Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Rising Tide - Understanding Sea Level Rise and Its Impact On Humanity
The Rising Tide - Understanding Sea Level Rise and Its Impact On Humanity
Uploaded by
Pek Jun KaiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Rising Tide - Understanding Sea Level Rise and Its Impact On Humanity
The Rising Tide - Understanding Sea Level Rise and Its Impact On Humanity
Uploaded by
Pek Jun KaiCopyright:
Available Formats
The Rising Tide: Understanding Sea Level Rise and Its
Impact on Humanity
Sea levels around the world are on the rise, a phenomenon largely attributed to climate
change. As global temperatures increase, glaciers and ice caps melt, and the thermal
expansion of seawater occurs, contributing to the gradual increase in sea levels. While
this rise may seem slow and gradual, its effects are already being felt and are set to
intensify in the coming decades.
Current Situation
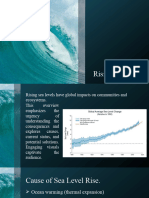
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), sea levels have
risen by about 8 inches (20 centimeters) since 1900, with the rate of rise nearly doubling
in the last two decades. This trend is expected to continue, with projections indicating a
further rise of at least several inches to over a foot (up to half a meter) by the end of this
century, depending on future greenhouse gas emissions and climate policies.
Impact on Coastal Communities
The consequences of rising sea levels are numerous and severe, particularly for coastal
communities. Low-lying areas, such as small island nations and coastal cities, are
particularly vulnerable. Increased flooding during high tides and storm surges, as well
as saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources, threaten homes, infrastructure, and
livelihoods.
Environmental Impact
The ecological impact of rising sea levels is also significant. Coastal habitats such as
wetlands, mangroves, and coral reefs face inundation, leading to loss of biodiversity and
vital ecosystems. Species that rely on these habitats for survival are at risk of extinction
or migration, disrupting entire ecosystems.
Economic Costs
The economic costs of sea level rise are substantial. Damage to infrastructure, including
roads, buildings, and utilities, requires costly repairs and adaptations. Disruption to
industries such as tourism and fisheries can have long-lasting effects on local
economies, leading to loss of jobs and income.
Global Migration and Security Concerns
Sea level rise also has implications for global migration and security. As coastal areas
become uninhabitable, populations may be forced to migrate inland or to other
countries, leading to potential conflicts over resources and land. Small island nations
face the existential threat of becoming uninhabitable, raising questions about their
sovereignty and future existence.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Efforts to mitigate and adapt to sea level rise are crucial. Reducing greenhouse gas
emissions through sustainable practices and policies is essential to slowing the rate of
rise. Adaptation measures, such as building sea walls, restoring coastal habitats, and
implementing early warning systems, can help communities prepare for and respond to
rising sea levels.
Conclusion
Sea level rise is a complex and urgent challenge that requires global cooperation and
action. While the impacts are already being felt, there is still time to mitigate the worst
effects by reducing emissions and implementing adaptation strategies. The future of
coastal communities and ecosystems depends on our ability to address this pressing
issue.
You might also like
- Hanbook On Integrated Food ProductionDocument69 pagesHanbook On Integrated Food Productioneaparducho100% (1)
- Gesp DRRM-2Document22 pagesGesp DRRM-2Mark TolenadaNo ratings yet
- Denr 2012 Coa Observation RecommendatoinDocument69 pagesDenr 2012 Coa Observation RecommendatoinAnthony Sutton100% (5)
- InternationalagreementsDocument7 pagesInternationalagreementsapi-324650488No ratings yet
- EcologyDocument7 pagesEcologyMahabat Kanbolot kyzyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Global WarmingDocument2 pagesCase Study Global WarmingMd. Kamrul HoqueNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Climate Change On Coastal CommunitiesDocument1 pageThe Impact of Climate Change On Coastal Communitiesshaikh.ahmed.2117.eNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Climate Change On Coastal CommunitiesDocument1 pageThe Impact of Climate Change On Coastal CommunitiesJavaTPMNo ratings yet
- Report On Environment Changes and Initiatives Taken: Priya Kumari 1/1/2022Document15 pagesReport On Environment Changes and Initiatives Taken: Priya Kumari 1/1/2022Priya KumariNo ratings yet
- Large Population and Assets To Be Affected by Sea Level RiseDocument4 pagesLarge Population and Assets To Be Affected by Sea Level RiseNeil AgshikarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14, Post AssessmentDocument3 pagesLesson 14, Post AssessmentKen TubungbanuaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate ChangeAdith M RNo ratings yet
- Global WarningsDocument4 pagesGlobal Warningsmanuelb4488No ratings yet
- Global ProblemDocument2 pagesGlobal ProblemjfafkdiutbuvzgewtaNo ratings yet
- 12345Document1 page12345Jovito De Gracia HernándezNo ratings yet
- Vision VAM 2020 (Essay) Climate ChangeDocument14 pagesVision VAM 2020 (Essay) Climate ChangeGaurang Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Meet11 STOW RahmaandityaDocument2 pagesMeet11 STOW RahmaandityaRahma NdityaNo ratings yet
- Coastal and Ocean Restoration Article: The Ocean and Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesCoastal and Ocean Restoration Article: The Ocean and Climate Changeepiwyioy yewirwyoiNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Impacts On The PlanetDocument1 pageClimate Change and Its Impacts On The PlanetJorge UribeNo ratings yet
- Coastal Adaptation To Climate Change and Sea-Level RiseDocument27 pagesCoastal Adaptation To Climate Change and Sea-Level RiseDiana ChumaceraNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate Changeandresuhardi74No ratings yet
- Climate As A Common Good Vol.2Document3 pagesClimate As A Common Good Vol.2some-thin-kingNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate ChangejfafkdiutbuvzgewtaNo ratings yet
- G7 2015 Future of The OceansDocument2 pagesG7 2015 Future of The OceansAna CaixetaNo ratings yet
- Paper 5Document1 pagePaper 5zeenia.shamraz1No ratings yet
- 73 A10006 PDFDocument5 pages73 A10006 PDFVithanage Chaminda PereraNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Global Warming and Its Impact On BangladeshDocument7 pagesClimate Change and Global Warming and Its Impact On BangladeshAminulHoqueNo ratings yet
- Unraveling The Complexity of Global WarmingDocument2 pagesUnraveling The Complexity of Global WarmingLiannaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its ImplicationsDocument1 pageClimate Change and Its ImplicationsHaykanush GevorgyanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change The Urgency of Collective ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesClimate Change The Urgency of Collective Responsibilityedrian.estpi11No ratings yet
- Final Report (Geology)Document14 pagesFinal Report (Geology)Zuha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Environmental Changes Analysis: North South UniversityDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Changes Analysis: North South UniversityRomi SikderNo ratings yet
- Climat Change b1Document2 pagesClimat Change b1Zeliha ÇavdarNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument2 pagesClimateNakanakanaknakNo ratings yet
- Oceanic Oases Under Threat: Climate Change and its Toll on Mediterranean, Gulf, and Indian Ocean EnclavesFrom EverandOceanic Oases Under Threat: Climate Change and its Toll on Mediterranean, Gulf, and Indian Ocean EnclavesNo ratings yet
- Global Warming A Looming CatastropheDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming A Looming Catastrophejames badinNo ratings yet
- 2 DXDocument2 pages2 DXSans RecourseNo ratings yet
- Space Geodesy GroupDocument3 pagesSpace Geodesy GroupdominiqueNo ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness Week 15 STSDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Awareness Week 15 STSRichie annNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesThe Effects of Climate Changeshanesha blackhoodNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Effects On Island Nations: An "Islands First" InitiativeDocument13 pagesClimate Change Effects On Island Nations: An "Islands First" Initiativeapi-340846639No ratings yet
- Academic Reading Sample 2Document4 pagesAcademic Reading Sample 2MaheshaSisirakumaraKulasekara0% (2)
- Mitigation of Climate ChangeDocument11 pagesMitigation of Climate ChangeAbelardo Llenes TalitodNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument2 pagesGlobal Warminghelene ganawaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Education-ADB Workshop-Lal - USPDocument38 pagesClimate Change and Education-ADB Workshop-Lal - USPRoberta V. GerpacioNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Sea Level RiseDocument2 pagesClimate Change and Sea Level RiseJai GodaraNo ratings yet
- 34 R 32Document1 page34 R 32Michael LeeNo ratings yet
- Effects of Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesEffects of Climate ChangeJan100% (1)
- Climate ChangeDocument14 pagesClimate ChangeAmmara aijazNo ratings yet
- The Looming Crisis-Understanding The Threat of Global Warming To EarthDocument2 pagesThe Looming Crisis-Understanding The Threat of Global Warming To Earthamansiem336No ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesClimate ChangeShadan NawazNo ratings yet
- TextDocument2 pagesTextAtharva MundadaNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of Climate Change Are We PreparedDocument3 pagesThe Challenges of Climate Change Are We PreparedEdward Alexis Vásquez BecerraNo ratings yet
- Climate Change (EnglishDocument29 pagesClimate Change (EnglishKrrish GehlotNo ratings yet
- Sastav - Klimatske PromeneDocument3 pagesSastav - Klimatske PromeneAnita GrnjaNo ratings yet
- Climate A UmDocument7 pagesClimate A UmsanthakumarNo ratings yet
- Climate Change1Document7 pagesClimate Change1Geraldine L. GaddiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Climate Change On Land Use and Environmental ChangeDocument65 pagesImpact of Climate Change On Land Use and Environmental ChangeSande Alota BocoNo ratings yet
- Rising Sea LevelDocument11 pagesRising Sea Levelmarbaschu86No ratings yet
- Saad Climate Change ProjectDocument9 pagesSaad Climate Change Projectsana jaleelNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument2 pagesClimatebruhbruhstopmanNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Global WarmingDocument47 pagesGroup 1 Global WarmingJohnrey FornalesNo ratings yet
- National Water Policy - Govenment of India PDFDocument13 pagesNational Water Policy - Govenment of India PDFBalakrishna KNo ratings yet
- Livelihood Vulnerability To Flood Hazard UnderstanDocument23 pagesLivelihood Vulnerability To Flood Hazard UnderstanRisma NiaNo ratings yet
- The Paris Agreement: For Young PeopleDocument18 pagesThe Paris Agreement: For Young PeopleNabilaSalsaNo ratings yet
- Up Researches On Disaster Risk Reduction and Management 2008-2011 CompDocument130 pagesUp Researches On Disaster Risk Reduction and Management 2008-2011 CompSandra Day100% (1)
- Climatechangeiisdfull 110629102724 Phpapp02Document38 pagesClimatechangeiisdfull 110629102724 Phpapp02Dev AshwaniNo ratings yet
- 22620-Article Text-47052-1-10-20180402Document452 pages22620-Article Text-47052-1-10-20180402Jung Eun Hwa TrisnaNo ratings yet
- Pdfcoffee.com Bdrrm Plan 2021 2025 PDF FreeDocument58 pagesPdfcoffee.com Bdrrm Plan 2021 2025 PDF Freeyhan mahaitNo ratings yet
- DRR - AgDocument5 pagesDRR - AgJune Blessing ThawNo ratings yet
- LDRRF Operational Guidebook - Rev 05 Oct 2011Document27 pagesLDRRF Operational Guidebook - Rev 05 Oct 2011Vikinguddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On "Climate Change Mitigation and Strategies: Global Perspectives"Document23 pagesTerm Paper On "Climate Change Mitigation and Strategies: Global Perspectives"KirataNo ratings yet
- ProvincialDevelopmentAndPhysicalFrameworkPlan (June2014) PDFDocument369 pagesProvincialDevelopmentAndPhysicalFrameworkPlan (June2014) PDFFroy Richmond Gabriel SilverioNo ratings yet
- Hyogo Framework For ActionDocument28 pagesHyogo Framework For ActionReymark Sacare BibarNo ratings yet
- 2021-Otsuka-Agriculture in A Changing World - Copy - Compressed-Dikompresi PDFDocument34 pages2021-Otsuka-Agriculture in A Changing World - Copy - Compressed-Dikompresi PDFmuhammad robbyNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Effects On Subsistence AgricultureDocument85 pagesClimate Change Effects On Subsistence AgricultureAden MahamoudNo ratings yet
- Makate Effective Scaling of Climate Smart Agriculture Innovations inDocument15 pagesMakate Effective Scaling of Climate Smart Agriculture Innovations inLuciano Quezada HenriquezNo ratings yet
- Global Environmental Change: A B C D e F GDocument16 pagesGlobal Environmental Change: A B C D e F Gmariajose garciaNo ratings yet
- Resilience Design in Smallholder Farming Systems ApproachDocument121 pagesResilience Design in Smallholder Farming Systems ApproachFarai MandisodzaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Sustainable Development-Shubham KaliaDocument7 pagesClimate Change and Sustainable Development-Shubham KaliaShubham KaliaNo ratings yet
- Ideology and Constitution of Pakistan - Final Notes - Muhammad Maaz TariqDocument24 pagesIdeology and Constitution of Pakistan - Final Notes - Muhammad Maaz Tariqhurairawaris.arain23No ratings yet
- Modified Resume DeshanDocument3 pagesModified Resume DeshanDeshan PasinduNo ratings yet
- BMKG EoI - University of East AngliaDocument10 pagesBMKG EoI - University of East AngliaezradelinaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliographysiaf khanNo ratings yet
- River Basin Management Plans Are Elaborated Pursuant To Article 155 (1), (Para 2) of The WaterDocument22 pagesRiver Basin Management Plans Are Elaborated Pursuant To Article 155 (1), (Para 2) of The WaterbotezflorinaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Tourism Guidebook For Local G PDFDocument173 pagesPhilippine Tourism Guidebook For Local G PDFJawo Jimenez0% (1)
- Climate Change Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation in ZimbabweDocument40 pagesClimate Change Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation in ZimbabweBrighton MugutaNo ratings yet
- Patent Technology Transfer AutomobileDocument26 pagesPatent Technology Transfer AutomobilefkkfoxNo ratings yet