Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antianginal Drugs (2) Atf
Antianginal Drugs (2) Atf
Uploaded by
jasonbournee221Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antianginal Drugs (2) Atf
Antianginal Drugs (2) Atf
Uploaded by
jasonbournee221Copyright:
Available Formats
AfraTafreeh.
com
Last edited: 10/21/2022
ANTIANGINAL DRUGS
Antianginal Drugs Medical Editor: Ana Guerra
OUTLINE
I) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ANGINA III) CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS V) RANOLAZINE
II) BETA BLOCKERS (A) CALCIUM CHANNEL (A) RANOLAZINE TREATMENT
(A) BETA BLOCKERS TREATMENT BLOCKERS TREATMENT ALGORITHM
ALOGORITH ALGORITHM VI) REVIEW QUESTIONS
IV) NITRATES VII) REFERENCES
(A) NITRATES TREATMENT VIII) ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS
ALGORITHM
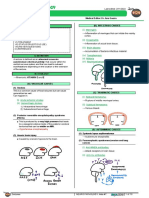
I) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ANGINA
(1) Atherosclerotic plaque or spasms
Occlusion of coronary arteries by atherosclerotic plaques or an spasm
AfraTafreeh.com
(2) Increased O2 demand by myocardial cells (MVO2)
Because of the poor amount of O2 that myocardial cells are receiving
(i) Stable angina
(ii) Vasospastic angina (AKA Prinzmetal or Variant)
o Reduction of oxygen supply to the myocardium but
i. At rest
still enough to prevent an infarction.
ii. Younger females with history of tobacco
i. Lasts less than ten minutes
smocking.
ii. Relieved by nitrates or by
iii. Triggered by triptanes, cocaine or alcohol.
iii. Relieved by exercise
iv. Occur more commonly during the morning.
Antianginal Drugs PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. 1 of 7
(iv) Unstable angina (v) NSTEMI
▪ Ischemia to the myocardium without exertion.
o Release of troponins from the myocardial cells.
o Due to unstable plaques
▪ No need of O2 demand
▪ Severe chest pain
▪ Infarction only affects partially the myocardium
walls.
(vi) STEMI
AfraTafreeh.com
AfraTafreeh.com
2 of 7 PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. Antianginal Drugs
AfraTafreeh.com
II) BETA BLOCKERS
First-line prophylactic medication
(i) Metoprolol
(ii) Atenolol
(iii) Propranolol (beta 1 and beta 2 activity)
(1) Mechanism of action (2) Adverse effects
Bradycardia
Hypotension or shock – Careful with patients with
1) Inhibition of nodal cells (chronotropic and decompensated heart failure.
dromotropic actions) Bronchoconstriction when using propranolol for its
▪ Decrease of HR effects on Beta 2 receptors.
1) Decrease of contractility
▪ Decrease of stroke volume
• Decrease of cardiac output
AfraTafreeh.com
Hypoglycemia unawareness
(B) BETA BLOCKERS TREATMENT ALOGORITHM
Patient with angina (i) Good for patients
(ii) Careful with patients with
Antianginal Drugs PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. 3 of 7
AfraTafreeh.com
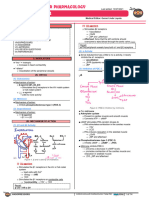
III) CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS
Second-line prophylactic medication
Preferred in patients with Prinzmetal or vasospastic angina
(1) Mechanism of Action
(i) Non-DHP CCB´s:
o Verapamil
o Diltiazem
1) Inhibition of nodal cells
2) Decrease of contractility
RECALL RECALL
Within the heart, Non-DHP calcium channels allow Ca++ to Within the arterial smooth muscle cells, DHP calcium
enter into the nodal cells and increase action potential channels allow Ca++ to enter into the cells and increase
action potential
(ii) DHP CCB´s: o Verapamil > diltiazem
o DHP CCB > Non-DHP CCB
o Amlodipine
o Nifedipine
1) Arterial smooth muscle cells relaxation
(2) Adverse Effects
Bradycardia
Decrease of contractility
2) Reduction of vasospasm on coronary artery DHP CCB: Reflex tachycardia due to decrease of SVR
cells Increase risk of mortality in post MI patients
(B) CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS TREATMENT ALGORITHM
Patient with angina
a. CCB: Either Non-DHP or DHP: Especially
if vasospasm or Prinzmetal; HTN,
COPD or DM
b. Nitrates
4 of 7 PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. Antianginal Drugs
AfraTafreeh.com
AfraTafreeh.com
IV) NITRATES
(1) Mechanism of Action
(i) On veins Tolerance:
Drug enters the venous smooth muscle cell
▪ Stimulation of guanylate cyclase
o Have a nitrate-free interval (10-12 hours)
o Inhibits contraction of the smooth cell
▪ Venodilation → Reduction of
preload → Reduction of CO
• Reduction of O2 demand
(ii) On arteries
Drugs enters the arterial smooth muscle cell
▪ Stimulation of guanylate cyclase
o Inhibits contraction of the smooth cell
▪ Coronary vasodilation → Increase
perfusion to the myocardium
(2) Drugs
(i) Short acting
▪ Sublingual or subdermal
(ii) Long acting
(B) NITRATES TREATMENT ALGORITHM
a. CCB: Either Non-DHP or DHP: Especially if vasospasm or Prinzmetal; HTN, COPD or DM
b. Nitrates: Long acting nitrates (ISDN, ISMN)
▪ More beneficial: Post MI, DM, COPD/ Asthma
▪ CI: HTN
AfraTafreeh.com
Antianginal Drugs PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. 5 of 7
AfraTafreeh.com
V) RANOLAZINE
(1) Mechanism of Action
(i) Ischemia without Ranolazine
(ii) Ischemia with Ranolazine
o Na+ influx into the cell → Increase of Na+/Ca++
o Inhibition of inward Na+ channel → No Ca++ influx
contratransporter
into the cell
(2) Adverse Effects
Drug interactions
Prolonged depolarization phase → QT interval → Increase risk of Torsades de Pointes
(B) RANOLAZINE TREATMENT ALGORITHM
a. CCB: Either Non-DHP or DHP: Especially
if vasospasm or Prinzmetal; HTN,
COPD or DM
b. Nitrates: Long acting nitrates (ISDN,
ISMN)
▪ More beneficial: Post MI, DM, COPD/
Asthma
▪ CI: HTN
AfraTafreeh.com
▪ Beneficial to patient with arrhythmias
6 of 7 PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. Antianginal Drugs
AfraTafreeh.com
VI) REVIEW QUESTIONS
3) Sarin is a nerve gas that is an
organophosphate cholinesterase inhibitor.
Which agent could be used as an antidote to
sarin poisoning?
b. Pilocarpine
c. Carbachol
d. Atropine
e. Physostigmine.
4) A patient with asthma was prescribed a β2
agonist for acute relief of bronchospasm, but
did not respond to treatment. Which drug is the
most likely next option for this patient?
a. Benztropine
b. Ipratropium
c. Oxybutynin
d. Physostigmine
5) A 50-year-old male who is noncompliant with
medications was recently diagnosed with
COPD. His physician would like to prescribed
an inhaled anticholinergic that is dosed once or
twice daily. Which drug is most appropriate for
this patient?
a. Atropine
b. Ipratropium
c. Tiotropium
d. Trospium
6) Which is the most effective drug for motion
sickness for a person planning to go on a
cruise?
a. Atropine
b. Fesoterodine
c. Scopolamine
d. Tropicamide
7) Which drug is useful in treating sinus
bradycardia?
a. Atropine
b. Cisatracurium
c. Neostigmine
d. Succinylcholine
AfraTafreeh.com
Antianginal Drugs PHARMACOLOGY: NOTE #14. 7 of 7
You might also like
- Drugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - KatzungDocument3 pagesDrugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - Katzungsarguss14100% (6)
- Nigel Fong's MRCP NotesDocument66 pagesNigel Fong's MRCP Noteslucas0% (1)
- Telemetry-Intermediate Care Skills ChecklistDocument4 pagesTelemetry-Intermediate Care Skills ChecklistnorthweststaffingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities in Administering Cardiovascular DrugsDocument76 pagesNursing Responsibilities in Administering Cardiovascular DrugsNikka Moreen Dagdag67% (6)
- UWORLD Notes by Systems (Usmle Grassroots)Document79 pagesUWORLD Notes by Systems (Usmle Grassroots)Had Moe100% (3)
- Understanding HemodynamicsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding HemodynamicsGiovanni Mictil86% (7)
- 14. Antianginal DrugsDocument7 pages14. Antianginal DrugsKhalid HabibNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument44 pagesDrugs For Ischemic Heart DiseaseMbah GapinbissiNo ratings yet
- ANS Drugs ReviewDocument14 pagesANS Drugs ReviewhectorNo ratings yet
- CVS MCQsDocument36 pagesCVS MCQsskNo ratings yet
- FullCVJune14Document29 pagesFullCVJune14roseNo ratings yet
- Asthma Treatment and PreventionDocument5 pagesAsthma Treatment and PreventionJohn Paul MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Antidysrhythmics UpdDocument3 pagesAntidysrhythmics UpdRyanMatiraNo ratings yet
- 11 Adrenergic Antagonists (Notes) AtfDocument14 pages11 Adrenergic Antagonists (Notes) AtfAnuki TodriaNo ratings yet
- 13 Antihypertensive Drugs (Notes - Q A) AtfDocument3 pages13 Antihypertensive Drugs (Notes - Q A) AtfFeven AbrahamNo ratings yet
- 4.03 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs PDFDocument8 pages4.03 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs PDFKarl ChavezNo ratings yet
- NR PampletDocument2 pagesNR Pampletneelimawanker chinnariNo ratings yet
- 140 - Neurology Pathology) Seizures - Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Treatment, ComplicationsDocument10 pages140 - Neurology Pathology) Seizures - Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Treatment, ComplicationsUssama MDNo ratings yet
- Anti Anginal DrugsDocument33 pagesAnti Anginal DrugsMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cardiology MCQDocument2 pagesCardiology MCQmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For CV and Respiratory DrugsDocument9 pagesReviewer For CV and Respiratory Drugsprinz1mendezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 2 NotesDocument21 pagesPharmacology 2 Notesgnikap_deleonNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2019 Dentistry ADocument7 pagesPharma 2019 Dentistry AA.No ratings yet
- Pharma S02 SBR6 Se02Document18 pagesPharma S02 SBR6 Se02sky vallartaNo ratings yet
- 036.12 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) VasopressorsDocument14 pages036.12 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) VasopressorsOliver JacobeNo ratings yet
- Whole Case1 DoneDocument5 pagesWhole Case1 Donejovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IIDocument178 pagesPharmacology IIMelanieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Review Questions For QuizDocument14 pagesPharmacology Review Questions For QuizusedforfunplocNo ratings yet
- I Varianti - Ing. - Card.Document10 pagesI Varianti - Ing. - Card.Kadircan KaraboğaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Int - MedDocument166 pagesMCQ Int - MedOmar Ahmed100% (1)
- GpatDocument21 pagesGpatDeepak Kumar100% (1)
- Case Analysis Kwento Ni RosarioDocument17 pagesCase Analysis Kwento Ni RosarioMeg YunsonNo ratings yet
- Preboards NP3Document7 pagesPreboards NP3Marco AglibotNo ratings yet
- Antianginal and Antiischemic DrugsDocument18 pagesAntianginal and Antiischemic DrugsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasDocument37 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used For Treatment Stable Angina PectorisDocument29 pagesDrugs Used For Treatment Stable Angina PectorisAditya Andra PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Deteriorating: BreathingDocument29 pagesDeteriorating: BreathingBibi MariamNo ratings yet
- Module 3.3 - CardioDocument12 pagesModule 3.3 - CardioCatherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- Migraine MedicationsDocument3 pagesMigraine MedicationsKhalid HabibNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs (3) AtfDocument1 pageAntiarrhythmic Drugs (3) AtfCharlieNo ratings yet
- 4 Pharma General AnestheticsDocument10 pages4 Pharma General AnestheticsisahNo ratings yet
- Prescribing in Chest PainDocument4 pagesPrescribing in Chest PainYY_1992No ratings yet
- 4-Ischemic Heart Disease AtfDocument102 pages4-Ischemic Heart Disease AtfAnsa QaiserNo ratings yet
- Beta-Adrenergic Receptor AntagonistsDocument5 pagesBeta-Adrenergic Receptor AntagonistsKabwe BrandonNo ratings yet
- One Liners: Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument27 pagesOne Liners: Antiarrhythmic DrugsskNo ratings yet
- Basic EcgDocument17 pagesBasic EcgJohn Vincent DerlaNo ratings yet
- SABER IM PrometricDocument71 pagesSABER IM Prometricisra zaidNo ratings yet
- Dpharmacy 2 Year 2133 Pharmacology and Toxicology May 2018Document1 pageDpharmacy 2 Year 2133 Pharmacology and Toxicology May 2018Sachin NagarNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of StrokeDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of StrokeAnonymous 7dsX2F8nNo ratings yet
- Answers-of-Medical-Emergency-1_230122_123907Document4 pagesAnswers-of-Medical-Emergency-1_230122_123907mert.serinken35No ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Document7 pagesMed Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Maxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 010) Pheochromocytoma (Notes)Document7 pagesEndocrinology Pathology - 010) Pheochromocytoma (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Anesthesia NutshellDocument388 pagesAnesthesia NutshellMuhammad UmerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology High YieldDocument167 pagesPharmacology High YieldAbdelaziz Shokry100% (1)
- ERD (First Week - MCQS)Document31 pagesERD (First Week - MCQS)Max TraderNo ratings yet
- نسخة Pharma1 diuretics and anti HTN. Manar.BQDocument6 pagesنسخة Pharma1 diuretics and anti HTN. Manar.BQAblah Hamdan ThaherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Drugs Used in ArrhythymiasDocument27 pagesChapter 4 Drugs Used in ArrhythymiasKaye ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardio 1Document5 pagesBasic Cardio 1Malek ZanNo ratings yet
- Hurst - Content Review - Cardio (Edit)Document8 pagesHurst - Content Review - Cardio (Edit)Elaine NorbergNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular System Complete HandoutDocument65 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular System Complete HandoutNicole LantinNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, The Compassionate, The MercifulDocument59 pagesIn The Name of Allah, The Compassionate, The MercifulMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Agent - WikipediaDocument23 pagesAntiarrhythmic Agent - WikipediaSai Jeevan SampathiraoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Cardiac and Renal Systems LecDocument10 pagesDrugs Affecting Cardiac and Renal Systems LecMichelle ErikaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case 1Document37 pagesDrug Study Case 1Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument4 pagesIsosorbide DinitrateManelle Singzon100% (1)
- Ischemic Stroke: Tarlac State University College of Science Department of NursingDocument21 pagesIschemic Stroke: Tarlac State University College of Science Department of NursingKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Basic Nursing PharmacologyDocument78 pagesBasic Nursing PharmacologyLloyd Rafael EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Cardiovascular SystemDocument24 pagesDrugs Affecting Cardiovascular SystemKhalid MortajaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Pharmacology Australian 7th Edition Bullock Test BankDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Pharmacology Australian 7th Edition Bullock Test Bankdorissamuelqpnrrz100% (31)
- Pharmacology Assignment 3Document31 pagesPharmacology Assignment 3Tujiyye kooNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Cardiac EmergenciesDocument18 pagesDrugs Used in Cardiac Emergencieshakky gamyNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris & Anti Anginal DrugsDocument46 pagesAngina Pectoris & Anti Anginal DrugsMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes 2014 PDFDocument260 pagesPharmacological Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes 2014 PDFSonoko KurobaNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument76 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseNasser AlorfiNo ratings yet
- SPC Isoket 1mg PDFDocument8 pagesSPC Isoket 1mg PDFNadia AfifahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology PDFMelanie PrinceNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument1 pageIsosorbide Dinitrate202110439No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs - Nurse - DR DianDocument67 pagesCardiovascular Drugs - Nurse - DR DianAndyk Strapilococus Aureus100% (2)
- Drug Data For TomDocument2 pagesDrug Data For TomAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practical 2022 - UnivDocument31 pagesClinical Practical 2022 - UnivAns SaroobNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityDocument118 pagesPharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityRojina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- UW - Cardiovascular - Educational ObjectivesDocument52 pagesUW - Cardiovascular - Educational ObjectivesUsama BilalNo ratings yet
- Test Tasks On Pharmacology Module2Document19 pagesTest Tasks On Pharmacology Module2Blessing NwosuNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Angina PectorisPadmanabha T SNo ratings yet
- Vasoconstrictors & VasodilatorsDocument37 pagesVasoconstrictors & VasodilatorsDrVarun Menon100% (1)
- Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Document36 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker (CCB)Nafisa TasnimNo ratings yet
- Cureus 0013 00000017832Document8 pagesCureus 0013 00000017832raulNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Management of Ischaemic Heart Disease and Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument50 pagesPharmacological Management of Ischaemic Heart Disease and Acute Myocardial InfarctionMuh Akbar BaharNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs and Medications Pharmacology QuizDocument12 pagesCardiovascular Drugs and Medications Pharmacology QuizIsabel Bibat DavidNo ratings yet