama AkbarNo ratings yet
- CH 1 IntroductionDocument38 pagesCH 1 IntroductionDaniel GetachewNo ratings yet
- Requirement Management12431221003bb222fdsdsdsdDocument18 pagesRequirement Management12431221003bb222fdsdsdsdniyati25No ratings yet
- OOSAD Chapter 3Document15 pagesOOSAD Chapter 3Shumet WoldieNo ratings yet
- Requirements EngineeringDocument9 pagesRequirements EngineeringHarshit BardeNo ratings yet
- Ssad Chap 4Document85 pagesSsad Chap 4Ziyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- CSE204 - Software RequirementsDocument14 pagesCSE204 - Software RequirementsjafarshehusaniNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement and AnalysisDocument43 pagesSoftware Requirement and Analysisaashishlisho2080No ratings yet
- Requirement Engineering Lab 1Document12 pagesRequirement Engineering Lab 1AKHILESH KULKARNINo ratings yet
- Requirement Engineering - Monitoring Elicitation Technique For End Product SoftwareDocument6 pagesRequirement Engineering - Monitoring Elicitation Technique For End Product SoftwareInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Medi Tracker DocumentationDocument105 pagesMedi Tracker DocumentationVema Bharath100% (2)
- SRS 10markDocument5 pagesSRS 10markElangovan MNo ratings yet
- Raw 3Document41 pagesRaw 3yarima1762No ratings yet
- SE Assignment 4Document8 pagesSE Assignment 4Tum BinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Requirement EngineeringDocument62 pagesChapter 4. Requirement Engineeringsukhmanaulakh54No ratings yet
- SR Chapter 2Document87 pagesSR Chapter 2Anas M AbughazalNo ratings yet
- Requirement EngineeringDocument6 pagesRequirement EngineeringNDDHSADNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction of SREDocument16 pagesLecture 1 Introduction of SRETalha JabbarNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Introduction To Software Requirement EngineeringDocument24 pagesCh1 Introduction To Software Requirement EngineeringShams SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper 14Document12 pagesLesson Proper 142204 Manabat, Ralph Matthew E.No ratings yet
- SWE Unit IIDocument16 pagesSWE Unit IIRAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- Srs and AnalysisDocument7 pagesSrs and AnalysisPuneet JangidNo ratings yet
- FSE Chapter 4Document74 pagesFSE Chapter 4Ermi TilaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5-6Document17 pagesLab 5-6NANA NANANo ratings yet
- CSC 411 Summary by TKDocument16 pagesCSC 411 Summary by TKKc MamaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Analyze Information System Requirements and SpecificationsDocument62 pagesLecture 2 - Analyze Information System Requirements and Specificationscharles mmariNo ratings yet
- SE Module2Document35 pagesSE Module2116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Requirement EngineeringDocument17 pagesRequirement EngineeringKishore AshrafNo ratings yet
- AM 1 Requirements Engineering LectureDocument19 pagesAM 1 Requirements Engineering Lecturezunair aliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Requirements Engineering and AnalysisDocument20 pagesLesson 3 Requirements Engineering and AnalysisAmit Rathi100% (1)
- April 18Document25 pagesApril 18Memes CornerNo ratings yet
- Relational AlgebraNewUpDocument21 pagesRelational AlgebraNewUpHasitha SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Structured Quey Language2-Database SystemsDocument28 pagesStructured Quey Language2-Database SystemsHasitha SanjayaNo ratings yet
- 1172-1591953801542-HND DDD W9 SQL Part1 PDFDocument20 pages1172-1591953801542-HND DDD W9 SQL Part1 PDFsl teachNo ratings yet
- Database NormalizationDocument32 pagesDatabase NormalizationHasitha SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Unified Modelling LanguageDocument2 pagesUnified Modelling LanguageHasitha SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Requirement Scenario - Question01Document1 pageRequirement Scenario - Question01Hasitha SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet ModelingDocument133 pagesSpreadsheet ModelingAshish Gondane100% (1)
- Internship Report FormatDocument27 pagesInternship Report FormatShreyas DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Xamarin Forms SuccinctlyDocument169 pagesXamarin Forms SuccinctlyBŕãhìm OūbålåoutNo ratings yet
- Usability & Usability EngineeringDocument37 pagesUsability & Usability Engineeringturturkeykey24No ratings yet
- Maharashtra Mahavidyalaya, Nilanga: Kadam Pradnya Biradar Anjali Nannure Pooja Bca Ty (Vi) 2022-23Document9 pagesMaharashtra Mahavidyalaya, Nilanga: Kadam Pradnya Biradar Anjali Nannure Pooja Bca Ty (Vi) 2022-23Dhiraj KadamNo ratings yet
- XMP64 JB Reseler Austarlia A4Document1 pageXMP64 JB Reseler Austarlia A4Déblocage icloud & Google 225No ratings yet
- A Systematic Literature Review of Factors Affecting Cloud Computing Adoption InternationallyDocument12 pagesA Systematic Literature Review of Factors Affecting Cloud Computing Adoption InternationallyMaster In TalentNo ratings yet
- PS KTDocument9 pagesPS KTAlhad KhistiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Sales Analyst: Internal Use - ConfidentialDocument2 pagesPre-Sales Analyst: Internal Use - ConfidentialAmarjeet KrishhnanNo ratings yet
- T3.QS Software ApplicationDocument64 pagesT3.QS Software Application槐序初夏No ratings yet
- 27 Mar 2021Document65 pages27 Mar 2021Devi InstituteNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument72 pagesProject Reportbca21066No ratings yet
- Guidelines College SPOCDocument6 pagesGuidelines College SPOCJonathan GamingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Service ProvidersDocument9 pagesCloud Service ProvidersNikunj Mani GuptaNo ratings yet
- GW Well Integrity Publication PDFDocument10 pagesGW Well Integrity Publication PDFRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Accenture ManualDocument11 pagesAccenture Manualmikedonovan4No ratings yet
- College Roommate AgreementDocument2 pagesCollege Roommate AgreementJazyl PeralesNo ratings yet
- 1 InfoSec+Risk MGMTDocument145 pages1 InfoSec+Risk MGMTIslamNo ratings yet
- 1Z0 1051 23demoDocument5 pages1Z0 1051 23demogpanura.65iNo ratings yet
- CT071-3-M-OOSSE-Question PaperDocument4 pagesCT071-3-M-OOSSE-Question PaperSAILESH MAHARJANNo ratings yet
- Project Report - Visual OS SchedulerDocument13 pagesProject Report - Visual OS Schedulerc201266No ratings yet
- Product Change Notice: Huawei PCN ALD-20160005 Antenna Connector ChangeDocument17 pagesProduct Change Notice: Huawei PCN ALD-20160005 Antenna Connector ChangeAnonymous CGk2roNo ratings yet
- Compfp: Instruction: Open Ms Word and Apply The Ff. RequirementsDocument2 pagesCompfp: Instruction: Open Ms Word and Apply The Ff. RequirementsIzza AnsamaNo ratings yet
- Aiag & Vda PfmeaDocument5 pagesAiag & Vda PfmeaRamzi hammamiNo ratings yet