Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mech E3
Uploaded by
redgeromagos29Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mech E3
Uploaded by
redgeromagos29Copyright:
Available Formats
MECH E3 – Mechanics of Deformable Bodies
1. Two forces acting at a point and angle between them is 120°. The larger force is of
magnitude 90 N and the resultant of these two forces is perpendicular to the smaller
force. Find the magnitude of smaller force and resultant.
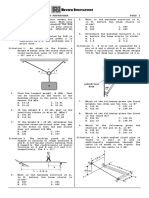
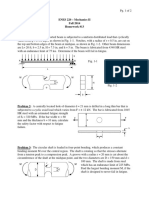
2. Two forces of 350 N and 275 N are acting on a hook and passing through point O as
shown. Determine the magnitude (N) of the resultant of thes250 Ne two forces.
350 N
275 N
30° 45°
3. Two forces 15 N and 30 N are acting at a point with an angle of 60° between them. Find
the magnitude and angle of resultant with the 15 N forces.
4. Force P1 of magnitude 10 N is acting along horizontal direction and force P2 acting
along vertical direction. The resultant P1 and P2 has magnitude of 20 N. Determine the
magnitude of force P2.
5. A hollow steel tube with an inside diameter of 80 mm must carry an axial tensile load of
330 kN. Determine the smallest allowable outside diameter of the tube if the working
stress is 110 MPa.
Situation:
The weight W shown is supported by cables AC and BC.
Given:
θ = 50°
α = 30°
Cable cross-sectional area = 201 mm 2
6. Compute the maximum value of W (kN) if the allowable tensile stress of the cable is 124
MPa.
7. If W = 32kN, what is the tensile force (kN) of cable AC?
8. If W = 32 kN, what is the minimum required cable diameter in mm?
A B
α C θ
Prepared by: Engr. Cyril L. Leccio
MECH E3 – Mechanics of Deformable Bodies
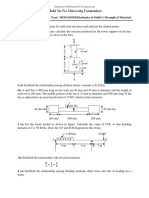
9. The uniform 1300 N bar AB carries a load P = 2200 N at A. The bar is supported by a
pin at B and the 12-mm diameter cable CD. Find the stress (MPa) in the cable.
1.2 m
A 0.9 m 0.9 m B
C
P
10. A force of 10 N is applied to one end of a 10 inches diameter circular rod. Calculate the
stress.
Prepared by: Engr. Cyril L. Leccio
You might also like
- Shades Eq Gloss Large Shade ChartDocument2 pagesShades Eq Gloss Large Shade ChartmeganNo ratings yet
- Best of The Photo DetectiveDocument55 pagesBest of The Photo DetectiveSazeed Hossain100% (3)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Statics of Rigid Bodies - First Term 2019: Y-AxisDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies - First Term 2019: Y-AxisLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- Preboard Problems FinalDocument5 pagesPreboard Problems FinalAngel MarkNo ratings yet
- Eu Clinical TrialDocument4 pagesEu Clinical TrialAquaNo ratings yet
- TimberDocument32 pagesTimberMarv de Jesus100% (1)
- Solved Problems Statically Indeterminate StructuresDocument5 pagesSolved Problems Statically Indeterminate StructuresChristopher Largado100% (1)
- Draw The SFD BMDDocument12 pagesDraw The SFD BMDAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technology Department of CegeDocument15 pagesMapua Institute of Technology Department of CegeNicole RodilNo ratings yet
- RELATION AND FUNCTION - ModuleDocument5 pagesRELATION AND FUNCTION - ModuleAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- SolveDocument2 pagesSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- Computer in Community Pharmacy by Adnan Sarwar ChaudharyDocument10 pagesComputer in Community Pharmacy by Adnan Sarwar ChaudharyDr-Adnan Sarwar Chaudhary100% (1)
- Tylenol CrisisDocument2 pagesTylenol CrisisNida SweetNo ratings yet
- Refresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review CenterDocument4 pagesRefresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review Centermichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium SystemsDocument12 pagesEquilibrium SystemsEmilio Joaquin FloresNo ratings yet
- 2021NOV PSAD UnlockedDocument7 pages2021NOV PSAD UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- April 2024 - PSAD 1Document2 pagesApril 2024 - PSAD 1rando12345No ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodiesdonald escalanteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety ChecklistDocument3 pagesChemical Safety ChecklistPillai Sreejith100% (10)
- A Sample Script For Public SpeakingDocument2 pagesA Sample Script For Public Speakingalmasodi100% (2)
- Activity Sheet Housekeeping Week - 8 - Grades 9-10Document5 pagesActivity Sheet Housekeeping Week - 8 - Grades 9-10Anne AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument4 pagesSOMrrameshsmit0% (1)
- Som-Mos-I 205Document4 pagesSom-Mos-I 205Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document2 pagesHomework 3123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanics of Def. Bodies + Normal StressDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Mechanics of Def. Bodies + Normal StressJQNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory - 1Document6 pagesStructural Theory - 1jessa marie sayconNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Aug 14, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Aug 14, 2023Abhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- WasaaapppDocument29 pagesWasaaapppManoy BermeoNo ratings yet
- DAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsDocument20 pagesDAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsJM De Guzman TuzonNo ratings yet
- B14 Homework 2Document15 pagesB14 Homework 2vicejuniorNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Feb Mar 2022Document3 pagesMechanics of Solids Feb Mar 2022SabareeshNo ratings yet
- VOL1Document3 pagesVOL1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress: Fundamentals of Deformable BodiesDocument3 pagesSimple Stress: Fundamentals of Deformable Bodiesreymart cereneoNo ratings yet
- TheoryLec01 Dec2019Document7 pagesTheoryLec01 Dec2019cristina23No ratings yet
- PI DesignDocument10 pagesPI DesignKarlNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Test Phy098 Feb 2021 ObjDocument5 pagesMid Term Test Phy098 Feb 2021 ObjanisahNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument4 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksMadan PanditNo ratings yet
- Refresher Modules DesignDocument11 pagesRefresher Modules Designyajnad_10No ratings yet
- Ge8251 Engineering Mechanics EnglishDocument4 pagesGe8251 Engineering Mechanics EnglishNAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Civil and MechnicalDocument15 pagesCivil and MechnicalLokeshNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)annamalai_s873323No ratings yet
- Som 2 16Document48 pagesSom 2 16chakravarthimeNo ratings yet
- OU - Coe OU - Coe: Faculty of EngineeringDocument2 pagesOU - Coe OU - Coe: Faculty of EngineeringPrashanth PinnojiNo ratings yet
- RC Exam Electronics 1.) 9.)Document3 pagesRC Exam Electronics 1.) 9.)Reiniel Cirujano AntonioNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Questions015-RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Questions015-RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Ce8395 QB PDFDocument10 pagesCe8395 QB PDFMohan Ragava LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Set-1 & 2 NumericalDocument18 pagesSet-1 & 2 NumericalHanamanagouda BevoorNo ratings yet
- Frames Subjected To Lateral Loads (Approximate Analysis) : Structural Theory: Lecture 02Document6 pagesFrames Subjected To Lateral Loads (Approximate Analysis) : Structural Theory: Lecture 02Michael Christ IcagoyNo ratings yet
- A1101Document6 pagesA1101Khaja BashaNo ratings yet
- SA 1 (4th) Dec2014Document2 pagesSA 1 (4th) Dec2014Akash DulakashoriaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials QP BANKDocument15 pagesStrength of Materials QP BANKmechfameNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Mos r15 JntuaDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper Mos r15 JntuaAnonymous ML4hh4MOyBNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Strength of Materials 1Document3 pagesProblem Sets Strength of Materials 1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- 220F14 Homework-13 PDFDocument2 pages220F14 Homework-13 PDFseabreezeNo ratings yet
- Homework On Equivalent Systems of ForcesDocument10 pagesHomework On Equivalent Systems of ForcesAsad YousafNo ratings yet
- CC Deform Bodies Basic ElectricalDocument92 pagesCC Deform Bodies Basic ElectricalnadyahginiceNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticeDocument2 pagesPhysics Practicedondon0% (1)
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document8 pagesCH 12Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument7 pagesStrength of MaterialsKanakath Ajith0% (1)
- Civil and Mechnical Finalkey PDFDocument15 pagesCivil and Mechnical Finalkey PDFNAVEEN BUDDARAPUNo ratings yet
- Ce Board May 2011Document3 pagesCe Board May 2011DHANYL KHRISSNA MIJARESNo ratings yet
- Probset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Document2 pagesProbset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Ralph Jayson SilangNo ratings yet
- Probset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Document2 pagesProbset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Ralph Jayson SilangNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Review MaterialDocument30 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Review MaterialVon Eric DamirezNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipDocument44 pagesReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Resolution: Owner/Operator, DocketedDocument4 pagesResolution: Owner/Operator, DocketedDonna Grace Guyo100% (1)
- Adhesive Film & TapeDocument6 pagesAdhesive Film & TapeJothi Vel MuruganNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Papanikolaou E. - Markatos N. - Int J Hydrogen EnergyDocument9 pages2011 - Papanikolaou E. - Markatos N. - Int J Hydrogen EnergyNMarkatosNo ratings yet
- RIBA PoWUpdate 131009 ProbynMiersDocument28 pagesRIBA PoWUpdate 131009 ProbynMiersYellowLightNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacology by ZebDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology by ZebSanam MalikNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training ReportDocument39 pagesA Summer Training ReportShubham SainyNo ratings yet
- Things You Can Do at Burnham ParkDocument2 pagesThings You Can Do at Burnham ParkBcpo TeuNo ratings yet
- Game ApiDocument16 pagesGame ApiIsidora Núñez PavezNo ratings yet
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 3 Parent Tip Sheet 1Document2 pagesEureka Math Grade 2 Module 3 Parent Tip Sheet 1api-324573119No ratings yet
- Cash Budget Sharpe Corporation S Projected Sales First 8 Month oDocument1 pageCash Budget Sharpe Corporation S Projected Sales First 8 Month oAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lightolier Lytecaster Downlights Catalog 1984Document68 pagesLightolier Lytecaster Downlights Catalog 1984Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Sic Mosfet and Si IgbtDocument10 pagesComparison of Sic Mosfet and Si IgbtYassir ButtNo ratings yet
- Haymne Uka@yahoo - Co.ukDocument1 pageHaymne Uka@yahoo - Co.ukhaymne ukaNo ratings yet
- Forensic My Cology Mcgraw HillDocument8 pagesForensic My Cology Mcgraw HillJayanti RaufNo ratings yet
- Tso C197Document6 pagesTso C197rdpereirNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About WDM Principle ADocument92 pagesBasic Knowledge About WDM Principle AJosé LópezNo ratings yet
- Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting MachineDocument61 pagesComputerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting Machine Computerized Flat Knitting MachineAmira's ClothesNo ratings yet
- Rule 7bDocument38 pagesRule 7bKurt ReoterasNo ratings yet
- DU Series MCCB CatalogueDocument8 pagesDU Series MCCB Cataloguerobinknit2009No ratings yet
- Growing Onion Management and Water NeedsDocument25 pagesGrowing Onion Management and Water NeedsKATE NAVAJANo ratings yet