Professional Documents
Culture Documents
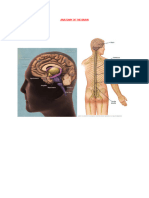
Major Parts of The Brain
Uploaded by
Briones, Rozen M.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Major Parts of The Brain
Uploaded by
Briones, Rozen M.Copyright:
Available Formats
See how the skin on this side of your hands is darker than the other side?
That’s just like the outer layer of the brain, called the cortex or the “gray matter”.
The outside of the brain is darker than the inside because it’s lined with neuron cell
bodies.
Cell bodies are also called soma.
Cell bodies keep the neuron healthy and functioning.
The muscles inside your hands represent the white matter of your brain.
White matter is made up of neuron axons.
Axons carry information from one neuron to another.
If you make a fist with your hands, you can form a shape that’s similar to your brain’s.
This is how human brains are able to squeeze so much gray matter cortex into the small
space within your skull.
Now take your hands, cross your wrists, and make the back of your hands touch each other.
This will help you remember that the left hemisphere of your brain controls the right
side of your body while the right hemisphere of your brain control the left side of your
body.
Look closer at your hands.
Thearea where they touch represents the corpus callosum.
The corpus callosum is a bundle of nerves that connect the two hemispheres of the brain
and help them to communicate with each other.
I like to think of it as the Golden Gate bridge of the brain.
Your wrists represent the brainstem.
The brain stem sits at the very bottom of your brain.
It’s the most basic part of your brain and regulates important life functions like breathing,
heart rate, sleeping, eating, and more.
This is also where signals from the right side of your body cross over to your left
brain and where signals from the left side of your body cross over to your right brain.
Your arms represent the spinal cord.
The spinal cord extends down your back.
It sends and receives information from the rest of your body.
Let’s focus on your left hemisphere.
Your front fingers represent your frontal lobe.
If you remember front fingers frontal lobe, you’ll remember that this is the part of
your brain responsible for complex and abstract abilities.
It sits right behind your forehead and is the most advanced part of your brain.
The frontal lobe helps you to make plans, imagine possible futures, and helps you to
control your emotions.
It doesn’t finish developing until your mid 20s, which is why a lot of kids and teenagers
can do impulsive things.
If you extend your index and middle finger, you’ll see the part of your hand that represents
the parietal lobe.
The parietal lobe integrates all the sensory information in your body.
Your sense of space, navigation, and touch all get relayed here.
But your brain doesn’t prioritize each part of your body equally.
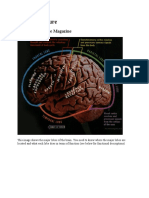
Take a look at this homunculus "map" of the primary motor cortex of the brain - you’ll
notice that the brain prioritizes information from your hands and face.
Look at the back of your hands.
You’ll notice they look like eyes.
This will help you remember that the occipital lobe, the area responsible for visual information,
is located in the back of your brain.
Have you ever hit the back of your head and seen stars?
It’s because you hit your occipital lobe.
Don’t worry though, your brain is protected by cerebrospinal fluid which cushions it against
most everyday injuries like this, just like an airbag in a car.
Take a look at your thumb.
See how it can lift away from the rest of your fist but remains attached?
That’s similar to the temporal lobe.
The back of the temporal lobe is connected to the parietal and occipital lobes, but the
front section can be lifted away from the rest of the brain.
The temporal lobe is responsible for understanding sounds and speech.
Here’s how I remember this: the thumb looks like a temporal lobe which is important for
talking.
If we take a closer look at the temporal lobe, we’ll find the limbic system.
The limbic system is responsible for emotions, learning, and memory.
Inside you’ll find the amygdala, an almond shaped structure just below your thumbnail.
The amygdala is responsible for basic emotions.
Further inside is the hippocampus.
It’s near the bone of your thumb.
The hippocampus is responsible for learning and memory.
You might also like
- Braincurriculum CH 2Document4 pagesBraincurriculum CH 2api-167698901No ratings yet
- Brain and Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesBrain and Nervous SystemBrenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their Functions PDFDocument26 pagesBrain Structures and Their Functions PDFNur Nashran Mahran100% (4)
- Dementia and The BrainDocument13 pagesDementia and The BrainLuminita AndreiNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Oct19 22 - Nervous System Part 1Document8 pagesScience 6 Oct19 22 - Nervous System Part 1Pardeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- Brain 9n7hDocument16 pagesBrain 9n7hAria MartinezNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument13 pagesHuman BrainAaniya AsadNo ratings yet
- Brain Parts and Their Functions in LearningDocument6 pagesBrain Parts and Their Functions in LearningChabbigillNo ratings yet
- Personal Development EpDocument3 pagesPersonal Development Epkristine angela baldestamonNo ratings yet
- Brain StudyDocument57 pagesBrain StudyJoeNo ratings yet
- Most popular types of Fonts and their usesDocument17 pagesMost popular types of Fonts and their usesameliaNo ratings yet
- Brain Basics_ Know Your Brain _ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeDocument4 pagesBrain Basics_ Know Your Brain _ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Strokesurajit halderNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Brain and FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of The Brain and FunctionsLee Ayn PoncardasNo ratings yet
- How The Brain WorksDocument12 pagesHow The Brain WorksAbdullah B.No ratings yet
- Introduction To BrainDocument3 pagesIntroduction To BrainrgdevikaNo ratings yet
- Know Your BrainDocument2 pagesKnow Your BrainJonance YeeNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure Images Explained in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesBrain Structure Images Explained in 40 CharactersChayanDasguptaNo ratings yet
- Bio Summary About CNSDocument3 pagesBio Summary About CNSNicholas LimarcoNo ratings yet
- Fore BrainDocument3 pagesFore BrainAngela EndayaNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsvijushaaNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Lesson 6Document30 pagesPersonal Development Lesson 6Nikka Irah CamaristaNo ratings yet
- The nervous system controls every part of your daily lifeDocument1 pageThe nervous system controls every part of your daily lifeTimothy Van Emil LopezNo ratings yet
- Discuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulseDocument3 pagesDiscuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulsePink PastaNo ratings yet
- Brainpower ComDocument10 pagesBrainpower ComIvy AguasNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Brain Development: 3eredityDocument6 pagesFactors That Affect Brain Development: 3eredityAlphie BersabalNo ratings yet
- General Brain Structure N FunctionDocument6 pagesGeneral Brain Structure N Function'Niq Hdyn100% (1)
- Class 5 - Science Chapter 4Document9 pagesClass 5 - Science Chapter 4aanya2706No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: The BrainDocument12 pagesCentral Nervous System: The BrainTrishNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument5 pagesAnaphy ReportingZyra Kim ResareNo ratings yet
- Brain & BehaviourDocument11 pagesBrain & Behaviourtekhminafareed12No ratings yet
- Understanding the BrainDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the BrainKeir ShattNo ratings yet
- Perdev Mod 5 Powers of The MindDocument14 pagesPerdev Mod 5 Powers of The MindHanimla OsapmaNo ratings yet
- The Human Brain Regions and Their FunctionsDocument35 pagesThe Human Brain Regions and Their FunctionsRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- The Brilliance of The BrainDocument5 pagesThe Brilliance of The Brainapi-219083677No ratings yet
- SubjectDocument11 pagesSubjectRoshni GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Brain QuestionsDocument4 pagesThe Brain QuestionsBibbyNo ratings yet
- Major Structures of The Brain and The Influence They Have On Cognition and Learning Name CollegeDocument4 pagesMajor Structures of The Brain and The Influence They Have On Cognition and Learning Name CollegeKioko NziokaNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument3 pagesBrainamu thaNo ratings yet
- 0301a AllDocument3 pages0301a AllWiendha LiendriasariNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewDocument2 pagesNervous System ReviewVinvieleen Francesca TalaveraNo ratings yet
- The Powers of the Mind RevealedDocument2 pagesThe Powers of the Mind RevealedErron Francisco NicolNo ratings yet
- Finalbrainlobes 1Document7 pagesFinalbrainlobes 1api-346994788No ratings yet
- BrainDocument4 pagesBrainKrizzel Anne MoralesNo ratings yet
- Area of The BrainDocument2 pagesArea of The Brainapi-507287383No ratings yet
- How The Brain WorksDocument6 pagesHow The Brain WorksAnonymous kbmKQLe0JNo ratings yet
- t2 S 1398 Ks2 Parts of The Brain Powerpoint Ver 4Document14 pagest2 S 1398 Ks2 Parts of The Brain Powerpoint Ver 4fandomstwentyoneNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human BrainDocument12 pagesBrain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human BrainElmir ƏzimovNo ratings yet
- Human Body HandbookDocument27 pagesHuman Body Handbookgksamy100% (1)
- Brain and MindDocument5 pagesBrain and MindMubashir AminNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and FunctionsAndrea RamirezNo ratings yet
- Neurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNeurons: Cells of The Nervous SystemItpixels OfficebackdoorNo ratings yet
- Understanding How The Brain Works: An Electrical and Chemical MachineDocument5 pagesUnderstanding How The Brain Works: An Electrical and Chemical MachineBenazir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Ashen WeerasingheNo ratings yet
- Brain 21370Document2 pagesBrain 21370daniel balteanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human BrainDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Human BrainIan Rhadel RaganasNo ratings yet
- The Power To ActDocument38 pagesThe Power To ActRed Lopez100% (1)
- Brain System: Parts and FunctionsDocument9 pagesBrain System: Parts and FunctionsChristhoper John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Letter of InvitationDocument2 pagesLetter of InvitationBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- BiosciDocument10 pagesBiosciBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Letter of RecommendationDocument2 pagesLetter of RecommendationBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Letter of AcknowledgementDocument2 pagesLetter of AcknowledgementBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentDocument4 pagesLaboratory EquipmentBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Zoology PRDocument136 pagesToaz - Info Zoology PRBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Lab Safety RulesDocument2 pagesLab Safety RulesBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Hans AspergerDocument1 pageHans AspergerBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Stress and Coping Models in Health PsychologyDocument5 pagesStress and Coping Models in Health PsychologyBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Answers in Intro2psychDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 Answers in Intro2psychBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- Letter of AdjustmentDocument2 pagesLetter of AdjustmentBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- NEET-SS General SurgeryDocument63 pagesNEET-SS General Surgeryadi100% (2)
- Management RTSDocument6 pagesManagement RTSilham Maulana ArifNo ratings yet
- SURGERY 07 BurnsDocument1 pageSURGERY 07 BurnsMikhail LamayoNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Festival DancesDocument41 pagesPhysical Education: Festival DancesPinoy Ziraniko VlogzNo ratings yet
- Walking MechanismDocument15 pagesWalking MechanismKamran AmeerNo ratings yet
- Finger Force Capability - 10.1.1.498.673Document103 pagesFinger Force Capability - 10.1.1.498.673Sidney M. SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ulna (Bone and Attachments) Flow ChartDocument2 pagesUlna (Bone and Attachments) Flow ChartNicoleta PSNo ratings yet
- Hip Pain in Pregnancy GTPS - Oct19-1Document3 pagesHip Pain in Pregnancy GTPS - Oct19-1Ryan CrossNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Physical Examination RemindersDocument23 pagesConduct of Physical Examination RemindersJazer DairoNo ratings yet
- Module I TranscriptorDocument20 pagesModule I TranscriptorthabisNo ratings yet
- First Aid Risk Assessment PDFDocument4 pagesFirst Aid Risk Assessment PDFAmin UllahNo ratings yet
- Abl8red24400Document2 pagesAbl8red24400Arif Rachmat HermawanNo ratings yet
- d100 Magic SwordsDocument1 paged100 Magic SwordsKirkNo ratings yet
- Wound Care ThesisDocument4 pagesWound Care Thesiscandacedaiglelafayette100% (2)
- User Manual: Model 4779 Tru-Trac® Traction UnitDocument46 pagesUser Manual: Model 4779 Tru-Trac® Traction UnitSejmet IngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome - Hand - OrthobulletsDocument7 pagesUlnar Tunnel Syndrome - Hand - OrthobulletsSylvia GraceNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Notes SMU Law AY 2020-21Document34 pagesCriminal Law Notes SMU Law AY 2020-21Pin Ern OngNo ratings yet
- Black and Decker Mouse Sander ms600bDocument32 pagesBlack and Decker Mouse Sander ms600bd sNo ratings yet
- 12 Oktober 2017 - Swan Neck Deformity Vs BoutonniereDocument48 pages12 Oktober 2017 - Swan Neck Deformity Vs BoutonniereGerard BennyNo ratings yet
- Civil LitigationDocument12 pagesCivil LitigationantcbeNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of BrainDocument54 pagesBlood Supply of Brainsaniasddq1110No ratings yet
- ContusionsDocument35 pagesContusionsSARVESH MAWALE100% (1)
- IBQs & MCQsDocument58 pagesIBQs & MCQsskNo ratings yet
- Skull and "Dysplasia" Means Abnormal BoneDocument3 pagesSkull and "Dysplasia" Means Abnormal BoneNoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- Ijser: Design and Fabrication of Patient Transferring DeviceDocument7 pagesIjser: Design and Fabrication of Patient Transferring DeviceARUN VNo ratings yet
- Incident at Monroe County Children's Detention CenterDocument2 pagesIncident at Monroe County Children's Detention CenterAdam PenaleNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 14Th Edition Fox Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesHuman Physiology 14Th Edition Fox Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFevelyn.trudnowski238100% (15)
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- 4-09 Trauma - Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument18 pages4-09 Trauma - Musculoskeletal TraumaEmil CotenescuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument84 pagesUntitledWardah AliNo ratings yet