Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ampathchat 45 Introducing The Iona Nipt
Uploaded by
alikiyaei82Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ampathchat 45 Introducing The Iona Nipt
Uploaded by
alikiyaei82Copyright:
Available Formats
November 2017 Edition no.
45
CHAT Ampath Genetics
Non-invasive prenatal testing
(NIPT):Introducing the IONA® test
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) The IONA® test estimates the probability that a foetus is
NIPT is a safe and accurate prenatal screen to calculate affected with the following aneuploidies:
the risk that a foetus has of being affected with a • Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
chromosomal condition, for example, Down Syndrome. • Trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome)
NIPT makes use of cell-free DNA released from the • Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome)
placenta into the maternal bloodstream (Figure 1).
Testing for sex chromosome aneuploidies (Turner Syndrome,
Klinefelter Syndrome, XYY Syndrome and XXX Syndrome)
is also available for singleton pregnancies.
Key features of the IONA® test
• Reliable: CE-IVD (European Conformity In Vitro
Diagnostic) NIPT performed at an accredited facility
• Fast: seven-day turnaround time
• Accurate: >99% detection rate
• Requires as little as 2% foetal fraction (see below)
• Available for singleton and twin pregnancies
• Can be performed on surrogate, donor and IVF
Figure 1: Cell-free DNA from the placenta is released into pregnancies
the maternal bloodstream during pregnancy. • Blood can be taken from 10 weeks gestational age
Measuring the amount of cell-free DNA is now possible How does the IONA® test work?
using a maternal blood sample. By calculating the ratio of During pregnancy, cell-free foetal DNA from the
DNA from the placenta, the risk of a foetus being affected apoptosing trophoblastic cells of the placenta enters the
with a chromosomal condition is calculated. maternal bloodstream (Figure 1). Using a maternal blood
sample, the IONA® test directly measures the cell-free DNA
A trisomy occurs when a foetus inherits three copies of a in the maternal plasma. The proportion of cell-free DNA
chromosome instead of the usual two copies. Similarly, a that is attributed to the foetus is called the foetal fraction.
monosomy occurs when one copy of a chromosome is
inherited. Both trisomies and monosomies are referred to as The IONA® test employs Next Generation Sequencing
aneuploidies, and are associated with adverse pregnancy (NGS) technology to count chromosome copy numbers.
outcomes (either miscarriage or a genetic condition). By calculating the ratio of cell-free DNA from the placenta
and the gestational carrier, the risk of a foetus being
The IONA® NIPT at Ampath affected by Trisomy 21, 18, 13 or a sex chromosome
Ampath Genetics is pleased to announce the abnormality is calculated.
implementation of the IONA® non-invasive prenatal test at its
National Reference Laboratory in Centurion, South Africa, as IONA® test results
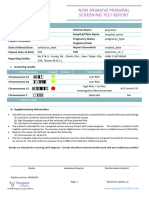
from November 2017. The IONA® test report gives a clear, easy-to-interpret result
of high risk or low risk for each trisomy, as well as sex
The IONA® test uses the latest advances in genetic chromosome aneuploidies (Table 1). Foetal fraction and
technology, allowing for fast and reliable results, while foetal sex (if requested) is also indicated.
reducing the need for invasive testing and associated risks
(such as procedure-related miscarriage).
Please contact your local Ampath pathologist for more information.
Edition no. 45
Table 1: IONA® test results Caution must also be used if the gestational carrier has had
an organ transplant (particularly from a male donor). This, in
The IONA® conjunction with the above, is of concern, as cell-free DNA
Background Clinical
Trisomy test from the gestational carrier is also present in the maternal
risk summary
risk score
bloodstream.
Trisomy 21 1:171 > 95% High-risk
invasive test
recommended Thus, during pregnancy, both cell-free DNA from the
gestational carrier and the foetus (placentally derived) are
Trisomy 18 1:542 < 1:1,000,000 Low risk
(< 0.0001%) present in the maternal bloodstream. Aneuploidies or the
presence of a Y-chromosome, derived from a male donor
Trisomy 13 1:1655 < 1:1,000,000 Low risk
(< 0.0001%) organ, which are maternally contributed to the cell-free
DNA in the circulating bloodstream, can confound findings
(as findings are ascribed to the foetus).
Foetal fraction (%) 10%
Foetal sex male It is important to note that all non-invasive foetal tests
performed on maternal blood are currently regarded as
Benefits of the IONA® test screening tests, and positive results should be followed up
The IONA® test has a higher detection rate and lower by an invasive diagnostic test (such as an amniocentesis).
false-positive rate than most conventional first and second Furthermore, NIPT results should be interpreted in
trimester screening tests available at present, giving conjunction with any/all other antenatal tests.
pregnant women, their families and their healthcare
providers greater confidence in the result and reducing the Ampath Genetics offers diagnostic prenatal genetic
need for unnecessary invasive and stressful tests, such as test options, including karyotyping, to confirm high-risk
chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis – both of which results identified by NIPT. Even though further invasive
carry a small risk of miscarriage. testing is unnecessary for a negative IONA® test result,
vigilance should still be maintained with regard to any
Clinical performance
foetal abnormalities, including those genetic disorders not
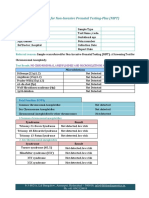
Table 2: Clinical performance of the IONA® test screened for by the IONA® test.
Detection False False Genetic counselling
Aneuploidy
rate positive rate negative rate Counselling from an HPCSA-registered genetic counsellor is
Trisomy 21 99% 0.02% 1.0% available, upon professional referral, to do the following:
Trisomy 18 91% 0.02% 8.6% • discuss the merits and pitfalls with regard to all types of
antenatal diagnostic options
Trisomy 13 100% 0.01% 0.0%
• offer support to parents who experienced foetal loss and
discuss laboratory testing to investigate possible causes
Overall accuracy >99.8%
• counsel, explain recurrence risks, and guide parents
Test failure rate <0.5% and families with regard to reproductive options
and laboratory testing in instances where a foetal
The clinical performance data of the IONA® test (Table 2)
abnormality has been identified
is based on >15 000 samples. The sensitivity for sex
chromosome aneuploidies and sex determination are >93%
For genetic counselling, contact Sarah Walters at
and >99%, respectively.
012 678 1350/62 or walterss@ampath.co.za.
Limitations of the IONA® test
Queries
Current NIPT technologies, including IONA®, cannot reliably
Please email nipt@ampath.co.za.
perform aneuploidy testing of Chromosome 13, 18 and 21
on cell-free DNA derived from more than two foetuses.
Alternatively, please contact:
Dr George Gericke (Clinical Geneticist)
When not to use the IONA® test
012 678 1350/61/62 l gerickeg@ampath.co.za
The IONA® test should not be used if the gestational carrier*:
Dr Lindsay Lambie (Clinical Geneticist)
• has cancer
• has had a recent blood transfusion
• is known to be chromosomally aneuploid for Trisomy 21
• is a known carrier of a mosaic cell line (such as XO)
IONA® is a registered trademark of Premaitha Health PLC. Premaitha
*As this test can also be used to test egg donor and surrogate pregnancies, the term Limited trading as Premaitha Health. Registered office: Rutherford House,
gestational carrier is used, as the donor and surrogate are not the biological mother. Manchester Science Park, Manchester, M15 6SW, United Kingdom.
Please contact your local Ampath pathologist for more information.
You might also like
- NeoBona BROCHURE PDFDocument2 pagesNeoBona BROCHURE PDFyousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- The Iona Test Reduces The Need For Invasive Procedures:: 100,000 PregnanciesDocument2 pagesThe Iona Test Reduces The Need For Invasive Procedures:: 100,000 PregnanciesionelaioneNo ratings yet
- Brochure Prenatal TestingDocument4 pagesBrochure Prenatal TestingMCuk2606No ratings yet
- HP NeobonaDocument1 pageHP Neobonayousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- The New Genetics - Paradigm Shifts in Prenatal Diagnosis - Jennifer Hoskovec, MS, CGCDocument41 pagesThe New Genetics - Paradigm Shifts in Prenatal Diagnosis - Jennifer Hoskovec, MS, CGCSanthaVenkataramanaraoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Chromosomal Microarray vs. NIPS Analysis of 5541 Low-Risk PregnanciesDocument6 pages2019 Chromosomal Microarray vs. NIPS Analysis of 5541 Low-Risk PregnanciesAhmed H. Ali ElbestaweyNo ratings yet
- Practical Genetic Counseling For The Laboratory - (7. Prenatal Screening Technologies and Test Issues)Document30 pagesPractical Genetic Counseling For The Laboratory - (7. Prenatal Screening Technologies and Test Issues)Hematology I Hematology INo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis: William'S Obstetrics 25 EditionDocument26 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis: William'S Obstetrics 25 EditionIndah Ria Rezeki MeirisaNo ratings yet
- Mackie Et al-2017-BJOG - An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument15 pagesMackie Et al-2017-BJOG - An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecologyalit92No ratings yet
- Ref 42 Principles of NIPTDocument9 pagesRef 42 Principles of NIPTKhải Nguyễn ThànhNo ratings yet
- NIPT - Stephanie Allen 01.10.14Document40 pagesNIPT - Stephanie Allen 01.10.14mochkurniawanNo ratings yet
- FullDocument6 pagesFullamarNo ratings yet
- 9 Rapid FishDocument6 pages9 Rapid FishwvywmdmknrNo ratings yet
- 2024.plancental, Maternal, Fetal, and Techical Origins of False Positive Cell Fre DNA Screening ResultsDocument9 pages2024.plancental, Maternal, Fetal, and Techical Origins of False Positive Cell Fre DNA Screening Resultsrpina.genNo ratings yet
- Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2023 Nov 9 Leyne eDocument8 pagesActa Obstet Gynecol Scand 2023 Nov 9 Leyne eBALTAZAR OTTONELLONo ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument5 pagesGENETICSmartinaNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Tests (NIPT) : Review Article: Maged MN, Mohamed MN, Lamia H.ShehataDocument6 pagesNon-Invasive Prenatal Tests (NIPT) : Review Article: Maged MN, Mohamed MN, Lamia H.Shehatazahra rahmaNo ratings yet
- L 25 Prenatal Diagnosis and Genetic CounselingDocument49 pagesL 25 Prenatal Diagnosis and Genetic Counselingcactus life foreverNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis and ScreeningDocument55 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis and ScreeningRania ZahoNo ratings yet
- Turner Syndrome: New Insights From Prenatal Genomics and TranscriptomicsDocument5 pagesTurner Syndrome: New Insights From Prenatal Genomics and TranscriptomicsNaman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Sage Trisomy Example Screening ReportDocument2 pagesSage Trisomy Example Screening ReportpathbiomedxNo ratings yet
- PIIS0002937822000412Document14 pagesPIIS0002937822000412Andrés Gaviria CNo ratings yet
- WM-1249-EN-001 PrenaTest Key Paper Summary PMCF-StudyDocument2 pagesWM-1249-EN-001 PrenaTest Key Paper Summary PMCF-StudytcNo ratings yet
- Screening Tests: Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal DiseaseDocument6 pagesScreening Tests: Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal DiseaseMischief ManagerNo ratings yet
- Flyer-Tpoo1-06-En HJK LongDocument4 pagesFlyer-Tpoo1-06-En HJK LongG.330No ratings yet
- Amnio Sin Tes IsDocument6 pagesAmnio Sin Tes Ishanan afifahNo ratings yet
- Prenatal TestingDocument26 pagesPrenatal TestingMar ClrNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 SKILLS LAB DAY 1 Laboratory and Diagnostics22Document55 pagesNCM 109 SKILLS LAB DAY 1 Laboratory and Diagnostics22Joseph DusichNo ratings yet
- Group A PDFDocument34 pagesGroup A PDFAnsa WaqarNo ratings yet
- V2.2023 Concert Genetic Testing - Non-Invasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS)Document13 pagesV2.2023 Concert Genetic Testing - Non-Invasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS)IOAN STOICANo ratings yet
- Prenatal ScreeningDocument55 pagesPrenatal ScreeningJohn BrittoNo ratings yet
- NIPT PLUS - DummyDocument4 pagesNIPT PLUS - DummyAakash vermaNo ratings yet
- Dsjuog-12-255 Yaron Zalel NiptDocument3 pagesDsjuog-12-255 Yaron Zalel NiptAhmed H. Ali ElbestaweyNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DiagnosisDocument11 pagesPrenatal DiagnosisSonia BalintNo ratings yet
- Good Clinical Practice Advice: Management of Twin PregnancyDocument8 pagesGood Clinical Practice Advice: Management of Twin PregnancyHambrian WijayaNo ratings yet
- Act. PrenatalDocument9 pagesAct. PrenatalJose Carlos de la Fuente LeonNo ratings yet
- NIPTDocument3 pagesNIPTUmber AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Evolution in Screening For Down Syndrome: ReviewsDocument7 pagesEvolution in Screening For Down Syndrome: ReviewsMayada Osman100% (1)
- NIFTYDocument6 pagesNIFTYAeson LamNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling 2009Document8 pagesGuidelines For Amniocentesis and Chorionic Villus Sampling 2009Atik ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Screening TestsDocument11 pagesScreening TestsMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Aneuploidy - Screening and Diagnostic TestingDocument8 pagesFetal Aneuploidy - Screening and Diagnostic TestingAngela FernandezNo ratings yet
- What Is Noninvasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS) ?Document5 pagesWhat Is Noninvasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS) ?Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Lab TestDocument13 pagesLab TestAnonymous VsPjwVNo ratings yet
- Báo AI TrisomyDocument7 pagesBáo AI TrisomyXuân Trường PhạmNo ratings yet
- 10 Bellcross Genetics NIPS CLIAC Nov2015Document30 pages10 Bellcross Genetics NIPS CLIAC Nov2015felicia susantoNo ratings yet
- Afp20141215p851 PDFDocument8 pagesAfp20141215p851 PDFViviane BarbosaNo ratings yet
- L18 prenatalDSDocument20 pagesL18 prenatalDSDrbee10No ratings yet
- Non Invasive Prenatal TestingDocument37 pagesNon Invasive Prenatal TestingniyikeplerNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Accuracy of Fetal Rhesus D Genotyping Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA During The First Trimester of PregnancyDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Accuracy of Fetal Rhesus D Genotyping Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA During The First Trimester of PregnancyRahmayani IsmaNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of Prenatal Diagnosis Associated With Mosaicism TOGDocument10 pagesPitfalls of Prenatal Diagnosis Associated With Mosaicism TOGMarNo ratings yet
- CHORIOAMNIONITISDocument32 pagesCHORIOAMNIONITISnurul azareeNo ratings yet
- Triple AssessentDocument8 pagesTriple Assessentfirdaus zaidiNo ratings yet
- Gendia Brochure NIPTDocument4 pagesGendia Brochure NIPTrajeshbhramaNo ratings yet
- Benchaib 2007Document8 pagesBenchaib 2007Tiffany LamNo ratings yet
- 1fg BasgDocument5 pages1fg BasgPrasetio Kristianto BudionoNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Medical Prenatal Diagnosis Chromosomal Abnormalities Amnion FetusDocument4 pagesProcedure: Medical Prenatal Diagnosis Chromosomal Abnormalities Amnion Fetusbbasya eihynaNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis Estimation of Foetal Age 1Document33 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis Estimation of Foetal Age 1Riya SinghNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Applied Genomics in Prenatal Screening and DiagnosisFrom EverandNoninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Applied Genomics in Prenatal Screening and DiagnosisLieve Page-ChristiaensNo ratings yet
- MJPRU Exam Scheme 2020 MA MSC Mcom Updated On 19 Feb 2020 PDFDocument8 pagesMJPRU Exam Scheme 2020 MA MSC Mcom Updated On 19 Feb 2020 PDFWaqar Ahmad AnsariNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics - 1 PDFDocument167 pagesLaboratory Manual of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics - 1 PDFkdk;lkd33% (3)
- Toxicity Research Paper On AntsDocument8 pagesToxicity Research Paper On AntsMazhar FarNo ratings yet
- Maj Pierce Butler Lists of Enslaved People PDFDocument74 pagesMaj Pierce Butler Lists of Enslaved People PDFBrian Sheffey100% (1)
- Allometry Proposal 1.1 - RevisedDocument11 pagesAllometry Proposal 1.1 - RevisedAnonymous 7BpT9OWPNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate Understandin G Of... The Learners Should Be Able To..Document3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate Understandin G Of... The Learners Should Be Able To..Sab Ibarreta100% (2)
- Anas Muaamar Jeff Ludovico BIOL 1406.SL7 EnzymesDocument5 pagesAnas Muaamar Jeff Ludovico BIOL 1406.SL7 Enzymesblackrose0No ratings yet
- Antinociceptive Activity of Buddleja Globosa (Matico)Document6 pagesAntinociceptive Activity of Buddleja Globosa (Matico)alinumlNo ratings yet
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY - Autoimmune Thyroid Disease - Old and New PlayersDocument12 pages(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY - Autoimmune Thyroid Disease - Old and New PlayersIoana BodescuNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Various Oil ExtraDocument23 pagesA Comparative Study of Various Oil ExtraAjay PurohitNo ratings yet
- Dake Chu: Cui WeiDocument61 pagesDake Chu: Cui WeiDave UlanNo ratings yet
- Crown-Of-Thorns Starfish and Coral Surveys Using The Manta Tow and Scuba Search TechniquesDocument42 pagesCrown-Of-Thorns Starfish and Coral Surveys Using The Manta Tow and Scuba Search TechniquesCrassostrea GigasNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentSanaa AndersonNo ratings yet
- The Revised Classification of EukaryotesDocument79 pagesThe Revised Classification of Eukaryoteskrishy19No ratings yet
- Wildlife Resources Conservation and Protection ActDocument49 pagesWildlife Resources Conservation and Protection ActMonefah Mulok50% (2)
- Chilli Crop Improvement - Training - IIHRDocument2 pagesChilli Crop Improvement - Training - IIHRVipasha Tanu RawatNo ratings yet
- More Actual ItemsDocument8 pagesMore Actual ItemsJomarie TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Cow/Calf Record Book: YearDocument64 pagesCow/Calf Record Book: YearNikson Rafael AmosNo ratings yet
- Ruhs Bsc. Nursing Examination 2017 Question PaperDocument27 pagesRuhs Bsc. Nursing Examination 2017 Question PaperSahil sharmaNo ratings yet
- CG000316 ChromiumNextGEMSingleCell3 - v3.1 CRISPR Screening RevC - FinalDocument77 pagesCG000316 ChromiumNextGEMSingleCell3 - v3.1 CRISPR Screening RevC - FinalW DongNo ratings yet
- MacromoleculesDocument12 pagesMacromoleculesJohn Edward SantosNo ratings yet
- Labmax 240Document43 pagesLabmax 240Dharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Si RNADocument29 pagesSi RNALuis MonteroNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography PDFDocument222 pagesIllustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography PDFVohinh NgoNo ratings yet
- InTech-Prenatal Evaluation of Fetuses Presenting With Short FemursDocument15 pagesInTech-Prenatal Evaluation of Fetuses Presenting With Short FemursadicrisNo ratings yet
- Sts Finals NotesDocument10 pagesSts Finals NotesRossy HidalgoNo ratings yet
- 2014 ModueDocument4 pages2014 ModueYogesh BorkarNo ratings yet
- Influence of Inorganic and Organic Nutrient Sources On Soil Properties and Rain-Fed Rice Tissue Nutrient Content in Gambella, EthiopiaDocument20 pagesInfluence of Inorganic and Organic Nutrient Sources On Soil Properties and Rain-Fed Rice Tissue Nutrient Content in Gambella, EthiopiaInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Petr Hájek, MD, Phd. Head of Anatomy Dept. Assoc. Prof. Dáša Slížová, MD, Phd. Senior LecturerDocument27 pagesAnatomy: Petr Hájek, MD, Phd. Head of Anatomy Dept. Assoc. Prof. Dáša Slížová, MD, Phd. Senior LecturerTodesengelNo ratings yet
- 017 Wuchereria BrugiaDocument21 pages017 Wuchereria BrugiaAyop KhNo ratings yet