Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revisao Aula Pre Intermediate Units 1-3
Revisao Aula Pre Intermediate Units 1-3
Uploaded by
anna.oliveira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
revisao aula pre intermediate units 1-3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesRevisao Aula Pre Intermediate Units 1-3
Revisao Aula Pre Intermediate Units 1-3
Uploaded by
anna.oliveiraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
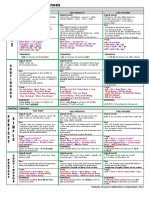
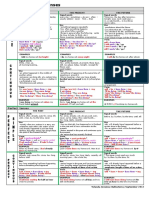
Verb tense When to use
Present simple Facts, things that are always true, states of
mind.
Present continuous (for present) Things that are happening while the person
is talking, temporary events that take place
“at the moment”.
Past simple Punctual actions in the past, to emphasize
that the action is finished.
Past continuous Continuous actions that started and ended
in the past, or that took place over a period
of time
Future (will) A spontaneous decision that took place at
the moment of the speech, promises,
offerings, when talking about the weather,
uncertain decisions.
Future (going to) THE TO BE VERB IS MANDATORY, predictions
that are more certain, usually the moment
appears, such as “this weekend”, “next
month”
Future (present continuous) Events that are certain and close in time
(today, tomorrow, in two hours)
Preposition of time When to use
In Years, months, seasons, periods of the day
(except fot night).
On Days of the week, holidays ended in “day”
(e.g.: St. Patrick’s day).
At Time (hour: minute), night, the weekend,
the moment.
Preposition of place When to use
In Countries, states, cities; when “inside” of a
3D space, such as bag, room or fridge;
private ways of transportation (car and van).
On Surfaces, floors, public transportations (bus,
train, plane), right/left.
At A specific point (the door, the traffic light) or
place (school, home, university), shops and
stores.
Word order in questions
Wh- word Auxiliary Subject Main verb Object ?
Where do you live ?
When is your ?
birthday
What do you do ?
How can you do that ?
How long is the trip going to take ?
*When the “to be” verb is the main verb, it is also its own auxiliary, so you just need to use it
once.
* The “wh- word” might have a complement, as in the case of “how long”, “what kind”. Every
part of the sentence that complements the sense of the “wh- question” is a part of it. That is
why you ask, “What kind of music do you like?” and not “what do you like kind of music?”
You might also like
- Sanskrit Full PDFDocument209 pagesSanskrit Full PDFSahaj Agarwal25% (4)
- Formal Essay Rubric: Organization (25 Percent)Document1 pageFormal Essay Rubric: Organization (25 Percent)Iana Cruz80% (5)
- Table of English Tenses PDFDocument1 pageTable of English Tenses PDFdetroitdogg75% (4)
- French Verb Tense Timeline21Document44 pagesFrench Verb Tense Timeline21Alexandar ApishaNo ratings yet
- Ivrit GuideDocument147 pagesIvrit GuideMedStu1234578% (9)
- Grammar in Context 2 Grammar in Context Seventh Edition 7Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesGrammar in Context 2 Grammar in Context Seventh Edition 7Th Edition Full Chaptercarolyn.west317100% (25)
- A Pocket Dictionary of The Spoken Arabic of Cair Sny2cwhe8doDocument1 pageA Pocket Dictionary of The Spoken Arabic of Cair Sny2cwhe8doMarija Avramovic0% (1)
- Untitled - Book Downloadable PDFDocument74 pagesUntitled - Book Downloadable PDFSónia100% (6)
- English Word Order: Who-What-Where-When-How-WhyDocument4 pagesEnglish Word Order: Who-What-Where-When-How-WhySkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- VERB TO BE ExercisesDocument3 pagesVERB TO BE ExercisesSara Cáceres100% (1)
- Teen Explorer 7 Ksiazka NauczycielaDocument324 pagesTeen Explorer 7 Ksiazka NauczycielaAdrian DraganNo ratings yet
- 1087494table of English Tenses 130929193446 Phpapp02Document1 page1087494table of English Tenses 130929193446 Phpapp02zulNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument2 pagesFuture Formsnata_makarNo ratings yet
- JabberwockyDocument3 pagesJabberwockyGilorie RuizNo ratings yet
- Adverb of TimeDocument12 pagesAdverb of TimeSomnath JagtapNo ratings yet
- College Entrance Exam Reviewer (Day 5) : Brought To You byDocument16 pagesCollege Entrance Exam Reviewer (Day 5) : Brought To You byBblack DeathNo ratings yet
- Tenses & Time ExpressionsDocument1 pageTenses & Time Expressionseva sarridoNo ratings yet
- 1.present Tences 1.1. Present (Future) Meaning 1.1.1. Present Simple (Indefinite)Document6 pages1.present Tences 1.1. Present (Future) Meaning 1.1.1. Present Simple (Indefinite)Анастасия АнастасияNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For MicroteachingDocument2 pagesGuidelines For MicroteachingYaniHuayguaNo ratings yet
- English Tenses Active & Pasive VoicesDocument8 pagesEnglish Tenses Active & Pasive Voicesmuhammad faheemNo ratings yet
- A"rmative, Negative, Questions: Present Simple Present ContinuousDocument1 pageA"rmative, Negative, Questions: Present Simple Present ContinuousFilipa SousaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledRadomir StanicNo ratings yet
- Vocabulario Varios IdiomasDocument200 pagesVocabulario Varios IdiomasAnonymous s7NowlkNo ratings yet
- Noun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction InterjectionDocument19 pagesNoun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction InterjectionFerizalGunawanNo ratings yet
- ANGLEŠČINA - Izpiski: Simple TensesDocument6 pagesANGLEŠČINA - Izpiski: Simple TensesInes ČučekNo ratings yet
- Focus-BrE5 StudentsBook Unit1-GrammarFocus PDFDocument3 pagesFocus-BrE5 StudentsBook Unit1-GrammarFocus PDFJulio Emmanuel MezaNo ratings yet
- Japanese Grammar SummaryDocument64 pagesJapanese Grammar SummaryDiana Di DonigavNo ratings yet
- Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousDocument1 pageSimple Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousGermanNo ratings yet
- Stressed Stressed Unstressed: Nothing But Money Is Sweeter Than HoneyDocument2 pagesStressed Stressed Unstressed: Nothing But Money Is Sweeter Than HoneyCafe com inglesNo ratings yet
- Prepositions - Time: English Usage ExampleDocument5 pagesPrepositions - Time: English Usage ExampleMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument6 pagesPrepositionsSadia SifatNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument3 pagesTENSES5krzhbvy4dNo ratings yet
- Repositions: PrepositionDocument5 pagesRepositions: PrepositionAnkita T. MooreNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported SpeechbrahimNo ratings yet
- Preposition: Place. Thus, Contrary To Other "Small Words", They Are Not An Element of Style, But AbsolutelyDocument9 pagesPreposition: Place. Thus, Contrary To Other "Small Words", They Are Not An Element of Style, But AbsolutelyAsya FahiraNo ratings yet
- Learning Module 3: Introduction-To-The-Basic-Parts-Of-SpeechDocument14 pagesLearning Module 3: Introduction-To-The-Basic-Parts-Of-SpeechSheene CerboNo ratings yet
- Dictionary Literature Study Tips: PrepositionsDocument3 pagesDictionary Literature Study Tips: PrepositionsCosmic KatharsisNo ratings yet
- Tablitsa Vremen Na Angl IazDocument3 pagesTablitsa Vremen Na Angl IazСофья БеклемещеваNo ratings yet
- Future: Present Progressive and Be Going To Present Progressive: Be Going ToDocument5 pagesFuture: Present Progressive and Be Going To Present Progressive: Be Going ToPetra BajacNo ratings yet
- Grammar Tenses: PresentDocument3 pagesGrammar Tenses: PresentPaola FloresNo ratings yet
- English Prepositions ReviewerDocument2 pagesEnglish Prepositions ReviewerMorris MananguiteNo ratings yet
- PREPOSITIONSDocument5 pagesPREPOSITIONSshareenNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses and Time Reference: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses and Time Reference: Simple PresentRita JapasNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Time and TenseDocument5 pagesWeek 13 Time and TenseMihaela Codrina AntonNo ratings yet
- Writing Review by DR Basil AldweikDocument13 pagesWriting Review by DR Basil AldweikMohamed SakrNo ratings yet
- Tense Forms (Simple Continuous)Document2 pagesTense Forms (Simple Continuous)fatimaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensessamira samNo ratings yet
- Present Past Tenses ReviewDocument26 pagesPresent Past Tenses ReviewOlga SafonovaNo ratings yet
- The Active Voice: (Indefinite) (Progressive) (Progressive)Document3 pagesThe Active Voice: (Indefinite) (Progressive) (Progressive)Elena PodlesnayaNo ratings yet
- The Group of Continuous TensesDocument2 pagesThe Group of Continuous TensesJuliaNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document26 pagesGroup 3MiaNo ratings yet
- Aaaa MaterialsDocument2 pagesAaaa Materialsmeshav749No ratings yet
- Time Contrasts ChartDocument1 pageTime Contrasts ChartAlexis YepezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Always, Ussualy.Document11 pagesPresent Simple: Always, Ussualy.epincarrNo ratings yet
- Grammar Second YearDocument5 pagesGrammar Second Yearcoucouc38No ratings yet
- Vreminja Tabela DobroDocument2 pagesVreminja Tabela DobroAntoni JakovleskiNo ratings yet
- Japanese Level 2 2169Document6 pagesJapanese Level 2 21692010s2723No ratings yet
- PrepositionDocument4 pagesPrepositionNeslihan ŞimşekNo ratings yet
- Tense Signal Words Use Form Ex Affirmative (+) Ex Negative (-) Ex Interrogative (?)Document4 pagesTense Signal Words Use Form Ex Affirmative (+) Ex Negative (-) Ex Interrogative (?)Yen RitaNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument3 pagesAdverbsjudsonmandume2002No ratings yet
- The Present TensesDocument4 pagesThe Present TensesAlexandra SiluyanovaNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses NewDocument3 pagesFuture Tenses NewtorbenteacherNo ratings yet
- Simple P VS P ProgressiveDocument15 pagesSimple P VS P ProgressiveAaly MoretthNo ratings yet
- Narrative TaskDocument12 pagesNarrative Taskdayu shintaNo ratings yet
- TimeDocument5 pagesTimeTibari HAFFARNo ratings yet
- The Dice ProjectDocument7 pagesThe Dice ProjectCheo LópezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 GrammarDocument5 pagesUnit 1 GrammarISIDRO JOSÉ SÁEZ MADRIDNo ratings yet
- Noun Feminine FormsDocument4 pagesNoun Feminine Formsهاني حبيب عزيز صالحNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of SentenceDocument20 pages4 Types of SentenceSarah Al ZaabiNo ratings yet
- Dawson.-Morphological Variation and Change in The Rigveda. The Case of Au Vs A, 2005Document359 pagesDawson.-Morphological Variation and Change in The Rigveda. The Case of Au Vs A, 2005Ana Hernández VivoNo ratings yet
- Retroalimentada NilDocument61 pagesRetroalimentada NilKaterineNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect - English Grammar - EFDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect - English Grammar - EFManuel DalelinoNo ratings yet
- Comm Skills QuestionsDocument18 pagesComm Skills QuestionsMartin NtowNo ratings yet
- School Competition 2011 / 2012 V Grade Name: - Points: - / 80Document5 pagesSchool Competition 2011 / 2012 V Grade Name: - Points: - / 80Mare BrzanovaNo ratings yet
- 513639.SSGL 37 07 - Mate KapovicDocument125 pages513639.SSGL 37 07 - Mate KapovicpskruškeNo ratings yet
- English Exercises 01aDocument6 pagesEnglish Exercises 01aProfesor Víctor BastidasNo ratings yet
- Ing Forms and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesIng Forms and InfinitivesSANLU HTUTNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Verb PatternsDocument2 pagesPresentation: Verb PatternsDinara İbrahim QızıNo ratings yet
- Talmy's Typological Perspective On Spatial ExpressionsDocument1 pageTalmy's Typological Perspective On Spatial ExpressionsAlkan MuratNo ratings yet
- Contoh Complete Lesson Plan RPH Bahasa Inggeris Form 1 2 3Document1 pageContoh Complete Lesson Plan RPH Bahasa Inggeris Form 1 2 3Citra Yoenita MhdNo ratings yet
- English Writing - DAY 1 PDFDocument4 pagesEnglish Writing - DAY 1 PDFDilla HarrisNo ratings yet
- Univerzita Karlova V Praze Filozofická Fakulta Český Egyptologický Ústav Historické Vědy - EgyptologieDocument377 pagesUniverzita Karlova V Praze Filozofická Fakulta Český Egyptologický Ústav Historické Vědy - Egyptologietormael_56No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan VerbDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan VerbHanna MikangcrzNo ratings yet
- General EnglishDocument2 pagesGeneral Englishpramod Singh negiNo ratings yet
- Stilistica LexicologieDocument84 pagesStilistica LexicologiePetr VelikovskýNo ratings yet
- 7 Cs of Communication (Eg)Document40 pages7 Cs of Communication (Eg)Vikram KatariaNo ratings yet
- The Pronouns Y and enDocument14 pagesThe Pronouns Y and enNoah KimNo ratings yet
- Ae Tt10 Present Simple Present Continuous p16Document24 pagesAe Tt10 Present Simple Present Continuous p16ElisabeteNo ratings yet