Professional Documents
Culture Documents
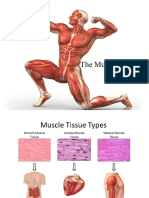
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal Muscles
Uploaded by
madeha gohar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesOriginal Title
skeletal muscles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views10 pagesSkeletal Muscles
Skeletal Muscles
Uploaded by
madeha goharCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
SKELETAL MUSCLES
· Individual muscle fibers stimulated by somatic
motor neuron
· each motor neuron branches to innervates a
number of neurons
· activation of varying number of motor neurons
results in gradations in the strength of
contraction of the whole muscle
· the more movable bony attachment of the
muscle is known as insertion
· the muscle is pulled towards its less movable
attachment known as origin
· The prime mover of any skeletal movement is
called agonist muscle e.g flexor
· the muscles that acts on same joint to produce
opposite actions are antagonistic muscles
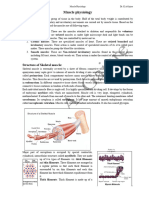
STRUCTURE OF SKELETAL MUSCLE
Epi(above)mysium(muscle)
(fibrous connective tissue within tendon extend
around the muscle in an irregular arrangement,
forming a sheath)
Fascicles
(connective tissue from above extends into the body
of muscles , subdividing it into columns)
Peri(around)mysium
(each fascicle is surrounded by its own connective
tissue sheath)
Endomysium
(basement membrane or basal lamina of muscle
fiber)
(thin connective tissue layer enveloping the plasma
membrane or sarcolemma of muscle fibers)
Sarcolemma
(each muscle fascicle is composed of muscle fibers.
Each of which is surrounded by sarcolemma)
· shape of muscle fibers is elongated.They are
multinucleate(Synctial structure).
· Straited appearance bcz of dark and light bands
· Dark band( A band from anisotropic)
· Light band ( I band isotropic)
· Thin dark lines in the middle of I band are Z
lines
· Graded contraction ( where contraction
strength is varied)
· motor end plate (specialized region of
sarcolemma)
· end plate potential (ACh from somatic neuron
upon depolariztion releases, nd stimulate
nicotinic receptors on endplate leading to
depolarization )
· motor unit ( Each somatic motor
neuron,together with all of the muscle fibers
that it innervate, is known as motor unit)
· graded contraction of whole muscles are
produced by variations in the number of motor
units that are activated.
STRUCTURE OF SARCOMERE
· Each subunit is composed of many subunits
known as myofibrils.
· Each myofibril contains even smaller structures
called myofilaments i.e thick & thin filament
· A band contain thick filament (Composed of
myosin). Thin filaments also extend into A band.
· I band contain thin filament (composed of
actin). Lighter area extended from the edge of
one stack of thick filament to the edge of next
stack of thick filament.
· H band (H for helle means bright) contains only
thick filaments. It is a central region brighter
than edges where thick and thin filaments
overlap
· Z line is thick dark line in the centre of I band
· M line is produced by protein filaments located
at the centre of the thick filaments ( A band).
which serve to anchor the thick filaments,
helping them to stay together during
contraction
· Titin filaments has amino terminal end in a Z
disc, a spring like portion running through the I
band and a longer portion bound to the thick
filament all the way to M line.
· The subunits from Z to Z are known as
sarcomere
MECHANISM OF CONTRACTION
You might also like
- Skeletal MuscleDocument98 pagesSkeletal MuscleMoon Moon100% (1)
- Classification of MusclesDocument50 pagesClassification of MusclesNoor HaleemNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument49 pagesMuscular TissueSteph VeeNo ratings yet
- Zoology PPT Muscular SystemDocument68 pagesZoology PPT Muscular SystemDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Crystallization Solution Forced Circulation Oslo DTB Crystallizer Gea - tcm11 34854 PDFDocument20 pagesCrystallization Solution Forced Circulation Oslo DTB Crystallizer Gea - tcm11 34854 PDFAshrita SamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryDocument13 pagesChapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement Power PointDocument14 pagesDistance and Displacement Power Pointdavgen100% (1)
- Gen. Physics 2 USLeM Week 1 Version 4Document10 pagesGen. Physics 2 USLeM Week 1 Version 4xibol14985No ratings yet
- Balancing TheoryDocument59 pagesBalancing TheoryVijay Patel100% (2)
- Advanced High Strength Sheet SteelsDocument415 pagesAdvanced High Strength Sheet SteelsYair Salinas Escutia100% (1)
- Histology of MuscleDocument49 pagesHistology of MuscleTewachew Dessie100% (1)
- Optical Microscope Basic Training PDFDocument96 pagesOptical Microscope Basic Training PDFAndrew HolmesNo ratings yet
- Grade 8, Quarter 3Document39 pagesGrade 8, Quarter 3Leisor Euqirdnam Oyacnub94% (16)
- Complete Overview of Lightning Arresters Part 3Document7 pagesComplete Overview of Lightning Arresters Part 3Robert GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue LectureDocument34 pagesMuscle Tissue LectureurjaNo ratings yet
- Célula Muscular, Macro y MicrobiologicoDocument11 pagesCélula Muscular, Macro y MicrobiologicoimanolNo ratings yet
- ANPH Midterm NotesDocument44 pagesANPH Midterm NotesClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- 副本 - Classification of musclesDocument31 pages副本 - Classification of musclesTan Ting WeiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy - ContentDocument14 pagesFunctional Anatomy - ContentxanaduNo ratings yet
- Eme 1Document20 pagesEme 1Tara LingatingNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesANAPHY - Muscular SystemSoleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- 3D. Muscle TissueDocument47 pages3D. Muscle Tissuejaf123xyNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument10 pagesMuscular SystemMarie Veatrice JacomilleNo ratings yet
- 589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyDocument3 pages589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyMalti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue: Mrs H. MwaleDocument52 pagesMuscle Tissue: Mrs H. MwaleAldridge KalengaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Muscular System: Movement: PSYN 103: Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument67 pagesChapter 7: Muscular System: Movement: PSYN 103: Human Anatomy and PhysiologyWindy LavarientosNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument24 pagesMuscle PhysiologyArmando AlehandroNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument22 pagesMuscle TissueNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument3 pagesSkeletal Musclekrystal1994No ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Sarcomere FinalDocument32 pagesSkeletal Muscle Sarcomere FinalCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)Document21 pagesAnatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)HumrazNo ratings yet
- Histology Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesHistology Muscle and Nervous Tissuejosh100% (1)
- Muscle and Nerve HistoPHysioDocument91 pagesMuscle and Nerve HistoPHysioashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesTopic 7 Muscular SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- MuscularDocument61 pagesMuscularFranz DiazNo ratings yet
- 5 Muscular SystemDocument55 pages5 Muscular SystemFareez HamidNo ratings yet
- TriChapter27 09 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesTriChapter27 09 Muscular Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- Done Skeletal Muscle Part 1Document44 pagesDone Skeletal Muscle Part 1Satt Michael Sobiono SantosNo ratings yet
- Structure of Skeletal MuscleDocument12 pagesStructure of Skeletal MuscledilsharakaviNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle PDFDocument45 pagesSkeletal Muscle PDFyusufalper7234No ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Contraction and The Motor UnitsDocument4 pagesSkeletal Muscle Contraction and The Motor UnitsAnonymous vnv6QFNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology: Human Physiology By-Liul M. ForDocument63 pagesMuscle Physiology: Human Physiology By-Liul M. ForKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- SDL MuscularDocument6 pagesSDL MuscularMonique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissuesDocument46 pagesMuscular TissuesDAVE CANALETANo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument58 pagesLocomotion and MovementdddNo ratings yet
- Faal Otot Dan GerakDocument46 pagesFaal Otot Dan GerakElsya Nur FadhillaNo ratings yet
- Histology 6 MuscleDocument88 pagesHistology 6 MuscleAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: DR Faisal Institute of Physiology and PharmacologyDocument61 pagesThe Muscular System: DR Faisal Institute of Physiology and PharmacologyTask BirdNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument30 pagesMuscle Tissued20231107667No ratings yet
- BN4201 Lecture Notes CompilationDocument38 pagesBN4201 Lecture Notes Compilationjieenlim123No ratings yet
- Report Summary and QuestionsDocument7 pagesReport Summary and QuestionsSkyNayvieNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle Tissues vNo ratings yet
- Handout MusclesDocument3 pagesHandout Musclesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue - HistologyDocument35 pagesMuscle Tissue - HistologyjabirNo ratings yet
- Histo MuscleDocument11 pagesHisto MuscleaikaNo ratings yet
- Topic 11.2: Movement: Human Elbow Joint Movement SystemsDocument1 pageTopic 11.2: Movement: Human Elbow Joint Movement SystemsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument50 pagesThe Muscular SystemArina GainaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 PDFDocument6 pagesLec 6 PDFАбу ДжудNo ratings yet
- Excitable Tissues 1Document8 pagesExcitable Tissues 1gojaisaiah787No ratings yet
- Locomotion & Movement (Muscles)Document41 pagesLocomotion & Movement (Muscles)DEEPANKAR SAHANo ratings yet
- Neuron Motor PeriferDocument15 pagesNeuron Motor PerifernunualoneNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingDocument46 pagesMuscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingRevanth VejjuNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument43 pagesMuscle TissueTiktok ethio dailyNo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument11 pagesMuscleJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYDocument38 pagesGeneral Veterinary Macroscopic Anatomy: MYOLOGYneanna100% (1)
- ArrhthmiasDocument44 pagesArrhthmiasmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- ENZYMES 2k20Document48 pagesENZYMES 2k20madeha goharNo ratings yet
- Biologics 1Document92 pagesBiologics 1madeha goharNo ratings yet
- AnaestheticsDocument25 pagesAnaestheticsmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Fibers, Sutures &surgical DressingsDocument55 pagesFibers, Sutures &surgical Dressingsmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument11 pagesCardiac Cyclemadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument34 pagesMuscle Physiologymadeha goharNo ratings yet
- ClottingDocument9 pagesClottingmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HeartDocument74 pagesPhysiology of Heartmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant AgentsDocument45 pagesAntidepressant Agentsmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument22 pagesSedative Hypnoticsmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Electrons in The Outer Shell Than The Semiconductor. Each Atom of DopantDocument38 pagesElectrons in The Outer Shell Than The Semiconductor. Each Atom of Dopantfisho abukeNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Crystalline SolidsDocument8 pagesAmorphous and Crystalline SolidsAli ImranNo ratings yet
- F&MDocument1 pageF&MrhonNo ratings yet
- WS1 - Reinforcement - Magnetic EffectsDocument2 pagesWS1 - Reinforcement - Magnetic EffectsOshin TiwariNo ratings yet
- Design of DC MotorDocument24 pagesDesign of DC MotorRaja DesinguNo ratings yet
- C18 Solved Problems 1 PDFDocument6 pagesC18 Solved Problems 1 PDFGerald Labios100% (2)
- Bulk Polymerization 2015Document14 pagesBulk Polymerization 2015Haiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- 2006 Chem 1112Document10 pages2006 Chem 1112matteiotoneNo ratings yet
- Beer Lambert LawDocument5 pagesBeer Lambert LawPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 30072-001-48J (E) .fm5 Page 1 Wednesday, June 23, 1999 4:04 PMDocument3 pages30072-001-48J (E) .fm5 Page 1 Wednesday, June 23, 1999 4:04 PMJose Miguel Cujilema CujilemaNo ratings yet
- Part 3 TpdeDocument5 pagesPart 3 TpdeGowtham RajNo ratings yet
- Friction, Centripetal, Centrifugal ForceDocument2 pagesFriction, Centripetal, Centrifugal ForceRahulNo ratings yet
- PS1Document1 pagePS1Matt Benjoemin PuertoNo ratings yet
- ch02 1Document6 pagesch02 1majahzcoNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry - 03 NMSI Chemical Nomenclature STUDENTDocument14 pagesAP Chemistry - 03 NMSI Chemical Nomenclature STUDENTAbdul SamiNo ratings yet
- Single Phase RectifiersDocument11 pagesSingle Phase RectifiersMiguel MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 Hours: P510/1 Physics Paper 1 Jul / Aug. 2019Document8 pages2 Hours: P510/1 Physics Paper 1 Jul / Aug. 2019ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- Electron MicroscopeDocument7 pagesElectron MicroscopeUmair FaheemNo ratings yet
- Particle Model of Matter-Summary NotesDocument5 pagesParticle Model of Matter-Summary NotesKhalid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- EE 164 Problem Set 5 SolutionDocument2 pagesEE 164 Problem Set 5 SolutionnenasukaNo ratings yet
- FUJI Luxel V6 Error Code GuideDocument3 pagesFUJI Luxel V6 Error Code GuideSantos Giuliano Cano PradaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Centrifugal PumpsDocument3 pagesAn Introduction To Centrifugal PumpsCaiyun LimNo ratings yet