Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hindbrain
Hindbrain
Uploaded by
Anoop Bhattacharya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageHindbrain
Hindbrain
Uploaded by
Anoop BhattacharyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
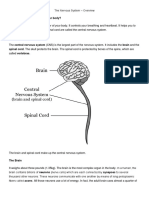
Hindbrain – you will find the hindbrain right above your spinal cord.
This is where the cerebellum is located. It resembles a wrinkled ball of tissue. It
is the hindbrain that directs the body’s respiratory and heart rates. It coordinates
bodily reflexes and is also responsible for movements you make automatically
or
by rote. For example, when you play the violin or run a marathon, the
cerebellum located in the hindbrain goes to work.
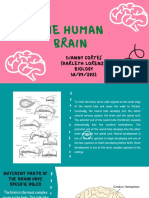
Looking deeper into the brain, we now focus on the cerebrum which has
two hemispheres. As we said earlier, the cerebrum is located in the forebrain.
These hemispheres are separated by a deep dividing line; this division does not
prevent the two hemispheres from sending messages to and from each other.
They look similar in appearance but differ in their functions.
Hemispheres of the Brain
Left hemisphere – when an individual utters words, it is the left
hemisphere that is working.
Right hemisphere – when an individual engages in abstract reasoning or
logic, it is the right hemisphere that enables him to practice these skills.
The brain and the body send signals to each other and when they do,
these signals cross over. This means that the right hemisphere controls the left
side of the body, while the left hemisphere controls the right side. Therefore,
when one side of the brain is affected or is hurt, the opposite side of the body is
affected. To put it more clearly, if an individual has had a stroke in the right
hemisphere of the brain, his left arm and leg are paralyzed.[7]
As we explore our thoughts and how they get processed in the brain, we
will need to know about the brain’s other components. Note that each
hemisphere is divided into sections – more commonly called lobes. These lobes
– frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal - have their own respective functions.
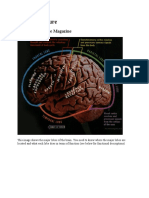
Frontal lobes – there are two frontal lobes located behind the forehead.
When you sit down and make a shopping list, plan an itinerary or argue with
your boss, these are the two lobes that enable you to perform these functions.
The frontal lobes are what the Neurological Institute of the NIH calls a
“shortterm
storage site”; that is, keeping one idea on standby while you weigh other
You might also like
- 7 1:2 Ounces of BrainDocument1 page7 1:2 Ounces of BrainMichael MuhammadNo ratings yet
- What's The Control Center of Your Body?Document3 pagesWhat's The Control Center of Your Body?caoimhin54No ratings yet
- Parts of The Brain and FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of The Brain and FunctionsLee Ayn PoncardasNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their Functions PDFDocument26 pagesBrain Structures and Their Functions PDFNur Nashran Mahran100% (4)
- Social EnginDocument243 pagesSocial EnginAnoop Bhattacharya100% (1)
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsVasudha RohatgiNo ratings yet
- PerDev Powers of The Mind Lesson ActivitiesDocument9 pagesPerDev Powers of The Mind Lesson Activitieskath santiagoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Brain Parts, Processes and FunctionsDocument19 pagesLesson 10 Brain Parts, Processes and FunctionsAlfredo ModestoNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument35 pagesBrainRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- The Human BrainDocument27 pagesThe Human BrainManuel Colindres 2.0No ratings yet
- Brain Regions: The Cerebral CortexDocument4 pagesBrain Regions: The Cerebral Cortexmohitnet1327No ratings yet
- What Are The Parts of The Brain and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Parts of The Brain and Their FunctionskimuyyyyNo ratings yet
- โท the BrainDocument39 pagesโท the BrainFadil Wanna-mart100% (1)
- 0301a AllDocument3 pages0301a AllWiendha LiendriasariNo ratings yet
- Perdev Mod 5 Powers of The MindDocument14 pagesPerdev Mod 5 Powers of The MindHanimla OsapmaNo ratings yet
- Brain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainFrom EverandBrain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainNo ratings yet
- Brain Basics - Know Your Brain - National Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeDocument4 pagesBrain Basics - Know Your Brain - National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Strokesurajit halderNo ratings yet
- CerebrumDocument8 pagesCerebrumBeing AhsanNo ratings yet
- Fore BrainDocument3 pagesFore BrainAngela EndayaNo ratings yet
- 1 BrainDocument2 pages1 BrainJonance YeeNo ratings yet
- What Comprises A Brain?Document2 pagesWhat Comprises A Brain?NataliaLizcanoNo ratings yet
- How The Brain WorksDocument12 pagesHow The Brain WorksAbdullah B.No ratings yet
- Lateralization. Language Functions, For Instance, Are More Concentrated in The Left Hemisphere in MostDocument2 pagesLateralization. Language Functions, For Instance, Are More Concentrated in The Left Hemisphere in MostVinvieleen Francesca TalaveraNo ratings yet
- Brain StudyDocument57 pagesBrain StudyJoeNo ratings yet
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASDocument16 pagesPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASJustin JoshNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure: Images From Time MagazineDocument6 pagesBrain Structure: Images From Time MagazineChayanDasguptaNo ratings yet
- Brain StructureDocument4 pagesBrain StructureSusheel KumarNo ratings yet
- Brain and MindDocument5 pagesBrain and MindMubashir AminNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument1 pageBrainTimothy Van Emil LopezNo ratings yet
- About BrainDocument4 pagesAbout Brainanand sahuNo ratings yet
- Brain and Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesBrain and Nervous SystemBrenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsvijushaaNo ratings yet
- Personal-Development-2 (3RD Quarter)Document5 pagesPersonal-Development-2 (3RD Quarter)karilesbackupaccNo ratings yet
- Brainpower ComDocument10 pagesBrainpower ComIvy AguasNo ratings yet
- Document 6Document16 pagesDocument 6Vaneeza AliNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13Document3 pagesZoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13humanupgrade100% (1)
- 2 - The Brain#1Document10 pages2 - The Brain#1Nur Ain Faezah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument13 pagesHuman BrainAaniya AsadNo ratings yet
- The Powers of The MindDocument2 pagesThe Powers of The MindErron Francisco NicolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Hap Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document15 pagesChapter 11 Hap Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20parmarpradeep252No ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their Functions 1 PDFDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and Their Functions 1 PDFAndrea RamirezNo ratings yet
- Braincurriculum CH 2Document4 pagesBraincurriculum CH 2api-167698901No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Document22 pagesControl and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Khushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Major Parts of The BrainDocument3 pagesMajor Parts of The BrainBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Nuer o ScienceDocument34 pagesBiological Basis of Nuer o ScienceNawal TariqNo ratings yet
- PERDEV ThePowerOfMindsDocument3 pagesPERDEV ThePowerOfMindsshanicegarridobioreNo ratings yet
- The Brain and BehaviourDocument6 pagesThe Brain and BehaviourJanova MariaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2: Central Nervous SystemDocument34 pagesLesson 1.2: Central Nervous SystemHarvie FilloneNo ratings yet
- Why The Brain Like Some Word Fonts More Than OthersDocument17 pagesWhy The Brain Like Some Word Fonts More Than OthersameliaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum: Gross Appearance DR - Aiza Nasir PTDocument25 pagesCerebrum: Gross Appearance DR - Aiza Nasir PTWaqar YounasNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - The BrainDocument11 pagesWeek 1 - The BrainNguyên VũNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemT-Bone02135No ratings yet
- BRAINDocument15 pagesBRAINashhar khanNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between The Right Brain and Left BrainDocument2 pagesWhat's The Difference Between The Right Brain and Left Brainamnro100% (1)
- t2 S 1398 Ks2 Parts of The Brain Powerpoint Ver 4Document14 pagest2 S 1398 Ks2 Parts of The Brain Powerpoint Ver 4fandomstwentyoneNo ratings yet
- PSY102 Intro To Psychology Unit 1 Describe The Functions of The Brain and The Spinal CordDocument3 pagesPSY102 Intro To Psychology Unit 1 Describe The Functions of The Brain and The Spinal CordLorette BarnardNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMaquirang Cris JaisonNo ratings yet
- Vagus Nerve: A Complete Guide to Activate the Healing power of Your Vagus Nerve – Reduce with Self-Help Exercises Anxiety, PTSD, Chronic Illness, Depression, Inflammation, Anger and TraumaFrom EverandVagus Nerve: A Complete Guide to Activate the Healing power of Your Vagus Nerve – Reduce with Self-Help Exercises Anxiety, PTSD, Chronic Illness, Depression, Inflammation, Anger and TraumaNo ratings yet
- What About Competition From NearbyDocument2 pagesWhat About Competition From NearbyAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Do Not Live As If You Have Ten Thousand Years LeftDocument1 pageDo Not Live As If You Have Ten Thousand Years LeftAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- By Noting Down The FactsDocument1 pageBy Noting Down The FactsAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Economist Joseph Schumpeter Called The Replacement of Existing ProductsDocument2 pagesEconomist Joseph Schumpeter Called The Replacement of Existing ProductsAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Learning FeaturesDocument2 pagesLearning FeaturesAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Of MinorityDocument1 pageOf MinorityAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument1 pageChapter TwoAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- HeyDocument1 pageHeyAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Frozen in Average and Succumb To The Mass Mediocratization of BehaviorDocument1 pageFrozen in Average and Succumb To The Mass Mediocratization of BehaviorAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Seriousness of The Situation and His Mind Literally Goes On OverdriveDocument1 pageSeriousness of The Situation and His Mind Literally Goes On OverdriveAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- End of Film ClipDocument1 pageEnd of Film ClipAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 140 Fault Current CalculationsDocument1 page140 Fault Current CalculationsAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Rabins' Method For Calculating Leakage Fields, Forces, and Inductances in TransformersDocument1 pageRabins' Method For Calculating Leakage Fields, Forces, and Inductances in TransformersAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 5.5 General Method For Determining InductancesDocument1 page5.5 General Method For Determining InductancesAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- RABINS1Document1 pageRABINS1Anoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Tony Benedict, CBPP President, ABPMP InternationalDocument1 pageTony Benedict, CBPP President, ABPMP InternationalAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Attendees To Give Me A Show of Hands, First For "Who Is FromDocument1 pageAttendees To Give Me A Show of Hands, First For "Who Is FromAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Last Digit of The Cube Root Is Also 1Document2 pagesLast Digit of The Cube Root Is Also 1Anoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Design-01Document21 pagesTransformer Design-01Anoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum IIDocument1 pageCorrigendum IIAnoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet