Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worked Examples On Leveling
Uploaded by
tsionasratbelayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worked Examples On Leveling
Uploaded by
tsionasratbelayCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Compute the elevation difference b/n two successive points if the staff reading on A & B are 2.
457
& 3.762 respectively, as BS and FS and the height of A is 2762.325m.
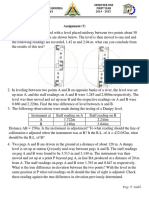
2. A theodolite is set up at station A and a 3 m long staff is held vertically at station B. The depression
angle reading at 2.5 m, marking on the staff is 6°10´. The horizontal distance between A and B is
2200m. Height of the instrument at station A is 1.1 m and R.L. of A is 880.88m. Apply the curvature
and refraction correction, and determine the R.L. of B (in m).
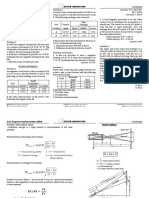
3. The theodolite is setup with height of 1.65m and a distance of 200.652m and a vertical angle of
920 44’15” are measured. If the staff reading & RL of A are 2.644m & 1500m respectively,
calculate the reduced level of point B.
4. The following readings were observed with a level: 1.143 (on BM, RL 612.28m), 1.765, 2.566,
3.820; 1.390, 2.262, 0.664, 0.433; 3.722, 2.886, 1.618 & 0.616. Reduce the levels by the Rise and
fall method
5. When the level is setup near point A, a staff reading of 1.435 as1.435 as BS & 2.381m as FS on A &
B respectively. On the next setup near point B, a reading of 3.026m on B and 1.054m on A
respectively. Calculate the altitude difference & elevation of point B if RL of A is 1508.764m.
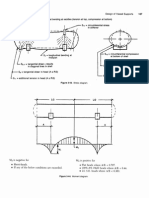
6. Two points P & Q are on the opposite banks of a river. The following observations were obtained
in reciprocal leveling and the RL of point P is 560.468.
7. Determine the distance for which the combined correction is 5mm.
8. A staff is held at a distance of 200m from a level and a reading of 2.758m is obtained. What is the
correction on the reading due to curvature and refraction?
9. The following readings refer to reciprocal levels taken with one level:
The distance AB is 1110m and the reduced level is of A is 2130.815m. Determine the following:
i. True RL of point B
ii. Combined Correction for curvature and Refraction
10. The following staff readings were observed and recorded on a field. Compute the elevation of
all points using rise and fall method.
11. Compute the elevation of the points using HI method
12. The following staff readings were taken in the field with an automatic level as: 3.775, 1.010,
1.735, 1.325, 2.642, 1.440, 1.815, 1.660, 1.530, 1.105, 2.640, 2.550, 2.325, 2.225, &2.458. The first
reading was taken on point A having a RL of 1420.640m & the last reading was taken on point B.
the instrument was shifted after the 4th, 7th and 11th readings. Calculate the elevation of point B.
13. The following is a page of level book. Fill in the missed readings & compute the RL of all points
and apply the appropriate checks.
14. A differential leveling loop is run from an established BM A to a point 3.32km away and back,
with a permissible of 17mm. Determine the constant value.( E=m√ )
15. A differential leveling loop began and closed on a BM of elevation 2103.895m. The BS & FS
distances were kept approximately equal. The readings listed below are taken starting the BM as:
1.023, 1.208; 0.843, 0.685; 0.982, 0.944; 1.864 & 1.879. Prepare: check for the permissible error
and adjust the notes.
You might also like
- Report LevellingDocument9 pagesReport LevellingAida Azhari92% (39)
- Problem Set 3Document11 pagesProblem Set 3Brix Mendoza20% (5)
- Plate No. 04Document2 pagesPlate No. 04elarzzzzNo ratings yet
- Elem Surveying Set 1Document2 pagesElem Surveying Set 1soontobengineer0% (1)
- Q1Document4 pagesQ1Ritsu TainakaNo ratings yet
- Examples On Levelling 2012Document10 pagesExamples On Levelling 2012Temesgen MekiteNo ratings yet
- Level Adjustmets by Broddett AbatayoDocument16 pagesLevel Adjustmets by Broddett AbatayoBroddett Bello Abatayo100% (1)
- Midterm ComprehensiveDocument4 pagesMidterm ComprehensiveDonna MelgarNo ratings yet
- Advance - Surveying ASSIGNMENTDocument8 pagesAdvance - Surveying ASSIGNMENTAmmar VanankNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Angles and DirectionsDocument73 pagesMeasurement of Angles and DirectionsSHEAN GAYLE ANGNo ratings yet
- Tutorial GeomaticsDocument6 pagesTutorial GeomaticsadilaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Surveying Assignment Questions - (PASHA - BHAI)Document3 pagesAdvanced Surveying Assignment Questions - (PASHA - BHAI)sayed nagdyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Danzyl VillatemaNo ratings yet
- Directions: Answer The Following Questions. Write Your SOLUTION and BOX Your Final Answer in Your NotebookDocument6 pagesDirections: Answer The Following Questions. Write Your SOLUTION and BOX Your Final Answer in Your NotebookKevin Abenojar NamayaNo ratings yet
- Dec 2011Document2 pagesDec 2011Aswathy M NNo ratings yet
- 7 Two-Peg Test and Longitudinal SectionDocument2 pages7 Two-Peg Test and Longitudinal SectionJason PaulNo ratings yet
- Ulo-1c Lets CheckDocument4 pagesUlo-1c Lets CheckHarrah CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Levelling 1Document22 pagesLevelling 1opulithe100% (1)
- The LengthDocument1 pageThe LengthRAIZZ67% (3)
- Anna University, ChennaiDocument10 pagesAnna University, ChennaiSabrina ShukriNo ratings yet
- Reciprocal LevelingDocument22 pagesReciprocal Levelingمهندس ابينNo ratings yet
- Reciprocal LevelingDocument22 pagesReciprocal Levelingمهندس ابينNo ratings yet
- QB 16cv44Document14 pagesQB 16cv44Anu RaichurNo ratings yet
- Pascua Project For Module 2 Problem Set With SolutionDocument14 pagesPascua Project For Module 2 Problem Set With SolutionDJ KillNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Chapter 02 Trigonometrical LevellingDocument2 pagesTutorial 1: Chapter 02 Trigonometrical Levellingmukesh kafleNo ratings yet
- 201 Questions AnswersDocument21 pages201 Questions Answersrohith51No ratings yet
- F. Trigonometric Leveling1Document6 pagesF. Trigonometric Leveling1Russell AyaquilNo ratings yet
- GEng 6Document5 pagesGEng 6Joycelyn UyNo ratings yet
- Dronacharya Group of Institutions, Greater Noida Department of CIVIL Engineering Semester: III Branch: CIVIL Session: 2015-16 Subject: Surveying LabDocument13 pagesDronacharya Group of Institutions, Greater Noida Department of CIVIL Engineering Semester: III Branch: CIVIL Session: 2015-16 Subject: Surveying LabVinay YadavNo ratings yet
- Evals in Surveying and Transpo Answer SheetDocument11 pagesEvals in Surveying and Transpo Answer SheetYedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2017-18 - CLE1003 - ETH - CDMM203 - VL2017185003456 - Assignment I - DA1Document5 pagesWINSEM2017-18 - CLE1003 - ETH - CDMM203 - VL2017185003456 - Assignment I - DA1Velchuri SairamNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL No. 1 REPORTDocument8 pagesPRACTICAL No. 1 REPORTChris AdaminovicNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Measurement of Vertical Distances Leveling MethodDocument12 pagesModule 3 Measurement of Vertical Distances Leveling MethodLance De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Surveying PDFDocument6 pagesSurveying PDFremster OñateNo ratings yet
- Bearings. Also Determine The Included Angles at A, B, C, D and EDocument6 pagesBearings. Also Determine The Included Angles at A, B, C, D and EHari HarishkumarNo ratings yet
- Differential LevelingDocument24 pagesDifferential LevelingMarc Dared CagaoanNo ratings yet
- 4b. METHODS FOR DETERMINING DIFFERENCE IN ELEVATIONDocument24 pages4b. METHODS FOR DETERMINING DIFFERENCE IN ELEVATIONJan Chris Villanueva100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Surveying - Set 3Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - Surveying - Set 3Mark Lester LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Eastings and NorthingsDocument34 pagesEastings and NorthingsDarren Hamilton50% (2)
- ExerciseDocument1 pageExercisemechelsabry319No ratings yet
- Ce-1254 - Surveying IiDocument9 pagesCe-1254 - Surveying IiMix TubeNo ratings yet
- Survey II Assignment: TriangulationDocument2 pagesSurvey II Assignment: TriangulationCharles SnyderNo ratings yet
- Surveing - CIT Question BankDocument9 pagesSurveing - CIT Question BankAmarjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Ce 1254 Surveying IIDocument19 pagesCe 1254 Surveying IIsaamyNo ratings yet
- Cartography 5 - Intervisibility and Map NamingDocument2 pagesCartography 5 - Intervisibility and Map NamingGie Marie GuarinoNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument6 pagesSurveyingMARK KEVIN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Sagar Institute of Science & Technology (Sistec) Department of Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesSagar Institute of Science & Technology (Sistec) Department of Civil EngineeringASHISH SINGH SENGARNo ratings yet
- Fieldwork 7Document4 pagesFieldwork 7James ColeNo ratings yet
- QUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)Document3 pagesQUIZ #1-A (Introduction, Distance, Correction and Leveling)nonononowayNo ratings yet
- Measuring Angles by RepetitionDocument5 pagesMeasuring Angles by RepetitionJoycelyn UyNo ratings yet
- Tacheometry Wk2Document12 pagesTacheometry Wk2Laki ENNo ratings yet
- 96BDocument3 pages96BJamie SchultzNo ratings yet
- Ce 121 12 - 022000Document13 pagesCe 121 12 - 022000Al-maizhar BakilNo ratings yet
- Surveying IIDocument17 pagesSurveying IISudipta PramanikNo ratings yet
- Essential Levelling - NotesDocument39 pagesEssential Levelling - NotesMd KhairulNo ratings yet
- Research Work 3Document11 pagesResearch Work 3Fer MaeNo ratings yet
- 1st Year AssignmentDocument8 pages1st Year AssignmentJigyasaNo ratings yet
- Squeeze Cementing JobDocument64 pagesSqueeze Cementing Jobkhushbu Hasan100% (2)
- Energies 13 04560Document20 pagesEnergies 13 04560Jay KayeNo ratings yet
- Ii (Specti I (& (LLTS) A F.Eading NDT: Traiim (GDocument1 pageIi (Specti I (& (LLTS) A F.Eading NDT: Traiim (Gআশার আলোNo ratings yet
- Learning Resource Pack Approval Sheet: Arlac Gricultural NiversityDocument5 pagesLearning Resource Pack Approval Sheet: Arlac Gricultural NiversityJohn Christian MejiaNo ratings yet
- Boardworks GCSE Science: Physics Heat TransferDocument32 pagesBoardworks GCSE Science: Physics Heat TransferJayNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering Holtz Kovacs 2nd Edition Solutions ManualDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering Holtz Kovacs 2nd Edition Solutions ManualKristyCampbelldxef100% (32)
- Design Modeling and Control of A Wall CL PDFDocument6 pagesDesign Modeling and Control of A Wall CL PDFRam KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.CFD Introduction NotesDocument47 pages1.CFD Introduction Notes刘伟轩No ratings yet
- June GR 11 Physical Sciences P1 MEMODocument14 pagesJune GR 11 Physical Sciences P1 MEMOAudlt mistreNo ratings yet
- McFarland Jahns 2013 Infolytica MagNetDocument8 pagesMcFarland Jahns 2013 Infolytica MagNetRoberto Eduardo Quintal PalomoNo ratings yet
- Thank You, Sir Isaac Newton!Document8 pagesThank You, Sir Isaac Newton!chicken01 a01chickenNo ratings yet
- Score Booster For Railway NTPC CBT 2/group D Exams - Day 3Document15 pagesScore Booster For Railway NTPC CBT 2/group D Exams - Day 3Jasabanta BeheraNo ratings yet
- Eim-11 q1 w1 Mod1.PDF-editedDocument11 pagesEim-11 q1 w1 Mod1.PDF-editedMarie TuraNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document27 pagesLec 4KuthuraikaranNo ratings yet
- Civil III Surveying I (10cv34) Question PaperDocument5 pagesCivil III Surveying I (10cv34) Question PaperkirannrgNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rectilinear Motion Form 2Document7 pagesKinematics of Rectilinear Motion Form 2Mohammad BatainehNo ratings yet
- İlk Sayfa LG BİREBİR SPLİT GENEL KATOLOK (11-12-13-14 SAYFALAR 1Document1 pageİlk Sayfa LG BİREBİR SPLİT GENEL KATOLOK (11-12-13-14 SAYFALAR 1kadir tanzaniaNo ratings yet
- NDT Summary-Steam Turbine InspectionDocument5 pagesNDT Summary-Steam Turbine InspectionOm Ar TanNo ratings yet
- Section 5.2 The Modern Periodic Table: Reading StrategyDocument2 pagesSection 5.2 The Modern Periodic Table: Reading StrategyRiley MillerNo ratings yet
- English Medium Lec. Physics-2 2020-Ok PDFDocument23 pagesEnglish Medium Lec. Physics-2 2020-Ok PDFSakib KhanNo ratings yet
- Saturn's RingDocument2 pagesSaturn's RingRobin GunawanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ayman Abd El-Hamid - Performance Based Design of StructuresDocument58 pagesDr. Ayman Abd El-Hamid - Performance Based Design of Structuresعبدالرحمن النجدي100% (1)
- Composite Book CatalogueDocument8 pagesComposite Book CatalogueYash ShahNo ratings yet
- 02 Lambauer Chapter2.4Document16 pages02 Lambauer Chapter2.4showravNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Boundary Value Problems E-NoteDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Boundary Value Problems E-NotexingmingNo ratings yet
- Exercises Component Method 2Document57 pagesExercises Component Method 2Vanderleia CalazansNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel SupportDocument36 pagesPressure Vessel SupportAndreea Luca83% (6)
- Single Phase Diagram - Real Gases - 003Document36 pagesSingle Phase Diagram - Real Gases - 003JatskinesisNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure Student Notes (With Hidden Answers)Document7 pagesForce and Pressure Student Notes (With Hidden Answers)3.4 (2022) LAU JING XUAN DESTINEENo ratings yet
- 2003 - Determination of Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curves For Near Surface Applications in Unconsolidated Sediments - Dal Moro Et Al.Document5 pages2003 - Determination of Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curves For Near Surface Applications in Unconsolidated Sediments - Dal Moro Et Al.Jimmy Johan Tapia VásquezNo ratings yet