Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chi Square
Chi Square
Uploaded by
Yash ThakurCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chi Square
Chi Square
Uploaded by
Yash ThakurCopyright:
Available Formats
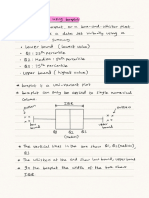
1.
Cross tabulation (Bi variate) & Complex cross tabulation (more than two variable)
2. Pictorial representation of cross tabulation (Clustered bar chart)
3. Checking assumptions (expected frequency of the cross tabulation cell should be
greater than 5)
4. Applying chi square and interpretation
5. Substitute: Fisher’s test
Objective of the study: To check whether there is any
associations between professions of a traveler and the airline
used by them.
Null Hyposthesis: Ho; there is no association b/w the
professions of a traveler and the airlines used by them.
Alternate Hypothesis: H1: there is association b/w the
professions of a traveler and the airlines used by them.
Test: Cross tab and Chi Square
Step 1 : Generate cross tab, analyse descriptive statistics
and analyse
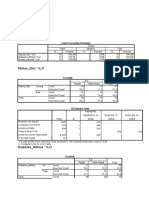
Profession of traveler * Airlines used Crosstabulation
Count
Airlines used
Air India Spice Jet Indigo Total
Profession of Goverment 35 45 38 118
traveler Coprorate 26 21 13 60
Student 27 20 33 80
Total 88 86 84 258
Expected frequency is greater than 5
Profession of traveler * Airlines used Crosstabulation
Airlines used
Spice
Air India Jet Indigo Total
Profession of Goverme Count 35 45 38 118
traveler nt Expected 40.2 39.3 38.4 118.0
Count
Coprorate Count 26 21 13 60
Expected 20.5 20.0 19.5 60.0
Count
Student Count 27 20 33 80
Expected 27.3 26.7 26.0 80.0
Count
Total Count 88 86 84 258
Expected 88.0 86.0 84.0 258.0
Count
Chi-Square Tests
Asymptotic
Significance
Value df (2-sided)
Pearson Chi-Square 8.764a 4 .067
Likelihood Ratio 8.948 4 .062
Linear-by-Linear .045 1 .832
Association
N of Valid Cases 258
a. 0 cells (0.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum
expected count is 19.53.
Significance value is greater than 0.05 hence we assume that
null hypothesis is true
You might also like
- BRM Data Analysis TechniquesDocument53 pagesBRM Data Analysis TechniquesS- AjmeriNo ratings yet
- Business and Economic Statistics Quiz 01 06Document25 pagesBusiness and Economic Statistics Quiz 01 06Ariane GaleraNo ratings yet
- MarksheetDocument2 pagesMarksheetPrabhakar Jha0% (1)
- Fraud Analytics Using Descriptive, Predictive, and Social Network Techniques: A Guide to Data Science for Fraud DetectionFrom EverandFraud Analytics Using Descriptive, Predictive, and Social Network Techniques: A Guide to Data Science for Fraud DetectionNo ratings yet
- FINAL ASSESSMENT ASSIGNMENT MBA Stats - Maths 28062020 105406pm PDFDocument3 pagesFINAL ASSESSMENT ASSIGNMENT MBA Stats - Maths 28062020 105406pm PDFHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Year Level Q1A: CrosstabDocument12 pagesYear Level Q1A: CrosstabJenniferNo ratings yet
- T2 rtPA60Document2 pagesT2 rtPA60AtragalusNo ratings yet
- Crosstabs: NotesDocument3 pagesCrosstabs: NotesNurul AnnisaniNo ratings yet
- Nama Kelompok: - DIAN AGUSTINI (5230019053) - Fitri - Ichsan Prodi: S1 Akuntansi 3BDocument4 pagesNama Kelompok: - DIAN AGUSTINI (5230019053) - Fitri - Ichsan Prodi: S1 Akuntansi 3BDIAN EFENDI AL MUHNINo ratings yet
- Output AgeDocument1 pageOutput AgeAtul PrasharNo ratings yet
- Decision Science June 2022Document13 pagesDecision Science June 2022Shruti MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Decision ScienceDocument13 pagesDecision ScienceRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Revision List With Links HigherDocument5 pagesRevision List With Links HigherBen StocksNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 4. Hasil Analisis Data: Case Processing SummaryDocument2 pagesLampiran 4. Hasil Analisis Data: Case Processing SummaryErbit AskarNo ratings yet
- Example 1: Case Processing SummaryDocument14 pagesExample 1: Case Processing SummaryAnkit KharkiaNo ratings yet
- Sikap Jurusan CrosstabulationDocument1 pageSikap Jurusan CrosstabulationM Aqil GibranNo ratings yet
- Case Processing SummaryDocument4 pagesCase Processing SummaryLavanya PrathimaNo ratings yet
- Jenis Kelamin Tingkat Pendidikan Crosstabulation: 1.gender DidikDocument5 pagesJenis Kelamin Tingkat Pendidikan Crosstabulation: 1.gender DidikMalaikatSetengahDewaNo ratings yet
- CAT Syllabus: Data Interpretation & Logical Reasoning Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension Quantitative AbilityDocument4 pagesCAT Syllabus: Data Interpretation & Logical Reasoning Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension Quantitative Abilitygeetikag_23No ratings yet
- Chi-Square TestDocument4 pagesChi-Square TesteswariNo ratings yet
- Kepatuhan: Chi-Square TestsDocument3 pagesKepatuhan: Chi-Square TestsFitri SulistianiNo ratings yet
- Cross TabsDocument7 pagesCross TabsNamichan17No ratings yet
- 038 - Febri Dwi Yani - Praktikum 3Document3 pages038 - Febri Dwi Yani - Praktikum 3Febri Dwi YaniNo ratings yet
- Hasil Uji Chi SquareDocument3 pagesHasil Uji Chi SquareLuphly TaluvtaNo ratings yet
- Lampiran SPSS: Frequency TableDocument2 pagesLampiran SPSS: Frequency TableHabib BaNo ratings yet
- Yuhaning Audiya - 1611020108 - Kelas B - IDK VIDocument9 pagesYuhaning Audiya - 1611020108 - Kelas B - IDK VIYuhaning AudiyaNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument11 pagesOutputisriana ismailNo ratings yet
- You Exec - Decision Making Models CompleteDocument32 pagesYou Exec - Decision Making Models CompleteRajasekar PonnaiahNo ratings yet
- Hypermesh ChecklistDocument2 pagesHypermesh Checklistvdmoorthy123No ratings yet
- Stat 2509 Exam Review Problems 1 AwoodsDocument23 pagesStat 2509 Exam Review Problems 1 AwoodsJoy CloradoNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument7 pagesAssignmentMaryam AbdulRahmanNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1: Case Processing SummaryDocument2 pagesTugas 1: Case Processing SummaryVndaNo ratings yet
- Bivariat Rina KharismaDocument7 pagesBivariat Rina KharismaazwarNo ratings yet
- TestDocument1 pageTestpreeti25No ratings yet
- Hasil Analisis Data Menggunakan SPSS Versi 16.0 1. Analisis UnivariatDocument3 pagesHasil Analisis Data Menggunakan SPSS Versi 16.0 1. Analisis UnivariatAminarsihNo ratings yet
- 10 Basic ToolsDocument91 pages10 Basic ToolsLOGANATHAN VNo ratings yet
- Conditions in Python: ObjectivesDocument19 pagesConditions in Python: ObjectivesNguyễn LinhNo ratings yet
- OUPUT SPSS UJI Goodness of Fit - IndependensiDocument3 pagesOUPUT SPSS UJI Goodness of Fit - IndependensiAmbar WatiNo ratings yet
- QC Tools: Parteo Diagram by Defective ItemsDocument80 pagesQC Tools: Parteo Diagram by Defective ItemsPrasanth PNo ratings yet
- Tugas Biostatistik Rahmawati Ningsih 2Document6 pagesTugas Biostatistik Rahmawati Ningsih 2rahmawati ningsihNo ratings yet
- Sampul ProposalDocument3 pagesSampul ProposalNajma RezaNo ratings yet
- DEFINITIONDocument7 pagesDEFINITIONhappijennycambelleNo ratings yet
- ChisquareandttestDocument12 pagesChisquareandttestnguyencongdanh1408No ratings yet
- Template Format Gauge R & RDocument5 pagesTemplate Format Gauge R & RQC-Metinca Prima Industrial WorksNo ratings yet
- Multi-Vari Chart (Graphing Using Minitab)Document57 pagesMulti-Vari Chart (Graphing Using Minitab)ClarkRMNo ratings yet
- SPSS Ott Survey OutputDocument8 pagesSPSS Ott Survey OutputjatinNo ratings yet
- CASE A Cre8tiveDocument3 pagesCASE A Cre8tivepanadol_o2No ratings yet
- Hasil Spss FixDocument15 pagesHasil Spss FixandarNo ratings yet
- Spss TaraDocument2 pagesSpss TaraMega RuchiNo ratings yet
- Done 4Document12 pagesDone 4Jurnal inNo ratings yet
- Decision ScienceDocument12 pagesDecision SciencedalveerchoudharyNo ratings yet
- Hasil Biva BajigurDocument2 pagesHasil Biva BajigurborisNo ratings yet
- Chi Square ResultsDocument3 pagesChi Square ResultsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Hasil Olahan DataDocument4 pagesHasil Olahan DataneeadiaNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Tutorial BIT MESRADocument3 pagesComputer Graphics Tutorial BIT MESRANaman MittalNo ratings yet
- MayurDocument9 pagesMayurDummy ComumnNo ratings yet
- LAB Report 2: Question 2#Document2 pagesLAB Report 2: Question 2#imzoo_wickedNo ratings yet
- Ey ResultsDocument22 pagesEy ResultsFiaz Ahmed LoneNo ratings yet
- Crosstab 2Document3 pagesCrosstab 2BudimanNo ratings yet
- Mws Com Int TXT Romberg ExamplesDocument4 pagesMws Com Int TXT Romberg Examplessofia cruzNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Attribute Measurement Systems AnalysisDocument15 pagesInstructions:: Attribute Measurement Systems AnalysisSead ZejnilovicNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab Fair Record FormatDocument140 pagesMetrology Lab Fair Record FormatnNo ratings yet
- Case Processing SummaryDocument4 pagesCase Processing SummaryJurnal inNo ratings yet
- NetherlandsDocument12 pagesNetherlandsYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Answer Even Q App-DDocument509 pagesAnswer Even Q App-DYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Vidhya MuruganathamDocument1 pageVidhya MuruganathamYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Harsh ShahDocument1 pageHarsh ShahYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Excel Assignment DatasetDocument89 pagesExcel Assignment DatasetYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Tushar SethiDocument1 pageTushar SethiYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- IT Committee - PlannersDocument1 pageIT Committee - PlannersYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- HP - Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesHP - Case AnalysisYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Course Outline PMDocument7 pagesCourse Outline PMYash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Electives Calculator MBA09Document7 pagesElectives Calculator MBA09Yash ThakurNo ratings yet
- Zedd77gmailcomsample Question of QTM1Document10 pagesZedd77gmailcomsample Question of QTM1Akash kumarNo ratings yet
- Nptel TT 7Document27 pagesNptel TT 7Kamal SahuNo ratings yet
- 2.5.the Histogram ExerciseDocument5 pages2.5.the Histogram ExerciseManoj Kumar NarayanasamyNo ratings yet
- Means and Variance of The Sampling Distribution of Sample MeansDocument19 pagesMeans and Variance of The Sampling Distribution of Sample MeansCHARLYN JOY SUMALINOGNo ratings yet
- Nama: Erika Oktavina NPM: 061118033 Prodi: Biologi/ 4A: StatisticsDocument10 pagesNama: Erika Oktavina NPM: 061118033 Prodi: Biologi/ 4A: StatisticsErika OktavinaNo ratings yet
- Research Methods For The Behavioral Sciences 4th Edition Stangor Test BankDocument9 pagesResearch Methods For The Behavioral Sciences 4th Edition Stangor Test Bankorlabasilwmw3v5100% (32)
- Stat Revision 3Document9 pagesStat Revision 3Charlston ChavezNo ratings yet
- StatProb Monthly Exam 2022 2023Document3 pagesStatProb Monthly Exam 2022 2023Marc AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Prob 07 Distributions 2Document10 pagesProb 07 Distributions 2Papun RoutNo ratings yet
- Measures of Position Quartile Decile and Percentile For Grouped and Ungrouped DataDocument6 pagesMeasures of Position Quartile Decile and Percentile For Grouped and Ungrouped DataBernard FloresNo ratings yet
- Correlation & RegressionDocument53 pagesCorrelation & Regressionvhj jhhj100% (1)
- 04 Percntiles Deciles and QuartilesDocument8 pages04 Percntiles Deciles and QuartilesPaulo EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Lab Introduction To STATADocument27 pagesLab Introduction To STATAAfifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Lecture ExamplesDocument6 pagesChapter 7 Lecture ExamplesDarian ChettyNo ratings yet
- Statistics Probability Review Midterm Exam SY 2022 2023Document4 pagesStatistics Probability Review Midterm Exam SY 2022 2023Dizzeus Leira Cabalum RamaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Graphical Representation IDocument16 pagesLecture 2 Graphical Representation Isuman shresthaNo ratings yet
- Online Games Played Frequency PercentageDocument4 pagesOnline Games Played Frequency PercentageCypress EmboltorioNo ratings yet
- D. Brian's Notes 2023Document69 pagesD. Brian's Notes 2023Jake TredouxNo ratings yet
- Ec1 12Document65 pagesEc1 12LOKENDRANo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median & ModeDocument5 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median & ModefillereyesNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument16 pagesStatisticsshiraj_sgNo ratings yet
- Example Martin USDocument12 pagesExample Martin USsadia anmolNo ratings yet
- 3A Business StatisticsDocument11 pages3A Business StatisticsParthNo ratings yet
- Box Plot Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesBox Plot Graphic Organizerapi-511315385No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentpriyanka singhNo ratings yet
- Lbolytc Chapter 3: Numerical Descriptive MeasuresDocument3 pagesLbolytc Chapter 3: Numerical Descriptive MeasuresRuss FajardoNo ratings yet
- Visualization Using PythonDocument42 pagesVisualization Using PythonYADAV RAHUL DALSHRINGAR StudentNo ratings yet