Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waves
Uploaded by
Yasser Abd-Elrazek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
waves
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageWaves
Uploaded by
Yasser Abd-ElrazekCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Waves - The Transfer of Energy (Approx.
1 page)
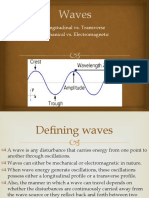
Waves are a disturbance that transfers energy from one point to another without the
actual movement of matter in the medium. Here's what we need to know:
Types of Waves: There are two main categories:
Transverse Waves: Particles in the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of
wave propagation (e.g., light waves, water waves).
Longitudinal Waves: Particles in the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of
wave propagation (e.g., sound waves).
Wave Properties: Wavelength (λ) - distance between two consecutive identical points
on a wave; Frequency (f) - number of wave cycles passing a point per unit time;
Amplitude (A) - maximum displacement of a particle from its rest position; Wave
Speed (v) - the rate at which the wave disturbance propagates, related to
wavelength and frequency by v = fλ.
Reflection and Refraction: When a wave encounters a barrier, it can reflect (bounce
back) or refract (bend) depending on the properties of the medium.
You might also like
- Waves and Optics Class Notes Part 1Document3 pagesWaves and Optics Class Notes Part 1reeta ramNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion PDFDocument23 pagesWave Motion PDFFRANCES VISAYA100% (1)
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer in ScienceJosh Deinille ManarinNo ratings yet
- Waves PPDocument21 pagesWaves PPMacha LaraNo ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- WAVES Chapter 9Document8 pagesWAVES Chapter 9shasagailNo ratings yet
- WAVESjsjDocument4 pagesWAVESjsjtinotaku58No ratings yet
- WavesDocument31 pagesWavesstefone cenizaNo ratings yet
- MY SO Waves Notes Powerpoint - Property of WavesDocument12 pagesMY SO Waves Notes Powerpoint - Property of WavesFirdaus Kamal BahrinNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument26 pagesWavesceline.the988No ratings yet
- WavesDocument11 pagesWavesIfrah ZiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Wave Motion (Hand-Out)Document24 pagesLecture 2 - Wave Motion (Hand-Out)Richard SaputuNo ratings yet
- Basic Wave PhenomenaDocument43 pagesBasic Wave Phenomena李彊No ratings yet
- Waves A Level NotesDocument72 pagesWaves A Level Notesdamilolaamos296No ratings yet
- General Wave PropertiesDocument5 pagesGeneral Wave Propertiessajid aliNo ratings yet
- Presentation On WavesDocument7 pagesPresentation On Wavesmaqsood ahmadNo ratings yet
- Waves 100Document6 pagesWaves 100Brook Rene JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 1 - WAVES - BasicsDocument24 pagesGrade 1 1 - WAVES - BasicsDannyelle BaileyNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Travelling WavesDocument36 pages4.2 Travelling WavesXavierNo ratings yet
- Properties of WavesDocument8 pagesProperties of Wavesjames paulo abandoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument8 pagesPhysicsHeather SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Waves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingDocument40 pagesWaves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingGellirose S. Bantayan100% (1)
- WAVES AROUND YOU (Grade 7 q3)Document23 pagesWAVES AROUND YOU (Grade 7 q3)Genelyn BorjaNo ratings yet
- Waves: By: Chris Lembalemba (Chrislembalemba@yahoo - Co M)Document33 pagesWaves: By: Chris Lembalemba (Chrislembalemba@yahoo - Co M)Michael GalarioNo ratings yet
- PSC 9Document17 pagesPSC 9AryannaNo ratings yet
- A Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesDocument5 pagesA Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesMercy PaduaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Travelling WavesDocument5 pages4.2 Travelling WavesEesha SajidNo ratings yet
- Waves and OscillationDocument25 pagesWaves and OscillationRudraksh JaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 8 Waves: DR - SalmaDocument45 pagesLecture - 8 Waves: DR - SalmaMuhammad TajammulNo ratings yet
- Waves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Document13 pagesWaves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Yuli AriyadiNo ratings yet
- Wave and Oscillatory MotionDocument9 pagesWave and Oscillatory MotionnishantNo ratings yet
- Waves As A Carrier of EnergyDocument39 pagesWaves As A Carrier of EnergyDaisy DuronNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 2 Phy General Properties of WavesDocument102 pagesIGCSE 2 Phy General Properties of WavesKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Waves and SoundDocument46 pagesMechanical Waves and SoundPortia A. Egken100% (1)
- Physic Notes DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPhysic Notes Definitionsfatimawaqar657No ratings yet
- There Are Two Types of WavesDocument5 pagesThere Are Two Types of WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- Two Types Waves: Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves Transverse WaveDocument2 pagesTwo Types Waves: Transverse Waves Longitudinal Waves Transverse WaveSamuel NigatuNo ratings yet
- 12.waves - SdaDocument2 pages12.waves - SdablueegofxNo ratings yet
- 2011-01-22 U13 General Properties of WavesDocument3 pages2011-01-22 U13 General Properties of WavesGanesh MuthupalaniNo ratings yet
- Articulo IeeeDocument5 pagesArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument21 pagesWAVESvipexe4113No ratings yet
- WavesDocument41 pagesWavesMimi CiervaNo ratings yet
- Radiation: Information From The CosmosDocument56 pagesRadiation: Information From The Cosmosglydel fedelicioNo ratings yet
- Oscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumDocument2 pagesOscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumApril Joy Gelilang PulgaNo ratings yet
- Waves NotesDocument13 pagesWaves NotescgozzardNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument6 pagesWave NotesVittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument27 pagesWavesBrianna MalcolmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 71 Simple Harmonic Motion and WavesDocument6 pagesChapter 71 Simple Harmonic Motion and WavesasdfNo ratings yet
- CL 11 CH 15Document15 pagesCL 11 CH 15Mariappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties and BehaviorsDocument7 pagesWave Properties and BehaviorssdafNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 LESSON 1 2Document8 pagesUnit 1 LESSON 1 2kachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- Sound and WavesDocument32 pagesSound and Wavesopoku jonathanNo ratings yet
- Properties of WavesDocument6 pagesProperties of WavesT. Christabel VijithaNo ratings yet
- Physics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World CommunicatesDocument5 pagesPhysics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World Communicatesuhhwot100% (1)
- Lecture-01 - PHY101 (BBA) (51+52) - 20-05-2021Document50 pagesLecture-01 - PHY101 (BBA) (51+52) - 20-05-2021KRZ. Arpon Root HackerNo ratings yet
- Waves - Lecture 1Document45 pagesWaves - Lecture 1Hisham MohamedNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument14 pagesWave MotionPraveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Waves and Wave EffectsDocument18 pagesWaves and Wave EffectsShadyNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument3 pagesWavesBushra Amir X-G-ANo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument1 pageKinematicsYasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 DAQDocument25 pagesLecture 5 DAQYasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- OdacityDocument1 pageOdacityYasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 5Document17 pagesDrawing 2 Book-Ch 5Yasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 4Document26 pagesDrawing 2 Book-Ch 4Yasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 3Document7 pagesDrawing 2 Book-Ch 3Yasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 2Document6 pagesDrawing 2 Book-Ch 2Yasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Drawing 2 Book-Ch 1Document10 pagesDrawing 2 Book-Ch 1Yasser Abd-ElrazekNo ratings yet