Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NIPT PLUS - Dummy
Uploaded by
Aakash vermaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NIPT PLUS - Dummy
Uploaded by
Aakash vermaCopyright:
Available Formats
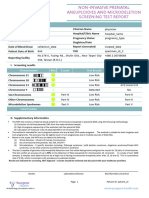
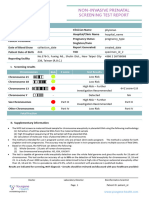
Test report for Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing-Plus (NIPT)
Sample Information
Patient Name Sample Type
Barcode No Test Name /code:
Visit ID Gestational age
Age/Gender Fetus number
Ref Doctor /hospital Collection Date
Report Date
Referral reason: Sample was referred for Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT); A Screening Test for
Chromosomal Aneuploidy.
Test Result: NO CHROMOSOMAL ANEUPLOIDIES AND MICRODELETIONS ARE DETECTED
Microdeletions
DiGeorge (22q11.2) Not Detected
Angelman (15q11.2) Not Detected
Prader-Willi (15q11.2) Not Detected
cri-du-chat (5p) Not Detected
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (4p) Not Detected
1p36 deletion Not Detected
Fetal Fraction: 8.99%
Common Chromosomal Aneuploidies Not detected
Sex Chromosome Aneuploidies Not detected
Chromosomal Aneuploidies for other chromosomes Not detected
1.Common chromosomal aneuploidies
Syndrome Result
Trisomy 21-Down Syndrome Not detected, low risk
Trisomy 18-Edwards Syndrome Not detected, low risk
Trisomy 13-Patau Syndrome Not detected, low risk
2. Sex Chromosomal aneuploidies
Syndrome Result
Turner syndrome (45, X) Not detected, low risk
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY) Not detected, low risk
XYY syndrome Not detected, low risk
XXX syndrome Not detected, low risk
6-3-862/A, Lal Bungalow, Ameerpet, Hyderabad – 500016, info@lifelinediagnostics.in,
Ph: +91 9542129919
Understanding the test Results: NIPT analysis can lead to one of the three following outcomes
A- No Aneuploidy Detected: Low probability of the fetus developing the specific chromosomal
aneuploidy
B- Aneuploidy Detected: High probability of the fetus developing the specific chromosome aneuploidy.
Confirmatory testing via amniocentesis/CVS is recommended.
c- No Results: The maternal sample could not generate test results due to unavoidable reasons,
therefore repeat sampling is recommended. Invasive testing is recommended if NO TEST RESULT is
obtained subsequent to the repeat sampling.
3: Other Chromosomal Aneuploidies
Syndrome Result
chromosome 1 Low risk
chromosome 2 Low risk
chromosome 3 Low risk
chromosome 4 Low risk
chromosome 5 Low risk
chromosome 6 Low risk
chromosome 7 Low risk
chromosome 8 Low risk
chromosome 9 Low risk
chromosome 10 Low risk
chromosome 11 Low risk
chromosome 12 Low risk
chromosome 14 Low risk
chromosome 15 Low risk
chromosome 16 Low risk
chromosome 17 Low risk
chromosome 19 Low risk
chromosome 20 Low risk
chromosome 22 Low risk
About the Test: The cell-free DNA that was extracted from the peripheral blood of the mother was
subjected to whole genome sequencing. The Next Generation Sequencing is performed using MGI
platform and analyzed through the JINKE NIPT technology.
The test can detect aneuploidy across the entire fetal genome (23 pairs of chromosomes) and can
interpret the results for Trisomy 13, Trisomy 18, and Trisomy 21, as well as sex chromosomes. This
test has a detection accuracy of up to 99 percent for fetal chromosomal aneuploidy
Recommendations:
• The above results need to be interpreted in the context of all clinical findings.
• Further follow up with your health provider is recommended.
• Follow up genetic sonogram recommended. Invasive testing to be considered in the event of
ultrasoundanomalies.
6-3-862/A, Lal Bungalow, Ameerpet, Hyderabad – 500016, info@lifelinediagnostics.in,
Ph: +91 9542129919
Test Limitations:
*If the fetal fraction is lower than 3.5%, the accuracy of the test may be reduced. To ensure the accuracy of
the results, we would recommend a re-sampling of the maternal blood one or two weeks later. If the fetal
fraction is less than 7%, the detection power of fetal microdeletion/microduplication syndrome (< 5 Mb)
is limited. We would recommend a more careful clinical observation or a higher coverage whole genome
sequencing re-test.
1. The results of this test are for reference only, not for the final diagnosis. If the test result is high risk,
genetic counseling and invasive prenatal diagnosis are needed. If a high risk of
microdeletion/microduplication syndrome is detected, prenatal diagnosis is recommended to be
combined with maternal chromosome analysis to exclude maternal influence. If the test result is low risk,
the fetus has a low risk of developing the target disease of this screening. However, the possibility of other
abnormalities cannot be excluded, and systematic ultrasound examinations and other prenatal
examinations should be conducted.
2. The results of this test include sex chromosome aneuploidies and other chromosomal aneuploidies. Compared
with trisomy 21, trisomy 18 and trisomy 13, the incidence of these aneuploidies is lower in the population, and
the data available is limited. Therefore, the possibility of false positive or false negative cannot be ruled out.
The current test is based on Whole Genome Sequencing of maternal cell free DNA followed by streamline
automated bioinformatics analysis for all chromosomes. In tests which also involve microdeletions, the relevant
tested microdeletions are noted.
3. This method is not suitable for testing: Gestational age <12+0 weeks; Pregnant women with twins or
multiple pregnancies; One partner has a definite chromosomal abnormality; Received allogeneic blood
transfusion, transplantation and allogeneic cell therapy within 1 year; Fetal ultrasound result suggested
that there were structural abnormalities and prenatal diagnosis was needed; A family history of genetic
diseases or a high risk of genetic diseases in the fetus; Pregnancy with malignant tumor; Other
conditions that the doctor considers may affect the accuracy of the results. Zscore reference range is
between -3 to +3.
4. Abnormalities caused by the following factors cannot be detected in this test: structural abnormalities such
as chimera and translocation in chromosomes; Chromosomal polyploidies (triploid, tetraploid, etc.);
Balanced translocation, inversion and ring of chromosomes; Uniparental disomy (UPD); Single/polygenic
diseases; Chromosomal regions with high duplication and fixation, such as the chromosomal abnormalities
of the proximal centromere and telomere.
5. The sample tested is the cell free DNA in peripheral blood of pregnant women, which mainly from placental
trophoblastic cells rather than direct fetal cells. Given the limitations of the current technical level of the
medical tests and the differences among pregnant women, there may still be false positives or false
negatives in rare cases, even if the testing staff has fulfilled job responsibilities and operational procedures.
6. The detection accuracy may be reduced to some extent for severely obese pregnant women (BMI >40) and
conception through in-vitro fertilization-embryo transfer, and the test results are only for reference.
7. The patient should provide complete, accurate and detailed personal information. The center shall not be
responsible for the interruption of testing services and inaccurate results caused by inaccurate information
or other misleading factors provided by the patient.
8. The test results in this report are only responsible for the samples submitted for inspection.
9. DISCLAIMER! NIPT is a screening test, a low risk does not exclude the above evaluated disorders
Important: On doing PNDT test, the undersigned hereby confirms that no sex chromosome information has been
passed on to anyone in whatsoever manner
6-3-862/A, Lal Bungalow, Ameerpet, Hyderabad – 500016, info@lifelinediagnostics.in,
Ph: +91 9542129919
References:
1. Jiang, F., et al., Noninvasive Fetal Trisomy (NIFTY) test: an advanced noninvasive prenatal diagnosis
methodology for fetal autosomal and sex chromosomal aneuploidies. BMC Med Genomics, 2012. 5: p. 57.
2. Chiu, R.W., et al., Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively parallel
genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008. 105(51): p. 20458-63.
3. Gregg, A.R., et al., Noninvasive prenatal screening for fetal aneuploidy, 2016 update: a position
statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med, 2016. 18(10): p. 1056-
65.
4. Chiu, R.W., et al., Non-invasive prenatal assessment of trisomy 21 by multiplexed maternal plasma DNA
sequencing: large scale validity study. BMJ, 2011. 342: p. c7401.
5. Bianchi, D.W., et al., Genome-wide fetal aneuploidy detection by maternal plasma DNA
sequencing. Obstetrics &Gynecology, 2012. 119(5): p. 890-901.
6. Chen, M., et al., Validation of fetal DNA fraction estimation and its application in noninvasive prenatal
testing for aneuploidy detection in multiple pregnancies. Prenatal Diagnosis, 2019. 39(13): p. 1273-1282.
-----------END OF REPORT---------
A. Radhika Dr. Siva Prasad Dr. Kiran Kumar
Co-Head Genomics Head- Genomics Consultant Genomics
6-3-862/A, Lal Bungalow, Ameerpet, Hyderabad – 500016, info@lifelinediagnostics.in,
Ph: +91 9542129919
You might also like
- Three Approaches To Psychotherapy GloriaDocument41 pagesThree Approaches To Psychotherapy GloriaLuisa Hernandezy67% (3)
- Self Discovery MaterialsDocument62 pagesSelf Discovery Materialsarojutony100% (8)
- TRN270532 Rubina-Pal 2694 275722 Panorama Report V1 PDFDocument3 pagesTRN270532 Rubina-Pal 2694 275722 Panorama Report V1 PDFSukhwinder KaurNo ratings yet
- End - Life of Care PPT 1 MainDocument48 pagesEnd - Life of Care PPT 1 MainNancy Singh60% (15)
- Evolution in Screening For Down Syndrome: ReviewsDocument7 pagesEvolution in Screening For Down Syndrome: ReviewsMayada Osman100% (1)
- Sage Microdeletion Example Screening ReportDocument4 pagesSage Microdeletion Example Screening ReportpathbiomedxNo ratings yet
- Sage SCA Example Screening ReportDocument3 pagesSage SCA Example Screening ReportpathbiomedxNo ratings yet
- QF-PCR For PrenatalDocument9 pagesQF-PCR For Prenatalhoa1405No ratings yet
- CHROMOSOMESDocument17 pagesCHROMOSOMESrydk2ptz92No ratings yet
- Sage Trisomy Example Screening ReportDocument2 pagesSage Trisomy Example Screening ReportpathbiomedxNo ratings yet
- NIPT Sample ReportDocument3 pagesNIPT Sample Reportvivek krishnanNo ratings yet
- Genetic screening and testing options for expecting parentsDocument5 pagesGenetic screening and testing options for expecting parentsmartinaNo ratings yet
- Act. PrenatalDocument9 pagesAct. PrenatalJose Carlos de la Fuente LeonNo ratings yet
- L18 prenatalDSDocument20 pagesL18 prenatalDSDrbee10No ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis and ScreeningDocument55 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis and ScreeningRania ZahoNo ratings yet
- Aneuploidy screening2 - CopyDocument48 pagesAneuploidy screening2 - CopyMonisha ArulalanNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Chromosomal Microarray Nov2015-3Document34 pagesPrenatal Chromosomal Microarray Nov2015-3suryasivNo ratings yet
- FullDocument6 pagesFullamarNo ratings yet
- PM - NaceDocument3 pagesPM - Nacemohammad tahirNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Aneuploidy ScreeningDocument80 pagesPrenatal Aneuploidy ScreeningBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Non Invasive Prenatal TestingDocument37 pagesNon Invasive Prenatal TestingniyikeplerNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Prenatal DiagnosticDocument33 pagesFingerprint Prenatal Diagnosticd17oNo ratings yet
- Next-gen sequencing and karyotyping diagnose Robertsonian translocation trisomy 13Document4 pagesNext-gen sequencing and karyotyping diagnose Robertsonian translocation trisomy 13christian roblesNo ratings yet
- What is karyotyping testDocument1 pageWhat is karyotyping testRajneesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Trisomy 18 SA CaseDocument5 pagesTrisomy 18 SA CaseRiniJuliyantiNo ratings yet
- Genetic disorders III (1) (1)Document42 pagesGenetic disorders III (1) (1)Bahzad AkramNo ratings yet
- QF-PCR March 09Document10 pagesQF-PCR March 09Phạm Quốc ToảnNo ratings yet
- Down syndrome screening resultsDocument11 pagesDown syndrome screening resultslightning proNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)Document13 pagesNon-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)Andy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Testing of A FetusDocument2 pagesGenetic Testing of A Fetusapi-353526506No ratings yet
- Brochure Prenatal TestingDocument4 pagesBrochure Prenatal TestingMCuk2606No ratings yet
- The New Genetics - Paradigm Shifts in Prenatal Diagnosis - Jennifer Hoskovec, MS, CGCDocument41 pagesThe New Genetics - Paradigm Shifts in Prenatal Diagnosis - Jennifer Hoskovec, MS, CGCSanthaVenkataramanaraoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DiagnosisDocument42 pagesPrenatal DiagnosisarunjyothishNo ratings yet
- Understanding Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Chromosomal AbnormalitiesnizobellNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument6 pagesChromosomesMUHAMMAD SHAYANNo ratings yet
- 2019 Chromosomal Microarray vs. NIPS Analysis of 5541 Low-Risk PregnanciesDocument6 pages2019 Chromosomal Microarray vs. NIPS Analysis of 5541 Low-Risk PregnanciesAhmed H. Ali ElbestaweyNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DiagnosticDocument60 pagesPrenatal DiagnosticNisaNo ratings yet
- Group A PDFDocument34 pagesGroup A PDFAnsa WaqarNo ratings yet
- Tema 4Document13 pagesTema 4Nerea OteguiNo ratings yet
- J of Obstet and Gynaecol - 2020 - Samura - Update On Noninvasive Prenatal Testing A Review Based On Current WorldwideDocument9 pagesJ of Obstet and Gynaecol - 2020 - Samura - Update On Noninvasive Prenatal Testing A Review Based On Current Worldwidejazz castañedaNo ratings yet
- Gendia Brochure NIPTDocument4 pagesGendia Brochure NIPTrajeshbhramaNo ratings yet
- Daffos Et AlDocument4 pagesDaffos Et AlEmese NagyNo ratings yet
- Discover Genetic Problems with Amniocentesis TestDocument5 pagesDiscover Genetic Problems with Amniocentesis TestMichael MikuruNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Aneuploidy Screening - FinalDocument75 pagesPrenatal Aneuploidy Screening - FinalBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Screening Tests: Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal DiseaseDocument6 pagesScreening Tests: Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal DiseaseMischief ManagerNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Genetic Screening DBiagnosis Hamamy 2010Document27 pagesPrenatal Genetic Screening DBiagnosis Hamamy 2010Georgie StephenNo ratings yet
- Free Fetal DNA: Prof KhaledDocument15 pagesFree Fetal DNA: Prof KhaledSohailKhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Bellcross Genetics NIPS CLIAC Nov2015Document30 pages10 Bellcross Genetics NIPS CLIAC Nov2015felicia susantoNo ratings yet
- Genetics in IVF, Prenatal DiagnosisDocument33 pagesGenetics in IVF, Prenatal DiagnosisavanthikagettyNo ratings yet
- Maternal Triple Screening Tests Detect Risks of Birth DefectsDocument8 pagesMaternal Triple Screening Tests Detect Risks of Birth Defectsfirdaus zaidiNo ratings yet
- PGT and Prenatal GeneticsDocument50 pagesPGT and Prenatal GeneticsavanthikagettyNo ratings yet
- Lab TestDocument13 pagesLab TestAnonymous VsPjwVNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics FinalsDocument18 pagesCytogenetics FinalsPatrick AbellaNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument152 pagesGeneticsReena CrNo ratings yet
- What Is Noninvasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS) ?Document5 pagesWhat Is Noninvasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS) ?Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- NeoBona BROCHURE PDFDocument2 pagesNeoBona BROCHURE PDFyousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- Prenatal TestingDocument26 pagesPrenatal TestingMar ClrNo ratings yet
- GEN NIPT - Scainconclusive Tcm63-1515179Document2 pagesGEN NIPT - Scainconclusive Tcm63-1515179ptsrvNo ratings yet
- 2024.Plancental, maternal, fetal, and techical origins of false positive cell fre DNA screening resultsDocument9 pages2024.Plancental, maternal, fetal, and techical origins of false positive cell fre DNA screening resultsrpina.genNo ratings yet
- Screening For Fetal Chromosomal AbdnormalitiesDocument22 pagesScreening For Fetal Chromosomal AbdnormalitiesAlejandra MurilloNo ratings yet
- TOG Evolution in Screening For Down SyndromeDocument7 pagesTOG Evolution in Screening For Down SyndromeMarNo ratings yet
- Karyotyping - Activity 2023Document5 pagesKaryotyping - Activity 2023Riley McCaffertyNo ratings yet
- Expense - OncequestDocument6 pagesExpense - OncequestAakash vermaNo ratings yet
- Typeform Invoice BTLWMgTYQCPq91RjvDocument1 pageTypeform Invoice BTLWMgTYQCPq91RjvAakash vermaNo ratings yet
- Sanger Dummy ReportDocument3 pagesSanger Dummy ReportAakash vermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NetworkingDocument29 pagesUnit 1 NetworkingVanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- MLPA Dummy ReportDocument3 pagesMLPA Dummy ReportAakash verma100% (1)
- MBC Maxwell Release 9-19-12Document2 pagesMBC Maxwell Release 9-19-12Sorin IordacheNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Discharge Instructions - Howard County General Hospital, Johns Hopkins MedicineDocument7 pagesPostpartum Discharge Instructions - Howard County General Hospital, Johns Hopkins MedicineA.No ratings yet
- Assessing & Measuring Operational Risk Why COSO Is InappropriateDocument41 pagesAssessing & Measuring Operational Risk Why COSO Is Inappropriateshecat2604710% (1)
- Growth Hormone Responses To Sub-Maximal and Sprint Exercise: Keith StokesDocument14 pagesGrowth Hormone Responses To Sub-Maximal and Sprint Exercise: Keith StokesganduaffNo ratings yet
- Feeding The Mind - PresentationDocument11 pagesFeeding The Mind - Presentationapi-708898253No ratings yet
- Meet Our Marketing Team!Document8 pagesMeet Our Marketing Team!Ben LawlessNo ratings yet
- 7a. Antibacterial AgentsDocument32 pages7a. Antibacterial AgentsNiala AlmarioNo ratings yet
- LRTP Draft 081915Document129 pagesLRTP Draft 081915Daily FreemanNo ratings yet
- MSDS H2O2 SolvayDocument14 pagesMSDS H2O2 SolvayVedastra AstaNo ratings yet
- Reflection'brain On FireDocument2 pagesReflection'brain On FireJevelyn AgdolNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Leadership and TeamworkDocument4 pagesGroup 5 Leadership and TeamworkRanets MamondoleNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Evans SyndromeDocument5 pagesA Case Report of Evans SyndromecatNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Lagos DocumentaryDocument6 pagesWelcome To Lagos DocumentaryDede SonntagNo ratings yet
- CAE Healthcare: Your Worldwide Training Partner of ChoiceDocument39 pagesCAE Healthcare: Your Worldwide Training Partner of Choicejfrías_2No ratings yet
- School Readiness Checklist For School Year 2020-2021: Monitoring Tool No. 1Document6 pagesSchool Readiness Checklist For School Year 2020-2021: Monitoring Tool No. 1Faye Angana100% (2)
- Look Sharp: Next Level Sex LessonsDocument140 pagesLook Sharp: Next Level Sex LessonsLester SaquerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With CCFDocument34 pagesNursing Management of Patient With CCFJayarani Ashok100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet Corrosive ChemicalDocument2 pagesSafety Data Sheet Corrosive Chemicalzubair1951No ratings yet
- Introduction To Retail PharmacyDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Retail PharmacyHairul MaisarNo ratings yet
- LIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS As of December 2012: DR No Generic Brand Strength Form CompanyDocument22 pagesLIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS As of December 2012: DR No Generic Brand Strength Form CompanyBenjamin TantiansuNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of MalariaDocument41 pagesDrug Therapy of MalariaAbby LiewNo ratings yet
- SMART Goal SettingDocument5 pagesSMART Goal SettingblakeloganNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Bibliography Final v2Document10 pagesAnnotated-Bibliography Final v2IrvingNo ratings yet
- Addiction Treatment Center in HoustonDocument8 pagesAddiction Treatment Center in Houstonemma rebel100% (1)
- TCV Campaign-2024Document41 pagesTCV Campaign-2024xtylishshehryarking786No ratings yet
- CephalhematomaDocument3 pagesCephalhematomaNazhar FarhanNo ratings yet
- High-Dose Corticosteroids Improve The Prognosis of Bell 'S Palsy Compared With Low-Dose Corticosteroids: A Propensity Score AnalysisDocument6 pagesHigh-Dose Corticosteroids Improve The Prognosis of Bell 'S Palsy Compared With Low-Dose Corticosteroids: A Propensity Score AnalysisRiyanti DeviNo ratings yet