Professional Documents
Culture Documents
System Hacking
System Hacking
Uploaded by
whatsapp88704717Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
System Hacking
System Hacking
Uploaded by
whatsapp88704717Copyright:
Available Formats
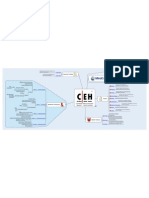
The Ethical Hacker's Guide To System Hacking
Attacker acquires information through techniques such as foot printing,
scanning and enumeration to hack the target system.
Footprinting Scanning Enumeration Module Vulnerability Analysis
It is the process of accumulating data This is a procedure for identifying This is a method of intrusive probing, Vulnerability Assessment is an Footprinting Scanning
System Hacking regarding a specific network environment. active hosts, open ports, and unnecessary through which attackers gather examination of the ability of a system or
In this phase, the attacker creates a profile services enabled on ports. Attackers use information such as network user lists, application, including current security CEH
concepts of the target organization, obtaining different types of scanning, such as port routing tables, security flaws, and procedures, and controls to with stand 2
information such as its IP address range, scanning network scanning, and simple network protocol data (SNMP) assault. Attackers perform this analysis Methodology Vulnerability
namespace and employees. vulnerability, scanning of target networks to identify security loopholes, in the target
Enumeration
Footprinting eases the process of
data. Analysis
or systems which help in identifying organization’s network, communication
system hacking by revealing its possible vulnerabilities. infrastructure, and end systems.
vulnerabilities 3
Clearing Logs Maintaining Access Gaining Access
Hacking Stage Escalating Privileges Hacking Stage Gaining Access
It involves gaining access to
To maintain future system access, After gaining access to the target low-privileged user accounts by
To acquire the rights of To bypass access attackers attempt to avoid recognition system, attackers work to maintain
CEH Hacking
cracking passwords through
Goal another user or Goal controls to gain System Hacking by legitimate system users. To remain high levels of access to perform
and admin access to the system 4 techniques such as brute forcing, Methodology
undetected, Attackers wipe out the malicious activities, such as stealing, password guessing, and social
Goals entries corresponding to their hiding or tampering with sensitive
Exploiting known Password cracking, engineering and then escalate their (CHM)
Technique used Technique used activities in the system log. files. privileges to administrative levels, to
system vulnerabilities Social engineering
perform a protected operation.
Non- Electronic Active Online Attack – Dictionary,
Hacking Stage Executing Applications Hacking Stage Hiding Files Hacking Stage Covering Tracks
Social Engineering Brute Forcing and Rule Based attack
Convincing people to reveal passwords Social Engineering
To create and maintain
Password Cracking Convincing people to reveal passwords
To hide attackers Types of Shoulder Surfing
Goal remote access Goal Goal To hide the evidence Attackers use this technique to gain Shoulder Surfing
malicious activities Looking at either the user’s keyboard or screen
of compromise 5 unauthorized access to vulnerable system. while he/she is logging in
Looking at either the user’s keyboard or screen
and data theft Such a technique is mostly successful due Password attacks while he/she is logging in
to weak or easy passwords. Dumpster diving Dumpster diving
Trojans, spywares, Searching for sensitive information in the Searching for sensitive information in the
Technique used Technique used Rootkits, stenography Technique used Clearing logs user’s trash-bins, printer trash bins, and
backdoors, keyloggers user’s trash-bins, printer trash bins, and
user desk for sticky notes. user desk for sticky notes.
Active Online Attack Active Online Attack – Password Guessing Active Online Attack – Dictionary,
Passive Online Attack Passive Online Attack – Wire Sniffing Active Online Attack – LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning Active Online Attack – Hash Injection Attack – Trojan/Spyware /Keylogger The attacker creates a list of all possible passwords Brute Forcing and Rule Based attack
Man in the Middle and replay attack from the information collected through social
• Attacker run packet sniffer tools on the local area engineering or any other way and tries them Dictionary
• In a MITM attack, the attacker acquires access to the network (LAN) to access and record the raw network • A hash injection attack allows an attacker to inject a
• LLMNR/NBT are two main elements of windows compromised hash into a local session and use the manually on the victim’s machine to crack the A dictionary file is loaded into the cracking
communication channels between victim and server to traffic. • Attacker installs Trojan/spyware/keylogger application that runs against user accounts
extract the information operating systems used to perform name resolution hash to validate network resources passwords.
• The captured data may include sensitive information on victim’s machine to collect victim’s usernames
• In a replay attack, packets and authentication tokens such as passwords (FTP, rlogin sessions, etc.) and for hosts present on the same link • The attacker finds and extracts a logged-on and passwords
are captured using a sniffer. After the relevant info is • The attacker cracks the NTLMv2 hash obtained from Find a valid user Brute Forcing
emails. domain admin account hash
extracted, the tokens are placed back on the network the victim’s authentication process • Trojan/spyware/keylogger runs in the background Create a list possible password The program tries every combination of
• Sniffed credentials are used to gain unauthorized • The attacker uses the extracted hash to log on
to gain access. • The extracted credentials are used to log on to the and sends back all user credentials to the attacker. characters until the password is broken
access to the target system to the domain controller. Rank passwords from
host system in the network
high probability to low Rule Based attack
Key in each password until correct This attack is used when the attacker gets
password is discovered some information about the password
Offline Online Attack – Rainbow table attack Offline Online Attack 1.Enable information security audit to monitor and track password attacks
2.Do not use the same password during password change
• DNA technique is used for recovering passwords Distributed Network Attack 3.Do not share passwords •An attacker can gain access to the network using a non-admin user
from hashes or password protected files using the •An attacker can gain access to the network using a non-admin user
4.Do not share passwords that can be found in a dictionary account and the next step would be to gain administrative privileges.
unused processing power of machines across the account and the next step would be to gain administrative privileges.
5.Do not cleartext protocols and protocols with weak encryption These
network to decrypt passwords These
6.Set the password change policy to 30 days •These privileges allow attacker to view critical/ sensitive information,
• The DNA manager is installed in a central location where • A Rainbow table attack is a precomputed table •These privileges allow attacker to view critical/ sensitive information,
machines running on DNA client can access it over the which contains word lists like dictionary files and brute How to Defend against 7.Avoid storing passwords in an unsecured location
8.Do not use any systems default passwords
Escalating delete files, or install malicious programs such as viruses, trojans, worms
delete files, or install malicious programs such as viruses, trojans, worms
etc.
network
• DNA manager coordinates the attack and allocates
force lists and their hash values.
6 Password Cracking
9.Make passwords hard to guess.
10.Ensure that applications neither store passwords to memory nor write them
7 Privileges
etc.
•Attacker performs privilege escalation attack which takes advantage of
•Attacker performs privilege escalation attack which takes advantage of
design flaws, programming errors, bugs, and configuration oversights in
small portions of the key search to machines that are design flaws, programming errors, bugs, and configuration oversights in
to disk in clear text. the OS and
distributed over the network the OS and
11.Use a random string or prefix or suffix with the password before encrypting software application to gain administrative access to the network and
• DNA client runs in the background consuming only software application to gain administrative access to the network and
12.Monitor servers’ logs for brute force attacks on user accounts its associated applications.
unused processor time its associated applications.
13.Lock out an account subjected to too many incorrect password guesses
• The program combines processing capabilities of
14.Enable SYSKEY with strong password to encrypt and protect SAM database
all the clients connected to network and use it to
crack the password
Scheduled Task - Access token Manipulation – Other privilege Techniques Type of privileges
•Windows task scheduler along with utilities such as ‘at’ and ‘schtasks’ can be used
1.Restrict the interactive logon privileges to schedule programs that can be executed at a specific date and time. •Windows operating system uses access tokens to determine the security
11.Change user account control settings to “Always Notify” context of a process or thread Access token Manipulation –
2.Use encryption technique to protect sensitive data •Attacker can use this technique to execute malicious programs at system startup,
maintain persistence, perform remote execution, escalate privileges etc. •Attackers can obtain access tokens of other users or generate spoofed
12.Restrict users from writing files to the search paths for • Windows operating system uses access tokens to
applications 3.Run users and applications on the least privileges Launch Demon tokens to escalate privileges and perform malicious activities by evading detection determine the security context of a process or thread
•LaunchD is used in MacOS and OS x boot up to complete the system initialization Application Shimming
13.Continuously monitor file system permissions using 4.Reduce the amount of code that runs with privilege process by loading parameters for each launch on demand system-level daemon •Windows applications compatibility framework, shim is used to provide • Attackers can obtain access tokens of other users or
auditing tools 5.Implement multi factor authentication and authorization •Daemons have plists that are linked to executable that run at start up
•Attacker can alter the daemons executable to maintain persistence or to compatibility between the older and newer versions of windows operating system. generate spoofed tokens to escalate privileges and • Horizontal – Refers to acquiring the same level of
14.Reduce the privileges of users and groups so that only 6.Perform de-bugging using bounds checkers and stress escalate privileges • Shims like RedirectEXE, injectDLL, GetProAddress, can be used by attackers perform malicious activities by evading detection
privileges that already has been granted but assuming
legitimate administrators can make service changes
15.Use whitelisting tools to identify and block malicious tests How to Defend against Plist Modification –
•Plist files in MacOS and OS X describe when programs should execute,
to escalate privileges, install backdoors disable, windows defenders etc.
File System Permissions weakness
Application Shimming
• Windows applications compatibility framework, shim is the identity of another user with the similar privileges
7.Run services as unprivileged accounts
8
executable file path, program parameters, required OS PERMISSIONS ETC. • If the file system permissions of binaries are not properly set, an attacker can
software •Attackers alter plist files to execute malicious code on behalf of a legitimate used to provide compatibility between the older and
• Vertical – Refers to gaining higher privileges than the
replace the target binary with a malicious file
16.Use fully qualified paths in all the windows applications 8.Test operating system and application coding
Privilege Escalation user to escalate privileges. newer versions of windows operating system.
17.Ensure that all executables are placed in write-protect errors and bugs thoroughly Setuid and Setgid
•In Linux and MacOS, is an application uses setuid or setgid then the application
•If the process that is executing this binary is having higher level
permissions, then the malicious binary also executes under higher level permissions. • Shims like RedirectEXE, injectDLL, GetProAddress, can be used by existing
directories Path Interception – attackers to escalate privileges, install backdoors disable, windows defenders etc.
18.In Mac operating systems make pilst files read-only 9.Implement a privilege separation methodology to limit will execute within the privileges of the owning user or group
•An Attacker can exploit the applications with the setuid or setgid flags to execute •Applications include many weaknesses and misconfigurations like unquoted File System Permissions weakness
19.Block unwanted system utilities or software that may be the scope of programming errors and bugs malicious code with elevated privileges. paths, path environment variable misconfiguration and search order hijacking • If the file system permissions of binaries are not properly set, an attacker can
Web shell –
used to schedule tasks 10.Patch and update the kernel regularly •A web shell is a web-based script that allows access to a web server
that lead to oath interception.
•Path interception helps an attacker to maintain persistence on a system and
replace the target binary with a malicious file
20.Patch and update the web servers regularly •Attackers create web shells to inject malicious script on a web server to maintain • If the process that is executing this binary is having higher level permissions,
persistent access and escalate privileges escalate privileges then the malicious binary also executes under higher level permissions.
Attackers execute malicious applications in this stage. RemoteExe – Remotely installs applications, executes Keystroke loggers are programs or hardware devices that
This is called “owning” the system. programs/scripts and updates files and folders on windows monitor each keystroke as user types on a keyboard, logs
The malicious programs attackers execute on target system: systems throughout the network. onto a file, or transmits them to a remote location.
B a c k d o o r s – Program designed to deny or disrupt operation,
gather information that leads to exploitation or loss of privacy, Tools used for executing application remotely helps attackers Legitimate applications for keyloggers include office and
gain unauthorized access to system resources. perform various malicious activities on target systems. After industrial settings to monitor employee’s computer activities
Executing
Once attacker gain higher privileges on the target system by
trying various privilege escalation attempts, they may attempt
C r a c k e r s – piece of software or program designed for cracking a
code or passwords.
Tools for Executing gaining administrative privileges, attackers use these tools to
install, execute, delete and/or modify the restricted resource on
and in-home environments where parents can monitor and spy
on children’s activity.
to execute a malicious application by exploiting a vulnerability K e y l o g g e r s – This can be hardware or a software type. In either
10 Applications
the victim machine. 11 Keyloggers
Applications to execute arbitrary code. case, the objective is to record each keystroke made on the
computer keyboards. It allows attacker to gather confidential
It allows attacker to gather confidential information about
victim such as email ID, passwords, banking details, chat
It allows attacker to modify the registry, change local admin
information about victim such as email ID, passwords, banking room activity, IRC, instant messaging etc.
passwords, disable local accounts, and copy/update/delete files
details, chat room activity, IRC etc.
and folders.
S p y w a r e - Spy software may capture screenshots and send Physical keyloggers are placed between the keyboard
them to a specified location defined by the hacker. hardware and the operating system.
How to Defend against keyloggers How to Defend Against keyloggers
Types of Keystroke Loggers
1) Use pop up blocker and avoid opening junk emails
Spyware allows attackers to gather information about a victim or organization such as email addresses, user logins, 2) Install antispyware/virus programs and keep the signatures up to date
Hardware keylogger measures
3) Install professional firewall software and anti-keylogging software Hardware Software
GPS Spyware
passwords, credit cards, banking credentials etc.
1) Restrict physical access to sensitive computer 4) Recognize phishing emails and delete them
Video Telephone/cellphone
5) Update and patch system software regularly
systems 6) Do not click on links in unwanted r doubtful emails that may point to PC/BIOS Embedded Application Keylogger
Mov, avi Video Editor Phone spy Spyera Spyware USB Spyware
Audio Spyware
malicious sites.
2) Periodically check all the computers and check Embedded Kernel Keylogger
ACTIVtrak USB Analyzer Spy Voice Recorder 7) Use keystroke interference software which inserts randomized characters
Free2x webcam recorder XNSPY mSpy
whether there is any hardware device connected to into every keystroke Keylogger Keyboard Hypervisor Based Keylogger
Spy Audio listening Device
iSpy iKeyMonitor Mobile spy
Veriato 360 USB Monitor
Spy USB Voice Recorder
Spyware 12 the computer
8) Scan the files before installing and use registry editor or process explorer
to check for the keystroke loggers External Keylogger Form Grabbing Based Keylogger
Netvizor USB Deview 9) Use windows on-screen keyboard accessibility utility to enter the password
Mobistealth 3) Use encryption between the keyboard and its driver or any other confidential information. PS/2 and USB Keylogger
NET video Spy OneSpy Activity Monitor Advanced USB Port Monitor Audio Spy
10) Install a host-based IDS, which can monitor your system and disable the
4) Use an anti-keylogger that detects the presence of Acoustic/CAM
FlexiSpy Soft Activity TS Monitor USB Monitor Pro Voice activated flash drive voice recorder installation of keyloggers
Eyeline Video Surveillance TheTruthSpy
Software a hardware keyloggersuch as oxynger KeyShield 11) Use automatic form -filing password manager or virtual keyboard to enter
Bluetooth keylogger
username and password
5) Use an On-screen keyboard and click on it. 12) Use software that frequently scans and monitors the changes in the system Wi-Fi Keylogger
or network.
How to Defend against Spyware
Root Kits Objectives of Rootkit
Try to avoid using any computer system which is not totally Install and use anti-spyware software Root Kits are programs that hide their presence as well To root the host system and gain remote backdoor access. Attackers Places a Rootkit by:
under control as attacker’s malicious activities, granting them full access
Perform web surfing safely and download cautiously To mask attacker tracks and presence of malicious
to the server or host at that time and in future. Scanning for vulnerable computers and servers on the web.
Adjust browser security settings to medium or higher for internet zone applications or processes.
Do not use administrative mode unless it is necessary Wrapping it in a special package like games.
Be cautious about suspicious emails and sites Rootkits replace certain operating system calls and utilities To gather sensitive data, network traffic, from the system to
Enable firewall to enhance the security level of the computer
Keep your operating system up to date
13 Hiding Files with its own m o d i f i e d v e r s i o n s of those routines that in turn which attackers might be restricted or possess no access.
Installing it on the public computers or corporate computers
through social engineering.
determine the security of the target system causing malicious
Do not download free music files, screensavers, or smiley faces from internet functions to be executed. To store other malicious programs on the system and act
Update the software regularly and use a firewall with outbound protection Launching zero day attack (privilege escalation, buffer overflow,
Beware of pop-up windows or webpages. as a server resource for bot updates. windows kernel exploitation, etc).
A typical rootkit comprises of backdoor programs,
Regularly check task manager report and MS configuration manager report
Carefully read all disclosures, including the license agreement and Ddos programs, packet-sniffers, log-wiping utilities,
Update virus definition files and scan the system for spyware regularly privacy statement before installing any application IRCBots, etc.
Classification of Stenography Stenography
Detecting Rootkits Detecting Rootkits
Types of Rootkits
Types of Rootkits
Enumerates key elements in the computer Integrity Based It compares a snapshot of the file system,
Cross View-based
Application Level Replaces regular application binaries with Acts as a hypervisor and modifies the boot
Stenography Stenography is a technique of hiding secret message with an Detection system such as system files, processes, Detection boot records or memory with a known Hypervisor Level
trusted baseline fake trojan or modifies the behavior of sequence of the computer system to load
ordinary message and extracting it at the destination to maintain and registry keys and compares them to an
Linguistic Stenography existing applications by injecting malicious the host operating system as a virtual
confidentiality of data. algorithm used to generate a similar data set Signature - Based This technique compares characteristics codes. machine
Semagrams open codes that does not rely on the common APIs. of all system processes and executable
Utilizing a graphic image as a cover is the most popular Detection
Any discrepancies between these two data files with a database of known rootkits Library Levels Replaces original system calls with fake Hardware / Firmware Hides in hardware devices or platform firm
method to conceal data in files.
Visual semagrams Covered Ciphers Null Cipher Stenography 14 sets indicate the presence of rootkit fingerprints ones to hide information about the attacker which is not inspected for code integrity
Text semagrams Jargon code Griller Cipher Attackers can use stenography to hide messages such as
Heuristic . Behavior Any deviation in the system’s normal activity Kernel Level Adds malicious code or replaces original
list of the compromised servers, source code for the hacking or behavior may indicate the presence of
Based Detection OS ker nel and device driver codes
Technical stenography tool, plans for future attacks etc. rootkit
Runtime Execution This technique compares runtime execution Boot Loader Level Replaces the original boot loader with one
Path Profiling paths of all system processes and executable controlled by a remote attacker.
files before and after the rootkit infection
Types of Stenography Covering Tracks Ways to Clear Online Tracks
Once intruders have successfully gained administrator access
Attackers clear online tracks maintained using web history, logs,
on a system, they will try to cover the tracks to avoid their
cookies, cache, downloads. This way the victims cannot notice
Image Web
detection. what online activities attacker have performed.
Document Spam/email Covering Attackers use the following techniques to cover tracks on the target Ways to Clear
15 What attackers do to clear their online tracks
Folder DVD-ROM system 16
Video Natural Text Tracks Online Tracks Delete history Disable password manager
Disable auditing – Disables auditing features
Hidden OS Delete private data Turnoff autocompletes
Audio Clearing Logs – clear/delete the system log entries Delete user JavaScript
Delete cookies
Whitespace Source Code Remove most recently used
Manipulating Logs -Manipulates logs in such a way that he/she will not be Clear cache on exit
Delete all downloads Delete saved sessions.
caught in legal actions.
You might also like
- Rules of EngagementDocument4 pagesRules of EngagementSYED JUNAID AHMEDNo ratings yet
- MindCert CEH Ethical Hacking MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CEH Ethical Hacking MindMapgarbett294No ratings yet
- Penetration Testing PresentationDocument15 pagesPenetration Testing PresentationArif Zina50% (2)
- Crack The User Data On Blackphone: Proof of ConceptDocument4 pagesCrack The User Data On Blackphone: Proof of ConceptGilbert Laszlo KallenbornNo ratings yet
- Pentest BlueprintDocument1 pagePentest Blueprinttoanquoc.doanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Intrusion-Detection SystemsDocument19 pagesAn Introduction To Intrusion-Detection SystemsGeraud TchadaNo ratings yet
- DNS CNAME TrackingDocument21 pagesDNS CNAME TrackingJesus VilchezNo ratings yet
- IRM 5 MaliciousNetworkBehaviourDocument2 pagesIRM 5 MaliciousNetworkBehaviourtaekNo ratings yet
- Malgene: Automatic Extraction of Malware Analysis Evasion SignatureDocument12 pagesMalgene: Automatic Extraction of Malware Analysis Evasion SignatureJuan Alfredo Salas SantillanaNo ratings yet
- Indirect Human Computer Inteaction - Based Biometrics For Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument9 pagesIndirect Human Computer Inteaction - Based Biometrics For Intrusion Detection SystemsChristian Tamayo CroocNo ratings yet
- A 99 Weka: Review Paper On IDS Classification Using KDD and NSL KDD Dataset inDocument6 pagesA 99 Weka: Review Paper On IDS Classification Using KDD and NSL KDD Dataset innancypeterNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapjayarajan100% (1)
- MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Access Control MindMap PDFZeeshan RanaNo ratings yet
- LiaoDocument10 pagesLiaoRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Penetration Testing: A Roadmap To Network SecurityDocument4 pagesPenetration Testing: A Roadmap To Network SecurityYoni sudarmanNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Using Text Categorization Techniques For Intrusion DetectionDocument9 pagesUsing Text Categorization Techniques For Intrusion DetectionkarmaNo ratings yet
- Memory ForensicsDocument70 pagesMemory ForensicsramdevNo ratings yet
- Ieee Paper N3PTU0N3Document12 pagesIeee Paper N3PTU0N3Jagadees 2410No ratings yet
- IRJET Intrusion Detection System Using SDocument6 pagesIRJET Intrusion Detection System Using Sanand.dhawaleNo ratings yet
- 3967.1 Pentest Product Sheet - FA - RGBDocument2 pages3967.1 Pentest Product Sheet - FA - RGBSteven HarleNo ratings yet
- OwezarskiDocument13 pagesOwezarskifarhanNo ratings yet
- Framework For Digital Forensic Evidence Collection With Chain of Custody (Coc)Document28 pagesFramework For Digital Forensic Evidence Collection With Chain of Custody (Coc)andrewrogers5836No ratings yet
- Process Monitoring On Sequences of System Call Count VectorsDocument5 pagesProcess Monitoring On Sequences of System Call Count VectorsMarc Aurele EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- A Review of Intrusion Detection SystemDocument3 pagesA Review of Intrusion Detection SystemEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Approach For Cyber SecurityDocument7 pagesData Mining Approach For Cyber Security38 keerti ToraviNo ratings yet
- Huawei Big Data-Based Anti-APT SolutionDocument4 pagesHuawei Big Data-Based Anti-APT SolutionLuis Filipe SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ceh Teoria Mod 6Document317 pagesCeh Teoria Mod 6heisembergNo ratings yet
- Fase de Reconocimiento en Pentesting Un Enfoque PrácticoDocument11 pagesFase de Reconocimiento en Pentesting Un Enfoque Prácticoxdpipe281997No ratings yet
- A Data Mining Framework For Building Intrusion Detection ModelsDocument13 pagesA Data Mining Framework For Building Intrusion Detection ModelsVu Dinh ThuNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Approaches For Intrusion DetectionDocument15 pagesData Mining Approaches For Intrusion DetectionLeonid VilNo ratings yet
- Penetration Testing Learning KitDocument51 pagesPenetration Testing Learning KitSpyDr ByTeNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Vajiheh Hajisalem, Shahram BabaieDocument14 pagesComputer Networks: Vajiheh Hajisalem, Shahram BabaieSikha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Assignment cs520 Week6 Chelsea HittDocument4 pagesAssignment cs520 Week6 Chelsea Hittapi-374891391No ratings yet
- Ethical Network Surveillance Using Packet Sniffing Tools: A Comparative StudyDocument11 pagesEthical Network Surveillance Using Packet Sniffing Tools: A Comparative StudyRezu JavNo ratings yet
- 02 Secure PrinsipDocument14 pages02 Secure PrinsipEko TriyantoNo ratings yet
- SOC Monitoring MindmapDocument1 pageSOC Monitoring MindmapWin ErNo ratings yet
- A Review of Anomaly Based Intrusion Detection Systems: V. Jyothsna V. V. Rama Prasad K. Munivara PrasadDocument10 pagesA Review of Anomaly Based Intrusion Detection Systems: V. Jyothsna V. V. Rama Prasad K. Munivara PrasadAnggi Saputri MaulaniNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing PDFDocument6 pagesVulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing PDFproftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- Krish 2Document8 pagesKrish 2pantiltNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V5I6P20) :bonealli Pedda UppalaiahDocument5 pages(IJCST-V5I6P20) :bonealli Pedda UppalaiahEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument5 pagesAbstract20-0576 DINESH VAMSINo ratings yet
- EasyChair Preprint 7115Document8 pagesEasyChair Preprint 7115rohi njathiNo ratings yet
- Signature Based Intrusion Detection System Using SNORT: Related PapersDocument8 pagesSignature Based Intrusion Detection System Using SNORT: Related PapersRoshanNo ratings yet
- ICIISDocument6 pagesICIISdejuNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Systems by Anamoly-Based Using Neural NetworkDocument6 pagesIntrusion Detection Systems by Anamoly-Based Using Neural NetworkInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- A Framework For Database Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesA Framework For Database Intrusion Detection SystemDrashti GaradhariaNo ratings yet
- Countermeasure For Detection of Honeypot DeploymentDocument5 pagesCountermeasure For Detection of Honeypot DeploymentHarshitha BMNo ratings yet
- 06Paper31101159IJCSISCameraReadypp 33-40Document9 pages06Paper31101159IJCSISCameraReadypp 33-40Chris MEDAGBENo ratings yet
- Malware Detection Using Statistical Analysys Byte Level File ContentDocument9 pagesMalware Detection Using Statistical Analysys Byte Level File Contentricksant2003No ratings yet
- Jpcap Winpcap Used For Network IntrusionDocument4 pagesJpcap Winpcap Used For Network Intrusionhoremheb1No ratings yet
- Detecting Advanced Persistent ThreatsDocument46 pagesDetecting Advanced Persistent Threatskk ddNo ratings yet
- Paper5 IJCISDocument7 pagesPaper5 IJCISManikandan K.p.No ratings yet
- Network PenetrationDocument12 pagesNetwork Penetrationksharisankar15No ratings yet
- Microsoft ATA Customer ReadyDocument26 pagesMicrosoft ATA Customer ReadyJoao JoseNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument20 pagesIntrusion Detection System4MH18CS086 Rakesh Mallika SNo ratings yet
- Learn Cyber SecurityDocument1 pageLearn Cyber SecurityPHẠM MINH TRÍNo ratings yet
- Attacks On Dynamic Protocol Detection of Open Source Network Security Monitoring ToolsDocument11 pagesAttacks On Dynamic Protocol Detection of Open Source Network Security Monitoring ToolszsboxqqmkgNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Systems and Intrusion Prevention SystemsDocument6 pagesIntrusion Detection Systems and Intrusion Prevention SystemsLiziane TammNo ratings yet
- Penetration Testing Fundamentals-2: Penetration Testing Study Guide To Breaking Into SystemsFrom EverandPenetration Testing Fundamentals-2: Penetration Testing Study Guide To Breaking Into SystemsNo ratings yet
- Penetration Testing Fundamentals -1: Penetration Testing Study Guide To Breaking Into SystemsFrom EverandPenetration Testing Fundamentals -1: Penetration Testing Study Guide To Breaking Into SystemsNo ratings yet
- AIS 12e Romney Chapter 6Document30 pagesAIS 12e Romney Chapter 6JustYourAverageStudentNo ratings yet
- Understanding SIP AuthenticationDocument4 pagesUnderstanding SIP AuthenticationSK_shivamNo ratings yet
- MSIS 1stF21BINSE3M01015Document4 pagesMSIS 1stF21BINSE3M01015Sana NasirNo ratings yet
- Cryptree: A Folder Tree Structure For Cryptographic File SystemsDocument10 pagesCryptree: A Folder Tree Structure For Cryptographic File SystemsloreNo ratings yet
- Wifi Event - Log30Document11 pagesWifi Event - Log30Lourdes Vera MedinaNo ratings yet
- DLP AntiDocument3 pagesDLP AntiRain CollinsNo ratings yet
- CEH Module 13: Hacking Email AccountsDocument48 pagesCEH Module 13: Hacking Email AccountsAhmad Mahmoud100% (1)
- M - Controller Self Signed CertificateDocument8 pagesM - Controller Self Signed Certificateshola ogundipeNo ratings yet
- Metasploit Framework by Achilli3stDocument81 pagesMetasploit Framework by Achilli3stSavan Patel100% (1)
- SQL InjectionDocument3 pagesSQL Injectiondanieldamalie9No ratings yet
- Graphical Password ReportDocument20 pagesGraphical Password ReportOmkar SangoteNo ratings yet
- Css Exp 1Document4 pagesCss Exp 1GG NHKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Securing Network DevicesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Securing Network DevicesDesmond Calini0% (1)
- MALWARE Chap3Document39 pagesMALWARE Chap3Nur SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Application of The Blockchain For Authentication and Verification of IdentityDocument9 pagesApplication of The Blockchain For Authentication and Verification of IdentitySaadia MooqaddasNo ratings yet
- Gmail ScenariosDocument2 pagesGmail ScenariosArshad Mubarak63% (8)
- Playfair CipherDocument8 pagesPlayfair CipherShivansh YashasviNo ratings yet
- Pasword Generator - Ref 1Document4 pagesPasword Generator - Ref 1modussarNo ratings yet
- SSTP Server For Windows 10Document14 pagesSSTP Server For Windows 10Marlo TinaNo ratings yet
- Password-Less SSH Setup: Getting StartedDocument2 pagesPassword-Less SSH Setup: Getting StartedAddiNo ratings yet
- CIS6013 Web-Application-Security ETH 1 AC41Document9 pagesCIS6013 Web-Application-Security ETH 1 AC41;(No ratings yet
- Charismathics Smart Security Interface © User Manual V 5.0 For LINUXDocument18 pagesCharismathics Smart Security Interface © User Manual V 5.0 For LINUXvazmutenNo ratings yet
- Cipher Methods: A02:-Nikhil Chhabria A10: - Kabir Kanjani A11: - Yash Khatri A12: - Shubham Koshti A49: - Siraj ShaikhDocument25 pagesCipher Methods: A02:-Nikhil Chhabria A10: - Kabir Kanjani A11: - Yash Khatri A12: - Shubham Koshti A49: - Siraj ShaikhdevalNo ratings yet
- Secure Website Standard IND 001Document26 pagesSecure Website Standard IND 001Mulugeta BeshahNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument63 pagesClassical Encryption TechniquesmanNo ratings yet
- Web Vulnerability Analysis and ImplementationDocument9 pagesWeb Vulnerability Analysis and ImplementationAndi DwiNo ratings yet
- S 1Document12 pagesS 1shabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Eb Converged It and OtDocument14 pagesEb Converged It and OtmykillerdroneNo ratings yet