Professional Documents
Culture Documents
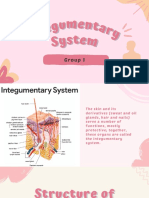
The Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Alexa Vera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageA lecture note about the integumentary system
Original Title
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA lecture note about the integumentary system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageThe Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Alexa VeraA lecture note about the integumentary system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
5.
Burns: Damage to the skin caused by heat,
THE INTEGUMENTARY chemicals, electricity, or radiation.
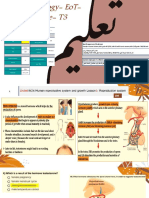
The integumentary SYSTEM
system, encompassing the skin, Recent Advances:
hair, nails, and glands, serves as the body's first line 1. Immunotherapy for Skin Cancer: Checkpoint
of defense against external pathogens, regulates inhibitors and targeted therapies have
temperature, and facilitates sensory perception. This revolutionized the treatment of advanced
review aims to dissect the intricate mechanisms melanoma.
underlying the integumentary system's functions, its 2. Gene Editing: CRISPR technology holds promise
physiological importance, common disorders, and for correcting genetic mutations underlying
recent advancements in dermatological research. inheritable skin disorders.
3. Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cells derived from skin
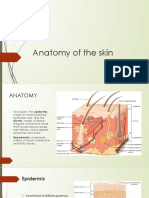
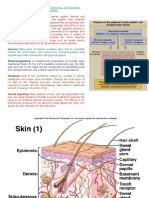
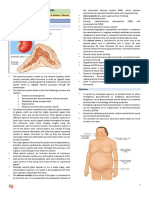
Anatomy and Physiology: tissue offer potential for regenerative medicine and
The integumentary system comprises three layers: wound healing.
the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The 4. Microbiome Research: Understanding the skin
epidermis, primarily composed of keratinocytes, microbiome's role in health and disease opens
forms a protective barrier against UV radiation and avenues for personalized skincare interventions.
pathogens. Beneath lies the dermis, consisting of 5. Nanotechnology in Dermatology: Nanostructures
connective tissue, blood vessels, nerve endings, and for drug delivery and imaging show potential for
appendages like hair follicles and sweat glands. The enhanced efficacy and diagnostics in
hypodermis, or subcutaneous layer, stores fat and dermatological conditions.
anchors the skin to underlying tissues.
The integumentary system plays a multifaceted role
Functions: in maintaining homeostasis and protecting the body
1. Protection: The skin acts as a physical barrier, from external threats. Advances in research and
preventing invasion by pathogens and harmful technology continue to unravel its complexities,
substances. offering novel therapeutic strategies and insights
2. Thermoregulation: Through mechanisms such as into human health and disease. Understanding the
sweating and vasodilation/vasoconstriction, the integumentary system's intricacies is crucial for
integumentary system regulates body temperature. dermatologists, researchers, and healthcare
3. Sensation: Specialized receptors in the skin allow professionals in providing effective care and
for the perception of touch, pressure, temperature, addressing dermatological challenges.
and pain.
4. Excretion: Sweat glands remove waste products
and help regulate electrolyte balance.
5. Synthesis of Vitamin D: UV radiation triggers
the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, essential for
calcium absorption and bone health.
Common Disorders:
1. Acne: A chronic inflammatory condition
affecting hair follicles and sebaceous glands.
2. Eczema: Characterized by dry, itchy patches of
skin due to inflammation and impaired barrier
function.
3. Psoriasis: An autoimmune disorder resulting in
rapid skin cell turnover, leading to thickened, scaly
patches.
4. Skin Cancer: Melanoma, basal cell carcinoma,
and squamous cell carcinoma are common forms of
skin cancer often linked to UV exposure.
You might also like
- Handbook of DermatologyDocument235 pagesHandbook of DermatologyNicholas MiteiNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Differential Diagnosis - A Case-Based Approach CNVTD PDFDocument1,196 pagesNeurologic Differential Diagnosis - A Case-Based Approach CNVTD PDFIoana Moraru100% (1)
- Dementia Proforma Symptoms Checklist in History For Cognitive DeclineDocument16 pagesDementia Proforma Symptoms Checklist in History For Cognitive DeclineAnand Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument16 pagesIntegumentary Systemshenric16100% (8)
- Physical Inactivity: Aging Men Hypertension Smoker ObesityDocument1 pagePhysical Inactivity: Aging Men Hypertension Smoker ObesityKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Skin and Function of The SkinDocument2 pagesLayers of The Skin and Function of The Skinjohn mwangiNo ratings yet
- Human Skin 1Document9 pagesHuman Skin 1Baciu DianaNo ratings yet
- 3D Bioprinting of SkinDocument32 pages3D Bioprinting of Skindaniel leon marinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Skinay254No ratings yet
- RetinoidDocument22 pagesRetinoidPresstisa AxeliaNo ratings yet
- Support in Complete DentureDocument30 pagesSupport in Complete DentureSahana Rangarajan100% (2)
- Integumentary SystemDocument17 pagesIntegumentary SystemNurani AtikasariNo ratings yet
- SDL IntegumentaryDocument4 pagesSDL IntegumentaryMonique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- 2014-The Pelvis PDFDocument564 pages2014-The Pelvis PDFFlorence LainscekNo ratings yet
- Dissertation LeucodermaDocument90 pagesDissertation LeucodermaRashmi Mishra100% (1)
- Prf. Zaama Djamila: Made By: Directed byDocument36 pagesPrf. Zaama Djamila: Made By: Directed byAlinou LinouNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary Systemlaraaa000911No ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Chapter OutlineDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System: Chapter OutlineRiy KimNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document34 pagesGroup 1Justin MallariNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument6 pagesPhysiologyFidiya NasirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Function of The SkinDocument9 pagesAnatomy & Function of The Skinعبدالعزيز احمد علي عتشNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Skin (Integument) - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 pagesAnatomy, Skin (Integument) - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfputri aisheNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument5 pagesSkinRodrigo Cantú ValdezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesUnit 1 The Integumentary SystemSharva BhasinNo ratings yet
- Mild AcidityDocument7 pagesMild AcidityDaniel Lee Eisenberg JacobsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3Document2 pagesLaboratory 3Reizel Grace PaladaNo ratings yet
- IV Levels of Organization of The Integumentary System288Document12 pagesIV Levels of Organization of The Integumentary System288Grimlock GrimmyNo ratings yet
- Protective Mechanism of The Body (Mucous Membrane)Document3 pagesProtective Mechanism of The Body (Mucous Membrane)Kirk CobainNo ratings yet
- Kamus ManusiaDocument822 pagesKamus ManusiaAhmad Abdullah100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument58 pagesIntroductionv_vijayakanth7656No ratings yet
- An Overview On Transdermal Patch Past, Present and Future PerspectiveDocument17 pagesAn Overview On Transdermal Patch Past, Present and Future PerspectiveSantanu PalNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Integument System: Djoko Legowo, Mkes., DRHDocument135 pagesPathology of Integument System: Djoko Legowo, Mkes., DRHPilar Mitra QurbanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Chapter 4Document4 pagesQuiz 2 Chapter 4fareedongodNo ratings yet
- Ijms-21-09769-V2Document18 pagesIjms-21-09769-V2Nikhola RisolNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument38 pagesIntegumentary SystemMiya GordNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 5 - Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesLaboratory Exercise 5 - Integumentary SystemAmanNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary System: Skin Hair Nails ExocrineDocument2 pagesIntergumentary System: Skin Hair Nails ExocrineDennis VolanteNo ratings yet
- BPED-2 Valenzuela Angelo Joseph Activity 2Document14 pagesBPED-2 Valenzuela Angelo Joseph Activity 2Angelo Joseph ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - SkinDocument29 pagesChapter 18 - SkinMohammad Riovaldo Radja NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Skin CareDocument2 pagesSkin CaredipanjliNo ratings yet
- Photo SkinDocument13 pagesPhoto SkinChan JianweiNo ratings yet
- Skin - BSNDocument32 pagesSkin - BSNAnita LopokoiyitNo ratings yet
- EpidermisDocument41 pagesEpidermisxcupcakex122006No ratings yet
- MidwiferyDocument84 pagesMidwiferyAya LumumbaNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation Induced Skin Damage Review of Protective and Preventive OptionsDocument33 pagesSolar Radiation Induced Skin Damage Review of Protective and Preventive OptionsAnnabel ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1 IntegumentaryDocument5 pages1 Integumentarytinampayjr3020No ratings yet
- Protective: It Provides A Physical Barrier Against Thermal andDocument30 pagesProtective: It Provides A Physical Barrier Against Thermal andJessica Alejandra Ortiz LinaresNo ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument6 pagesIntegumentarytrisha anne uberasNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument59 pagesIntegumentary SystemJihaifa AjidùNo ratings yet
- Non Melanoma Skin CancerDocument66 pagesNon Melanoma Skin CancerSalmanArif0% (1)
- Maranatha University The Integumentary SystemDocument40 pagesMaranatha University The Integumentary SystemKojo Yeboah EnchillNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Dermatological SkinPADAS FK UKDDocument24 pagesAssessment of Dermatological SkinPADAS FK UKDmichafuteNo ratings yet
- Limson - Human AnatomyDocument20 pagesLimson - Human AnatomyFaye RabulanNo ratings yet
- Thanik 2011Document9 pagesThanik 2011dora guzmanNo ratings yet
- SGD B5 - : Functional Structure of The Skin and Its AppendicesDocument3 pagesSGD B5 - : Functional Structure of The Skin and Its AppendicesMichelle HutahurukNo ratings yet
- Wound Bioburden: (To Fulfill The Task of Wound Care Subject)Document24 pagesWound Bioburden: (To Fulfill The Task of Wound Care Subject)Fransiska Marchelina HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Sistema Inmune y PielDocument53 pagesSistema Inmune y PielKevin MendozaNo ratings yet
- M13 - Dermatology - Chapter 1Document10 pagesM13 - Dermatology - Chapter 1Idham BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Medsurg 7 Assessment: Integumentary System: Structures and FunctionsDocument7 pagesMedsurg 7 Assessment: Integumentary System: Structures and FunctionsjefrocNo ratings yet
- Tecnologí A Cosmé Tica 2020Document56 pagesTecnologí A Cosmé Tica 2020HAIDY FRANCONo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Anfisman2Document30 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Anfisman2Aswin Gumelar R.No ratings yet
- Structure & Funtion NailsDocument5 pagesStructure & Funtion NailsrikaNo ratings yet
- Dermaltoxicology 140821050243 Phpapp02Document25 pagesDermaltoxicology 140821050243 Phpapp02kush PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatric DisordersDocument13 pagesThe Role of The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatric DisordersKalilNo ratings yet
- Bone Healing, Regeneration and Repair: On BiomolecoulerDocument26 pagesBone Healing, Regeneration and Repair: On BiomolecoulerSarah Nabella PutriNo ratings yet
- 1.acute PharyngitisDocument88 pages1.acute PharyngitisIhsan Hanif0% (1)
- Journal of The Neurological Sciences: SciencedirectDocument12 pagesJournal of The Neurological Sciences: SciencedirectBotez MartaNo ratings yet
- Ramji 2015Document13 pagesRamji 2015AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar StrokeDocument12 pagesCerebellar StrokewhitecloudsNo ratings yet
- (BMED66) HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Laboratory Lecture The Lymphatic System Lesson 12Document13 pages(BMED66) HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Laboratory Lecture The Lymphatic System Lesson 12Cerisse MaeNo ratings yet
- Adaptations To The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesAdaptations To The Endocrine SystemZineil BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Ebook MriDocument26 pagesEbook MrikadekNo ratings yet
- Endo Lect Adrenal Androgens and Medullary HormonesDocument38 pagesEndo Lect Adrenal Androgens and Medullary HormonesdoctorrfarrukhNo ratings yet
- 4 5843476213649116596Document9 pages4 5843476213649116596خلدون سليمNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology 2006pdf-215-231 PDFDocument17 pagesTextbook of Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology 2006pdf-215-231 PDFDania RambinaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument9 pagesCase StudySamantha AdduruNo ratings yet
- Fasting and Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical ApplicationDocument31 pagesFasting and Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Application3141scribdNo ratings yet
- Detailed EoT Coverage 9 ADVDocument50 pagesDetailed EoT Coverage 9 ADVNKANo ratings yet
- Dementia: Mr. Hari Krishna G LDocument28 pagesDementia: Mr. Hari Krishna G LHARI KRISHNA G L100% (2)
- Week 7: Endocrine Disorders Adrenal Glands (One Each Upper Portion of Kidney)Document87 pagesWeek 7: Endocrine Disorders Adrenal Glands (One Each Upper Portion of Kidney)Ivy LarrazabalNo ratings yet
- Menigeal LymphoidDocument10 pagesMenigeal LymphoidRenju KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Chatterbox Magazine Edition 141 - April/May 2023Document44 pagesChatterbox Magazine Edition 141 - April/May 2023Christine Jones100% (1)
- Reading ComprehensionDocument13 pagesReading ComprehensiontarsyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Examination SynopsisDocument26 pagesNervous System Examination Synopsisaarti chandeNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment Prepared PDFDocument9 pagesNewborn Assessment Prepared PDFBasmalah AlzabenNo ratings yet
- Mendonca Derick Fronto-Orbital Advancement RevisitedDocument9 pagesMendonca Derick Fronto-Orbital Advancement Revisitedraden chandrajaya listiandokoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyJojo JustoNo ratings yet