Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 5 Case Study
Uploaded by
parneciohazelannOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 5 Case Study
Uploaded by
parneciohazelannCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study analysis entitled:
Case study on adoption of new
technology for innovation
Perspective of institutional and corporate
entrepreneurship
By Junghee Han and Chang-min Park
Presented by BSMA 4D - Group 5
Juarez, Rylyn
Liguaton, Diovie Mae
Parnecio, Hazel
Puedan, Kaye
Tacsan, Mary Jane
FACTS:
⚫ The case study examines the role of institutional entrepreneurship and
corporate entrepreneurship in the adoption of new technology.
⚫ The study focuses on Kumho Tire, which was the first tire manufacturer to
use radio-frequency identification (RFID) for passenger car tires.
⚫ Kumho Tire invested in advanced information and communication
technology to develop the cutting-edge RFID technology.
⚫ K-Tire belonged to the second tier of global tire manufacturers, rather than
being among the market leaders with significant market shares.
⚫ The company concentrated resources on communication processes and
enhancing the quality of human resources to create a distinct corporate
entrepreneurship.
⚫ K-Tire construct it’s manufacture, logistics, and marketing tracking system,
which consists of infrastructure across various sections such as manufacture,
logistics, and marketing for the first time thanks to RFID adoption.
⚫ The study is published in the Asia Pacific Journal of Innovation and
Entrepreneurship and is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
(CC BY 4.0) license.
ISSUES:
⚫ The main issue addressed in the case study is the role of institutional
entrepreneurship and corporate entrepreneurship in coping with firm
impasses and achieving a competitive advantage through the adoption of
new technology.
⚫ The study aims to understand the factors that facilitate innovation and
adoption of new technology, such as corporate and institutional situations,
technological situations, and environmental situations.
⚫ It seeks to provide insights that could be valuable for start-up companies
looking to foster corporate and institutional entrepreneurship from their
inception to ensure growth and survival.
ALTERNATIVE COURSE OF ACTION (ACA’s):
1. Continuously monitor and evaluate the outcomes
— Consistently monitor and evaluate the outcomes of technological
activities to determine their impact on innovation, performance, and
competitiveness. This may include tracking key metrics, requesting
feedback from stakeholders, and performing post-implementation
assessments to identify areas for improvement and fine-tune the
adoption strategy.
2. Create corporate entrepreneurship projects within your
organization
— Implement measures to foster entrepreneurial attitudes among
employees. This could entail the establishment of specialist innovation
hubs or interdisciplinary teams tasked with researching and evaluating
emerging technology. Giving employees the tools, information, and
motivation they need to drive innovation can play a critical role in
supporting the incorporation of new technologies for innovative
reasons.
3. Stimulate collaboration and alliances
— Promote collaboration across multiple entities, such as
organizations, universities, research institutes, and government
authorities, in order to facilitate the exchange of resources, knowledge,
and expertise while adopting new technology. These collaborative
alliances can successfully manage resource constraints, provide access
to specialized talents, and accelerate innovation uptake.
4. Encourage lifelong learning and skill development
— Businesses should invest in training and development activities to
improve their employees' expertise in emerging technology. These
efforts may include organizing workshops, webinars, or collaborating
with educational institutions to provide customized training courses.
Companies may streamline the integration and successful use of
cutting-edge technologies by building a team with the necessary
competence.
COST AND BENEFIT ANALYSIS:
1. Continuously monitor and evaluate the outcomes
A cost and benefit analysis for continuous monitoring and evaluation
entails comparing expenses such as labor, technology, data
management, training, and time to benefits such as improved decision-
making, quality enhancement, cost reduction, risk mitigation, customer
satisfaction, and compliance adherence. The particular outcomes vary
depending on the business and industry, so a thorough analysis is
required to determine the financial justification and scope of
implementation.
2. Create corporate entrepreneurship projects within your
organization
Establishing corporate entrepreneurship efforts within your business
necessitates an initial financial commitment, the likelihood of
disruptions due to employee time reallocation, the possibility of project
setbacks, and an increased demand for managerial resources. On the
positive note, it can spur innovation, provide a competitive advantage,
increase employee involvement, diversify your business portfolio,
create cash, present significant learning opportunities, and strengthen
relationships with stakeholders. The success of this venture is
dependent on efficiently controlling these expenses and benefits while
aligning with your organization's strategic objectives.
3. Stimulate collaboration and alliances
When fostering collaboration and forming partnerships, it is critical to
compare the costs of time, resources, financial commitments, and the
potential for setbacks to the benefits of securing resource access, risk
reduction, increased creativity, market expansion, cost-effectiveness,
and a competitive edge. The decision should be made after carefully
assessing these aspects and taking into account the specific context,
industry, and goals at hand.
4. Encourage lifelong learning and skill development
Encouragement of lifelong learning and skill development has costs
such as money expenditure, time commitment, and missed
opportunities. Personal development, career advancement, flexibility,
innovation, economic growth, social benefits, reduced unemployment,
long-term cost savings, and increased quality of life are among the
benefits. Overall, the long-term benefits frequently outweigh the initial
expenditures, making lifelong learning a worthwhile investment for
both individuals and society.
BEST ALTERNATIVE COURSE OF ACTION:
➢ Monitoring and evaluating the outcomes of technology adoption initiatives is a
crucial step in the process of adopting new technology for innovation. It helps
organizations assess the impact of their initiatives and make informed decisions
regarding the future direction of their technology adoption strategies.
Here are some further details on monitoring and evaluating outcomes:
⚫ Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Start by identifying and defining
the KPIs that will be used to measure the outcomes of the technology
adoption initiatives. These KPIs should align with the organization's overall
goals and objectives. For example, KPIs may include improvements in
efficiency, cost reduction, customer satisfaction, or revenue growth.
⚫ Collect and Analyze Data: Implement a data collection and analysis system
to track relevant data and metrics related to the technology adoption
initiatives.
⚫ Gather Stakeholder Feedback: Engage with relevant stakeholders, including
employees, customers, and partners, to gather their feedback on the
outcomes of the technology adoption initiatives.
⚫ Conduct Post-Implementation Reviews: After the initial implementation of
the technology, conduct post-implementation reviews to evaluate the
overall outcomes and effectiveness of the adoption initiatives.
⚫ Benchmarking and Comparison: Compare the outcomes of the technology
adoption initiatives with industry benchmarks or competitors' performance
to gain a broader perspective.
⚫ Adjust and Refine Strategy: Based on the findings from monitoring and
evaluating the outcomes, make necessary adjustments and refinements to
the technology adoption strategy.
⚫ Continual Improvement: Monitoring and evaluating outcomes should be an
ongoing process, as technology adoption and innovation are iterative and
dynamic. Continually assess the impact of technology adoption initiatives,
gather new data, and update KPIs to ensure that the organization is on track
towards achieving its innovation and business objectives.
CONCLUSION
The case study on the adoption of new technology for innovation from the
perspective of institutional and corporate entrepreneurship, focusing on Kumho Tire,
offers critical insights into the intersection of innovation, entrepreneurship, and
technology adoption. It showcases how an organization, even outside the market
leader category, can leverage strategic entrepreneurship to gain a competitive edge
through the early adoption of technology, in this case, radio-frequency identification
(RFID) for passenger car tires.
RECOMMENDATIONS
⚫ Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement a robust system for
monitoring and evaluating technology adoption outcomes. Define KPIs
aligned with organizational goals, gather stakeholder feedback, conduct
post-implementation reviews, and compare performance with industry
benchmarks.
⚫ Strategic Collaboration: Foster a collaborative ecosystem involving external
stakeholders, industry experts, and regulatory agencies. Collaborative
alliances can help manage resource constraints and accelerate innovation.
⚫ Invest in Human Capital: Invest in training and development programs to
enhance employees' expertise in emerging technology. This includes
workshops, webinars, and partnerships with educational institutions.
⚫ Innovation Hubs: Establish specialized innovation hubs or interdisciplinary
teams within the organization dedicated to researching and evaluating
emerging technologies. Empower employees with the tools, information,
and motivation needed to drive innovation.
⚫ Strategic Resource Allocation: Allocate resources strategically to enhance
technology infrastructure and communication processes early in the
innovation journey.
⚫ Adaptive Strategy: Embrace an iterative approach to technology adoption,
adjusting and refining the strategy based on ongoing monitoring and
evaluation. Continual improvement is key.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
⚫ Role of Entrepreneurship: Institutional and corporate entrepreneurship
played a pivotal role in Kumho Tire's ability to adopt and implement RFID
technology, leading to improved supply chain management and customer
satisfaction.
⚫ Strategic Investment: Kumho Tire's early investment in advanced
information and communication technology laid the foundation for
successful RFID adoption, emphasizing the importance of technology
infrastructure.
⚫ Resource Allocation: The company's commitment to enhancing
communication processes and human resources quality resulted in the
development of a distinctive corporate entrepreneurship culture, fostering
innovation.
⚫ Collaborative Ecosystem: Collaborative efforts involving external
stakeholders, regulatory agencies, industry specialists, and partnerships
played a significant role in creating an environment conducive to technology
adoption.
⚫ Validation through Pilots: The use of pilot projects and proof-of-concept
studies allowed Kumho Tire to assess the feasibility and benefits of RFID
technology, mitigating risks associated with full-scale adoption.
⚫ Continuous Learning: Encouraging lifelong learning and skill development
among employees was instrumental in building the necessary expertise to
support technology adoption.
You might also like
- SAMPLE MCQuestions ByTopicsDocument45 pagesSAMPLE MCQuestions ByTopicsVeeru ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Planning is a useless endeavor because developments in e-business and e-commerce and in the political, economic, and societal environments are moving too quickly nowadays.” Do you agree or disagree with this statement? Why?Document11 pagesPlanning is a useless endeavor because developments in e-business and e-commerce and in the political, economic, and societal environments are moving too quickly nowadays.” Do you agree or disagree with this statement? Why?riya7sen100% (8)
- Competing With Information TechnologyDocument12 pagesCompeting With Information TechnologyArtur100% (47)
- Cause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenDocument11 pagesCause Analysis For Spun Pile Crack and BrokenRony LesbtNo ratings yet
- Areas of Management Advisory Services 1Document34 pagesAreas of Management Advisory Services 1Paulina Naranjo67% (3)
- Understand What Is A Benchmark and How It Is UsedDocument8 pagesUnderstand What Is A Benchmark and How It Is UsedSharah Del Tabudlong TudeNo ratings yet
- SDS ERSA Rev 0Document156 pagesSDS ERSA Rev 0EdgarVelosoCastroNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking for Businesses: Measure and improve your company's performanceFrom EverandBenchmarking for Businesses: Measure and improve your company's performanceNo ratings yet
- 1 BenchmarkingDocument6 pages1 BenchmarkingTiwaan02No ratings yet
- VP Global Strategic Initiatives in Portland OR Resume Brian SheetsDocument4 pagesVP Global Strategic Initiatives in Portland OR Resume Brian SheetsBrianSheetsNo ratings yet
- Aashto M288-17 Product Selection GuideDocument1 pageAashto M288-17 Product Selection GuideDem DemNo ratings yet
- Business Process Mapping: How to improve customer experience and increase profitability in a post-COVID worldFrom EverandBusiness Process Mapping: How to improve customer experience and increase profitability in a post-COVID worldNo ratings yet
- Probation Period ReportDocument17 pagesProbation Period ReportMiranti Puspitasari0% (1)
- The Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageDocument5 pagesThe Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageHenny ZahranyNo ratings yet
- 4 Operations SrtrategyDocument37 pages4 Operations SrtrategyRosni ShahNo ratings yet
- How to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationFrom EverandHow to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Vehicle CardDocument44 pagesHitachi Vehicle CardKieran RyanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Unit 5Document8 pagesStrategic Management Unit 5Borish LiffinNo ratings yet
- BA7302-Strategic Management Unit 5 Strategic Issues in Managing Technology and InnovationDocument15 pagesBA7302-Strategic Management Unit 5 Strategic Issues in Managing Technology and InnovationRevathiGNo ratings yet
- Accessing External Sources of Technology1Document25 pagesAccessing External Sources of Technology1Sidharth SahuNo ratings yet
- Innovation Management: Article C: Developing An Innovation StrategyDocument23 pagesInnovation Management: Article C: Developing An Innovation Strategyaishariaz342No ratings yet
- Partnership and ResourcesDocument9 pagesPartnership and ResourcesDunia MiqdadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Textbook Solutions Business StrategyDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Textbook Solutions Business StrategyNicolasNo ratings yet
- Management Processes CatDocument6 pagesManagement Processes CatSteve OgolaNo ratings yet
- Technology DevelopmentDocument18 pagesTechnology DevelopmentprabigyanNo ratings yet
- Technology Development - TransferDocument33 pagesTechnology Development - TransferRohit BhandariNo ratings yet
- OM Chapter 2Document13 pagesOM Chapter 2daniel jemiamNo ratings yet
- SBM - Practice Case StudiesDocument5 pagesSBM - Practice Case StudieskrishnaguptaNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking: Navigation Search Improve This Article Talk PageDocument11 pagesBenchmarking: Navigation Search Improve This Article Talk PagePrasenjit SakyaNo ratings yet
- 406 Unit 5Document23 pages406 Unit 5febaNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Benchmarking Is The Process of Comparing One's Business Processes andDocument11 pagesBenchmarking Benchmarking Is The Process of Comparing One's Business Processes andNithish PujariNo ratings yet
- ChandlerDocument9 pagesChandlerSerwanga DavisNo ratings yet
- Bench Marking Is The Process of Comparing OneDocument7 pagesBench Marking Is The Process of Comparing OneVinitha JoseNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Technology Strategy and CompetitivenessDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Technology Strategy and CompetitivenessGorkhali BhaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1 ED Shubham Jagtap MIS: 732391012Document7 pagesAssignment No.1 ED Shubham Jagtap MIS: 732391012shubhamshubhshubh20No ratings yet
- Core Values of Total Quality Management 1. Customer-Driven QualityDocument6 pagesCore Values of Total Quality Management 1. Customer-Driven QualityLloydNo ratings yet
- MODULE1APPLICATIONDocument6 pagesMODULE1APPLICATIONrica mae sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Technology Unit 4Document20 pagesTechnology Unit 4feba100% (1)
- The Growth and Recognition of Project Management Training Have Changed Significantly Over The Past Few YearsDocument12 pagesThe Growth and Recognition of Project Management Training Have Changed Significantly Over The Past Few YearsRCC NPCCNo ratings yet
- Block 4 MS 91 Unit 5Document11 pagesBlock 4 MS 91 Unit 5Anonymous P1xUTHstHTNo ratings yet
- Week 10Document21 pagesWeek 10Arishragawendhra NagarajanNo ratings yet
- BTW LessonDocument7 pagesBTW LessonKaye TayagNo ratings yet
- The Global Environment and Operations StrategyDocument10 pagesThe Global Environment and Operations StrategyMarkjeremy AmbrayNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Is The Process of Comparing One's Business Processes and Performance Metrics ToDocument9 pagesBenchmarking Is The Process of Comparing One's Business Processes and Performance Metrics ToatetejNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Developing Conpetitive Strategy PDF FreeDocument6 pagesChapter 04 Developing Conpetitive Strategy PDF FreeYoel ParkNo ratings yet
- Article On Benchmarking by Kenneth CrowDocument17 pagesArticle On Benchmarking by Kenneth Crowkary290790No ratings yet
- TBEM Core Values & ConceptsDocument5 pagesTBEM Core Values & ConceptsSmita Dutt MitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Funtional Level StrategiesDocument4 pagesChapter 9: Funtional Level StrategiesAnonymous zHsbRY9No ratings yet
- 3 R's of SCDocument5 pages3 R's of SCatishdkNo ratings yet
- White Paper Innovation 1108Document7 pagesWhite Paper Innovation 1108Satish RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Innovation and TechnologyDocument5 pagesChapter 7 - Innovation and TechnologyMuse ManiaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management - Module 6Document12 pagesKnowledge Management - Module 6CH ANIL VARMANo ratings yet
- Imei Cat 1 QB AnsDocument27 pagesImei Cat 1 QB Ansmsk.official321No ratings yet
- QuestionDocument9 pagesQuestionMayank SinhaNo ratings yet
- SCM Unit-4 WordDocument9 pagesSCM Unit-4 WordNeelam YadavNo ratings yet
- How Organization Might Use Their Operations To Gain A Competitive AdvantageDocument5 pagesHow Organization Might Use Their Operations To Gain A Competitive AdvantageSHAILA JEAN TAYABANNo ratings yet
- Balance ScorecardDocument21 pagesBalance Scorecardfixs2002100% (1)
- Technology in Society: Waqar Ahmed, Arsalan Najmi, Minhaj IkramDocument9 pagesTechnology in Society: Waqar Ahmed, Arsalan Najmi, Minhaj IkramRetno Puspa RiniNo ratings yet
- Competing With Informatio N Technolog yDocument115 pagesCompeting With Informatio N Technolog yMelaku GetuNo ratings yet
- PPM Us en WP Catalyst PmoDocument9 pagesPPM Us en WP Catalyst PmoBunmi Olatemiju LijofiNo ratings yet
- Week 9 - Module 4Document5 pagesWeek 9 - Module 4Delight MarquezNo ratings yet
- Survey Analysis Report: Determine Your Innovation Lab Scenario To Optimize Success and Avoid FailureDocument13 pagesSurvey Analysis Report: Determine Your Innovation Lab Scenario To Optimize Success and Avoid FailureKlly CadavidNo ratings yet
- OCD Activity-Mourene Joby and Radhika V HDocument7 pagesOCD Activity-Mourene Joby and Radhika V HRADHIKA V HNo ratings yet
- Tata MotorsDocument3 pagesTata MotorsAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Topic One ProcurementDocument35 pagesTopic One ProcurementSaid Sabri KibwanaNo ratings yet
- ISO Position ToleranceDocument15 pagesISO Position ToleranceНиколай КалугинNo ratings yet
- RSW - F - 01 " ": Building UtilitiesDocument4 pagesRSW - F - 01 " ": Building Utilities62296bucoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Part2 csc159Document26 pagesCHAPTER 2 Part2 csc159Wan Syazwan ImanNo ratings yet
- Regulasi KampenDocument81 pagesRegulasi KampenIrWaN Dompu100% (2)
- Passage To Abstract Mathematics 1st Edition Watkins Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesPassage To Abstract Mathematics 1st Edition Watkins Solutions ManualMichaelWilliamscnot100% (50)
- My BaboogDocument1 pageMy BaboogMaral Habeshian VieiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 What Is Statistics?Document18 pagesChapter 01 What Is Statistics?windyuriNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Glass - ENDocument2 pagesAcoustic Glass - ENpeterandreaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ENTR401 - Second Sem 2022 - 2023Document6 pagesCourse Outline ENTR401 - Second Sem 2022 - 2023mahdi khunaiziNo ratings yet
- 06 SAP PM Level 1 Role Matrix Template SampleDocument5 pages06 SAP PM Level 1 Role Matrix Template SampleRiteshSinhmar100% (1)
- Installing Surge Protective Devices With NEC Article 240 and Feeder Tap RuleDocument2 pagesInstalling Surge Protective Devices With NEC Article 240 and Feeder Tap RuleJonathan Valverde RojasNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Chapter Answers Chapter 7 PDFDocument12 pagesEnd-Of-Chapter Answers Chapter 7 PDFSiphoNo ratings yet
- Inverter 2 chiềuDocument2 pagesInverter 2 chiềuKhánh Nguyễn MinhNo ratings yet
- Supply List & Resource Sheet: Granulation Techniques DemystifiedDocument6 pagesSupply List & Resource Sheet: Granulation Techniques DemystifiedknhartNo ratings yet
- TM Mic Opmaint EngDocument186 pagesTM Mic Opmaint Engkisedi2001100% (2)
- The Bio-Based Economy in The NetherlandsDocument12 pagesThe Bio-Based Economy in The NetherlandsIrving Toloache FloresNo ratings yet
- Community Profile and Baseline DataDocument7 pagesCommunity Profile and Baseline DataEJ RaveloNo ratings yet
- Agma MachineDocument6 pagesAgma Machinemurali036No ratings yet
- Kübler 5800-5820 - enDocument5 pagesKübler 5800-5820 - enpomsarexnbNo ratings yet
- Halloween EssayDocument2 pagesHalloween EssayJonathan LamNo ratings yet
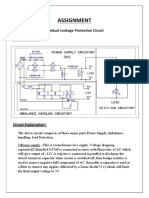
- Assignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramDocument2 pagesAssignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramShivam ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Geocell Reinforced Slopes by Considering Bending EffectDocument13 pagesStability Analysis of Geocell Reinforced Slopes by Considering Bending EffectRakesh KapoorNo ratings yet
- "Tell Me and I Forget, Teach Me and I May Remember, Involve MeDocument1 page"Tell Me and I Forget, Teach Me and I May Remember, Involve MeBesufkad Yalew YihunNo ratings yet