Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3rd Theory 3
Uploaded by
Taushif AhammedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3rd Theory 3
Uploaded by
Taushif AhammedCopyright:
Available Formats
Agro-based Industries in India
INTRODUCTION
Agribusiness denotes the collective business activities that are performed from farm to fork.
It covers the supply of agricultural inputs, the production and transformation of agricultural
products and their distribution to final consumers. Agribusiness is one of the main
generators of employment and income worldwide.
Agribusiness is characterized by raw materials that are mostly perishable, variable in quality
and not regularly available. The sector is subject to stringent regulatory controls on
consumer safety, product quality and environmental protection. Traditional production and
distribution methods are being replaced by more closely coordinated and better planned
linkages between agribusiness firms, farmers, retailers and others in the supply chains.
Scope for Agri business in India:
Agri business is a complex system of input sector, production sector, processing-
manufacturing sector, transport and marketing sector. Therefore, it is directly related to
industry and domestic market.
1. India has a vast geographic spread, varied agro-climatic conditions ranging from temperate
to tropical which facilitates and promoting the production of temperate, sub-tropical and
tropical agricultural commodities. India is the seventh-largest country in the world with the
total land area 3287263KM2 and also blessed with varied Agro-climatic zones. There are 20
Agro- climatic zones (ACZ) and nearly 46 out of 60 soil types in the country.
2. The domestic market for processed foods is not only huge but is growing at a fast pace. The
domestic demand for processed food products is very high and ever increasing, the scope
for export earing is also a major factor to push up agricultural sector for enhanced income
and increased employment options.
3. There is huge scope for processing in the food sector for increasing the income, exports and
employment. At present, present, processing is done at primary level only and the rising
standard of living expands opportunities for secondary and tertiary processing of
agricultural commodities. Most of the food processing units are in the unorganized sector
and Indian food market continues to be dominates by the fresh foods segment. According
to one estimate, Indian food market comprises 10% processed segment 15% semi-
processing in organized as well as un-organized sector is reported to be around 2% in fruit
and vegetables, 37% in milk, 21% inn meat, 6% in poultry and 11% in marine fish. The
highest share of processed food is in the dairy sector, where 37% of the total produce in
processed, of this only 15% is processed by the organized sector. The overall value addition
in food products, which is currently 8%, is likely to increase to 35% by the year 2025. India
has 35000 modern rice mills, 91000 rice hullers, 4500 shellers, 8300 hullers-cum- shellers,
20000 pulse mills, 400 fish processing unit and 5198 processing unit of fruits and
vegetables.
4. There is growing demand for agricultural inputs like; seed, feed and fodder, organic and
inorganic fertilizers, bio-fertilizers etc.
5. Applications of biotechnology in agriculture have an immense scope in production of
quality seed, bio-control agents, and microbes for bakery products.
6. The vast coastal line (7517 KM) and internal water resources provides vast opportunity for
production of inland, marine and ornamental fish culture. With an annual fish production of
6 million metric tons, India occupies the third position in fish production and second in fresh
water fish production.
7. The livestock wealth gives enormous scope for production of meat, milk and milk products,
poultry products etc. India has largest population of livestock in the world. India has 16%
of cattle, 57% of buffaloes, 17% of goats and 5% of sheep population of the world.
8. There is growing demand for forestry products such as match, pulp & paper, plywood. The
forest area (21%) and resources can be utilized for production of by-products of forestry.
9. The global market is huge for sugar, coffee, tea, cotton, jute and processed foods such as
sauce spices, meat, dairy product, poultry products, fishery products, vegetables and fruits
are equally large and whose demand in the international market is buoyant. The domestic
market as well as the export market can be exploited to the fullest extent with high
production aided by modern technology and intensive marketing.
10. Mushroom production can be taken up on large scale in the country for domestic
consumption and its export can be enhance with upgrading in the state of art of their
production.
11. There are a good scope of plantation crops viz. cocoa, coconut, cashew, rubber, arecanut
etc.
12. Agri business recently, is combining the diverse commercial enterprises, using
heterogeneous combination of labour, materials, capital and technology.
13. The improved agricultural production provides opportunities for employment in marketing,
transport, cold storage and warehousing, credit and insurance services.
14. Agri business provides crucial forward and backward linkages. Backward linkage includes
supply of input, credit, production technologies, farm services etc., while a forward linkage
includes storage, processing, transportation and marketing aspects.
IMPORTANCE
Establishment of agro-based industries is based on the availability of raw material.
• Agro-based industries have to set up at rural areas where raw material may be
available in plenty – helps in the up-liftment of the rural economy.
• Provide rural population an opportunity for employment.
• Generate income and thereby improve economic condition of people – which in turn
creates potential for demand-based industries.
• Provide an opportunity for the dispersal of industries instead of concentrating at a
particular place.
• Solve the problem of exploitation of farming community by traders and middlemen.
• Farmers could be assured of better price for their produce.
• Encourage to bring more and more areas under various crops – increase agricultural
production and improve nation’s economy.
• Transportation cost of agricultural products can be minimized – thereby help to
minimize cost of finished goods.
• Avoid wastage of perishable agricultural products.
• Help to develop backward areas based on their suitability for setting up agro-
industries.
• Prevent migration of people from rural to urban areas.
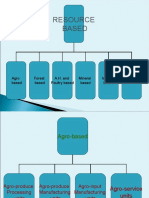
Industries are divided into four groups.
1. Resource based
2. Demand based
3. Skill based
4. Ancillary
Again, the resource-based industries are divided into agro-based, forest based, animal
husbandry and poultry based, mineral based, marine based, etc. Agro-based industries are
those industries which have either direct / indirect link with agriculture. Industries which
are based on agricultural produce and industries which support agriculture come under agro-
based industries.
TYPES OF AGRO-BASED INDUSTRIES
There are four types of agro-based industries.
1. Agro-produce processing units
They merely process the raw material so that it can be preserved and transported at cheaper
cost. No new product is manufactured. Ex: Rice mills, Dal mills, etc.
2. Agro-produce manufacturing units
Manufacture entirely new products. Finished goods will be entirely different from its
original raw material. Ex: Sugar factories, bakery, solvent extraction units, textile mills, etc.
3. Agro-inputs manufacturing units
Industrial units which produce goods either for mechanization of agriculture or for
increasing productivity come under this type. Ex: Agricultural implements, seed industries,
pumpset, fertilizer and pesticide units, etc.
4. Agro service centres
Agro service centres are workshops and service centres which are engaged in repairing and
servicing of pumpsets, diesel engines, tractors and all types of farm equipment.
NEED FOR AGRO-BASED INDUSTRIES
➢ Suitable to rural areas as they are raw material oriented.
➢ For upliftment of rural economy.
➢ To solve the problem of unemployment.
➢ To generate income and increase standard of living.
➢ For decentralization and dispersal of industries.
➢ To reduce disparity between rural and urban areas.
➢ To encourage balanced growth between agriculture and industry.
➢ To solve the problem of exploitation of farming community.
➢ To reduce transportation costs.
➢ To give big push to agriculture and act as a source of demand and supply.
➢ To avoid wastage of perishable agricultural products.
➢ To prevent migration of rural people.
➢ To develop suitable backward areas.
➢ To improve infrastructural facilities.
INSTITUTIONAL ARRANGEMENTS FOR PROMOTION OF AGRO BASED
INDUSTRIES
Following Ministries & Departments at the Centre and State level are at present looking
after development of agro based industries.
1. Ministry of Agriculture: Deals with rice mills, oil mills, sugar mills, bakeries, cold
storage, etc.
2. Khadi and village industries board: Covers traditional agro based industries like
“gur‟, handicrafts, khandasari, etc.
3. Director General of Trade and Development: Looks after the industries engaged in
the manufacture of tractors, power tillers, diesel engines, pump sets, etc.
4. Agro-industries Development Corporation: In each state mainly supply agricultural
machinery, inputs and agricultural advisory services to farmers. Some corporations have
also undertaken certain manufacturing activities in agro-industries sector.
5. Small Industry Development Organization: Deals with small agro-industries like
hosiery, processing of food products, beverages, food and fruit preservation, agricultural
implements, pesticide formulations, etc.
CONSTRAINTS IN ESTABLISHING AGRO BASED INDUSTRIES
1. Proper guidance is not available to entrepreneurs.
2. It involves some element of risk taking
3. Change in crops / cropping pattern
4. Change in variety of crop due to technological improvement
5. Failure of monsoon may hit the raw material supply.
6. Proper guidance, training for modern and sophisticated agro-industries are not available.
7. As modern small industries are capital intensive; supply of finance will be a considerable
problem.
8. Promotional activities such as conducting, intensive campaigns, identifying candidate
industries and explaining to entrepreneurs about prospects are inadequate.
9. Uncertainty about future market demands.
10. Absence of information about quantity and quality of market.
11. Multiplicity of agricultural produce and absence of suitable methodology to select best
suited industries to a given region.
12. Seasonal supply of agricultural produce may result in underutilization of capacity of the
units as the unit will not be working throughout the year. Ex: Sugarcane
13. Industries based on fruits and vegetables may not get the same variety throughout the
year, but they may get some other variety.
14. Absence of proper integration among the various agencies of development in the district.
video link:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vhFre--h1Ws
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jg4FW88ClPQ
You might also like
- About Cropin StartupDocument16 pagesAbout Cropin StartupMadhavilatha25% (4)
- Agro Based IndustriesDocument35 pagesAgro Based IndustriesMrinal Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Agriculture and Forestry Notes by Ayesha YounasDocument65 pagesAgriculture and Forestry Notes by Ayesha YounasAadil Jutt88% (17)
- Food for All in Africa: Sustainable Intensification for African FarmersFrom EverandFood for All in Africa: Sustainable Intensification for African FarmersNo ratings yet
- Agro-Based Industries PDFDocument4 pagesAgro-Based Industries PDFKaran PatelNo ratings yet
- Resource Based: Agro Based Forest Based A.H. and Poultry Based Mineral Based Marine BasedDocument35 pagesResource Based: Agro Based Forest Based A.H. and Poultry Based Mineral Based Marine BasedMylavarapu Satyamachiraju87% (15)
- Abm 5221Document57 pagesAbm 5221davidmarkam14No ratings yet
- Iabm 1Document28 pagesIabm 1Pratiksha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Agriculture in India Has A Significant History. Today, India Ranks Second Worldwide inDocument6 pagesAgriculture in India Has A Significant History. Today, India Ranks Second Worldwide inVimaladhithan VimalNo ratings yet
- Rural Development: Important of AgricultureDocument5 pagesRural Development: Important of AgricultureHamad RazaNo ratings yet
- 2nd LectureDocument3 pages2nd LectureTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- NTCCDocument32 pagesNTCCecohonours 2017-18No ratings yet
- India Is A Country of Villages Whose Total Number Is Approximately 5Document28 pagesIndia Is A Country of Villages Whose Total Number Is Approximately 5ramakntaNo ratings yet
- J.S.S.College, Dharwad: Bba Departement 3 SemesterDocument39 pagesJ.S.S.College, Dharwad: Bba Departement 3 SemesterhatebookNo ratings yet
- ST Peters UMC Agriculture CommitteeDocument5 pagesST Peters UMC Agriculture CommitteeTadiwanashe C BeteraNo ratings yet
- Agro-Based Industries in Kadapa DistrictDocument278 pagesAgro-Based Industries in Kadapa DistrictKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP PP P P PP P PPP PPP PPP PP P P P P P PPPP!P"#$P%P&#!P # $P 'P P (!# $P) PPPP P'P !PP P PP PPPPPP#PP P ' P P PDocument7 pagesPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP PP P P PP P PPP PPP PPP PP P P P P P PPPP!P"#$P%P&#!P # $P 'P P (!# $P) PPPP P'P !PP P PP PPPPPP#PP P ' P P PChamp MehtaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 01 Agri. Business ManagementDocument187 pagesCHAPTER - 01 Agri. Business Management10rohi10No ratings yet
- Agriculture and IndustryDocument33 pagesAgriculture and IndustryNyle's BresenNo ratings yet
- Agro Processing Sector in IndiaDocument20 pagesAgro Processing Sector in IndiaKavita Baeet88% (8)
- Chapter 1 - The Scope and Importance of AgrifisheryDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - The Scope and Importance of AgrifisheryJayson G. GunioNo ratings yet
- Agriculture and Forestry Notes by Ayesha YounasDocument60 pagesAgriculture and Forestry Notes by Ayesha Younasاسد رضاNo ratings yet
- Processed Food - For The Changed-LifestyleDocument7 pagesProcessed Food - For The Changed-LifestyleAmar AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Lit 102 Act No. 1Document5 pagesLit 102 Act No. 1Jarden Vega SolabarNo ratings yet
- Role of Agriculture in Indian Economy - SilpaDocument18 pagesRole of Agriculture in Indian Economy - Silpaprasanth prasannanNo ratings yet
- Food Processing Unit ProblemsDocument24 pagesFood Processing Unit ProblemsKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Categories:: and and and andDocument6 pagesCategories:: and and and andpushpak_dcNo ratings yet
- Indian Agri IndustryDocument27 pagesIndian Agri IndustryAzhar Abbas100% (7)
- Agro Sector Rough 1Document4 pagesAgro Sector Rough 1Tonmoy Dash100% (1)
- Agro Industry Scenario: An IntroductionDocument8 pagesAgro Industry Scenario: An IntroductionSandeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Industries LinkagesDocument12 pagesAgriculture Industries LinkagesPADHY STORESNo ratings yet
- 1110pm24 DR I Sundar PDFDocument8 pages1110pm24 DR I Sundar PDFANUSHA MNo ratings yet
- Proposed Lake Kachira Lowland Rice Plantation Project - Main DocumentDocument23 pagesProposed Lake Kachira Lowland Rice Plantation Project - Main DocumentHerbert BusharaNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument11 pages09 - Chapter 1 PDFVishalchettriNo ratings yet
- ABM 111 Theory NotesDocument32 pagesABM 111 Theory NotesDeepti SinglaNo ratings yet
- Rural Banking (5 - 7)Document44 pagesRural Banking (5 - 7)dubakoor dubakoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Agribusiness and Agricultural MarketingDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Agribusiness and Agricultural MarketingAref Wanu100% (1)
- Agri-Econ Past PapersDocument19 pagesAgri-Econ Past PapersSyed Muhammad Naqi Raza SheraziNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Agri-Business: Assignment ONDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Agri-Business: Assignment ONpritam pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument9 pagesMini ProjectlakunarasimharaoNo ratings yet
- Introdtion Agricultural EconomicsDocument10 pagesIntrodtion Agricultural EconomicsNkamusiima DianahNo ratings yet
- My Corporate FarmingDocument26 pagesMy Corporate FarmingWeena Yancey M MominNo ratings yet
- SodhgangaDocument26 pagesSodhgangaSripada PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- 3.moa Final Report - English 2020 NewDocument161 pages3.moa Final Report - English 2020 NewBethmi JayawardenaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter 6 Rural Development 1Document68 pages12 Chapter 6 Rural Development 1ashrielthomasNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument16 pagesStrategic ManagementAnkita GangwarNo ratings yet
- National Commission On Farmers ReportDocument8 pagesNational Commission On Farmers ReportAbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- Agro Based Industries in IndiaDocument7 pagesAgro Based Industries in Indiapranavtamhane45No ratings yet
- Current Rice Proposal PDFDocument35 pagesCurrent Rice Proposal PDFSalli Marindha91% (11)
- Places and Landscapes Chapter 2 To 5Document34 pagesPlaces and Landscapes Chapter 2 To 5Juliana Mae FabrigarNo ratings yet
- Agri Science Lesson 1 NotesDocument5 pagesAgri Science Lesson 1 NotesSeth AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Preident Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The 2013 a.S.K. Nairobi International Trade Fair, Jamhuri Park Showground, NairobiDocument4 pagesPreident Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The 2013 a.S.K. Nairobi International Trade Fair, Jamhuri Park Showground, NairobiState House KenyaNo ratings yet
- Agro MarketingDocument23 pagesAgro Marketingshaluagarwal1000No ratings yet
- Mrunal Sir's Economy 2020 Batch - Handout PDFDocument46 pagesMrunal Sir's Economy 2020 Batch - Handout PDFssattyyaammNo ratings yet
- FINAL Agriculture and IndustryDocument14 pagesFINAL Agriculture and IndustryNyle's BresenNo ratings yet
- Occ. Mindoro BackgroundDocument15 pagesOcc. Mindoro BackgroundRamon SalvoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Industry Profile: 1.1.1 The Food Industry IncludesDocument71 pages1.1 Industry Profile: 1.1.1 The Food Industry IncludesBhavaniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 01 Agri Business ManagementDocument187 pagesCHAPTER 01 Agri Business ManagementEufemia GumbanNo ratings yet
- Role and Importance of Agriculture in The CaribbeanDocument13 pagesRole and Importance of Agriculture in The CaribbeanJagdeesh Gosine33% (3)
- 12 Food ProcessingDocument5 pages12 Food ProcessingTanay BansalNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture ABMDocument5 pages1st Lecture ABMTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- 2nd LectureDocument3 pages2nd LectureTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- Problems and Prospects of Rainfed Agriculture in IndiaDocument20 pagesProblems and Prospects of Rainfed Agriculture in IndiaTaushif Ahammed0% (1)
- Diseases of GramDocument8 pagesDiseases of GramTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- FSN Lecture - 3 (Class Notes)Document3 pagesFSN Lecture - 3 (Class Notes)Taushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- Diseases of CoconutDocument16 pagesDiseases of CoconutTaushif AhammedNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument20 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationSandeep Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Raz tm16 FarmfriendsDocument7 pagesRaz tm16 FarmfriendsDonald PoliNo ratings yet
- Building A Sustainable Business PDFDocument282 pagesBuilding A Sustainable Business PDFmarlynrich3652No ratings yet
- Study Id51572 Indoor-FarmingDocument40 pagesStudy Id51572 Indoor-Farmingkausthubh vitthalNo ratings yet
- Herrera (Ms - Act 3)Document3 pagesHerrera (Ms - Act 3)Ma JayNo ratings yet
- Kuru Dec2019Document52 pagesKuru Dec2019Rafi S ANo ratings yet
- Grp-01-Nh008-Acm-Lsp-Dwg-Dd-13101 (Base One) Palm&tree (1) - LegendDocument1 pageGrp-01-Nh008-Acm-Lsp-Dwg-Dd-13101 (Base One) Palm&tree (1) - LegendMohamed Gamal ElderaaNo ratings yet
- Kienyeji Chicken Farming in KenyaDocument3 pagesKienyeji Chicken Farming in KenyatkNo ratings yet
- Ukk Kelas Vii PKBM Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesUkk Kelas Vii PKBM Bahasa InggrisEka Albar FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Consommation Civc 2014 en Tasting-SheetDocument1 pageBrochure Consommation Civc 2014 en Tasting-SheetТатьяна БондареваNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Farm-Level Adoption of Cultural Practices For Banana Xanthomonas Wilt Control in Uganda 1754Document12 pagesDeterminants of Farm-Level Adoption of Cultural Practices For Banana Xanthomonas Wilt Control in Uganda 1754Eric Silva AraujoNo ratings yet
- Project Feasibility Report On Maize Processing in Himachal Pradesh - SurinderDocument56 pagesProject Feasibility Report On Maize Processing in Himachal Pradesh - SurinderSurinder Chugh100% (5)
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature Reviewmonique100% (4)
- Inter-Varietal Differences in Grapevine Bud Fertility and Grape Fruit Quality of Between Local and Introduced Cultivars (Vitis Vinifera L.) Grown Under Sub-Humid EnvironmentDocument7 pagesInter-Varietal Differences in Grapevine Bud Fertility and Grape Fruit Quality of Between Local and Introduced Cultivars (Vitis Vinifera L.) Grown Under Sub-Humid EnvironmentSilviu PintilieNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Grafting Season On Cleft Grafting For Deploying Commercial Propagation of Tamarind (Tamarindus Indica) in Tamil NaduDocument5 pagesOptimization of Grafting Season On Cleft Grafting For Deploying Commercial Propagation of Tamarind (Tamarindus Indica) in Tamil NaduMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ganga Kaveri Seeds PVT LTDDocument18 pagesGanga Kaveri Seeds PVT LTDshindedattatriNo ratings yet
- Acp Nci Module 1Document63 pagesAcp Nci Module 1Earl Jose100% (2)
- SIE6001 - Capstone - Final Report - 1802173 - Clorence TanDocument64 pagesSIE6001 - Capstone - Final Report - 1802173 - Clorence TanAlex LeeNo ratings yet
- AFA - Horticulture 7-8 ExploratoryDocument77 pagesAFA - Horticulture 7-8 ExploratoryBaric DelNo ratings yet
- Study Material For PPATH-312Document92 pagesStudy Material For PPATH-312demonkingf6No ratings yet
- RDO No. 17A - Tarlac CityDocument523 pagesRDO No. 17A - Tarlac CityANNLNo ratings yet
- 2021 The NCT Manual Jan18Document183 pages2021 The NCT Manual Jan18John Philip Tagala100% (1)
- Farmers Contract Ics FilesDocument1 pageFarmers Contract Ics Fileslatinpalyec_54201057No ratings yet
- GROUP B Social Enterprise (AURO Chocolate PH)Document2 pagesGROUP B Social Enterprise (AURO Chocolate PH)john cyril abejeroNo ratings yet
- PBG-504 (P) Assignment 6Document3 pagesPBG-504 (P) Assignment 6gojicag445No ratings yet
- "Yes, But Not To The Fullest in My Opinion." - Threjann Ace NoliDocument2 pages"Yes, But Not To The Fullest in My Opinion." - Threjann Ace NoliJANNo ratings yet
- Improved Open-Sun Drying Method For Local Swamp Rice in UgandaDocument12 pagesImproved Open-Sun Drying Method For Local Swamp Rice in UgandaNoelle CaballeraNo ratings yet
- Crop Diversification in Odisha: An Empirical Assessment: Chittaranjan Nayak and Chinmaya Ranjan KumarDocument15 pagesCrop Diversification in Odisha: An Empirical Assessment: Chittaranjan Nayak and Chinmaya Ranjan KumarParameswar DasNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Corporate Farming Program On Rice Farming (Case Study On Farmer Group Semangat 45)Document9 pagesImplementation of Corporate Farming Program On Rice Farming (Case Study On Farmer Group Semangat 45)Mamta AgarwalNo ratings yet