Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Private Water Supply Piping Definitions: Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Private Water Supply Piping Definitions: Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Uploaded by
Ahmad mkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Private Water Supply Piping Definitions: Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Private Water Supply Piping Definitions: Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Uploaded by
Ahmad mkCopyright:
Available Formats
Private Water Supply Piping Definitions
Fire Department Connection. A connection through which the fire department
can pump supplemental water into the sprinkler system, standpipe, or other
system, furnishing water for fire extinguishment to supplement existing water
supplies.
Fire Pump. A pump supplying water at the flow and pressure required by
waterbased fire protection systems.
Hose House. An enclosure located over or adjacent to a hydrant or other water
supply designed to contain the necessary hose nozzles, hose wrenches, gaskets,
and spanners to be used in fire fighting in conjunction with and to provide aid to
the local fire department.
Hydrant Butt. The hose connection outlet of a hydrant.
Hydraulically Calculated Water Demand Flow Rate. The water flow rate for a
system or hose stream that has been calculated using accepted engineering
practices.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Pressure
Residual Pressure. The pressure that exists in the distribution system, measured
at the residual hydrant at the time the flow readings are taken at the flow hydrants.
Static Pressure. The pressure that exists at a given point under normal distribution
system conditions measured at the residual hydrant with no hydrants flowing.
Pressure Regulating Device. A device designed for the purpose of reducing,
regulating, controlling, or restricting water pressure. Examples include pressure-
reducing valves, pressure-control valves, and pressure-restricting devices.
Pumper Outlet. The hydrant outlet intended for use by fire departments for taking
supply from the hydrant for pumpers.
Rated Capacity. The flow available from a hydrant at the designated residual
pressure (rated pressure) either measured or calculated.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Test
Flow Test. A test performed by the flow and measurement of water from one
hydrant and the static and residual pressures from an adjacent hydrant for the
purpose of determining the available water supply at that location.
Flushing Test. A test of a piping system using high velocity flows to remove debris
from the piping system prior to it being placed in service.
Hydrostatic Test. A test of a closed piping system and its attached appurtenances
consisting of subjecting the piping to an increased internal pressure for a specified
period of duration to verify system integrity and leak rates.
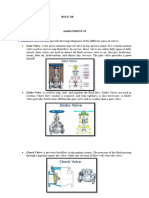
Valve.
Check Valve. A valve that allows flow in one direction only. Indicating Valve. A
valve that has components that show if the valve is open or closed. Examples are
outside screw and yoke (OS&Y) gate valves and underground gate valves with
indicator posts.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Hydrant Definitions
Hydrant. An exterior valved connection to a water supply system that provides
hose connections.
Dry Barrel Hydrant. This is the most common type of hydrant; it has a control
valve below the frost line between the footpiece and the barrel. A drain is
located at the bottom of the barrel above the control valve seat for proper
drainage after operation.
Flow Hydrant. The hydrant that is used for the flow and flow measurement of
water during a flow test.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Private Fire Hydrant. A valved connection on a water supply system having one
or more outlets and that is used to supply hose and fire department pumpers
with water on private property. Where connected to a public water system, the
private hydrants are supplied by a private service main that begins at the point
of service designated by the authority having jurisdiction, usually at a manually
operated valve near the property line.
Public Hydrant. A valved connection on a water supply system having one or
more outlets and that is used to supply hose and fire department pumpers with
water.
Residual Hydrant. The hydrant that is used for measuring static and residual
pressures during a flow test.
Wet Barrel Hydrant. A type of hydrant that sometimes is used where there is
no danger of freezing weather. Each outlet on a wet barrel hydrant is provided
with a valved outlet threaded for fire hose.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Storage Definitions
Available Height for Storage. The maximum height at which commodities can be
stored above the floor and still maintain necessary clearance from structural
members and the required clearance below sprinklers.
Available Height for Storage. For new sprinkler installations, the maximum
height of storage is the height at which commodities can be stored above the
floor where the minimum required unobstructed space below sprinklers is
maintained. For the evaluation of existing situations, the maximum height of
storage is the maximum existing height if space between the sprinklers and
storage is equal to or greater than required.
Clearance. The distance from the top of storage to the ceiling sprinkler
deflectors.
Conventional Pallets. A material-handling aid designed to support a unit load
with openings to provide access for material-handling devices
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Array
Closed Array. A storage arrangement where air movement through the pile is
restricted because of 6 in. (152 mm) or less vertical flues.
Open Array. A storage arrangement where air movement through the pile is
enhanced because of vertical flues larger than 6 in. (152 mm).
Open Array. Fire tests conducted to represent a closed array utilized 6 in. (152
mm) longitudinal flues and no transverse flues. Fire tests conducted to represent
an open array utilized 12 in. (305 mm) longitudinal flues.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Rack Storage
Aisle Width. The horizontal dimension between the face of the loads in racks
under consideration.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
Bulkhead. A vertical barrier across the rack.
Face Sprinklers. Standard sprinklers that are located in transverse flue spaces
along the aisle or in the rack, are within 18 in. (0.46 m) of the aisle face of
storage, and are used to oppose vertical development of fire on the external face
of storage.
Face Sprinklers. All face sprinklers should be located within the rack structure.
The flue spaces are generally created by the arrangement of the racks, and
“walkways” should not be considered flue spaces.
The term face sprinklers must be located at transverse flues within racks. Face
sprinklers are not effective if located outside the flue space, even if they are
within 18 in. (0.46 m) of the rack face.
Dr. Awni Alkhazaleh
You might also like
- Plumbing Glossary PDFDocument45 pagesPlumbing Glossary PDFMaru PabloNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandPrevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To TheoryDocument14 pages2 Introduction To TheoryNurul Izzah Wahidul AzamNo ratings yet
- Dr. Awni AlkhazalehDocument15 pagesDr. Awni AlkhazalehAhmad mkNo ratings yet
- Active Fire Protection Systems Include Standpipe, Sprinkler, and Spray Systems Designed To Extinguish The Fire Outright orDocument5 pagesActive Fire Protection Systems Include Standpipe, Sprinkler, and Spray Systems Designed To Extinguish The Fire Outright orRossana Aclao AgustinNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Drainage in BuildingDocument21 pagesWater Supply and Drainage in BuildingAnu KpNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting ResearchDocument6 pagesFire Fighting ResearchRaymond ZuYang Hng100% (1)
- Two Otherwise Separate Systems or Sources, Potable Water Water, Steam, Gas or ChemicalDocument4 pagesTwo Otherwise Separate Systems or Sources, Potable Water Water, Steam, Gas or ChemicalDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- NaysDocument12 pagesNaysMark AriolaNo ratings yet
- PLUMBINGDocument4 pagesPLUMBINGKhian PinedaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing TerminologiesDocument13 pagesPlumbing TerminologiesMariane PadullaNo ratings yet
- Arson ReportDocument10 pagesArson Reportmarvin custodioNo ratings yet
- System Component Definitions: Dr. Awni AlkhazalehDocument24 pagesSystem Component Definitions: Dr. Awni AlkhazalehAhmad mkNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Drainage SystemDocument33 pagesSanitary Drainage SystemMai Cres Brazil CrescencioNo ratings yet
- Types of ValvesDocument47 pagesTypes of Valvesgsmrbharath_91No ratings yet
- Plumbing GlossaryDocument45 pagesPlumbing GlossarydonvantuongNo ratings yet
- Guide To Check Valves For Fire ProtectionDocument11 pagesGuide To Check Valves For Fire Protectionm.sofiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- G. Dry and Wet StandpipeDocument10 pagesG. Dry and Wet Standpipehermano balbonNo ratings yet
- Stand Pipe System: Prepared BY Homer C. Panganiban Jr. PMEDocument39 pagesStand Pipe System: Prepared BY Homer C. Panganiban Jr. PMEJay Mark CayonteNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Sprinkler Design Criteria 1. Sprinkler Installation Nfpa 13Document16 pagesComparison of Sprinkler Design Criteria 1. Sprinkler Installation Nfpa 13coolth2No ratings yet
- Types of ValvesDocument71 pagesTypes of ValvespurvaNo ratings yet
- Fire Sprinkler SystemDocument8 pagesFire Sprinkler SystemMuhammad Zuhairi IINo ratings yet
- Building Utilities ReviewerDocument10 pagesBuilding Utilities ReviewerClaris Cainto100% (1)
- PlumbingDocument51 pagesPlumbingHaymanot Baynesagn100% (1)
- Hydraulic Bench Is A Very Useful Apparatus in Hydraulics and Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesHydraulic Bench Is A Very Useful Apparatus in Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanicsroy macabodbodNo ratings yet
- Zamora Bsce3b Cea132 Assignment-2Document9 pagesZamora Bsce3b Cea132 Assignment-2Mrdy CaiNo ratings yet
- Fire Hydrant Sysetm - Nfpa 14Document35 pagesFire Hydrant Sysetm - Nfpa 14Jitendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Information On Fire Flow Testing of Hydrants PDFDocument5 pagesInformation On Fire Flow Testing of Hydrants PDFMohamed MasryNo ratings yet
- ValvesDocument4 pagesValvesKevinNavidadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document4 pagesChapter 14Jessa Mae CatabayNo ratings yet
- Fire Hydrant System NFPA 14Document27 pagesFire Hydrant System NFPA 14abdullahaboelhassan10No ratings yet
- The Branch Supply Duct As Far As Practical From The OutletDocument11 pagesThe Branch Supply Duct As Far As Practical From The OutletKevinNavidadNo ratings yet
- Study Stack - Master Plumber Table ReviewDocument10 pagesStudy Stack - Master Plumber Table ReviewIvilyn RachoNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Pump CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesDiaphragm Pump CharacteristicslamiaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT and Latest EquipmentDocument10 pagesEXPERIMENT and Latest EquipmentMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaNo ratings yet
- Uty TerminologyDocument5 pagesUty TerminologyNicole Erika EnriquezNo ratings yet
- BLDG Util SummaryDocument6 pagesBLDG Util SummaryJhudiel Dela ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Definition of Terms ArTY 1Document14 pagesModule 01 Definition of Terms ArTY 1JOSE RAFAEL COLUMNANo ratings yet
- Fire Sprinkler SystemsDocument9 pagesFire Sprinkler SystemsVin Bds100% (1)
- RSWMT01 Plumbing System - Ar BuDocument11 pagesRSWMT01 Plumbing System - Ar BuIan GamitNo ratings yet
- Utilities: Plumbing Answer KeyDocument10 pagesUtilities: Plumbing Answer KeyLouie Xannel Medina100% (2)
- ConclusionDocument1 pageConclusionGeny Atienza100% (1)
- PlumbingDocument21 pagesPlumbingzim03No ratings yet
- Plumbing SystemsDocument10 pagesPlumbing Systemsjenny sagunNo ratings yet
- Valves ArticuloDocument5 pagesValves ArticuloJohanna SanabriaNo ratings yet
- M2.7 ValvesDocument27 pagesM2.7 ValvesUJWAL UMESHNo ratings yet
- Plumbing TerminologiesDocument25 pagesPlumbing TerminologiesJames AsasNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Plumbing Terms Water The SubstanceDocument12 pagesWeek 2 Plumbing Terms Water The SubstanceIvy Pearl TabagNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document9 pagesActivity 3Rachita SheelavantNo ratings yet
- Rain Bird Valve Install TipsDocument16 pagesRain Bird Valve Install Tipsrideslide20005544No ratings yet
- Fire Hydrant - WikipediaDocument9 pagesFire Hydrant - WikipediaVaibhav SawantNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment No.1 ObjectivealiNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Definition of Terms Part 2Document73 pagesPlumbing Definition of Terms Part 2kristina aquinoNo ratings yet
- Nfpa 25Document36 pagesNfpa 25Sreenath S KallaaraNo ratings yet
- Building UtilitiesDocument14 pagesBuilding Utilitiesjohn kyleNo ratings yet
- Aclao-Assignment #2 (Engineering Utilities 2)Document9 pagesAclao-Assignment #2 (Engineering Utilities 2)mel john aclaoNo ratings yet
- BddeftermsDocument11 pagesBddeftermsamor BagonNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Blowdown AnalysisDocument2 pagesFundamental of Blowdown AnalysisFriday HumphreyNo ratings yet
- Training ManualDocument27 pagesTraining ManualDinanath SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ValvesDocument9 pagesPlumbing Valvesruel_galutanNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EPC ContractDocument16 pagesIntroduction To EPC Contractvinayak_geotechNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Patients With CHFDocument4 pagesDental Management of Patients With CHFarjayNo ratings yet
- Om Yoga Uk June 2015Document148 pagesOm Yoga Uk June 2015John Muriatti100% (2)
- Iso 20783-1-2011Document12 pagesIso 20783-1-2011Mahmoud MoussaNo ratings yet
- Rosicrucian Rosicrucian M Mo On No Og Grra Ap PH HSS: Index of Index ofDocument42 pagesRosicrucian Rosicrucian M Mo On No Og Grra Ap PH HSS: Index of Index ofFerdinand Wilfredo De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Mechanical AnalysisDocument22 pagesDynamic Mechanical Analysisrudy ammeNo ratings yet
- Prince PDFDocument9 pagesPrince PDFNK NikhilNo ratings yet
- Batov ASNT Fall Conference 2016Document3 pagesBatov ASNT Fall Conference 2016Alan MontagueNo ratings yet
- Social Perception: Nonverbal CommunicationDocument5 pagesSocial Perception: Nonverbal CommunicationMaria ZareenNo ratings yet
- Storyboard - Normalcy and Prudent Parenting Elearning CourseDocument37 pagesStoryboard - Normalcy and Prudent Parenting Elearning Courseapi-87117284No ratings yet
- Fritsjurgens System M+/MDocument12 pagesFritsjurgens System M+/Mdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Coping With Negative Thinking in DepressionDocument22 pagesCoping With Negative Thinking in DepressionFrescura1No ratings yet
- 4RevisedECONOMIC TRAITS of Layers and BroilersDocument27 pages4RevisedECONOMIC TRAITS of Layers and BroilersRamesh BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Results Management in Norwegian Development CooperationDocument36 pagesResults Management in Norwegian Development CooperationVgslavonNo ratings yet
- G5 Direct ShearDocument5 pagesG5 Direct ShearFairiey Izwan AzaziNo ratings yet
- Mindup ProgramDocument8 pagesMindup Programapi-210400247No ratings yet
- July 17 2021 Committee Meeting of Health MinutesDocument4 pagesJuly 17 2021 Committee Meeting of Health MinutesArniel Fred Tormis FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ispad Clinical Practice ConsDocument2 pagesIspad Clinical Practice ConsNiraj SinghNo ratings yet
- S.B. 43Document22 pagesS.B. 43Circa NewsNo ratings yet
- FR AnachemDocument5 pagesFR AnachemYüri ÄnnNo ratings yet
- JSA Erection & Dismantling of ScaffoldingDocument3 pagesJSA Erection & Dismantling of ScaffoldingMc Evans MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi ReservationsDocument2 pagesAbu Dhabi ReservationsSanketh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Institute of Mathematics: Linear Programming AssignmentsDocument4 pagesInstitute of Mathematics: Linear Programming AssignmentsRayyan CablesNo ratings yet
- Coke and Great Depression - The Big LieDocument13 pagesCoke and Great Depression - The Big LieN yatesNo ratings yet
- 8 - MRCP Part 1 - Recall May 2013Document28 pages8 - MRCP Part 1 - Recall May 2013Mohamed El-sayedNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Insurance Regulatory and Development AuthorityDocument27 pagesConstitution of Insurance Regulatory and Development Authoritymaha27No ratings yet
- Wacker VAEDocument52 pagesWacker VAEfahmyazizNo ratings yet
- Chem 201 - Paper B - Nov 2021Document7 pagesChem 201 - Paper B - Nov 2021arnomasvosveNo ratings yet
- Effects of Water-Cement Ratio On The Compressive Strength of ConcreteDocument9 pagesEffects of Water-Cement Ratio On The Compressive Strength of ConcreteJOHN ORELLE MANGAHASNo ratings yet