Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025
Uploaded by
Rafiya95z MynirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025
Uploaded by
Rafiya95z MynirCopyright:
Available Formats
M.E.
S INDIAN SCHOOL, DOHA – QATAR
Notes 2024 – 2025
Section: Boys’/Girls’ Date:01.04.2024
Class & Div.: X (All Divisions) Subject: Physics
Lesson / Topic: LIGHT
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
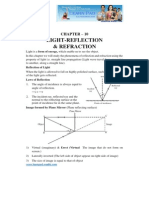
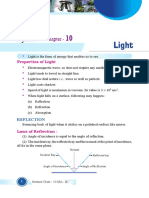
1. What is light?
Ans: Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object. An object reflects light that
falls on it. This reflected light when received by our eyes, enables us to see things.
2. What is meant by Reflection of light?
Ans: It is the phenomenon of bouncing back of light to the same medium on striking the surfaces
of any object. Reflection is of two types, Regular reflection and irregular reflection.
3. Explain the laws of reflection of light.
Ans:(i). The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection. (< i = < r)
(ii). The incident, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane.
4. Describe the characteristics of image formed by plane mirrors.
Ans:1) Virtual (imaginary) &Erect (Virtual The image that do not form on a screen)
2) Laterally inverted (The left side of object appears on the right side of image)
3) The size of image is equal to that of object.
4) The image formed is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
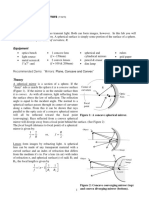
5. What are spherical mirrors?
Ans: Those mirrors, whose reflecting surfaces are spherical, are called spherical mirrors.
Spherical mirrors are of two types, (i) Concave mirror (ii) Convex mirror.
(i) Concave mirror: -
A spherical mirror, whose reflecting surface is curved inwards, that is, faces
towards the centre of the sphere, is called a concave mirror.
(ii) Convex mirror.
A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards, is called a convex
mirror.
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
7. Explain the following terms related to spherical mirrors.
(i) Pole(P); (ii) Principle axis; (iii) Centre of Curvature (C); (iv) Aperture
(v) Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror(R); (vi) Principal focus(F) and focal length(f).
Ans:
(i) Pole (P): The centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror.
(ii) Principal axis: Imaginary straight line passing through the pole (P) and the centre of
curvature (C) of a spherical mirror.
(iii) Centre of Curvature (C): The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror forms a part of
asphere. This sphere has a centre. This point is called the centre of curvature.
(iv) Aperture: The diameter (width) of reflecting spherical surface.
(v) Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror(R): The radius of the hollow sphere of glass, of
which the spherical mirror is a part. (i.e. The separation between the pole and the centre of
curvature PC = R)
(vi) Principal focus(F): The point on the principal axis, where all parallel rays meet after
reflection.
(vii) Focal length (f): The length between the pole and focus point (i.e., PF = f)
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
Note: Relationship between focal length (f) and Radius of curvature (R). [f= 𝑹 ]
𝟐
8. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20cm. What is its focal length?
Ans: Given, radius of curvature of the mirror (R ) = 20cm
Focal length (f)= 𝑅 f= 20 = 10 cm
2 2
9. Describe the rules for tracing images formed by spherical mirrors.
Ans: Rule: (i). A ray of light which is parallel to principal axis always pass through focus
or vice-versa.
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
Rule: (ii).A ray of light, which passing through centre of curvature (it is also known as
normal at the point of incidence on spherical mirror) will retrace it’s path
after reflection.
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
Rule: (iii).A ray of light falling on pole get reflected at the same angle on the other side of
principal axis. (A ray of light incident obliquely towards the pole of a mirror is
reflected obliquely after the reflection.)
Note: - A ray of light passes through centre of curvature is always act as normal at the point of
incidence. If we know the normal, we can draw angle of incidence and angle of reflection.
Home Work: A ray of light incident on a convex mirror as shown.
Redraw the diagram and complete the path of this ray after
reflection from the mirror. Mark angle of incidence and angle of
reflection.
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
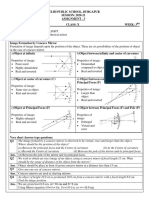
10. Draw and explain the image formation by concave mirror.
1. Object at infinity 2. Object beyond C
Position of image: Between F &C
Position of image: At focus Nature: Real and inverted
Nature: Real and inverted Size: Small
Size: Highly diminished
3. Object at C 4.Object between C&F
Position of image: At C
Nature: Real and inverted Position of image: Beyond C
Size: Same size of the object Nature: Real and inverted
Size: Enlarged
5.Object at F 5.Object between F & P
Position of image: At infinity
Nature: Real and inverted Position of image: Behind the mirror
Size: Highly Enlarged Nature: Virtual and erect
Size: Enlarged
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
11. Explain the image formation of convex mirrors.
1. Object at infinity 2.Anywhere between infinity and pole of the mirror
Position of image: At Focus(F)
Nature: Virtual and erect
Position of image: Between P &F
Size: Highly diminished
Nature: Virtual and erect
Size: Very small
12. What are the uses of concave and convex mirrors?
Ans: Uses of Concave Mirror
1. In torches, search light and headlight of vehicle concave mirror is used as reflector.
2. Used to see large image of face as shaving mirror
3. Used by dentist to see large images of the teeth
4. Large concave mirror used to focus sunlight (heat) in solar furnaces.
5. Used in Reflecting type astronomical telescope.
Uses of Convex Mirror
1. It is used as a rear view mirror in vehicles.
2.It is used as reflector in street lamps.
3.They are used in magnifying glass, in securities and also used intelescopes .
13. Mention the types of mirror used as (i) rear view mirrors, (ii) having mirrors. List the reasons
to justify your answers in each case.
Ans: (i) Convex mirror - Convex mirror always forms virtual, small and erect image between the
pole and focus of an object placed anywhere in front of it. In addition, convex mirrors
provide a wider field of view of traffic behind him.
(ii) Concave mirror – Concave mirror forms an erect and enlarged image of the face when it
is held closer (between F & P) to the face.
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
14.Mention the sign convention for reflection by spherical
mirrors.Ans:1. The object is always placed to the left side of
mirror.
2. All distance should be measured from pole (P),
parallel to principal axis.
3. Take 'P' as origin. Distances measured
Right of the origin (+ x - Axis) are taken
positive
Left of the origin (– x-Axis) are taken negative
Perpendicular to and above principal axis (+y-Axis) are taken positive
Perpendicular to and below principal axis (–y-Axis) are taken negative
Note:-
TYPE OF MIRROR u v f R Height of Height of the image
the object
Real Virtual Real Virtual
Concave mirror - - + - - + - +
Convex mirror - No real + + + + No real +
image image
Homework:-What will be the signs of u, v and f for a convex mirror as per sign convention?
15.What is mirror formula?
Ans:The formula which gives the relation between object distance (u), the image distance (v)
1 1 1
and the focal length (f) of the mirror is known as mirror formula. [ v+ u= f ]
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
Mirror formula:
1 1 1 1 1 1
v +u = fie.,image distance+object distance = focal length
size of image h' v
Magnification = = (or) Magnification =
size of object h u
If m>1, image is enlarged;
If m<1, image is diminished;
If m=1, Same size.
If m = +ve the image is virtual and if m= -ve the image is real.
R
f= where, ‘R’ is the radius of curvature. (or) R= 2f
2
16. An object of size 7cm is placed at 27 cm is front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm.
At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focussed image
can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Ans: Given, u = 27 cm, = 18 cm ( It is concave), h = 7 cm
From mirror formula
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 1
v u f v (27) (18) v 18 27 54 54.
v = 54 cm. The screen must be placed at a distance of 54 cm from the mirror in front
of it.
v 54
m 2.
u 27 The image is real, inverted and enlarged.
Size of the image h = m.h = (2) 7 cm = 14 cm. Thus, the image is of 14 cm length and
is an inverted image i.e., formed below the principal axis.
17. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed
at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where
is the image located?
Ans:Distance of object from concave mirror u = 10 cm.
As magnification of image is 3 and image is real, hence m = 3
v
m
u Hence v mu (3)(10) 30cm Thus image is formed 30 cm in front of the
concave mirror.
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
18. An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find
the position and nature of the image.
Ans:A convex mirror has a positive focal length. Therefore, = + 15 cm, u = 10 cm.
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 5
15 v (10)
As f v u v 15 10 v 30
v = + 6 cm.
The image is formed 6 cm behind the mirror, it is virtual image.
19. An object 5 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of
radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Ans: Given, Radius of curvature of mirror R = 30 cm,
= 𝑅 =30= 15 cm. It is a convex mirror. Therefore, = + 15 cm,
2 2
u = 20 cm, h = 5.0 cm
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 7
As v u f v 20 15 v 15 20 v 60
60
cm
v= 7 .
60
3 v
m 7
The image is virtual, behind the mirror, and erect. u 20 7
As m = + 3< 1 It is erect(+ve) and diminished (m<1).
7
3 15
m.h 5cm cm
The size of image, h = 7 7
Homework:-
1. 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the
location of image and magnification.( Ans v = +6.6cm, m = + 0.55,virtual, erect, diminished)
2. An object of size 5 cm is placed at a distance of 25cm from the pole of a concave mirror of
radius of curvature 30 cm . Calculate the distance and size of the image so formed . What will
be the nature of the image.(Ans v = -37.5 cm, hi= -7.5 cm, real , inverted, enlarged)
F 061, Rev 01, dtd 10th March 2020
You might also like
- Unilever IFE EFE CPM MatrixDocument7 pagesUnilever IFE EFE CPM MatrixNabeel Raja73% (11)
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDocument16 pagesLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNo ratings yet
- BIOETHICSDocument4 pagesBIOETHICSSherylou Kumo SurioNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument22 pagesLight Reflection and Refractionapi-246793885100% (1)
- Chapter Notes Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesChapter Notes Light - Reflection & Refractionroseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- Light FinalDocument8 pagesLight Finalghs NambalNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionAnant WatsNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorDocument3 pagesSpherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorLeah ClovisNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument18 pagesReflection and Refraction Notessundeepika2008No ratings yet
- CLASS 10 LIGHT - REFLECTION NotesDocument14 pagesCLASS 10 LIGHT - REFLECTION NotesDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Reflection Notes Grade 10Document9 pagesReflection Notes Grade 10Parv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Study Notes 2015-16Document15 pagesClass 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Study Notes 2015-16dvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Revision Notes Light Reflection & RefractionDocument19 pagesClass 10 Science Revision Notes Light Reflection & RefractionMadhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and Refractionuma mishraNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light FINALDocument8 pagesReflection of Light FINALPrakritiNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionANJALI RANANo ratings yet
- 09.ray Optics FDocument92 pages09.ray Optics FParulNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and Refractionismgilovamunisa150No ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDocument12 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37No ratings yet
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDocument6 pages2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171No ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionGarvit Khare50% (2)
- 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument43 pages10 Light Reflection and Refractiong8one2020No ratings yet
- Science 10th PDFDocument189 pagesScience 10th PDFMD Moon100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10Document19 pagesStudy Material Class 10Shivam Tiwari100% (2)
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDocument29 pagesG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractiondjshlok359No ratings yet
- 09.ray Optics-FDocument92 pages09.ray Optics-Fsiddharth sharmaNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument72 pagesLight WavesJeffrey MaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 CDFDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 10 CDFPuppala Vardhan50% (2)
- Curved Mirrors o LevelDocument14 pagesCurved Mirrors o LevelAZORYNo ratings yet
- 05 Light 20-52Document33 pages05 Light 20-52Manas AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Science 10 - Optics NotesDocument5 pagesScience 10 - Optics NotesRina Marie Besin CartesianoNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign3Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign3Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Focal-Length.Document11 pagesDetermination of The Focal-Length.mohammed1998No ratings yet
- Lecture and Worksheet - LensesDocument13 pagesLecture and Worksheet - LensesJaymar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Reflection of LightDocument29 pagesRay Optics: Reflection of LightAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractionapi-24735088292% (25)
- Physics Cl10 Assign1Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign1Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument41 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractionapi-268345960No ratings yet
- Physics Class XIIDocument177 pagesPhysics Class XIIManavendra PratapNo ratings yet
- Reflection Notes 10 - d56209cc 3417 4c65 8bcb 76afb65c8af6Document7 pagesReflection Notes 10 - d56209cc 3417 4c65 8bcb 76afb65c8af6Jethro ToryilaNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign2Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign2Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Light Reflection Q-AnsDocument6 pagesChapter-10 Light Reflection Q-AnsParvanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Document22 pagesCH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Mohammad MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Light Class XDocument109 pagesLight Class XLekshmipriya PNo ratings yet
- Virtual Class Room Physics For Grade 10Document3 pagesVirtual Class Room Physics For Grade 10bamlak zewdieNo ratings yet
- 10th Physics Chapter 10.light-Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument39 pages10th Physics Chapter 10.light-Reflection and Refraction NotesTapas Banerjee100% (4)
- Chapter 10 - QWADocument58 pagesChapter 10 - QWADr.K E Reby RoyNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionShubham Jain100% (1)
- Properties of LightDocument10 pagesProperties of LightKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection 1Document22 pagesLight Reflection 1psnarayanan99No ratings yet
- 7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living ScienceDocument3 pages7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living SciencesabletarsingNo ratings yet
- 113184208-Ppt-Properties of Light and The Image FormationDocument50 pages113184208-Ppt-Properties of Light and The Image FormationAzmi HolisNo ratings yet
- LightDocument18 pagesLightAyush BarnwalNo ratings yet
- 10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision MaterialDocument33 pages10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision Material12-Criswin v geo-8ANo ratings yet
- Viewing the Constellations with Binoculars: 250+ Wonderful Sky Objects to See and ExploreFrom EverandViewing the Constellations with Binoculars: 250+ Wonderful Sky Objects to See and ExploreNo ratings yet
- How To Survive Economic CollapseDocument4 pagesHow To Survive Economic CollapseZub AleandruNo ratings yet
- Tallado V. ComelecDocument3 pagesTallado V. ComelecLorelain ImperialNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTINGDocument2 pagesACCOUNTINGtrixie manitoNo ratings yet
- 1702758529Document3 pages1702758529Szymon SłomskiNo ratings yet
- Case Digest - WitnessDocument9 pagesCase Digest - WitnessEmmagine E EyanaNo ratings yet
- TWG 2019 Inception Reports forERG 20190717 PDFDocument95 pagesTWG 2019 Inception Reports forERG 20190717 PDFGuillaume GuyNo ratings yet
- Taqwa (Pıety) Beıng Conscıous of Maıntaınıng Allah's PleasureDocument1 pageTaqwa (Pıety) Beıng Conscıous of Maıntaınıng Allah's PleasuretunaNo ratings yet
- Athet Pyan Shinthaw PauluDocument6 pagesAthet Pyan Shinthaw PaulupurifysoulNo ratings yet
- Law Amendment and Reform (Consolidation) Ordinance (Cap. 23) (1971 Edition)Document16 pagesLaw Amendment and Reform (Consolidation) Ordinance (Cap. 23) (1971 Edition)Jeff YanNo ratings yet
- MilenaPopovaThesisWithCorrectionsAsSubmitted PDFDocument233 pagesMilenaPopovaThesisWithCorrectionsAsSubmitted PDFkakka kikkareNo ratings yet
- Moral Dilemmas in Health Care ServiceDocument5 pagesMoral Dilemmas in Health Care ServiceYeonnie Kim100% (1)
- Elizabeth Stevens ResumeDocument3 pagesElizabeth Stevens Resumeapi-296217953No ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: Irb04-43Document27 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: Irb04-43IRSNo ratings yet
- Notes: 1 Yorùbá Riddles in Performance: Content and ContextDocument25 pagesNotes: 1 Yorùbá Riddles in Performance: Content and ContextDofono ty NísèwèNo ratings yet
- Stamp Duty (Amendment) Act, 2022Document5 pagesStamp Duty (Amendment) Act, 2022Kirunda ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Obsa Ahmed Research 2013Document55 pagesObsa Ahmed Research 2013Ebsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1972Document37 pagesIndian Contract Act 1972Ashutosh Saraiya100% (2)
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics Quarter 2 - Module 5 EducationDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics Quarter 2 - Module 5 EducationMhecy Sagandilan100% (4)
- Bagabag National High School Instructional Modules in FABM 1Document2 pagesBagabag National High School Instructional Modules in FABM 1marissa casareno almueteNo ratings yet
- NeoLiberalism and The Counter-EnlightenmentDocument26 pagesNeoLiberalism and The Counter-EnlightenmentvanathelNo ratings yet
- Journal Jul Dec14 Art4Document16 pagesJournal Jul Dec14 Art4paromita bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- "Land Enough in The World" - Locke's Golden Age and The Infinite Extension of "Use"Document21 pages"Land Enough in The World" - Locke's Golden Age and The Infinite Extension of "Use"resperadoNo ratings yet
- Complete ES1 2023 Vol1Document334 pagesComplete ES1 2023 Vol1Chandu SeekalaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Is The Provision of Initial Care For An Illness or InjuryDocument2 pagesFirst Aid Is The Provision of Initial Care For An Illness or InjuryBasaroden Dumarpa Ambor100% (2)
- Suffixes in Hebrew: Gender and NumberDocument11 pagesSuffixes in Hebrew: Gender and Numberyuri bryanNo ratings yet
- Dharma DuraiDocument3 pagesDharma Duraivsection managerNo ratings yet
- Fashion OrientationDocument7 pagesFashion OrientationRAHUL16398No ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm ExamRafael CensonNo ratings yet